Image-Based Numerical Investigation in an Impending Abdominal Aneurysm Rupture
Abstract
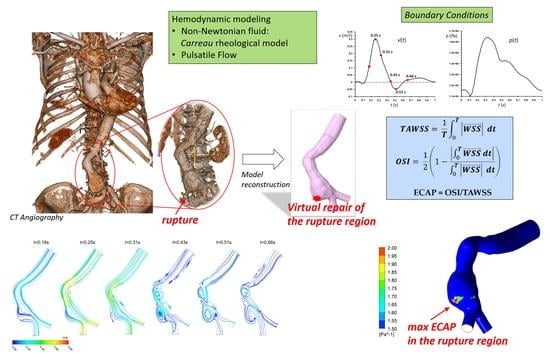
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-Rupture Patient-Specific Model Reconstruction
2.2. Governing Equations and Numerical Setup

2.3. Hemodynamic Parameters
3. Results and Conclusions


Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, C.G.; Kent, K.C. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.S.; Pier, B.; Biesheuvel, A. Dynamics of pulsatile flow through model abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 758, 150–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L.; et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanhainen, A.; Verzini, F.; Van Herzeele, I.; Allaire, E.; Bown, M.; Cohnert, T.; Dick, F.; van Herwaarden, J.; Karkos, C.; Koelemay, M.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 8–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vorp, D.A. Biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Teng, Z.Z.; Elkhawad, M.; Tarkin, J.M.; Joshi, N.; Boyle, J.R.; Buscombe, J.R.; Fryer, T.D.; Zhang, Y.; Park, A.Y.; et al. High structural stress and presence of intraluminal thrombus predict abdominal aortic aneurysm 18F-FDG uptak. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 004656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haller, S.J.; Crawford, J.D.; Courchaine, K.M.; Bohannan, C.J.; Landry, G.J.; Moneta, G.L.; Azarbal, A.F.; Rugonyi, S. Intraluminal thrombus is associated with early rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laine, M.T.; Vänttinen, T.; Kantonen, I.; Halmesmäki, K.; Weselius, E.; Laukontaus, S.; Salenius, J.; Aho, P.; Venermo, M. Rupture of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in Patients Under Screening Age and Elective Repair Threshold. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2016, 51, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, S.C.; Gardner, J.B.; Meissner, M.H.; Johansen, K.H. Rupture in small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 28, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, R.C.; Messina, C.R.; Brewster, D.C.; Ottinger, L.W. Autopsy study of unoperated abdominal aortic aneurysms. The case for early resection. Circulation 1977, 56 (Suppl. S3), II161-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vande Geest, J.P.; Di Martino, E.S.; Bohra, A.; Makaroun, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. A biomechanics-based rupture potential index for abdominal aortic aneurysm risk assessment: Demonstrative application. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1085, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, A.; Gee, M.W.; Reeps, C.; Pongratz, J.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Wall, W.A. A Comparison of Diameter, Wall Stress, and Rupture Potential Index for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture Risk Prediction. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3124–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijsen, F.; Katagiri, Y.; Barlis, P.; Bourantas, C.; Collet, C.; Coskun, U.; Daemen, J.; Dijkstra, J.; Edelman, E.; Evans, P.; et al. Expert recommendations on the assessment of wall shear stress in human coronary arteries: Existing methodologies, technical considerations, and clinical applications. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3421–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, J.J.; Chien, S. Effects of Disturbed Flow on Vascular Endothelium: Pathophysiological Basis and Clinical Perspectives. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 327–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ku, D.N.; Giddens, D.P.; Zarins, C.K.; Glagov, S. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 1985, 5, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecchi, E.; Giglioli, C.; Valente, S.; Lazzeri, C.; Gensini, G.F.; Abbate, R.; Mannini, L. Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbell, J.M.; Shi, Z.D.; Dunn, J.; Jo, H. Fluid mechanics, arterial disease, and gene expression. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takehara, Y.; Isoda, H.; Takahashi, M.; Unno, N.; Shiiya, N.; Ushio, T.; Goshima, S.; Naganawa, S.; Alley, M.; Wakayama, T.; et al. Abnormal flow dynamics result in low wall shear stress and high oscillatory shear index in abdominal aortic dilatation: Initial in vivo assessment with 4D-flow MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, L.J.; Powell, J.T.; Norman, P.E.; Miller, K.; Doyle, B.J. A comparison of hemodynamic metrics and intraluminal thrombus burden in a common iliac artery aneurysm. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, e2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorescu, G.P.; Song, H.N.; Tressel, S.L.; Hwang, J.; Dikalov, S.; Smith, D.A.; Boyd, N.L.; Platt, M.O.; Lassègue, B.; Griendling, K.; et al. Bone morphogenic protein 4 produced in endothelial cells by oscillatory shear stress induces monocyte adhesion by stimulating reactive oxygen species production from a nox1-based NADPH oxidase. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arzani, A.; Suh, G.-Y.; Dalman, R.L.; Shadden, S.C. A longitudinal comparison of hemodynamics and intraluminal thrombus deposition in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H1786–H1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Rourke, M.J.; McCullough, J.P.; Kelly, S. An investigation of the relationship between hemodynamics and thrombus deposition within patient-specific models of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2012, 226, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqui, E.; de Donato, G.; Giannace, G.; Panzano, C.; Setacci, C.; Palasciano, G. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysm in nonagenarians: A single-centre experience. Vascular 2021, 29, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Donato, G.; Pasqui, E.; Nano, G.; Lenti, M.; Mangialardi, N.; Speziale, F.; Ferrari, M.; Michelagnoli, S.; Tozzi, M.; Palasciano, G.; et al. Long-term results of treatment of infrarenal aortic aneurysms with low-profile stent grafts in a multicenter registry. J. Vasc Surg. 2022, 75, 1242–1252.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichting, H. Boundary Layer Theory, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, N.B. Aspects of fluid dynamics applied to the larger arteries. J. Biol. 1999, 199, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.J.; Kuhn, D.C.S.; Lozowy, R.J.; Kulbisky, G.P. Low wall shear stress predominates at sites of abdominal aortic aneurysm 460 rupture. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferziger, J.H.; Peric, M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; ISBN 978-3-540-42074-3. [Google Scholar]
- Forneris, A.; Marotti, F.B.; Satriano, A.; Moore, R.D.; Di Martino, E.S. A novel combined fluid dynamic and strain analysis approach identified abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2020, 6, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibeshi, S.S.; Collins, W.E. The rheology of blood flow in a branched arterial system. Appl. Rheol. 2005, 15, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, B.; Gharahi, H.; Lim, C.; Jaberi, F.; Choi, J.; Lee, W.; Baek, S. Association of intraluminal thrombus, hemodynamic forces, and abdominal aortic aneurysm expansion using longitudinal CT images. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.B.; Peng, L.; Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, T. Role of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysm ruptures: A hemodynamic point of view. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 4263–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenos, M.; Rambhia, S.H.; Alemu, Y.; Einav, S.; Labropoulos, N.; Tassiopoulos, A.; Ricotta, J.J.; Bluestein, D. Patient-based abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk prediction with fluid structure interaction modeling. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vande Geest, J.P.; Sacks, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. The effects of aneurysm on the biaxial mechanical behavior of human abdominal aorta. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thubrikar, M.J.; Labrosse, M.; Robicsek, F.; Al-Soudi, J.; Fowler, B. Mechanical properties of abdominal aortic aneurysm wall. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2001, 25, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Cohnert, T.; Holzapfel, G.A. Diameter-related variations of geometrical, mechanical, and mass fraction data in the anterior portion of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 49, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolipaka, A.; Illapani, V.S.P.; Kenyhercz, W.; Dowell, J.D.; Go, M.R.; Starr, J.E.; Vaccaro, P.S.; White, R.D. Quantification of abdominal aortic aneurysm stiffness using magnetic resonance elastography and its comparison to aneurysm diameter. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Achille, P.; Tellides, G.; Figueroa, C.A.; Humphrey, J.D. A haemodynamic predictor of intraluminal thrombus formation in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 470, 20140163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozowy, R.J.; Kuhn, D.C.S.; Ducas, A.A.; Boyd, A. The relationship between pulsatile flow impingement and intraluminal thrombus deposition in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, A.S.; Shadden, S.C.; Figueroa, C.A.; Park, J.M.; Tedesco, M.M.; Herfkens, R.J.; Dalman, R.L.; Taylor, C.A. Quantification of hemodynamics in abdominal aortic aneurysms during rest and exercise using magnetic resonance imaging and computational fluid dynamics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 1288–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelma, C.; Watton, P.N.; Ventikos, Y. Transitional flow in aneurysms and the computation of haemodynamic parameters. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.P.P.; Borghi, A.; Mohiaddin, R.H.; Wood, N.B.; Thom, S.; Xu, X.Y. Analysis of flow patterns in a patient-specific thoracic aneurysm model. Comput. Struct. 2009, 87, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzirakis, K.; Kamarianakis, Y.; Metaxa, E.; Kontopodis, N.; Ioannou, C.V.; Papaharilaou, Y. A robust approach for exploring hemodynamics and thrombus growth associations in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, B.J.; McGloughlin, T.M.; Kavanagh, E.G.; Hoskins, P.R. From detection to rupture: A serial computational fluid dynamics case study of a rapidly expanding, patient-specific, ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. In Computational Biomechanics for Medicine: Fundamental Science and Patient-Specific Applications; Doyle, B., Miller, K., Wittek, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, D.; Zandvoort, H.J.A.; Schoneveld, A.; Vink, A.; Vos, J.A.; Hoogen, L.L.V.D.; de Vries, J.-P.P.; Pasterkamp, G.; Moll, F.L.; van Herwaarden, J.A. Intraluminal abdominal aortic aneurysm thrombus is associated with disruption of wall integrity. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 57, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boniforti, M.A.; Di Bella, L.; Magini, R. On the role of hemodynamics in predicting rupture of the abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2021, 22, 957–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudah, E.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Loong, T.H.; Bordone, M.; Pua, U.; Narayanan, S. CFD modelling of abdominal aortic aneurysm on hemodynamic loads using a realistic geometry with CT. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 472564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Usmani, A.Y.; Muralidhar, K. Effect of aorto-iliac bifurcation and iliac stenosis on flow dynamics in an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2017, 49, 035513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchi, T.; Kumar, S.D.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Narayanan, S. A review of computational methods to predict the risk of rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysms. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 861627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Mesh Element Size (mm) | TAWSS (Pa) |
|---|---|
| 1.3 | 2.78073 |
| 0.9 | 2.91181 |
| 0.6 | 2.98067 |
| 0.5 | 3.10283 |
| 0.42 | 3.05512 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boniforti, M.A.; Cesaroni, M.C.; Magini, R.; Pasqui, E.; de Donato, G. Image-Based Numerical Investigation in an Impending Abdominal Aneurysm Rupture. Fluids 2022, 7, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7080269
Boniforti MA, Cesaroni MC, Magini R, Pasqui E, de Donato G. Image-Based Numerical Investigation in an Impending Abdominal Aneurysm Rupture. Fluids. 2022; 7(8):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7080269
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoniforti, Maria Antonietta, Maria Chiara Cesaroni, Roberto Magini, Edoardo Pasqui, and Gianmarco de Donato. 2022. "Image-Based Numerical Investigation in an Impending Abdominal Aneurysm Rupture" Fluids 7, no. 8: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7080269
APA StyleBoniforti, M. A., Cesaroni, M. C., Magini, R., Pasqui, E., & de Donato, G. (2022). Image-Based Numerical Investigation in an Impending Abdominal Aneurysm Rupture. Fluids, 7(8), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7080269