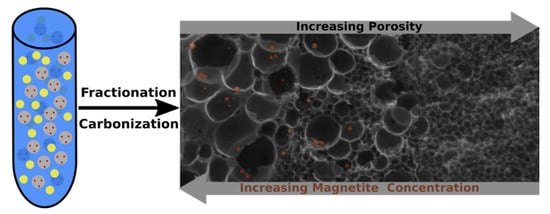
Anisotropic Magnetism in Gradient Porous Carbon Composite Aerogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Modification Agents
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Homogeneous Doping of Gradient Porous Carbons
3.2. Homogeneous Modification of Gradient Porous Carbon Composites
3.3. Synthesis of Gradient Porous Magnetic Carbons
3.4. Synthesis of Carbons Exhibiting Gradient Porosity and Anisotropic Magnetization
3.5. Tailored Adjustment of Gradients and Functionalities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fratzl, P.; Weinkamer, R. Nature’s hierarchical materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 1263–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, S.; Ozin, G.A. Synthesis of inorganic materials with complex form. Nat. Cell Biol. 1996, 382, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-H.; Huang, S.-Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Su, B.-L. Applications of hierarchically structured porous materials from energy storage and conversion, catalysis, photocatalysis, adsorption, separation, and sensing to biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3479–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.K.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired structural materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.-W.; Ma, Y.; Cölfen, H. Biomimetic mineralization. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 17, 415–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beda, A.; Villevieille, C.; Taberna, P.-L.; Simon, P.; Ghimbeu, C.M. Self-supported binder-free hard carbon electrodes for sodium-ion batteries: Insights into their sodium storage mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 5558–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzigar, M.R.; Talapaneni, S.N.; Joseph, S.; Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Scaranto, J.; Ravon, U.; Al-Bahily, K.; Vinu, A. Recent advances in functionalized micro and mesoporous carbon materials: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2680–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Guo, S. Towards high-efficiency nanoelectrocatalysts for oxygen reduction through engineering advanced carbon nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1273–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinle, A.; Elsaesser, M.S.; Husing, N. Sol–gel synthesis of monolithic materials with hierarchical porosity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3377–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, B.; Shiota, I. Functionally gradient materials. MRS Bull. 1995, 20, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Zhang, N.; Akram, A. State of the art review of functionally graded materials. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Sukkur, Pakistan, 30–31 January 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenthaler, S.; Zink, C.; Spencer, N.D. Surface-chemical and -morphological gradients. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, K.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B.; Liang, L.; Chai, G.; Liu, A. Smart design of wettability-patterned gradients on substrate-independent coated surfaces to control unidirectional spreading of droplets. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, T.; Leterrier, Y.; Karimi, A.; Månson, J.-A.E. A novel synthetic strategy for bioinspired functionally graded nanocomposites employing magnetic field gradients. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7246–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Nakanishi, H.; Pollanen, J.; Smoukov, S.; Halperin, W.P.; Grzybowski, B.A. Nanoparticle-loaded aerogels and layered aerogels cast from SOL-gel mixtures. Small 2011, 7, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachtenberg, J.E.; Placone, J.K.; Smith, B.T.; Fisher, J.P.; Mikos, A.G. Extrusion-based 3D printing of poly(propylene fumarate) scaffolds with hydroxyapatite gradients. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 532–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, J.-Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhong, Y.-H.; Du, A.; Shen, J. Fabrication of gradient density SiO2 aerogel. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 58, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiligtag, F.J.; Leccardi, M.J.I.A.; Erdem, D.; Süess, M.J.; Niederberger, M. Anisotropically structured magnetic aerogel monoliths. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13213–13221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Santandreu, A.; Kellogg, W.; Gupta, S.; Ogoke, O.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.-L.; Dai, L. Carbon nanocomposite catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions: From nitrogen doping to transition-metal addition. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 83–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Mao, S.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Metal/Porous Carbon composites for heterogeneous catalysis: Old catalysts with improved performance promoted by n-doping. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8090–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinnrock, A.; Schupp, D.; Cölfen, H. Nanoparticle gradient materials by centrifugation. Small 2018, 14, e1803518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Sun, D. Graded/gradient porous biomaterials. Materials 2009, 3, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, M.; Yuan, R. Gas diffusion through differently structured gas diffusion layers of PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, R.; Shabani, B. Review of gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane-based technologies with a focus on unitised regenerative fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3834–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Doh, S.; Park, H.S.; Kim, M.H. The effect of through plane pore gradient GDL on the water distribution of PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubenrauch, C.; Menner, A.; Bismarck, A.; Drenckhan, W. Emulsion and foam templating-promising routes to tailor-made porous polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10024–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.A.; Werner, J.G.; Wiesner, U. One-pot synthesis of hierarchically macro- and mesoporous Carbon materials with graded porosity. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Guo, S. High-performance electromagnetic wave absorption by designing the multilayer graphene/thermoplastic polyurethane porous composites with gradient foam ratio structure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Cai, Q.; Tang, S. Novel approach for fabrication and characterisation of porosity-graded material. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozoń, Ł.; Szlązak, K.; Święszkowski, W.; Garstecki, P.; Stubenrauch, C.; Barbetta, A.; Guzowski, J. 3D-printing of functionally graded porous materials using on-demand reconfigurable microfluidics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7620–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Xue, L. Continuous gradient nanoporous film enabled by delayed directional diffusion of solvent and selective swelling. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5864–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Pan, N.; Fan, W.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sui, K. Ultrafast fabrication of gradient nanoporous all-polysaccharide films as strong, superfast, and multiresponsive actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Luo, Z.; Kong, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H. Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3--based dual-gradient cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4516–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, P.; Sofie, S.; Deibert, M.; Smith, R.; Gorokhovsky, V. Thin film YSZ coatings on functionally graded freeze cast NiO/YSZ SOFC anode supports. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 39, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yao, M.; Xia, C. Anode substrate with continuous porosity gradient for tubular solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 38, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Feng, J.; Heil, T.; Wang, G.-C.; Adler, P.; Antonietti, M.; Oschatz, M. Strong metal oxide-support interactions in carbon/hematite nanohybrids activate novel energy storage modes for ionic liquid-based supercapacitors. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Thieme, S.; Brückner, J.; Oschatz, M.; Biemelt, T.; Mondin, G.; Althues, H.; Kaskel, S. Nanocasting hierarchical carbide-derived carbons in nanostructured opal assemblies for high-performance cathodes in lithium—Sulfur batteries. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12130–12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Cheng, L.; Ren, S.; Li, Z. Effect of core-shell microspheres as pore-forming agent on the properties of porous alumina ceramics. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Li, X.; Iqbal, A.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; et al. Anisotropic MXene aerogels with a mechanically tunable ratio of electromagnetic wave reflection to absorption. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1900267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yin, X.; Zhu, M.; Han, M.; Hou, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6332–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Hou, Z.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Flexible and thermostable graphene/Sic nanowire foam composites with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11803–11810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinnrock, A.; Cölfen, H. Putting a new spin on it: Gradient centrifugation for analytical and preparative applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 10026–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hagedorn, K.; Cölfen, H.; Polarz, S. Functional gradient inverse opal Carbon monoliths with directional and multinary porosity. Adv. Mater. 2016, 29, 1603356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahner, J.; Klinkenberg, N.; Frisch, M.; Brauchle, L.; Polarz, S. Creating directionality in nanoporous carbon materials: Adjustable combinations of structural and chemical gradients. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yavuz, C.T.; Prakash, A.; Mayo, J.; Colvin, V.L. Magnetic separations: From steel plants to biotechnology. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podoynitsyn, S.N.; Sorokina, O.N.; Kovarski, A.L. High-gradient magnetic separation using ferromagnetic membrane. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 397, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, U.E.; Ulrich, T. Magnetic field effects in chemical kinetics and related phenomena. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 51–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cao, G.; Gai, Z.; Hong, K.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. Porous carbon protected magnetite and silver hybrid nanoparticles: Morphological control, recyclable catalysts, and multicolor cell imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9446–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotbagi, T.V.; Shaughnessy, K.H.; LeDoux, C.; Cho, H.; Tay-Agbozo, S.; Van Zee, J.; Bakker, M.G. Copolymerization of transition metal salen complexes and conversion into metal nanoparticles supported on hierarchically porous carbon monoliths: A one pot synthesis. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, L.P.; Landfester, K. Magnetic polystyrene nanoparticles with a high magnetite content obtained by miniemulsion processes. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2003, 204, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.A.; Wilkie, C. Thermal degradation of blends of polystyrene and poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) and the copolymer, poly(styrene-co-sodium 4-styrenesulfonate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 66, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arganda-Carreras, I.; Kaynig, V.; Rueden, C.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Schindelin, J.E.; Cardona, A.; Seung, H.S. Trainable Weka Segmentation: A machine learning tool for microscopy pixel classification. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2424–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; Dezonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahner, J.; Hug, N.; Polarz, S. Anisotropic Magnetism in Gradient Porous Carbon Composite Aerogels. C 2021, 7, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7010022
Bahner J, Hug N, Polarz S. Anisotropic Magnetism in Gradient Porous Carbon Composite Aerogels. C. 2021; 7(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahner, Jochen, Nicolas Hug, and Sebastian Polarz. 2021. "Anisotropic Magnetism in Gradient Porous Carbon Composite Aerogels" C 7, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7010022
APA StyleBahner, J., Hug, N., & Polarz, S. (2021). Anisotropic Magnetism in Gradient Porous Carbon Composite Aerogels. C, 7(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7010022