Effect of Shear History on Solid–Liquid Transition of Particulate Gel Fuels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological Characteristics
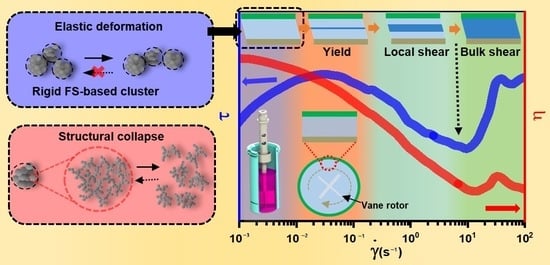
2.2. Repetitive Ramp Shear Sweep
2.3. Structural Evolutions under Different Shear Protocols
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation
4.3. Characterization
4.3.1. Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy (CFM)
4.3.2. Cryonic Transmission Electron Microscopy (Cryo-TEM)
4.3.3. Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
4.3.4. Rheological Characterization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, A.; Guan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Song, J. Preparation and characterization of metalized JP-10 gel propellants with excellent thixotropic performance. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushkov, D.O.; Nigay, A.G.; Yanovsky, V.A.; Yashutina, O.S. Effects of the initial gel fuel temperature on the ignition mechanism and characteristics of oil-filled cryogel droplets in the high-temperature oxidizer medium. Energy Fuel 2019, 33, 11812–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerieri, P.M.; Jacob, R.J.; DeLisio, J.B.; Rehwoldt, M.C.; Zachariah, M.R. Stabilized microparticle aggregates of oxygen-containing nanoparticles in kerosene for enhanced droplet combustion. Combust. Flame 2018, 187, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liao, W.; Wu, W.; Feng, F. Combustion characteristics of inorganic kerosene gel droplet with fumed silica as gellant. Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci. 2019, 103, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.C.; Homan-Cruz, G.D.; Stahl, J.M.; Petersen, E.L. The effects of SiO2 and TiO2 on the two-phase burning behavior of aqueous HAN propellant. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, J.L.; Yetter, R.A.; Asay, B.W.; Lloyd, J.M.; Sanders, V.E.; Risha, G.A.; Son, S.F. Effect of nano-aluminum and fumed silica particles on deflagration and detonation of nitromethane. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2009, 34, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; DeLisio, B.J.; Holdren, S.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zachariah, R.M. Mesoporous silica spheres incorporated aluminum/poly (vinylidene fluoride) for enhanced burning propellants. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Cao, J.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Review on design, preparation and performance characterization of gelled fuels for advanced propulsion. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, G.; Wang, B. The micromorphology and large amplitude oscillatory shear behaviors of hydrocarbon gel fuels filled with fumed silica and aluminium sub-microparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 130013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, K.; Cayre, O.J.; Harbottle, D. Interfacial particle dynamics: One and two step yielding in colloidal glass. Langmuir 2016, 32, 13472–13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkar, M.; Sadeghi, S.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U. Structural characterization of CVD custom-synthesized carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposites in large-amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS) mode: Effect of dispersion characteristics in confined geometries. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudoulas, T.B.; Germann, N. Nonlinear rheological behavior of gelatin gels: In situ gels and individual gel layers filled with hard particles. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2019, 556, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Rogers, S.A. Optimal conditions for pre-shearing thixotropic or aging soft materials. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.; Yang, M. Structure of fumed silica gels in dodecane: Enhanced network by oscillatory shear. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.; Santos, P.H.S.; Campanella, O.H.; Anderson, W.E. Rheological and thermal behavior of gelled hydrocarbon fuels. J. Propul. Power 2011, 27, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, C.J.; Kogan, M.; Solomon, M.J. Structure and dynamics of colloidal depletion gels: Coincidence of transitions and heterogeneity. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 041403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Grenard, V.; Pecorario, S.; Taberlet, N.; Dolique, V.; Manneville, S.; Divoux, T.; McKinley, G.H.; Swan, J.W. Hydrodynamics control shear-induced pattern formation in attractive suspensions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Liu, W. The influence of continuous shear, shear history and relaxation on the rheological behavior of SiO2/glycerine suspensions. Appl. Rheol. 2015, 25, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, L.; Aksel, N. Transition pathways between solid and liquid state in suspensions. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, L.; Peukert, S.; Aksel, N. Investigation of the solid–liquid transition of highly concentrated suspensions in oscillatory amplitude sweeps. J. Rheol. 2002, 46, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Wilhelm, M.; Klein, C.O.; Cho, K.S.; Nam, J.G.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H. A review of nonlinear oscillatory shear tests: Analysis and application of large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1697–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.H.; Carignano, M.A.; Campanella, O. Effect of shear history on rheology of time-dependent colloidal silica gels. Gels 2017, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibaud, T.; Perge, C.; Lindström, S.B.; Taberlet, N.; Manneville, S. Multiple yielding processes in a colloidal gel under large amplitude oscillatory stress. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, A.; Kirichek, A.; Chassagne, C. Effect of pre-shearing on the steady and dynamic rheological properties of mud sediments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 116, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.E.; Hart, A.J.; McKinley, G.H. Improved rheometry of yield stress fluids using bespoke fractal 3D printed vanes. J. Rheol. 2020, 64, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboeuf, S.; Ducloué, L.; Lenoir, N.; Ovarlez, G. A mechanism of strain hardening and Bauschinger effect: Shear-history-dependent microstructure of elasto-plastic suspensions. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 8756–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, F.; Magnin, A.; Piau, J.M. Thixotropic colloidal suspensions and flow curves with minimum: Identification of flow regimes and rheometric consequences. J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Tong, Z. Large amplitude oscillatory shear rheology for nonlinear viscoelasticity in hectorite suspensions containing poly(ethylene glycol). Polymer 2011, 52, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Temperature dependence of aging kinetics of hectorite clay suspensions. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2015, 444, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewoldt, R.H. Defining nonlinear rheological material functions for oscillatory shear. J. Rheol. 2013, 57, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadala-Maria, F.; Acrivos, A. Shear-induced structure in a concentrated suspension of solid spheres. J. Rheol. 1980, 24, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsi, F.; Gadala-Maria, F. Fore-and-aft asymmetry in a concentrated suspension of solid spheres. J. Rheol. 1987, 31, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. Liquid-to-solid transition of concentrated suspensions under complex transient shear histories. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 061404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. Correlations between local flow mechanism and macroscopic rheology in concentrated suspensions under oscillatory shear. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2433–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kee, D. Yield stress measurement techniques: A review. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; De Kee, D. Double concentric cylinder geometry with slotted rotor to measure the yield stress of complex systems: A numerical study. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, W. Dynamic wall slip behavior of yield stress fluids under large amplitude oscillatory shear. J. Rheol. 2017, 61, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugre, E.Y.-M.; Gnagne, T. Vane geometry for measurement of influent rheological behaviour in dry anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 155, 111928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Choi, J.; Hwang, B.; Choi, H. A lab-scale experimental approach to evaluate rheological properties of foam-conditioned soil for EPB shield tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 128, 104667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoman, B.; Marron, G.; Potanin, A. Rheological characterization of flow inception of thixotropic yield stress fluids using vane and T-bar geometries. Rheol. Acta 2021, 60, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P. Understanding sol-gel transition through a picture. A short tutorial. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn 2020, 94, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, K.; Shi, J.; Wu, F.; Zhu, X.; Dong, W.; Xie, A. Metal/nitrogen co-doped hollow carbon nanorods derived from self-assembly organic nanostructure for wide bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 2022, 228, 109424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basrur, V.R.