Wavelet-Based Adaptive Eddy-Resolving Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Wall-Bounded Compressible Turbulent Flows
Abstract
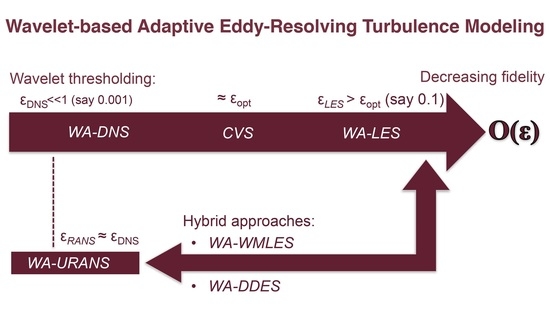
:1. Introduction
2. Wavelet-Favre Filtered/Averaged Navier–Stokes Equations
3. Adaptive Wavelet Collocation Method
4. Wall-Resolving Approach
5. Wall-Modeling Approaches
5.1. Wavelet-Based Adaptive Unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes
5.2. Wavelet-Based Adaptive Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation
5.3. Wavelet-Based Adaptive Wall-Modeled Large Eddy Simulation
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNS | Direct Numerical Simulation |
| WTF | Wavelet Thresholding Filter |
| WA-DNS | Wavelet-based Adaptive Direct Numerical Simulation |
| CVS | Coherent Vortex Simulation |
| WA-LES | Wavelet-based Adaptive Large Eddy Simulation |
| SGS | SubGrid-Scale |
| RANS | Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| WA-URANS | Wavelet-based Adaptive Unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| WA-DDES | Wavelet-based Adaptive Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation |
| CFL | Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy |
| WA-WMLES | Wavelet-based Adaptive Wall Modeled Large Eddy Simulation |
| AWC | Adaptive Wavelet Collocation |
| A-AWC | Anisotropic Adaptive Wavelet Collocation |
| AMD | Anisotropic Minimum-Dissipation |
| BL | Boundary Layer |
| SA | Spalart-Allmaras |
| AMD | Anisotropic Minimum-Dissipation |
| EL | Exchange Location |
| ODE | Ordinary Differential Equation |
References
- Slotnick, J.; Khodadoust, A.; Alonso, J.; Darmofal, D.; Gropp, W.; Lurie, E.; Mavriplis, D. CFD Vision 2030 Study: A Path to Revolutionary Computational Aerosciences; Technical Report, NASA/CR-2014-218178; NAS: Hampton, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rogallo, R.S.; Moin, P. Numerical simulation of turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1984, 16, 99–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Moin, P. Grid-point requirements for large eddy simulation: Chapman’s estimates revisited. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 011702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, C.; Hussaini, M.Y.; Quarteroni, A.; Thomas, A., Jr. Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lele, S.K. Compact finite difference schemes with spectral-like resolution. J. Comput. Phys. 1992, 103, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, O.V. Solving multi-dimensional evolution problems with localized structures using second generation wavelets. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2003, 17, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadmalayeri, A.; Vezolainen, A.; Brown-Dymkoski, E.; Vasilyev, O.V. Parallel adaptive wavelet collocation method for PDEs. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 298, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, K.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wavelet methods in computational fluid dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 473–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, D.E.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Kevlahan, N.K.R. CVS and SCALES simulation of 3-D isotropic turbulence. J. Turbul. 2005, 6, N37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadmalayeri, A.; Vezolainen, A.; Vasilyev, O.V. Reynolds number scaling of coherent vortex simulation and stochastic coherent adaptive large eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. A fully adaptive wavelet-based approach to homogeneous turbulence simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 695, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wavelet-based adaptive simulations of three-dimensional flow past a square cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 748, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown-Dymkoski, E. Adaptive Wavelet-Based Turbulence Modeling for Compressible Flows in Complex Geometry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De Stefano, G.; Brown-Dymkoski, E.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wavelet-based adaptive large-eddy simulation of supersonic channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 901, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Vasilyev, O.; Hussaini, M.Y. Wavelet-based adaptive delayed detached eddy simulations for wall-bounded compressible turbulent flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 873, 1116–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Vasilyev, O.V.; De Stefano, G.; Yousuff Hussaini, M. Wavelet-based adaptive unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes simulations of wall-bounded compressible turbulent flows. AIAA J. 2020, 58, 1529–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Hussaini, M.Y. Wavelet-based adaptive wall-modeled large eddy simulation method for compressible turbulent flows. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2021, 6, 094606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farge, M.; Schneider, K.; Pellegrino, G.; Wray, A.A.; Rogallo, R.S. Coherent vortex extraction in three-dimensional homogeneous turbulence: Comparison between CVS-wavelet and POD-Fourier decompositions. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 2886–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, D.E.; Vasilyev, O.V. Stochastic coherent adaptive large eddy simulation method. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, 2497–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. Stochastic coherent adaptive large eddy simulation of forced isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 646, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wavelet-based adaptive large-eddy simulation with explicit filtering. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 238, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadmalayeri, A.; Vezolainen, A.; De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. Fully adaptive turbulence simulations based on Lagrangian spatio-temporally varying wavelet thresholding. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 749, 794–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, G.; Nejadmalayeri, A.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wall-resolved wavelet-based adaptive large-eddy simulation of bluff-body flows with variable thresholding. