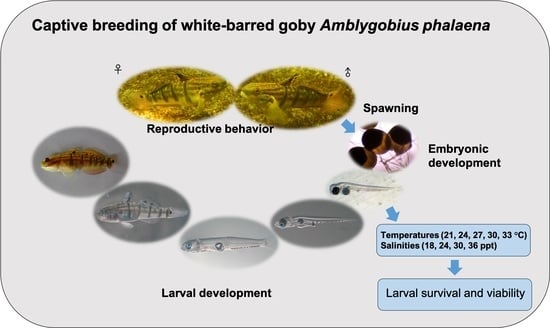
Captive Reproductive Behavior, Spawning, and Early Development of White-Barred Goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) and Examined Larval Survival and Viability at Different Water Temperatures and Salinities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Broodstock Maintenance
2.2. Reproductive Behavior
2.3. Spawning Record and Egg Collection
2.4. Embryonic Development Observation
2.5. Live Prey Preparation
2.6. Larval Rearing
2.7. Observation and Measurement of Larvae and Juveniles
2.8. Experiment 1: Effects of Different Temperatures on Larval Survival and Viability
2.9. Experiment 2: Effects of Different Salinities on Larval Survival and Viability
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Reproductive Behavior
3.2. Spawning
3.3. Embryonic Development
3.4. Larval and Juvenile Development
3.5. Experiment 1
3.6. Experiment 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pouil, S.; Tlusty, M.F.; Rhyne, A.L.; Metian, M. Aquaculture of marine ornamental fish: Overview of the production trends and the role of academia in research progress. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmtag, M.R. The Marine Ornamental Species Trade. In Marine Ornamental Species Aquaculture; Calado, R., Olivotto, I., Planas, M., Holt, G.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E. Exploitation of Coral Reef Fishes for the Aquarium Trade; Marine Conservation Society: Ross-on-Wye, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Rhyne, A.L.; Tlusty, M.F.; Schofield, P.J.; Kaufman, L.; Morris, J.A., Jr.; Bruckner, A.W. Revealing the appetite of the marine aquarium fish trade: The volume and biodiversity of fish imported into the United States. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, F.P.A.; Valenti, W.C.; Calado, R. Traceability issues in the trade of marine ornamental species. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammannagoda, S.T. Sustainable Fishing Methods in Asia Pacific Region. In Sustainable Aquaculture, Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future; Hai, F.I., Visvanathan, C., Boopathy, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zeng, C.; Jerry, D.R.; Cobcroft, J.M. Recent advances of marine ornamental fish larviculture: Broodstock reproduction, live prey and feeding regimes, and comparison between demersal and pelagic spawners. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1518–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, I.; Planas, M.; Simões, N.; Holt, G.J.; Avella, M.A.; Calado, R. Advances in breeding and rearing marine ornamentals. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 135–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reef to Rainforest Media. Available online: https://www.reef2rainforest.com/2019/08/28/coral-magazines-captive-bred-marine-fish-species-list-for-2019/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Darcy, G.H. Comparison of Ecological and Life History Information on Gobiid Fishes, with Emphasis on the South-Eastern United States; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFC-15; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1980.
- Olivotto, I.; Zenobi, A.; Rollo, A.; Migliarini, B.; Avella, M.; Carnevali, O. Breeding, rearing and feeding studies in the cleaner goby Gobiosoma evelynae. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shei, M.; Mies, M.; Olivotto, I. Other Demersal Spawners and Mouthbrooders. In Marine Ornamental Species Aquaculture; Calado, R.I., Olivotto, I.M., Planas, M., Holt, G.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Archambeault, S.; Ng, E.; Rapp, L.; Cerino, D.; Bourque, B.; Solomon-Lane, T.; Grober, M.; Rhyne, A.; Crow, K. Reproduction, larviculture and early development of the bluebanded goby, Lythrypnus dalli, an emerging model organism for studies in evolutionary developmental biology and sexual plasticity. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1899–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choosri, S.; Pratoomyot, J.; Munkongsomboon, S.; Phuangsanthia, W. Embryonic development of Blueband goby, Valenciennea strigata under the laboratory conditions. Khon Kaen Agr. J. 2019, 47, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Oungern, D.; Pichikul, P.; Wudtisin, I.; Muthuwan, V. Embryonic development of yellow prawn-goby, Cryptocentrus cinctus (Herre, 1936) in the Hatchery. Burapha Scuence J. 2021, 26, 1918–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, P.S.; Leu, M.Y.; Meng, P.J. Year-round natural spawning, early development, and the effects of temperature, salinity and prey density on captive ornate goby Istigobius ornatus (Rüppell, 1830) larval survival. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majoris, J.E.; Francisco, F.A.; Atema, J.; Buston, P.M. Reproduction, early development, and larval rearing strategies for two sponge-dwelling neon gobies, Elacatinus lori and E. colini. Aquaculture 2018, 483, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzani, A.S.; Pham, N.K.; Lin, J.; Neto, A.O. Reproductive behavior, embryonic and early larval development of the red head goby, Elacatinus puncticulatus. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 145, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, R.; Faria, C.; Gil, F.; Gonçalves, E.J. Early Development of Gobies. In The Biology of Gobies; Patzner, R.A., Van Tassell, J.L., Kovacic, M., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 403–462. [Google Scholar]
