Graphene Oxide/Fe-Based Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Application in Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
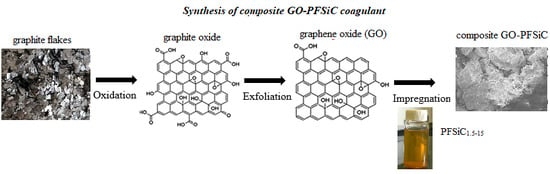
2.1. Preparation of Graphene Oxide (GO)
2.2. Preparation of PFSiC
2.3. Preparation of Composite GO-PFSiC Material
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. FT-Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.3. X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy (XRD)
2.5. Batch Coagulation Experiments
2.5.1. Coagulation Experiments Performed by Jar-Tests
2.5.2. Turbidity Removal
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Coagulation Performance
3.2.1. Determination of Optimum Coagulation Experimental Conditions
3.2.2. Determination of the Optimum Dosage and Type of Material
3.2.3. Determination of Optimum pH
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simate, G.S.; Iyuke, S.E.; Ndlovu, S.; Heydenrych, M. The heterogeneous coagulation and flocculation of brewery wastewater using carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Jiang, L.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Sulfonated graphene for persistent aromatic pollutant management. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3959–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallios, G.; Tolkou, A.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Stefusova, K.; Vaclavikova, M.; Deliyanni, E. Adsorption of arsenate by nano scaled activated carbon modified by iron and manganese oxides. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danô, M.; Viglašová, E.; Galamboŝ, M.; Rajec, P.; Novák, I. Sorption behaviour of pertechnetate on oxidized and reduced surface of activated carbon. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 314, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliyanni, E.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Matis, K.A. Activated carbons for the removal of heavy metal ions: A systematic review of recent literature focused on lead and arsenic ions. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Avranas, A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Multi-parametric adsorption effects of the reactive dye removal with commercial activated carbons. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, M.J.; May, S.; Mebberson, N.; Pendleton, P.; Vasilev, K.; Plush, S.E.; Hayball, J.D. Activated carbon, carbon nanotubes and graphene: Materials and composites for advanced water purification. C J. Carbon Res. 2017, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Pokatilov, E.P.; Nika, D.L.; Balandin, A.A.; Bao, W.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Extremely high thermal conductivity of graphene: Prospects for thermal management applications in nanoelectronic circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 151911–151913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Chen, W.; Feng, Y.P.; He, P.M. Tuning the electronic structure of graphene by an organic molecule. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.G.; Wei, X.D.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dwivedi, V.; Chi, C.; Wu, J. Graphene oxide/ferric hydroxide composites for efficient arsenate removal from drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setshedi, K.Z.; Bhaumik, M.; Onyango, M.S.; Maity, A. High-performance towards Cr (VI) removal using multi-active sites of polypyrrole–graphene oxide nanocomposites: Batch and column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamud, H.; Ivanov, P.; Russell, B.C.; Regan, P.H.; Ward, N.I. Selective sorption of uranium from aqueous solution by graphene oxide-modified materials. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 316, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, C.P. Preparation of a magnetic reduced-graphene oxide/tea waste composite for high-efficiency sorption of uranium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Removal of arsenic, chromium and uranium from water sources by novel nanostructured materials including graphene-based modified adsorbents: A mini review of recent developments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzebska, A.M.; Kurtycz, P.; Olszyna, A.R. Recent advances in graphene family materials toxicity investigations. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1320–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological interactions of graphene-family nanomaterials: An interdisciplinary review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muscatello, J.; Jaeger, F.; Matar, O.K.; Müller, E.A. optimizing water transport through graphene-based membranes: Insights from nonequilibrium molecular dynamics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12330–12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.-H.; Williams, C.J.; Derby, B.; Szekely, G. Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Ζ.; Yan, H.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. Flocculation performance and mechanism of graphene oxide for removal of various contaminants from water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3037–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmeguid, E.; Aboubaraka, A.E.; Aboelfetoh, E.F.; Ebeid, E.-Z.M. Coagulation effectiveness of graphene oxide for the removal of turbidity from raw surface water. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 738–746. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Jin, X.; Wang, F.; You, Y.; Chu, D.; Zetterlund, P.B.; Joshi, R.K. Cation-induced coagulation in graphene oxide suspensions. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 13, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Moussas, P.A. Polyferric silicate sulphate (PFSiS): Preparation, characterization and coagulation behavior. Desalination 2008, 224, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoupanos, N.D.