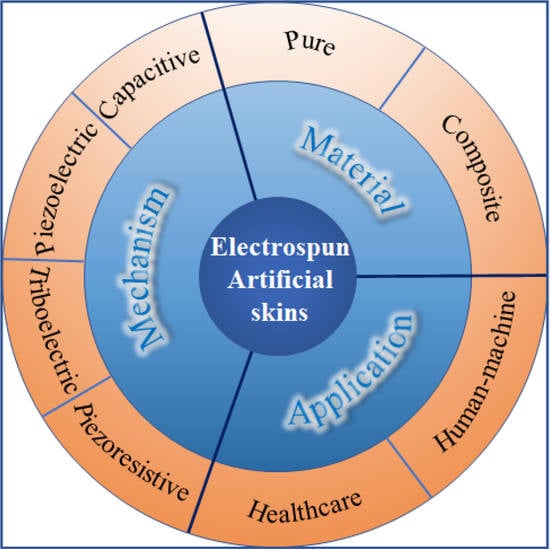
Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrospinning Method
3. Materials
3.1. Pure Polymer Nanofibers
3.2. Polymer Composite Nanofibers Incorporated with Nanofillers
4. Working Mechanism
4.1. Piezoresistive Effect
4.2. Capacitive Effect
4.3. Piezoelectric Effect
4.4. Triboelectric Effect
5. Application of the Electrospinning Nanofibers Based Artificial Skins
5.1. Healthcare Monitoring
5.2. Intelligent HMI
6. Summary and Outlook
6.1. Low Preparation Effectivity of Electrospun Artificial Skins
6.2. Biosafety Issues of Bionic Artificial Skin
6.3. Signal Interference Problem in Multi-Directional Detection
6.4. The Processing of the Acquired Signals by Artificial Skin
6.5. System Integration of Artificial Skin Devices
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, W.-Y.; Huang, W. Stretchable Thin-Film Electrodes for Flexible Electronics with High Deformability and Stretchability. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3349–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Z.; Yang, J. A New Class of Electronic Devices Based on Flexible Porous Substrates. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhao, K.; Yu, D.-G.; Zheng, X.; Huang, C. Advances in Biosensing and Environmental Monitoring Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 404–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Fong, H. Electrospun polyimide nanofibers and their applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 61, 67–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; Leblanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Zhu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, W.; Li, B.; Jin, R.; Han, N.; Wu, J.; et al. Sebum-MembraneInspired Protein-Based Bioprotonic Hydrogel for Artificial Skin and Human-Machine Merging Interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Mun, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Park, S.; Bao, Z.; Park, S. Electronic Skin: Recent Progress and Future Prospects for Skin-Attachable Devices for Health Monitoring, Robotics, and Prosthetics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortos, A.; Bao, Z. Skin-inspired electronic devices. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, P.; Huang, W.; Li, C.; Han, N.; Mu, S.; Zhou, H.; Mao, Y. Intrinsically Stretchable Polymer Semiconductor Based Electronic Skin for Multiple Perceptions of Force, Temperature, and Visible Light. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Superstable and Intrinsically Self-Healing Fibrous Membrane with Bionic Confined Protective Structure for Breathable Electronic Skin. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202200226. [Google Scholar]
- Persano, L.; Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Girardo, S.; Pisignano, D.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene). Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, B.; Jiang, P. Highly Thermally Conductive Yet Electrically Insulating Polymer/Boron Nitride Nanosheets Nanocomposite Films for Improved Thermal Management Capability. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun Medicated Nanofibers for Wound Healing: Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cheng, Y.F.; Yue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, L.; Cai, B.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, H.Z.; et al. High-performance flexible pressure sensor with a self-healing function for tactile feedback. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, M.; Yang, Y.; Kang, F. Carbon Nanofibers Prepared via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2547–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, X.; Ge, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Highly Stretchable, Anti-Corrosive and Wearable Strain Sensors Based on the PDMS/CNTs Decorated Elastomer Nanofiber Composite. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 362, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Kim, I.S.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.D.; Li, M.M.; Duvail, J.L.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yin, H.L. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, C.; Numata, K.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Seib, F.P. The Biomedical Use of Silk: Past, Present, Future. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1800465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziai, Y.; Petronella, F.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; Zakrzewska, A.; Kowalewski, T.A.; Augustyniak, W.; Li, X.; Calogero, A.; Sabała, I.; et al. Chameleon-inspired multifunctional plasmonic nanoplatforms for biosensing applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus fibre production methods: From specifics to technological convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Diverse Morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of Advanced Electrospinning Techniques: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Chung, M.; Kwon, J.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. 2D and 3D electrospinning technologies for the fabrication of nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering: A review. WIREs Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2020, 12, e1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Yu, D.G.; Ge, R. Electrospun nanofiber-based glucose sensors for glucose detection. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 944428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Fukuda, K.; Ma, S.; Wang, G.; Someya, T.; et al. Ultrathin Hydrogel Films toward Breathable Skin-Integrated Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 35, 2206793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Electrospun polymer biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Xu, B.; Wu, M.; Jing, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y. Breathable, washable and wearable woven-structured triboelectric nanogenerators utilizing electrospun nanofibers for biomechanical energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, D. Polymer-Based Nanofiber–Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Medical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.; Shao, J. Hybrid films prepared from a combination of electrospinning and casting for offering a dual-phase drug release. Polymers 2022, 14, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Yu, S.-H. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Lan, L.; Zhao, F.