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 788, 303–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, O.; Kevlahan, N.R. Hybrid wavelet collocation–Brinkman penalization method for complex geometry flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2002, 40, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Dymkoski, E.; Kasimov, N.; Vasilyev, O.V. A Characteristic Based Volume Penalization Method for General Evolution Problems Applied to Compressible Viscous Flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 262, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Goldstein, D.E. A-priori dynamic test for deterministic/stochastic modeling in large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2005, 169, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, G.; Goldstein, D.E.; Vasilyev, O.V. On the role of subgrid-scale coherent modes in large-eddy simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 525, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasilyev, O.V.; De Stefano, G.; Goldstein, D.E.; Kevlahan, N.K.R. Lagrangian dynamic SGS model for Stochastic Coherent Adaptive Large Eddy Simulation. J. Turbul. 2008, 9, N11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Goldstein, D.E. Localized Dynamic Kinetic Energy-based Models for Stochastic Coherent Adaptive Large Eddy Simulation. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 045102.1–045102.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V. Hierarchical adaptive eddy-capturing approach for modeling and simulation of turbulent flows. Fluids 2021, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, G.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Brown-Dymkoski, E. Wavelet-based adaptive unsteady Reynolds-averaged turbulence modelling of external flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 837, 765–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Vasilyev, O.V.; De Stefano, G.; Hussaini, M.Y. Wavelet-based adaptive unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes computations of wall-bounded internal and external compressible turbulent flows. In Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018; p. 0545. [Google Scholar]
- Spalart, P.R. Detached-eddy simulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Kawai, S.; Bodart, J.; Bermejo-Moreno, I. Large eddy simulation with modeled wall-stress: Recent progress and future directions. Mech. Eng. Rev. 2016, 3, 15–00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spalart, P.R.; Deck, S.; Shur, M.; Squires, K.; Strelets, M.K.; Travin, A. A new version of detached-eddy simulation, resistant to ambiguous grid densities. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2006, 20, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shur, M.L.; Spalart, P.R.; Strelets, M.K.; Travin, A.K. A hybrid RANS-LES approach with delayed-DES and wall-modelled LES capabilities. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Larsson, J. Wall-modeling in large eddy simulation: Length scales, grid resolution, and accuracy. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 015105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girimaji, S.; Abdol-Hamid, K. Partially-averaged Navier Stokes model for turbulence: Implementation and validation. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2005; p. 502. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, J.; Von Terzi, D. Hybrid LES/RANS methods for the simulation of turbulent flows. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2008, 44, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouat, B.; Schiestel, R. Analytical insights into the partially integrated transport modeling method for hybrid Reynolds averaged Navier–Stokes equations-large eddy simulations of turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 085106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.; Bhushan, S.; Alam, M.; Thompson, D. Investigation of a dynamic hybrid RANS/LES modelling methodology for finite-volume CFD simulations. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2013, 91, 643–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Lien, F.; Yee, E. Feedback-controlled forcing in hybrid LES/RANS. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2006, 20, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shur, M.; Spalart, P.; Strelets, M.; Travin, A. Detached-eddy simulation of an airfoil at high angle of attack. Eng. Turbul. Model. Exp. 1999, 4, 669–678. [Google Scholar]
- Balaras, E.; Benocci, C.; Piomelli, U. Two-layer approximate boundary conditions for large-eddy simulations. AIAA J. 1996, 34, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabot, W.; Moin, P. Approximate wall boundary conditions in the large-eddy simulation of high Reynolds number flow. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2000, 63, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Larsson, J. Dynamic non-equilibrium wall-modeling for large eddy simulation at high Reynolds numbers. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 015105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.I.; Moin, P. An improved dynamic non-equilibrium wall-model for large eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.T.; Park, G.I. Wall-modeled large-eddy simulation for complex turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2018, 50, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, P.A. Some recent developments in turbulence closure modeling. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2018, 50, 77–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhou, Y.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Hussaini, M.Y. Adaptive wavelet-based delayed detached eddy simulations of anisothermal channel flows with high transverse temperature gradients. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019; p. 1558. [Google Scholar]
