Effect of Sugars on Gelation Kinetics of Gelatin Gels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Rheological Measurements
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. DTRTs on Multi-Component Aqueous Gelatin Solutions
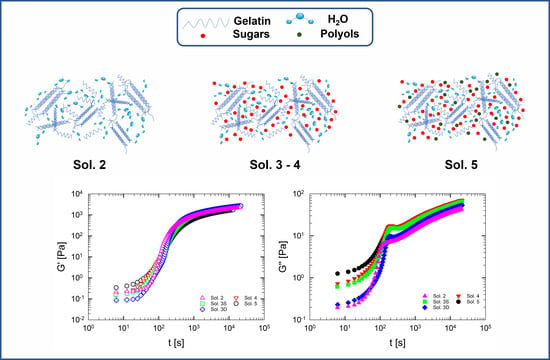
3.2. Isothermal Gelation of Multi-Component Aqueous Gelatin Solutions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poppe, J. Gelatin. In Thickening and Gelling Agents for Food; Imeson, A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 98–123. [Google Scholar]
- Netter, A.B.; Goudoulas, T.B.; Germann, N. Effects of Bloom number on phase transition of gelatin determined by means of rheological characterization. LWT 2020, 132, 109813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila Rodríguez, M.I.; Rodríguez Barroso, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Pu’ad, N.M.; Lee, T.; Nayan, N.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.; Abdullah, H. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialisation. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veis, A. The physical chemistry of gelatin. Int. Rev. Connect. Tissue Res. 1965, 3, 113–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djabourov, M.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Gelation of aqueous gelatin solutions. II. Rheology of the sol-gel transition. J. Phys. 1988, 49, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Nikoo, M.; Boran, G.; Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Collagen and gelatin. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Colby, R.H.; Lusignan, C.P.; Howe, A.M. Physical gelation of gelatin studied with rheo-optics. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 10009–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Duhamel, C.; Hellio, D.; Djabourov, M. All gelatin networks: 1. Biodiversity and physical chemistry. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7208–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabourov, M. Architecture of gelatin gels. Contemp. Phys. 1988, 29, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dille, M.; Haug, I.; Draget, K. Chapter 34–Gelatin and collagen. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 3rd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Thorston, UK, 2021; pp. 1073–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, Y.; Tao, N.; Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Application of Gelatin in Food Packaging: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Wu, Y.; Woshnak, L.L.; Mitmesser, S.H. Effects of hydrocolloids, acids and nutrients on gelatin network in gummies. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartel, R.W.; Joachim, H.; Hofberger, R. Confectionery Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, A.; Asghar, A.; Aslam Maan, A. Chapter 13–Food Gels: Gelling Process and New Applications. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications; Ahmed, J., Ptaszek, P., Basu, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Thorston, UK, 2017; pp. 335–353. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burey, P.; Bhandari, B.; Rutgers, R.; Halley, P.; Torley, P. Confectionery Gels: A Review on Formulation, Rheological and Structural Aspects. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 176–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Nawawi, S.; Heikel, Y. Factors affecting gelation of high-ester citrus pectin. Process Biochem. 1997, 32, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hartel, R.W. Confectionery gels: Gelling behavior and gel properties of gelatin in concentrated sugar solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.B. Sugar Confectionery Manufacture; Blackie: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Burey, P.; Bhandari, B.; Howes, T.; Gidley, M. Hydrocolloid gel particles: Formation, characterization, and application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakenfull, D.; Scott, A. Stabilization of gelatin gels by sugars and polyols. Food Hydrocoll. 1986, 1, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tau, T.; Gunasekaran, S. Thermorheological evaluation of gelation of gelatin with sugar substitutes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y. Effect of interaction between sorbitol and gelatin on gelatin properties and its mechanism under different citric acid concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Matubayasi, N. Gelation: The role of sugars and polyols on gelatin and agarose. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 13210–13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenner, R.; Matubayasi, N.; Shimizu, S. Gelation of carrageenan: Effects of sugars and polyols. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, S.; Al-Marhoobi, I.M.; Deszczynski, M.; Mitchell, J.R.; Abeysekera, R. Gelatin vs. polysaccharide in mixture with sugar. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.; Giannouli, P.; Martin, E.; Brooks, M.; Morris, E. Effect of sugars, galactose content and chainlength on freeze–thaw gelation of galactomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, H. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and microstructure of κ-carrageenan gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Watase, M. Effects of sugars and polyols on the gel-sol transition of kappa-carrageenan gels. Thermochim. Acta 1992, 206, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, E.; Nishinari, K. Effects of sugar on the sol-gel transition in gellan gum aqueous solutions. In Physical Chemistry and Industrial Application of Gellan Gum; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, H.; Einhorn-Stoll, U.; Senge, B. Structure formation in sugar containing pectin gels–Influence of Ca2+ on the gelation of low-methoxylated pectin at acidic pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Wang, Z.; Brenner, T.; Kikuzaki, H.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K. Sucrose release from agar gels: Effects of dissolution order and the network inhomogeneity. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Revel, S.; Morris, K.; Spiller, D.G.; Serpell, L.C.; Adams, D.J. Low molecular weight gelator–dextran composites. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6738–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, S.; Panja, S.; Adams, D.J. Using Rheology to Understand Transient and Dynamic Gels. Gels 2022, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Deeth, H.; Sopade, P.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, N. Rheology, texture and microstructure of gelatin gels with and without milk proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acierno, S.; Pasquino, R.; Grizzuti, N. Rheological techniques for the determination of the crystallization kinetics of a polypropylene–EPR copolymer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 98, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, V.; Avallone, P.R.; Vitiello, G.; Silvestri, B.; Grizzuti, N.; Pasquino, R.; Luciani, G. Adding Humic Acids to Gelatin Hydrogels: A Way to Tune Gelation. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X. Sol-gel transition of methylcellulose in phosphate buffer saline solutions. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Nijenhuis, K.; Winter, H.H. Mechanical properties at the gel point of a crystallizing poly (vinyl chloride) solution. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S. Incipient behaviour of gelatin gels. Rheol. Acta 1991, 30, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, P.R.; Raccone, E.; Costanzo, S.; Delmonte, M.; Sarrica, A.; Pasquino, R.; Grizzuti, N. Gelation kinetics of aqueous gelatin solutions in isothermal conditions via rheological tools. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J. Chapter 15–Rheological Properties of Gelatin and Advances in Measurement. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications; Ahmed, J., Ptaszek, P., Basu, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Thorston, UK, 2017; pp. 377–404. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, J.; Bello, H.R.; Vinograd, J.R. The mechanism of gelation of gelatin the influence of pH, concentration, time and dilute electrolyte on the gelation of gelatin and modified gelatins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1962, 57, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, C.; Cuvelier, G.; Launay, B. Concentration dependence of the critical viscoelastic properties of gelatin at the gel point. Rheol. Acta 1993, 32, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, P.R.; Pasquino, R.; Costanzo, S.; Sarrica, A.; Delmonte, M.; Greco, F.; Grizzuti, N. On the inverse quenching technique applied to gelatin solutions. J. Rheol. 2021, 65, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Li, L. Thermoreversible gelation and viscoelasticity of κ-carrageenan hydrogels. J. Rheol. 2016, 60, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Duhamel, C.; Hellio, D.; Ajdari, A.; Djabourov, M. All gelatin networks: 2. The master curve for elasticity. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7158–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F. Thermoreversible gelation driven by coil-to-helix transition of polymers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 5392–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornall, J.L.; Terentjev, E.M. Helix–coil transition of gelatin: Helical morphology and stability. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, V.; Muller, S.; Ravey, J.C.; Parker, A. Gelation kinetics of gelatin: A master curve and network modeling. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Normand, V. Glassy dynamics of gelatin gels. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4916–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Radha, A. Molecular architectures and functional properties of gellan gum and related polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Majeste, J.C.; Montfort, J.P.; Allal, A.; Marin, G. Viscoelasticity of low molecular weight polymers and the transition to the entangled regime. Rheol. Acta 1998, 37, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquino, R.; Zhang, B.; Sigel, R.; Yu, H.; Ottiger, M.; Bertran, O.; Aleman, C.; Schlüter, A.; Vlassopoulos, D. Linear viscoelastic response of dendronized polymers. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8813–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Water [wt%] | Gelatin [wt%] | Sucrose [wt%] | Dextrose [wt%] | Sorbitol [wt%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol. 2 | 93.2 | 6.8 | - | - | - |
| Sol. 3S | 69.4 | 6.8 | 23.8 | - | - |
| Sol. 3D | 90.9 | 6.8 | - | 2.3 | - |
| Sol. 4 | 67.1 | 6.8 | 23.8 | 2.3 | - |
| Sol. 5 | 64.4 | 6.8 | 23.8 | 2.3 | 2.7 |
| [°C] | [°C] | Ramp Rate [°C/min] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23.2 | 31.3 | 1 | |
| Sol. 2 | 19.7 | 31.6 | 3 |
| 17.6 | 32.2 | 5 | |
| 25.9 | 34.5 | 1 | |
| Sol. 3S | 20.9 | 36.3 | 3 |
| 17.7 | 36.4 | 5 | |
| 23.5 | 31.8 | 1 | |
| Sol. 3D | 20.3 | 32.7 | 3 |
| 17.1 | 33.2 | 5 | |
| 25.9 | 35.3 | 1 | |
| Sol. 4 | 20.9 | 35.7 | 3 |
| 18.7 | 35.4 | 5 | |
| 27.9 | 35.9 | 1 | |
| Sol. 5 | 23.1 | 36.9 | 3 |
| 21.2 | 36.9 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avallone, P.R.; Romano, M.; Sarrica, A.; Delmonte, M.; Pasquino, R.; Grizzuti, N. Effect of Sugars on Gelation Kinetics of Gelatin Gels. Fluids 2022, 7, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7050163
Avallone PR, Romano M, Sarrica A, Delmonte M, Pasquino R, Grizzuti N. Effect of Sugars on Gelation Kinetics of Gelatin Gels. Fluids. 2022; 7(5):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7050163
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvallone, Pietro Renato, Martina Romano, Andrea Sarrica, Marco Delmonte, Rossana Pasquino, and Nino Grizzuti. 2022. "Effect of Sugars on Gelation Kinetics of Gelatin Gels" Fluids 7, no. 5: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7050163
APA StyleAvallone, P. R., Romano, M., Sarrica, A., Delmonte, M., Pasquino, R., & Grizzuti, N. (2022). Effect of Sugars on Gelation Kinetics of Gelatin Gels. Fluids, 7(5), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7050163