The Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Aggregation in Aqueous Media Is Sensitive to Surface Charge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. SWCNT Sample Preparation
2.2. Kinetics of SWCNT Aggregation Induced by Divalent Cations
2.3. AFM Imaging of the SWCNT Aggregation Process
2.4. Oligopeptide-Mediated SWCNT Aggregation and Its Redispersion
2.5. EC50 of SWCNT Aggregation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kinetics of SWCNT Aggregation
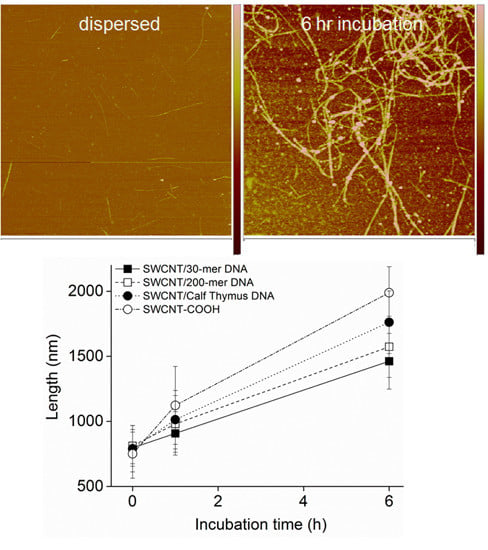
3.2. Intermediates of SWCNT Aggregates Imaged by AFM
3.3. Dependence of SWCNT Aggregation on KCl Concentration
3.4. Potential Mechanisms of SWCNT Aggregation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-Shell Carbon Nanotubes of 1-nm Diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethune, D.S.; Kiang, C.H.; Devries, M.S.; Gorman, G.; Savoy, R.; Vazquez, J.; Beyers, R. Cobalt-Catalysed Growth of Carbon Nanotubes with Single-Atomic-Layer Walls. Nature 1993, 363, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Bangsaruntip, S.; Drouvalakis, K.A.; Kam, N.W. S.; Shim, M.; Li, Y.M.; Kim, W.; Utz, P.J.; Dai, H. Noncovalent Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes for Highly Specific Electronic Biosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4984–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Yi, H.; Ham, M.-H.; Qi, J.; Yun, D.S.; Ladewski, R.; Strano, M.S.; Hammond, P.T.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-Templated Self-Assembled Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Highly Efficient Electron Collection in Photovoltaic Devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, N.W.S.; O’Connell, M.; Wisdom, J.A.; Dai, H. Carbon Nanotubes as Multifunctional Biological Transporters and Near-Infrared Agents for Selective Cancer Cell Destruction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11600–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wieckowski, S.; Pastorin, G.; Benincasa, M.; Klumpp, C.; Briand, J.-P.; Gennaro, R.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A. Targeted Delivery of Amphotericin B to Cells by Using Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6358–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Jagota, A.; Semke, E.D.; Diner, B.A.; McLean, R.S.; Lustig, S.R.; Richardson, R.E.; Tassi, N.G. DNA-Assisted Dispersion and Separation of Carbon Nanotubes. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backes, C.; Schmidt, C.D.; Hauke, F.; Boettcher, C.; Hirch, A. High Population of Individualized SWCNTs through the Adsorption of Water-Soluble Perylenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, B.; Park, J.B.; Ximiao, H.; Cheng, W. Comparative Dispersion Studies of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, B.; Kim, G.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.B.; Kopelman, R.; Cheng, W. Fluorophore and Dye-Assisted Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11676–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagan, J.A.; Bauer, B.J.; Hobbie, E.K.; Becker, M.L.; Hight Walker, A.R.; Simpson, J.R.; Chun, J.; Obrzut, J.; Bajpai, V.; Phelan, F.R.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes: Measuring Dispersion and Length. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itkis, M.E.; Perea, D.E.; Niyogi, S.; Richard, S.M.; Hamon, M.A.; Hu, H.; Zhao, B.; Haddon, R.C. Purity Evaluation of As-Prepared Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Soot by Use of Solution-Phase Near-IR Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L. Temperature and pH-Responsive Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Dispersions. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, D.; Geckeler, K.E. pH-Sensitive Dispersion and Debundling of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Lysozyme as a Tool. Small 2006, 2, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dai, L.; Smet, M. Light-Controlled Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersions in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9233–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobusawa, K.; Ikeda, A.; Kikuchi, J.; Kawano, S.; Fujita, N.; Shinkai, S. Reversible Solubilization and Precipitation of Carbon Nanotubes through Oxidation-Reduction Reactions of a Solubilizing Agent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4577–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Chen, G.; Peddle, J.; Zhao, Y. Reversible Dispersion and Releasing of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Stimuli-Responsive TTFV-Phenylacetylene Polymers. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ngo, T.H.; Smet, M. Reversible Dispersion of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Based on a CO2-Responsive dispersant. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16667–16671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Che, Y.; Smaldone, R.A.; Xu, M.; Bunes, B.R.; Moore, J.S.; Zang, L. Reversible Dispersion and Release of Carbon Nanotubes Using Foldable Oligomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14113–14117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyogi, S.; Boukhalfa, S.; Chikkannanavar, B.; McDonald, T.J.; Heben, M.J.; Doorn, S.K. Selective Aggregation of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes via Salt Addition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1898–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyogi, S.; Densmore, C.G.; Doorn, S.K. Electrolyte Tuning of Surfactant Interfacial Behavior for Enhanced Density-Based Separation of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, M.V.; Arif, R.N.; Frolov, A.I.; Kolar, M.; Romanova, A.O.; Rozhin, A.G. Salting out in Organic Solvents: A New Route to Carbon Nanotube Bundle Engineering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 12399–12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.F.; Tessmer, I.; Holden Thorp, H.; Erie, D.E. Atomic Force Microscopy Studies of DNA–Wrapped Carbon Nanotube Structure and Binding to Quantum Dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10648–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, N.B.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Aggregation Kinetics of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Aquatic Systems: Measurements and Environmental Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7963–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, D.; Zhang, W.; Powell, T.; Rattanaudompol, U. Aggregation Kinetics and Transport of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes at Low Surfactant Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4458–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y. Aggregation Kinetics of SDBS-Dispersed Carbon Nanotubes in Different Aqueous Suspensions. Colloids Surf. A 2012, 409, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Okamura, J.; Shinkai, S. Colloidal Nature of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Electrolyte Solution: The Schulze-Hardy Rule. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7172–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, M.W.; Anderson, J.S.; Ameen, A.L.; Poler, J.C. Aggregation Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Nonaqeous Solvents: Critical Coagulation Concentrations and Transient Dispersion Stability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23267–23272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.; Cheng, W. Mechanisms of Carbon Nanotube Aggregation and the Reversion of Carbon Nanotube Aggregates in Aqueous Medium. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10899–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolev, N.; Berezhnoy, N.V.; Eom, K.D.; Tam, J.P.; Nordenskiöld, L. A Universal Description for the Experimental Behavior of Salt-(In)dependent Oligocation-Induced DNA Condensation. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2009, 37, 7137–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolev, N.; Lyubartsev, A.P.; Nordenskiöld, L. Cation-Induced Polyelectrolyte-Polyelectrolyte Attraction in Solutions of DNA and Nucleosome Core Particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 158, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.N.; Chaturvedi, H.; Poler, J.C. Critical coagulation concentrations for carbon nanotubes in nonaqueous solvent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11583–11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| SWCNT/30-mer DNA | SWCNT/200-mer DNA | SWCNT/Calf Thymus DNA | SWCNT-COOH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta Potential (mV) | −37.7 ± 8.8 | −38.9 ± 9.3 | −40.1 ± 7.6 | −48.9 ± 11.2 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koh, B.; Cheng, W. The Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Aggregation in Aqueous Media Is Sensitive to Surface Charge. C 2016, 2, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2010006
Koh B, Cheng W. The Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Aggregation in Aqueous Media Is Sensitive to Surface Charge. C. 2016; 2(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoh, Byumseok, and Wei Cheng. 2016. "The Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Aggregation in Aqueous Media Is Sensitive to Surface Charge" C 2, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2010006
APA StyleKoh, B., & Cheng, W. (2016). The Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Aggregation in Aqueous Media Is Sensitive to Surface Charge. C, 2(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2010006