- Courant, R.; Friedrichs, K.; Lewy, H. Über die partiellen differenzengleichungen der mathematischen physik. Math. Ann. 1928, 100, 32–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Interpolating Wavelet Transforms; Technical Report 408; Department of Statistics, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilyev, O.V.; Bowman, C. Second-generation wavelet collocation method for the solution of partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 165, 660–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown-Dymkoski, E.; Vasilyev, O.V. Adaptive-Anisotropic Wavelet Collocation Method on general curvilinear coordinate systems. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 333, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasilyev, O.V.; Kevlahan, N.K.R. An adaptive multilevel wavelet collocation method for elliptic problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 206, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozema, W.; Bae, H.J.; Moin, P.; Verstappen, R. Minimum-dissipation models for large-eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 085107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, G.; Kim, J.; Moser, R. A numerical study of turbulent supersonic isothermal-wall channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 305, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, C.; Petrovan Boiarciuc, M.; Haberkorn, M.; Comte, P. Large eddy simulation of compressible channel flow. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2008, 22, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.; Allmaras, S. A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. In Proceedings of the 30th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 1992; p. 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regele, J.D.; Vasilyev, O.V. An adaptive wavelet-collocation method for shock computations. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2009, 23, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, D.; Paschal, K.; Yao, C.; Harris, J.; Schaeffler, N.; Washburn, A. A separation control CFD validation test case. Part 1: Baseline & steady suction. In Proceedings of the 2nd AIAA Flow Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 28 June–1 July 2004; p. 2220. [Google Scholar]
- Rumsey, C.L.; Gatski, T.; Sellers, W., III; Vasta, V.; Viken, S. Summary of the 2004 computational fluid dynamics validation workshop on synthetic jets. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachalo, W.; Johnson, D. Transonic, turbulent boundary-layer separation generated on an axisymmetric flow model. AIAA J. 1986, 24, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysi, H.; Sarkar, S.; Friedrich, R. Compressibility effects and turbulence scalings in supersonic channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 509, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakumar, P. DNS/LES Simulations of Separated Flows at High Reynolds Numbers. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015; p. 2783. [Google Scholar]
- Bodart, J.; Larsson, J. Wall-Modeled Large Eddy Simulation in Complex Geometries with Application to High-Lift Devices; Annual Research Briefs; Center for Turbulence Research, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Avdis, A.; Lardeau, S.; Leschziner, M. Large eddy simulation of separated flow over a two-dimensional hump with and without control by means of a synthetic slot-jet. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2009, 83, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.I. Wall-modeled large-eddy simulation of a high Reynolds number separating and reattaching flow. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 3709–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P.S.; Malik, M.R. Wall–modeled large eddy simulation of flow over a wall–mounted hump. In Proceedings of the 46th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016; p. 3186. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, A.; Malik, M.R. Large-eddy simulation of flow over a wall-mounted hump with separation and reattachment. AIAA J. 2018, 56, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, D.; Paschal, K.B.; Yao, C.S.; Harris, J.; Schaeffler, N.W.; Washburn, A.E. Experimental investigation of separation control part 1: Baseline and steady suction. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Method | Resolution | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA-LES | 216 | |||||||||
| LES [58] | 219 | − | − | |||||||
| DNS [57] | 19 | 12 | 222 |
| Case | CFL3D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh size | 6.6 K | 7.5 K | 9.3 K | 11.0 K | 209.8 K |
| 0.0026879 | 0.0026900 | 0.0026972 | 0.0026984 | 0.0027056 | |
| Error | 0.654% | 0.576% | 0.310% | 0.266% | – |
| Grid | WA-WMLES | WMLES [67] | WMLES [68] | WMLES [69] | WRLES [70] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 600 | 300 | 360 | 25 | |
| (3.8 ∼ 38) | (12 ∼ 180) | (12 ∼ 200) | (15 ∼ 100) | 7.2 | |
| 40 | 100 | 120 | 180 | 12.5 | |
| 1.2 | 3.6 | ||||
| 13 | 20 | 50 | 36 | 0.8 | |
| (2.0 ∼ 33) | |||||
| Span size/c | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Total size/million | 7.5 | 9.4 | 12.9 | 11 | 420 |
| Case | Separation () | Reattachment () | Bubble Length () | Error in Bubble |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA-WMLES | 0.677 | 1.138 | 0.461 | 6.0% |
| WMLES [68] | 0.680 | 1.084 | 0.404 | −7.1% |
| WMLES [69] | 0.655 | 1.105 | 0.450 | 3.4% |
| WRLES [70] | 0.641 | 1.09 | 0.449 | 3.2% |
| Experiment [71] | 0.665 () | 1.10 () | 0.435 | – |
| Method | Model Form Adaptation | Wall Effect | Mesh Size | Computational Cost | Fidelity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; De Stefano, G.; Hussaini, M.Y.; Vasilyev, O.V. Wavelet-Based Adaptive Eddy-Resolving Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Wall-Bounded Compressible Turbulent Flows. Fluids 2021, 6, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6090331
Ge X, De Stefano G, Hussaini MY, Vasilyev OV. Wavelet-Based Adaptive Eddy-Resolving Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Wall-Bounded Compressible Turbulent Flows. Fluids. 2021; 6(9):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6090331
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xuan, Giuliano De Stefano, M. Yousuff Hussaini, and Oleg V. Vasilyev. 2021. "Wavelet-Based Adaptive Eddy-Resolving Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Wall-Bounded Compressible Turbulent Flows" Fluids 6, no. 9: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6090331
APA StyleGe, X., De Stefano, G., Hussaini, M. Y., & Vasilyev, O. V. (2021). Wavelet-Based Adaptive Eddy-Resolving Methods for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Wall-Bounded Compressible Turbulent Flows. Fluids, 6(9), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6090331