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. All-electrospun flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on metallic MXene nanosheets. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, G.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Yan, C.; Cheng, C.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; et al. Continuously prepared highly conductive and stretchable SWNT/MWNT synergistically composited electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane yarns for wearable sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2258–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Hou, C.; Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kimura, H.; Du, W. Embedding NiS Nanoflakes in Electrospun Carbon Fibers Containing NiS Nanoparticles for Hybrid Supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leote, R.J.B.; Beregoi, M.; Enculescu, I.; Diculescu, V.C. Metallized electrospun polymeric fibers for electrochemical sensors and actuators. Curr. Opin. Elrctrochem. 2022, 34, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hou, L.; Yue, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Miao, B.; Wang, N.; Bai, J.; Cui, Z.; et al. Progress of Fabrication and Applications of Electrospun Hierarchically Porous Nanofibers. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 604–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jin, G.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Srinivasan, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chen, J. Multi-functional electrospun nanofibres for advances in tissue regeneration, energy conversion & storage, and water treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Nauman, S.; Lubineau, G.; Alharbi, H.F. Post Processing Strategies for the Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of ENMs (Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes): A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, R.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Multistructured Electrospun Nanofibers for Air Filtration: A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 23293–23313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Pan, H.; Xie, G.; et al. High-performance piezoelectric composites via beta phase programming. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; He, E.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, D.P.; Diao, Y.; Chen, X. A fish-scale derived multifunctional nanofiber membrane for infected wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 5284–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, R.Y.; Sampath Kumar, T.S.; Doble, M. Electrospun Nanofibers of Curdlan (β-1,3 Glucan) Blend as a Potential Skin Scaffold Material. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 30, 1600417. [Google Scholar]
- Parangusan, H.; Ponnamma, D.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.A. Stretchable Electrospun PVDF-HFP/Co-ZnO Nanofibers as Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 754. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini-Alvand, E.; Khorasani, M.T. Fabrication of electrospun nanofibrous thermoresponsive semi-interpenetrating poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/polyvinyl alcohol networks containing ZnO nanoparticle mats: Characterization and antibacterial and cytocompatibility evaluation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhao, H.; Yue, L.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Lu, S.; Chen, G.; Gao, S.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16747–16789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yin, M.; Wei, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, D. Recent advances in morphology, aperture control, functional control and electrochemical sensors applications of carbon nanofibers. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 656, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoei-Dalfard, A.; Shahba, A.; Zaare, F.; Sargazi, G.; Seyedalipour, B.; Karami, Z. Lipase immobilization on a novel class of Zr-MOF/electrospun nanofibrous polymers: Biochemical characterization and efficient biodiesel production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Ning, X.; Wang, N. Tailoring moisture electroactive Ag/Zn@cotton coupled with electrospun PVDF/PS nanofibers for antimicrobial face masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Sonseca, A.; López, D.; Fiori, S.; Peponi, L. Shape memory effect on electrospun PLA-based fibers tailoring their thermal response. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Shakoori, P.; Arab-Bafrani, Z. Design and characterization of keratin/PVA-PLA nanofibers containing hybrids of nanofibrillated chitosan/ZnO nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhani, M.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G. Fabrication and characterization of mucoadhesive bioplastic patch via coaxial polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers with antimicrobial and wound healing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavičiūtė, E.; Pupkevičiūtė, S.; Juškaitė, V.; Žilius, M.; Stanys, S.; Pavilonis, A.; Briedis, V. Formation and Investigation of Electrospun PLA Materials with Propolis Extracts and Silver Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 8612819. [Google Scholar]
- Munawar, M.A.; Schubert, D.W. Revealing Electrical and Mechanical Performances of Highly Oriented Electrospun Conductive Nanofibers of Biopolymers with Tunable Diameter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrudo, F.F.F.; Mikael, P.E.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Udangawa, R.W.; Paradiso, P.; Chapman, C.A.; Hoffman, P.; Colaco, R.; Cabral, J.M.S.; Morgado, J.; et al. Polyaniline-polycaprolactone fibers for neural applications: Electroconductivity enhanced by pseudo-doping. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 120, 111680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tremblay, P.L.; Zhang, T. Optimizing the electrical conductivity of polyacrylonitrile/polyaniline with nickel nanoparticles for the enhanced electrostimulation of Schwann cells proliferation. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, M.A.; Schubert, D.W. Thermal-Induced Percolation Phenomena and Elasticity of Highly Oriented Electrospun Conductive Nanofibrous Biocomposites for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeralingam, S.; Badhulika, S. Bi(2)S(3)/PVDF/Ppy-Based Freestanding, Wearable, Transient Nanomembrane for Ultrasensitive Pressure, Strain, and Temperature Sensing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Samimi, A.; Khorram, M.; Abdi, M.M.; Golestaneh, S.I. Fabrication and characterization of conductive polypyrrole/chitosan/collagen electrospun nanofiber scaffold for tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Peng, Z.; Tang, W.; Li, N.; Liu, F. Assembly of DNA-unctionalized gold nanoparticles on electrospun nanofibers as a fluorescent sensor for nucleic acids. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5568–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhou, W.; Liang, X.; Zhou, G.; Han, C.C.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of a long-term controlled drug release system based on simple blended electrospun fibers. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandatang, N.; Pongsomboon, S.A.; Jumpapaeng, P.; Suwanakood, P.; Saengsuwan, S. Antimicrobial electrospun nanofiber mats of NaOH-hydrolyzed chitosan (HCS)/PVP/PVA incorporated with in-situ synthesized AgNPs: Fabrication, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, R.; Sumathi, V.; Tamilselvi, A.; Kavukcu, S.B.; Aruni, A.W. Functionalized electrospun nanofibers for high efficiency removal of particulate matter. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner Filiz, B.; Basaran Elalmis, Y.; Bektas, I.S.; Kanturk Figen, A. Fabrication of stable electrospun blended chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for designing naked-eye colorimetric glucose biosensor based on GOx/HRP. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejabri Kandeh, S.; Amini, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Simultaneous trace-level monitoring of seven opioid analgesic drugs in biological samples by pipette-tip micro solid phase extraction based on PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers followed by HPLC-UV analysis. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Pan, W.; Gao, Q. Preparation of carboxymethyl starch/polyvinyl-alcohol electrospun composite nanofibers from a green approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, K.; Shi, W.; Cai, J. Preparation and performance evaluation of chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofiber membrane for heavy metal ions and organic pollutants removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamady Hussein, M.A.; Ulag, S.; Abo Dena, A.S.; Sahin, A.; Grinholc, M.; Gunduz, O.; El-Sherbiny, I.; Megahed, M. Chitosan/Gold Hybrid Nanoparticles Enriched Electrospun PVA Nanofibrous Mats for the Topical Delivery of Punica granatum L. Extract: Synthesis, Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5133–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xia, X.; Chen, J.; Xia, D.; Xu, R.; Zou, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, C. Paclitaxel-loaded lignin particle encapsulated into electrospun PVA/PVP composite nanofiber for effective cervical cancer cell inhibition. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathmanapan, S.; Sekar, M.; Pandurangan, A.K.; Anandasadagopan, S.K. Fabrication of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle–Incorporated Coaxial Nanofiber for Evaluating the In Vitro Osteogenic Potential. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 194, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzi, M.; Shabani, I.; Mohandesi, J.A. Enhanced mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol electrospun nanofibers by incorporation of graphene nanoplatelets. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 125, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Adhikary, P.; Jana, S.; Biswas, A.; Sencadas, V.; Gupta, S.D.; Tudu, B.; Mandal, D. Electrospun gelatin nanofiber based self-powered bio-e-skin for health care monitoring. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, M.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membranes by electro-spinning for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425–426, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Lee, S.; Matsuhisa, N.; Inoue, D.; Yokota, T.; Hashizume, D.; Someya, T. Highly Durable Nanofiber-Reinforced Elastic Conductors for Skin-Tight Electronic Textiles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7905–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Rault, F.; Lewandowski, M.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Salaun, F. Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers 2021, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castkova, K.; Kastyl, J.; Sobola, D.; Petrus, J.; Stastna, E.; Riha, D.; Tofel, P. Structure-Properties Relationship of Electrospun PVDF Fibers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Jose, R.; Mustapha, M.; Saheed, M.S.M. Ultrasensitive aptasensor using electrospun MXene/polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber composite for Ochratoxin A detection. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-G.; Javed, H.; Zhang, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Westerhoff, P.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Porous Electrospun Fibers Embedding TiO2 for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.I.; Yoon, S.; Kim, T.E.; Wi, H.; Kim, K.J.; Woo, E.J.; Sadleir, R.J. Nanofiber web textile dry electrodes for long-term biopotential recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Q.; Jin, X.; Ke, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Huang, C. Facile Strategy for Fabrication of Flexible, Breathable, and Washable Piezoelectric Sensors via Welding of Nanofibers with Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38023–38030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Suh, I.W.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Polyvinylidene fluoride/silk fibroin-based bio-piezoelectric nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical application. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 15, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, P.; Sobola, D.; Castkova, K.; Knapek, A.; Burda, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Dallaev, R.; Tofel, P.; Trcka, T.; Grmela, L.; et al. Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Electrospun Fibers Doped by Carbon Flakes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Das, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Sengupta, P.; Datta, P. Flexible Nanogenerator from Electrospun PVDF-Polycarbazole Nanofiber Membranes for Human Motion Energy-Harvesting Device Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, M.; Martin-Alfonso, J.E.; Sanchez, M.C.; Valencia, C.; Franco, J.M. Electrospun lignin-PVP nanofibers and their ability for structuring oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, H.