Formation of Alginate/Chitosan Interpenetrated Networks Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheological Properties of Alginate/Chitosan Systems
2.2. Characterization by IR Spectroscopy
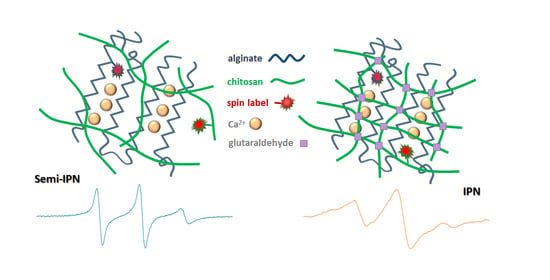
2.3. Nanoscale Features Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coviello, T.; Matricardi, P.; Marianecci, C.; Alhaique, F. Polysaccharide hydrogels for modified release formulations. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.R. Interpenetrating polymer networks. Styrene-divinylbenzenecopolymers with two and three interpenetrating networks, and their sulphonates. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, C.M. Interpenetrating polymer networks (IPN): Structure and mechanical behavior. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Kobayashi, S., Müllen, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, L.H. Interpenetrating polymer networks: An overview. In Interpenetrating Polymer Networks (ACS Advances in Chemistry Volume 239); Klempner, D., Sperling, L.H., Utracki, L.A., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matricardi, P.; Di Meo, C.; Coviello, T.; Hennink, W.E.; Alhaique, F. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks polysaccharide hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Guo, G.; Ma, P.X. Multifunctional Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on methacrylated alginate for the delivery of small molecule drugs and sustained release of protein. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3246–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Bagher, Z.; Kamrava, S.K.; Ehterami, A.; Alizadeh, R.; Farhadi, M.; Falah, M.; Komeili, A. Alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing olfactory ectomesenchymal stem cells for sciatic nerve tissue engineering. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15357–15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoratto, N.; Matricardi, P. 4—Semi-IPNs and IPN-based hydrogels. In Polymeric Gels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kildeeva, N.R.; Perminov, P.A.; Vladimirov, L.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Mikhailov, S.N. About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 35, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtat, D.; Mahlous, M.; Benamer, S.; Nacer Khodja, A.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Oral delivery of insulin from alginate/chitosan crosslinked byglutaraldehyde. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ramay, H.R.; Hauch, K.D.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, M. Chitosan–alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3919–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Huang, L. Feasibility of chitosan-alginate (Chi-Alg) hydrogel used as scaffold for neural tissue engineering: A pilot study in vitro. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltran-Vargas, N.E.; Peña-Mercado, E.; Sánchez-Gómez, C.; Garcia-Lorenzana, M.; Ruiz, J.C.; Arroyo-Maya, I.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Campos-Terán, J. Sodium alginate/chitosan scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering: The influence of its three-dimensional material preparation and the use of gold nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khapre, M.A.; Pandey, S.; Jugade, R.M. Glutaraldehyde-cross-linked chitosan–alginate composite for organic dyes removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummino, M.L.; Magnacca, G.; Cimino, D.; Laurenti, E.; Nisticò, R. The innovation comes from the sea: Chitosan and alginate hybrid gels and films as sustainable materials for wastewater remediation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peppas, N.A.; Huang, Y.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Ward, J.H.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical foundations and structural design of hydrogels in medicine and biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ionita, G.; Ariciu, A.-M.; Turcu, O.; Chechik, V. Properties of polyethylene glycol/cyclodextrin hydrogels revealed by spin probe and spin labelling methods. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, I.; Ariciu, A.-M.; Popescu, E.I.; Mocanu, S.; Neculae, A.V.F.; Savonea, F.; Ionita, G. Evaluation of the accessibility of molecules in hydrogels using a scale of spin probes. Gels 2022, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, G.; Ariciu, A.-M.; Smith, D.K.; Chechik, V. Ion exchange in alginate gels—Dynamic behaviour revealed by electron paramagnetic resonance. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8968–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, E.I.; Aricov, L.; Mocanu, S.; Matei, I.; Hristea, E.; Baratoiu, R.; Leonties, A.; Petcu, C.; Alexandrescu, E.; Ionita, G. Subtle influence on alginate gel properties through host-guest interactions between covalently appended cyclodextrin and adamantane units. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 8083–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontieş, A.R.; Băran, A.; Ioniţă, G.; Matei, I.; Mocanu, S.; Baratoiu, R.; Hristea, E.; Aricov, L. Physicochemical changes of alginate and polyacrylate mixture induced by interactions of the appended units. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Cao, C.; Wang, Q.; Gonzalez, M.; Dolbowb, J.E.; Zhao, X. Design of stiff, tough and stretchy hydrogel composites via nanoscale hybrid crosslinking and macroscale fiber reinforcement. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 7519–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, E.; Kamińska-Dwórznicka, A.; Kot, A. The rheological properties and texture of agar gels with canola oil—Effect of mixing rate and addition of lecithin. Gels 2022, 8, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontieş, A.R.; Răducan, A.; Culiţă, D.C.; Alexandrescu, E.; Moroşan, A.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Aricov, L. Laccase immobilized on chitosan-polyacrylic acid microspheres as highly efficient biocatalyst for naphthol green B and indigo carmine degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, D.; Matsuhiro, B.; Rossi, M.; Caruso, F. FT-IR spectra of alginic acid block fractions in three species of brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, C.; Finch, D.S.; Ralph, B. Determination of the cation content of alginate thin films by FTi.r. spectroscopy. Polymer 1997, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoogmoed, C.G.; Busscher, H.J.; de Vos, P. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy studies of alginate-PLL capsules with varying compositions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 67, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.L.; Braga, C.R.C.; Fook, M.V.L.; Raposo, C.M.O.; Carvalho, L.H.; Canedo, E.L. Application of infrared spectroscopy to analysis of chitosan/clay nanocomposites. In Infrared Spectroscopy—Materials Science, Engineering and Technology; Theophanides, T., Ed.; Intechopen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Shan, C.L.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Xu, F.; Han, L.R.; Ibrahim, M.; Guo, L.B.; Xie, L.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Turhan, M.; Gunasekaran, S. Selected properties of pH-sensitive, biodegradable chitosan–poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budianto, E.; Muthoharoh, S.P.; Nizardo, N.M. Effect of crosslinking agents, pH and temperature on swelling behavior of cross-linked chitosan hydrogel. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2015, 3, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; Taktak, N.E.M.; Awad, O.M.; Elfiki, S.A.; Abou El-Ela, N.E. Preparation and characterization of biopolymers chitosan/alginate/gelatin gel spheres crosslinked by glutaraldehyde. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2017, 56, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderberger, D. EPR spectroscopy in polymer science. In EPR Spectroscopy. Topics in Current Chemistry Volume 321; Drescher, M., Jeschke, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budil, D.E.; Lee, S.; Saxena, S.; Freed, J.H. Nonlinear-least-squares analysis of slow-motion EPR spectra in one and two dimensions using a modified Levenberg—Marquardt algorithm. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1996, 120, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stones, T.J.; Buckman, T.; Nordio, P.L.; McConnell, H.M. Spin-labeled biomolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 54, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyrton, A.C.; Monteiro, C.A., Jr. Some studies of crosslinking chitosan–glutaraldehyde interaction in a homogeneous system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 26, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | alginate | alginate chitosan | alginate chitosan | alginate chitosan | alginate chitosan | alginate chitosan | chitosan |
| Crosslinker | Ca2+ | Ca2+ | GA 1 |
|
| Ca2+ + GA | GA |
| System | G′ (Pa) | Yield Stress (Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24,470 | 51 |
| 2 | 16,890 | 493 |
| 3 | 3227 | 103 |
| 4 | 5826 | 166 |
| 5 | 28,230 | 633 |
| 6 | 17,530 | 158 |
| 7 | 164 | 13 |
| Sample | τ1 × 1010 (s) | 2aN (G) | τ2 × 108 (s) | 2Azz (G) | % of the Slow Component |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlgT_Alg | 9.45 | 34.04 | - | - | - |
| AlgT_Alg+Chit | 9.97 | 34.04 | - | - | - |
| AlgT_1 | 9.94 | 32.6 | 6.71 | 57.42 | 71.1 |
| AlgT_2 | 9.94 | 32.6 | 6.71 | 57.42 | 72.1 |
| AlgT_3 | 10.35 | 33.86 | - | - | - |
| AlgT_4 | 10.3 | 32.7 | 6.28 | 56.36 | 90.0 |
| AlgT_5 | 9.60 | 32.4 | 8.50 | 58.08 | 78.5 |
| AlgT_6 | 9.60 | 32.4 | 7.20 | 57.18 | 75.7 |
| AlgT_7 | 6.32 | 33.74 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joly, J.-P.; Aricov, L.; Balan, G.-A.; Popescu, E.I.; Mocanu, S.; Leonties, A.R.; Matei, I.; Marque, S.R.A.; Ionita, G. Formation of Alginate/Chitosan Interpenetrated Networks Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy. Gels 2023, 9, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9030231
Joly J-P, Aricov L, Balan G-A, Popescu EI, Mocanu S, Leonties AR, Matei I, Marque SRA, Ionita G. Formation of Alginate/Chitosan Interpenetrated Networks Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy. Gels. 2023; 9(3):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9030231
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoly, Jean-Patrick, Ludmila Aricov, George-Alin Balan, Elena Irina Popescu, Sorin Mocanu, Anca Ruxandra Leonties, Iulia Matei, Sylvain R. A. Marque, and Gabriela Ionita. 2023. "Formation of Alginate/Chitosan Interpenetrated Networks Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy" Gels 9, no. 3: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9030231
APA StyleJoly, J. -P., Aricov, L., Balan, G. -A., Popescu, E. I., Mocanu, S., Leonties, A. R., Matei, I., Marque, S. R. A., & Ionita, G. (2023). Formation of Alginate/Chitosan Interpenetrated Networks Revealed by EPR Spectroscopy. Gels, 9(3), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9030231