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Raghavan, S.R. Synergistic Gelation of Silica Nanoparticles and a Sorbitol-Based Molecular Gelator to Yield Highly-Conductive Free-Standing Gel Electrolytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radlinski, A.P.; Mastalerz, M.; Hinde, A.L.; Hainbuchner, M.; Rauch, H.; Baron, M.; Lin, J.S.; Fan, L.; Thiyagarajan, P. Application of SAXS and SANS in evaluation of porosity, pore size distribution and surface area of coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, C.P.; Krebsz, M.; Booty, S.J. Understanding the role of hydrogen bonding in the aggregation of fumed silica particles in triglyceride solvents. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2018, 527, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.R.; Walls, H.J.; Khan, S.A. Rheology of silica dispersions in organic liquids: New evidence for solvation forces dictated by hydrogen bonding. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7920–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.S.; Harwell, J.H.; Grady, B.P. Rheological characterization of yield stress gels formed via electrostatic heteroaggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6743–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Kawaguchi, M. Shear-induced changes in rheological reponses and neutron scattering properties of hydrophobic silica suspensions at low silica concentrations. J. Disper Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Nandagopalan, P.; Baek, S.W.; Miglani, A. Rheology of solid-like ethanol fuel for hybrid rockets: Effect of type and concentration of gellants. Fuel 2017, 209, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.C.-H. Yield stress: A time-dependent property and how to measure it. Rheol. Acta 1986, 25, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, P.C.F.; Mewis, J.; Bonn, D. Yield stress and thixotropy: On the difficulty of measuring yield stresses in practice. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Q. Thickening of the immobilized polymer layer using trace amount of amine and its role in promoting gelation of colloidal nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 9015–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Process | < 0.02 s−1 | < 0.05 s−1 | < 10 s−1 | > 10 s−1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | n | R2 | K | n | R2 | K | n | R2 | K | n | R2 | ||
| A200-5 | first ramp up | 610 | 0.396 | 0.989 | 140 | 0.04 | 0.997 | 86 | <0.01 | 0.963 | 66 | 0.101 | 0.992 |
| first ramp down | 15 | 0.051 | 0.993 | 13 | 0.064 | 0.993 | 9 | −0.048 | 0.969 | 36 | 0.201 | 0.927 | |
| second ramp up | 12 | 0.024 | 0.994 | 15 | 0.103 | 0.993 | 4 | −0.909 | 0.950 | 22 | 0.293 | 0.991 | |
| second ramp down | 15 | 0.095 | 0.994 | 10 | 0.015 | 0.993 | 8 | −0.050 | 0.969 | 39 | 0.157 | 0.931 | |
| A200-5-Al-10 | first ramp up | 1118 | 0.429 | 0.991 | 228 | 0.05 | 0.993 | 77 | <0.001 | 0.890 | 74 | 0.132 | 0.984 |
| first ramp down | 83 | 0.004 | 0.995 | 58 | −0.091 | 0.994 | 72 | −0.034 | 0.968 | 72 | 0.092 | 0.936 | |
| second ramp up | 68 | −0.036 | 0.995 | 30 | −0.239 | 0.994 | 15 | −0.515 | 0.979 | 119 | −0.018 | 0.992 | |
| second ramp down | 64 | 0.095 | 0.961 | 67 | 0.063 | 0.901 | 60 | −0.054 | 0.977 | 55 | −0.050 | 0.997 | |
| A200-5-Al-20 | first ramp up | 1874 | 0.414 | 0.961 | 468 | 0.118 | 0.991 | 140 | <0.001 | 0.906 | 173 | 0.039 | 0.992 |
| first ramp down | 128 | −0.044 | 0.995 | 116 | −0.067 | 0.994 | 114 | −0.070 | 0.970 | 118 | 0.119 | 0.933 | |
| second ramp up | 146 | −0.032 | 0.995 | 106 | −0.108 | 0.994 | 66 | −0.297 | 0.970 | 31 | 0.403 | 0.991 | |
| second ramp down | 126 | −0.039 | 0.995 | 106 | −0.081 | 0.994 | 126 | −0.016 | 0.967 | 124 | 0.006 | 0.935 | |
| A200-5-Al-30 | first ramp up | 5592 | 0.464 | 0.991 | 1117 | 0.186 | 0.985 | 303 | <0.001 | 0.912 | 237 | 0.103 | 0.996 |
| first ramp down | 221 | −0.052 | 0.994 | 172 | −0.114 | 0.994 | 180 | −0.098 | 0.979 | 169 | 0.167 | 0.930 | |
| second ramp up | 267 | −0.025 | 0.994 | 172 | −0.137 | 0.994 | 106 | −0.340 | 0.971 | 2 | 1.071 | 0.990 | |
| second ramp down | 179 | −0.032 | 0.995 | 168 | −0.049 | 0.993 | 170 | −0.045 | 0.967 | 139 | 0.083 | 0.936 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Effect of Shear History on Solid–Liquid Transition of Particulate Gel Fuels. Gels 2023, 9, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110902
Li J, Li Y, Xiao W, Wang J, Wang B. Effect of Shear History on Solid–Liquid Transition of Particulate Gel Fuels. Gels. 2023; 9(11):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jian, Yaning Li, Wei Xiao, Jingyan Wang, and Boliang Wang. 2023. "Effect of Shear History on Solid–Liquid Transition of Particulate Gel Fuels" Gels 9, no. 11: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110902
APA StyleLi, J., Li, Y., Xiao, W., Wang, J., & Wang, B. (2023). Effect of Shear History on Solid–Liquid Transition of Particulate Gel Fuels. Gels, 9(11), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110902