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Tsoleridis, C.A. A systematic study for the characterization of a novel coagulant (polyaluminium silicate chloride). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 342, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Synthesis and coagulation performance of composite poly-aluminum-ferric-silicate-chloride coagulants in water and wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.; Mitrakas, M.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Ernst, E.; Zouboulis, A. Fluoride removal from water by composite Al/Fe/Si/Mg pre-polymerized coagulants: Characterization and application. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.; Tzollas, N.; Tolkou, A.; Mitrakas, M.; Ernst, M.; Zouboulis, A. Use of novel composite coagulants for arsenic removal from waters—Experimental insight for the application of polyferric sulfate (PFS). Sustainability 2017, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolkou, A.; Zouboulis, A. Application of composite pre-polymerized coagulants for the treatment of high-strength industrial wastewaters. Water 2020, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Mitrakas, M.; Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Batch and continuous dosing of conventional and composite coagulation agents for fouling control in a pilot-scale MBR. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Water Quality and Health—Review of Turbidity: Information for Regulators and Water Suppliers; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E., Jr. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Maity, A.; Pillay, K. Impact of process parameters on removal of Congo red by graphene oxide from aqueous solution. J. Env. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Gkotsis, P.K.; Castellana, M.; Cartechini, F.; Zouboulis, A.I. Production of demineralized water for use in thermal power stations by advanced treatment of secondary wastewater effluent. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesha, G.K.; Kumara, A.V.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Sampath, S. Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-shafai, N.M.; El-khouly, M.E.; El-kemary, M. Fabrication andcharacterization of graphene oxide—titanium dioxidenanocomposite for degradation of some toxic insecticides. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neolaka, Y.A.B.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.N.; Riwu, A.A.P.; Iqbal, M.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Kusuma, H.S. The adsorption of Cr(VI) from water samples using graphene oxide-magnetic (GO-Fe3O4) synthesized from natural cellulose-based graphite (kusambi wood or Schleichera oleosa): Study of kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6544–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussas, P.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Synthesis, Characterization and coagulation behavior of a composite coagulation reagent by the combination of Polyferric Sulphate (PFS) and cationic polyelectrolyte. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 96, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaiah, A.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposites and their tribological properties under magnetic field. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.; Hosseini, M. Magnetite graphene oxide/Lauric acid nanoparticles modified by ethylenediaminetetra acetic acid and its applications as an adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) ions. Synth. Met. 2016, 220, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, R.; Tjiu, W.W.; Pan, J.; Liu, T. Synthesis of Fe nanoparticles@graphene composites for environmental applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhong, W.; Wu, X.; Qiu, J. Facile synergetic dispersion approach for magnetic Fe3O4@graphene oxide/polystyrene tri-component nanocomposite via radical bulk polymerization. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, M.S.; Kumar, K.Y.; Prashanth, M.K.; Prasanna, B.P.; Vinuth, R. Adsorption and antimicrobial studies of chemically bonded magnetic graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposite for water purification. J. Water Process. Eng. 2017, 17, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Coagulant Type | Molar Ratios | Category |
|---|---|---|
| GO | - | Graphene Oxide |
| PFSiC1.5-15 | [OH]/[Al] = 1.5; [Fe]/[Si]= 15 | FeCl3+pSi+NaOH |
| GO-PFSiC1.5-15-1 | [OH]/[Al] = 1.5; [Fe]/[Si] = 15; [GO]/[Fe] = 1 | Fe-impregnated GO |
| GO-PFSiC1.5-15-0.5 | [OH]/[Al] = 1.5; [Fe]/[Si] = 15; [GO]/[Fe] = 0.5 | Fe-impregnated GO |
| GO-PFSiC1.5-15-0.3 | [OH]/[Al] = 1.5; [Fe]/[Si] = 15; [GO]/[Fe] = 0.3 | Fe-impregnated GO |
| Type of Sample to Be Treated | Turbidity (NTU) | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Simulated surface water | 17.2 | 7.6 ± 0.2 |
| Rapid Mixing Period | Slow Mixing Period | Sedimentation (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (min) | Mixing Rate (rpm) | Duration (min) | Mixing Rate (rpm) | |
| 1–2.5 | 160 | 10 | 40 | 30–60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Graphene Oxide/Fe-Based Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Application in Water Treatment. C 2020, 6, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/c6030044
Tolkou AK, Zouboulis AI. Graphene Oxide/Fe-Based Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Application in Water Treatment. C. 2020; 6(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/c6030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolkou, Athanasia K., and Anastasios I. Zouboulis. 2020. "Graphene Oxide/Fe-Based Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Application in Water Treatment" C 6, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/c6030044
APA StyleTolkou, A. K., & Zouboulis, A. I. (2020). Graphene Oxide/Fe-Based Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Application in Water Treatment. C, 6(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/c6030044