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, C.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Ke, K.; Bao, R.-Y.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W. Boosting piezoelectric response of PVDF-TrFE via MXene for self-powered linear pressure sensor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 202, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, G.; Li, M.; Han, X.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, Q.; Yang, P.; Dai, L.; et al. All electrospun fabrics based piezoelectric tactile sensor. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 415502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.M.S.; Rahman, M.T.; Salauddin, M.; Sharma, S.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Cho, H.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. Electrospun PVDF-TrFE/MXene Nanofiber Mat-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Smart Home Appliances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4955–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Y. A novel PVDF-TiO(2)@g-C(3)N(4) composite electrospun fiber for efficient photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light irradiation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, M.; Chen, W.-C.; Cho, C.-J.; Veeramuthu, L.; Chen, L.-G.; Li, K.-Y.; Tsai, M.-L.; Lai, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; et al. Enhanced piezoelectric and photocatalytic performance of flexible energy harvester based on CsZn0.75Pb0.25I3/CNC–PVDF composite nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, T.; Maharjan, P.; Cho, H.; Park, C.; Yoon, S.H.; Sharma, S.; Salauddin, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Rana, S.M.S.; Park, J.Y. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on MXene functionalized polyvinylidene fluoride composite nanofibers. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, T.; Jin, L.; Yan, C.; Huang, H.; Chu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, D.; Tian, G.; Gao, Y.; et al. Cowpea-structured PVDF/ZnO nanofibers based flexible self-powered piezoelectric bending motion sensor towards remote control of gestures. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jin, H.; Dong, S.; Huang, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Xuan, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; et al. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on electrospun PVDF-graphene nanosheet composite nanofibers for energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Jiang, P. Synergistic effect of graphene nanosheet and BaTiO3 nanoparticles on performance enhancement of electrospun PVDF nanofiber mat for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Yang, D.; Park, B.C.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. A stretchable strain sensor based on a metal nanoparticle thin film for human motion detection. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11932–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.L.; Xia, G.T.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, K. Self-Powered Electronic Skin for Remote Human-Machine Synchronization. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Hang, C.-Z.; Zhao, X.-F.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Ma, R.-G.; Wang, J.-C.; Lu, H.-L.; Zhang, D.W. Advance on flexible pressure sensors based on metal and carbonaceous nanomaterial. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.L. Fiber/Fabric-Based Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Flexible/Stretchable and Wearable Electronics and Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, N.; Xu, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in flexible tactile sensors for intelligent systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, Y. Functionalized Fiber-Based Strain Sensors: Pathway to Next-Generation Wearable Electronics. Nanomicro. Lett. 2022, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, X.; Tian, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Qu, L. Recent Progress on Smart Fiber and Textile Based Wearable Strain Sensors: Materials, Fabrications and Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 361–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Awuye, D.E.; Guan, M.; Zhu, Y. Electrospinning-Based Biosensors for Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gong, H.; Li, W.; Gao, F.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, S. A flexible and highly sensitive pressure sensor based on three-dimensional electrospun carbon nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13898–13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. A flexible and self-formed sandwich structure strain sensor based on AgNW decorated electrospun fibrous mats with excellent sensing capability and good oxidation inhibition properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7035–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, T.; Kato, Y.; Sekitani, T.; Iba, S.; Noguchi, Y. Murase, networks of pressure and thermal sensors with organic transistor active matrixes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12321–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, C.; DiMaio, J.R.; McAllister, E.; Hossini, R.; Wagener, E.; Ballato, J.; Priya, S.; Ballato, A.; Smith, D.W. Enhanced piezoelectric performance from carbon fluoropolymer nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 124104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, H.; He, L.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Mao, Y. 3D printed triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered human-machine interactive sensor for breathing-based language expression. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7460–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qin, C.; Feng, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y. Non-contact cylindrical rotating triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting kinetic energy from hydraulics. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chao, M.; Liang, E. A paper triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered electronic systems. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14499–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Fang, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tian, B.; Verma, P.; Maeda, R.; Jiang, Z. An ultrasensitive and stretchable strain sensor based on a microcrack structure for motion monitoring. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, M.; Li, Z.; Li, X. Self-Powered Flexible Sensor Based on the Graphene Modified P(VDF-TrFE) Electrospun Fibers for Pressure Detection. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, G.; Yu, W.; Li, G.; Meng, C.; Guo, S. Wearable, ultrathin and breathable tactile sensors with an integrated all-nanofiber network structure for highly sensitive and reliable motion monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; He, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L. A Highly Sensitive and Flexible Strain Sensor Based on Dopamine-Modified Electrospun Styrene-Ethylene-Butylene-Styrene Block Copolymer Yarns and Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2022, 14, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Pin, K.Y.; Reddy, V.S.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Ji, D.; Serrano-García, W.; Bhargava, S.K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chinnappan, A. Micro/nanofiber-based noninvasive devices for health monitoring diagnosis and rehabilitation. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 41309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, S.; Singh, Z.; Sharma, A.K.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K.; Mahajan, A. Self-powered biocompatible humidity sensor based on an electrospun anisotropic triboelectric nanogenerator for non-invasive diagnostic applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, J. Flexible multifunctional graphite nanosheet/electrospun-polyamide 66 nanocomposite sensor for ECG, strain, temperature and gas measurements. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadkule, S.S.; Sarma, S. High-performance flexible temperature sensor from hybrid nanocomposite for continuous human body temperature monitoring. Polym. Compos. 2022, 44, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamma, D.; Parangusan, H.; Tanvir, A.; AlMa’adeed, M.A.A. Smart and robust electrospun fabrics of piezoelectric polymer nanocomposite for self-powering electronic textiles. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chen, H.; Kim, E.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, J.; Jeon, S.; et al. Flexible temperature sensors made of aligned electrospun carbon nanofiber films with outstanding sensitivity and selectivity towards temperature. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Tang, M.; Yang, C.; Luan, H. Microstructured Flexible Pressure Sensor Based on Nanofibrous Films for Human Motions and Physiological Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19191–19197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. An ultrathin stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator with coplanar electrode for energy harvesting and gesture sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12361–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhong, J.; Lin, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Jiang, H.; Wu, N.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Electrospun polyetherimide electret nonwoven for bi-functional smart face mask. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sultana, A.; Garain, S.; Xie, M.; Bowen, C.R.; Henkel, K.; Schmeiβer, D.; Mandal, D. A Self-Powered Wearable Pressure Sensor and Pyroelectric Breathing Sensor Based on GO Interfaced PVDF Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Tang, A.; Wan, C.; Sui, T.; Zhang, D.; Ju, X. A Washable, Permeable, and Ultrasensitive Sn-Based Textile Pressure Sensor for Health Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2023, 70, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.; Chen, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Flexible fiber-based hybrid nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting and physiological monitoring. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shang, L. Smart Film Actuators for Biomedical Applications. Small 2022, 18, e2105116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chhetry, A.; Ko, S.; Park, J.Y. A Hybrid Ionic Nanofibrous Membrane Based Pressure Sensor with Ultra-High Sensitivity over Broad Pressure Range for Wearable Healthcare Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 34th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Virtual, 25–29 January 2021; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Lv, C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Lu, G.; Jia, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun bifunctional MXene-based electronic skins with high performance electromagnetic shielding and pressure sensing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeralingam, S.; Priya, S.; Badhulika, S. NiO nanofibers interspersed sponge based low cost, multifunctional platform for broadband UV protection, ultrasensitive strain and robust finger-tip skin inspired pressure sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-F.; Cheng, C.; Yang, C.-C.; Hsiao, W.-T.; Yang, C.-R. A wearable and highly sensitive capacitive pressure sensor integrated a dual-layer dielectric layer of PDMS microcylinder array and PVDF electrospun fiber. Org. Electron. 2021, 98, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, N.; He, J.; You, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, K.; Shao, W.; Liu, F.; Chu, Y.; Ding, B. A Stretchable, Highly Sensitive, and Multimodal Mechanical Fabric Sensor Based on Electrospun Conductive Nanofiber Yarn for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jang, S.; Lee, D.; Ra, Y.; Kam, D.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, D.; Seo, K.D.; Choi, D. Self-powered hybrid triboelectric–piezoelectric electronic skin based on P(VDF-TrFE) electrospun nanofibers for artificial sensory system. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2022, 4, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Zeng, W.; Asci, C.; Del-Rio-Ruiz, R.; Sonkusale, S. Recent progress in electrospun nanomaterials for wearables. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, S.; Kong, D. A stretchable and breathable form of epidermal device based on elastomeric nanofibre textiles and silver nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 9748–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, K.; Nan, N.; You, X.; Shao, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. Highly sensitive, self-powered and wearable electronic skin based on pressure-sensitive nanofiber woven fabric sensor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Chen, T.; Wang, A.; Xu, R.; Xiao, X. Highly Sensitive and Flexible Capacitive Pressure Sensor Based on a Dual-Structured Nanofiber Membrane as the Dielectric for Attachable Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, H.B.; Yeon, S.M.; Park, J.; Lee, N.K. Flexible and Stretchable Piezoelectric Sensor with Thickness-Tunable Configuration of Electrospun Nanofiber Mat and Elastomeric Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24773–24781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, G.; Pan, L.; Chen, D. Electrospun flexible PVDF/GO piezoelectric pressure sensor for human joint monitoring. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2022, 129, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. Wearable flexible sweat sensors for healthcare monitoring: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chang, A.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Hollister, J.; Che, Z.; Wan, X.; Yin, J.; Wang, S.; Lee, S.; et al. Air-Permeable Textile Bioelectronics for Wearable Energy Harvesting and Active Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 2201703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Luo, W.L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Yun, M.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Ag/alginate nanofiber membrane for flexible electronic skin. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 445502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, M.; Shang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-sensitive and durable strain sensor with sandwich structure and excellent anti-interference ability for wearable electronic skins. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; He, J.; Nan, N.; Sun, X.; Qi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, W.; Liu, F.; Cui, S. Stretchable capacitive fabric electronic skin woven by electrospun nanofiber coated yarns for detecting tactile and multimodal mechanical stimuli. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12981–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Schubert, D.W. Highly Sensitive Ultrathin Flexible Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Carbon Black Fibrous Film Strain Sensor with Adjustable Scaffold Networks. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Li, G.; Meng, C.; Guo, S. Printable, flexible, breathable and sweatproof bifunctional sensors based on an all-nanofiber platform for fully decoupled pressure–temperature sensing application. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araldi da Silva, B.; de Sousa Cunha, R.; Valério, A.; De Noni Junior, A.; Hotza, D.; Gómez González, S.Y. Electrospinning of cellulose using ionic liquids: An overview on processing and applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalali, S.; Mahdavi Varposhti, A.; Abrishami, S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Asadnia, M.; Huang, S.; Peng, S.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, S. A Review on Wearable Electrospun Polymeric Piezoelectric Sensors and Energy Harvesters. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 308, 2200442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, G.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; et al. A Bioinspired, Durable, and Nondisposable Transparent Graphene Skin Electrode for Electrophysiological Signal Detection. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.W.; Sunwoo, S.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Baik, S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Soft Bioelectronics Based on Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5068–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Fei, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, J. Recent Progress of Wearable Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors Based on Nanofibers, Yarns, and Their Fabrics via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8, 2201161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, G.; Wei, Q.; Su, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y. Degradable MXene-Doped Polylactic Acid Textiles for Wearable Biomonitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5600–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.-C.; Ku, H.-J.; Cho, C.-J.; Chen, W.-C.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Rwei, S.-P.; Borsali, R.; Kuo, C.-C. An intrinsically stretchable and ultrasensitive nanofiber-based resistive pressure sensor for wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Wang, H.; You, X.; Tao, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Shao, W.; Cui, S. Core-sheath nanofiber yarn for textile pressure sensor with high pressure sensitivity and spatial tactile acuity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qin, S.; Haick, H.; Wang, Y. Toward a new generation of permeable skin electronics. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 3051–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. Electrospun nanofiber-based soft electronics. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifuzzaman, M.; Zahed, M.A.; Sharma, S.; Yoon, S.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. Laser-Carbonized Mxene-Reinforced Hierarchical Nanofibers for Breathable and Reusable Electrophysiological E-Tattoos. In Proceedings of the 2021 21st International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–24 June 2021; pp. 904–907. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Yu, M.; Feng, L.W.; Tang, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Soft Fiber Electronics Based on Semiconducting Polymer. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 4693–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, H.; Hu, D.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, J.; Chang, X.; et al. Stretchable strain and temperature sensor based on fibrous polyurethane film saturated with ionic liquid. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lou, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.; Li, X. A Highly Sensitive, Breathable, and Biocompatible Wearable Sensor Based on Nanofiber Membrane for Pressure and Humidity Monitoring. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luo, J.; Huang, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, M.; Tang, L.; Xue, H.; Gao, J.; Mai, Y.-W. A highly stretchable, super-hydrophobic strain sensor based on polydopamine and graphene reinforced nanofiber composite for human motion monitoring. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 181, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhan, P.; Ren, M.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Significant Stretchability Enhancement of a Crack-Based Strain Sensor Combined with High Sensitivity and Superior Durability for Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7405–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Lan, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Q.; Shen, X. Conductive Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanofibrous Membranes with Superior Softness for High-Resolution Pressure Sensing and Electrophysiology Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Z.-C.; Yang, Y.; Deng, B.-W.; Yin, B.; Ke, K.; Yang, M.-B. Flexible TPU strain sensors with tunable sensitivity and stretchability by coupling AgNWs with rGO. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4040–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Geng, J.; Lin, C.; Li, G.; Peng, H.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, G. Flexible multifunctional TPU strain sensors with improved sensitivity and wide sensing range based on MXene/AgNWs. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Han, K.S.; Cao, V.A.; Nah, J. Ultra-flexible nanofiber-based multifunctional motion sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Chai, Y.; et al. Permeable superelastic liquid-metal fibre mat enables biocompatible and monolithic stretchable electronics. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Cheng, W.; Xin, M.; Zhu, T.; Du, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Versatile self-assembled electrospun micropyramid arrays for high-performance on-skin devices with minimal sensory interference. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Gong, Q.; Xie, G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Muscle Fibers Inspired High-Performance Piezoelectric Textiles for Wearable Physiological Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ning, C.; Cheng, R.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. All-Nanofiber Self-Powered Skin-Interfaced Real-Time Respiratory Monitoring System for Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Diagnosing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Patnam, H.; Manchi, P.; Paranjape, M.V.; Kurakula, A.; Yu, J.S. Biocompatible electrospun fibers-based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and healthcare monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Deng, W.; Chu, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Fan, X.; Song, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tian, G.; et al. Hierarchically Microstructure-Bioinspired Flexible Piezoresistive Bioelectronics. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11555–11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xiao, X.; Carlo, A.D.; Yin, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, J. Advances in Wearable Strain Sensors Based on Electrospun Fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wan, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Miao, L.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Self-Powered Multifunctional Electronic Skin for a Smart Anti-Counterfeiting Signature System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22357–22364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Ma, C.; Uzabakiriho, P.C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, G. Mechanical Gradients Enable Highly Stretchable Electronics Based on Nanofiber Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 35997–36006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, B.; Yang, K.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, C. A high-performance piezoresistive sensor based on poly (styrene-co-methacrylic acid)@polypyrrole microspheres/graphene-decorated TPU electrospun membrane for human motion detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tang, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhuang, X.; Yan, J. Highly sensitive, direction-aware, and transparent strain sensor based on oriented electrospun nanofibers for wearable electronic applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qin, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, C.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y. An ultra-wide sensing range film strain sensor based on a branch-shaped PAN-based carbon nanofiber and carbon black synergistic conductive network for human motion detection and human–machine interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 6296–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Jana, S.; Mallick, Z.; Ghosh, S.K.; Dutta, B.; Sarkar, S.; Sinha, C.; Mandal, D. Two-Dimensional MOF Modulated Fiber Nanogenerator for Effective Acoustoelectric Conversion and Human Motion Detection. Langmuir 2021, 37, 7107–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Guo, D.; Dong, S.; Dhakal, R.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Kim, N.Y. A high-performance wearable pressure sensor based on an MXene/PVP composite nanofiber membrane for health monitoring. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, O.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, J.H. Wearable high-performance pressure sensors based on three-dimensional electrospun conductive nanofibers. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. Mechanically robust, stretchable, autonomously adhesive, and environmentally tolerant triboelectric electronic skin for self-powered healthcare monitoring and tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, K.; Chai, B.; Qiao, S.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, P.; Huang, X. Core-shell structured silk Fibroin/PVDF piezoelectric nanofibers for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022, 4, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, R.; Lin, L. A flexible tactile sensor that uses polyimide/graphene oxide nanofiber as dielectric membrane for vertical and lateral force detection. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 405205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Cong, H.; Jiang, G.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; He, H. A Review on PVDF Nanofibers in Textiles for Flexible Piezoelectric Sensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1522–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Sun, X.-C.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.-S.; Hua, J.-G.; Yu, Y.-H.; Li, S.-X.; Dai, Y.-Z.; Song, X.-Y.; et al. Flexible pressure sensor based on PVDF nanofiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 280, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X. A flexible capacitive sensor based on the electrospun PVDF nanofiber membrane with carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 299, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Thapa, K.; Ojha, G.P.; Seo, M.-K.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Sohn, J.I. Metal-organic frameworks-based triboelectric nanogenerator powered visible light communication system for wireless human-machine interactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, Q.; Fan, S.; Guo, Q.; Bi, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, J. Hyaline and stretchable haptic interfaces based on serpentine-shaped silver nanofiber networks. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, T.; Zi, J.; Zhang, D.; Geng, X.; Yang, P. Multifunctional device integrating dual-temperature regulator for outdoor personal thermal comfort and triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered human-machine interaction. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; Di, P.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wan, P. Flexible breathable photothermal-therapy epidermic sensor with MXene for ultrasensitive wearable human-machine interaction. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Meng, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Chen, G.; Qin, Y.; Han, M.; Li, X. Self-Powered Tactile Sensor for Gesture Recognition Using Deep Learning Algorithms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25629–25637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Chen, B.; Liang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Transparent and Stretchable Strain Sensors with Improved Sensitivity and Reliability Based on Ag NWs and PEDOT:PSS Patterned Microstructures. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1901360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, X.; Que, M.; Peng, Z.; Wang, H.; Pan, C. A Highly Stretchable Transparent Self-Powered Triboelectric Tactile Sensor with Metallized Nanofibers for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kaliannagounder, V.K.; Unnithan, A.R.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S.; Ramachandra Kurup Sasikala, A. Development of In-Situ Poled Nanofiber Based Flexible Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Motion Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Bing, Y.; Li, F.; Mei, H.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T. An All-Nanofiber-Based, Breathable, Ultralight Electronic Skin for Monitoring Physiological Signals. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Nauman, S.; Khan, Z.M. Electrospun nanofibrous yarn based piezoresistive flexible strain sensor for human motion detection and speech recognition. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, X.; Yu, J.; Qian, S.; Hou, X.; Cui, M.; Yang, Y.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Chou, X. A high-resolution flexible sensor array based on PZT nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 155503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Romano, J.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Electrospun bundled carbon nanofibers for skin-inspired tactile sensing, proprioception and gesture tracking applications. npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Razmjou, A.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Kottapalli, A.; Asadnia, M. Sensitive and Flexible Polymeric Strain Sensor for Accurate Human Motion Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Gu, F.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Jin, H.; Pan, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Flexible, Permeable, and Recyclable Liquid-Metal-Based Transient Circuit Enables Contact/Noncontact Sensing for Wearable Human-Machine Interaction. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2201534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, B.; Chen, A.; Wang, L.; Shen, G. Biocompatible liquid metal coated stretchable electrospinning film for strain sensors monitoring system. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Feng, T.; Wu, J.; Zhu, P.; Mao, Y. Deep-Learning-Assisted Noncontact Gesture-Recognition System for Touchless Human-Machine Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liang, F.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Hu, C.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, F.; et al. Ultra-robust stretchable electrode for e-skin: In situ assembly using a nanofiber scaffold and liquid metal to mimic water-to-net interaction. InfoMat 2022, 4, e12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; He, L.; Gong, M.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Shi, F.; Zhang, L.; Wan, P. Breathable Ti(3)C(2)T(x) MXene/Protein Nanocomposites for Ultrasensitive Medical Pressure Sensor with Degradability in Solvents. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9746–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Jiang, C.; Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Flexible Noncontact Sensing for Human-Machine Interaction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Wan, P.; Ma, D.; Zhong, M.; Liao, M.; Ye, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L. Flexible Breathable Nanomesh Electronic Devices for On-Demand Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Liu, Q.; Ren, J.; Chen, W.; Pei, Y.; Kaplan, D.L.; Ling, S. Electro-Blown Spun Silk/Graphene Nanoionotronic Skin for Multifunctional Fire Protection and Alarm. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Lu, L.; Pan, Z.; Mao, Y. Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020223
Chen X, Li H, Xu Z, Lu L, Pan Z, Mao Y. Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(2):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020223
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingwei, Han Li, Ziteng Xu, Lijun Lu, Zhifeng Pan, and Yanchao Mao. 2023. "Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction" Biomimetics 8, no. 2: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020223
APA StyleChen, X., Li, H., Xu, Z., Lu, L., Pan, Z., & Mao, Y. (2023). Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction. Biomimetics, 8(2), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020223