- Herler, J.; Munday, P.L.; Hernaman, V. Gobies on Coral Reefs. In The Biology of Gobies; Patzner, R.A., Van Tassell, J.L., Kovacic, M., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 493–529. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R.F. Micronesian Reef Fishes: A Comprehensive Guide to the Coral Reef Fishes of Micronesia, 3rd ed.; Coral Graphics: Barrigada, Guam, USA, 1999; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- Akihito, P. Genus Amblygobius. In The Fishes of the Japanese Archipelago; Masuda, H., Amaoka, K., Araga, C., Uyeno, T., Yoshino, T., Eds.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1984; pp. 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, M.; Shimizu, M.; Nose, Y. Food Habits of Teleostean Reef Fishes in Okinawa Island, Southern Japan; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1984; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- LiveAquaria. Available online: https://www.liveaquaria.com/product/206/sleeper-banded (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Hernaman, V.; Munday, P.L. Life-history characteristics of coral reef gobies. II. Mortality rate, mating system and timing of maturation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 290, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takegaki, T. Monogamous mating system and spawning cycle in the gobiid fish, Amblygobius phalaena (Gobiidae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2000, 59, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takegaki, T. Female egg care subsequent to removal of egg-tending male in a monogamous goby, Amblygobius phalaena (Gobiidae): A preliminary observation. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Côté, I.M. Monogamy in marine fishes. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2004, 79, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, J.A.; Zeng, C. Development of captive breeding techniques for marine ornamental fish: A review. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2010, 18, 315–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.A.; Hill, J.E. Design criteria for recirculating, marine ornamental production systems. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielder, D.S.; Bardsley, W.J.; Allan, G.L.; Pankhurst, P.M. The effects of salinity and temperature on growth and survival of Australian snapper, Pagrus auratus larvae. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zang, W. Effects of salinity on embryos and larvae of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, M.Y.; Tai, K.Y.; Meng, P.J.; Tang, C.H.; Wang, P.H.; Tew, K.S. Embryonic, larval and juvenile development of the longfin batfish, Platax teira (Forsskål, 1775) under controlled conditions with special regard to mitigate cannibalism for larviculture. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, M.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tu, Y.H.; Chiu, P.S.; Yu, B.H.; Wang, J.B.; Tew, K.S.; Meng, P.J. Natural spawning, early development and first successful hatchery production of the bluestreak cleaner wrasse, Labroides dimidiatus (Valenciennes, 1839), with application of an inorganic fertilization method in larviculture. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.S.; Leu, M.Y. Captive spawning, early development and larviculture of the dwarf hawkfish, Cirrhitichthys falco (Randall, 1963) with experimental evaluation of the effects of temperature, salinity and initial prey on hatching success and first feeding. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groover, E.M.; Alo, M.M.; Ramee, S.W.; Lipscomb, T.N.; Degidio, J.M.L.A.; DiMaggio, M.A. Development of early larviculture protocols for the melanurus wrasse Halichoeres melanurus. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, I.; Chemello, G.; Vargas, A.; Randazzo, B.; Piccinetti, C.C.; Carnevali, O. Marine ornamental species culture: From the past to “Finding Dory”. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 245, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, M.; Chadha, N.K.; Madhu, K.; Madhu, R.; Sawant, P.B.; Francis, B. Optimization of temperature improves embryonic development and hatching efficiency of false clown fish, Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier, 1830 under captive condition. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.C. Effect of salinity on the survival activity and larviculture of anemonefish (Amphiprion clarkii). J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhu, X.M.; Liu, M.; Lin, J.Y.; Wu, K.C. Effects of temperature on survival, development, growth and feeding of larvae of yellowtail clownfish Amphiprion clarkii (Pisces: Perciformes). Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2011, 31, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunobe, T. Reproductive behavior in six species of Eviota (Gobiidae) in aquaria. Ichthyol. Res. 1998, 45, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.S.; Huang, C.H.; Ho, S.W.; Yeh, S.L. Spawning, embryonic and larval development of the mangrove goby Mugilogobius cavifrons (Gobiidae) reared in captivity. Thalassas 2023, 39, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarangkoon, W.; Mahae, N.; Tanyaros, S. The effect of different feed types on the growth rate and biochemical composition of the marine ciliate, Euplotes sp. J. Fish. Environ. 2018, 42, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.J.; Sadovskaya, I.; Hwang, J.S.; Souissi, S. Assessment of the fecundity, population growth and fatty acid composition of Apocyclops royi (Cyclopoida, Copepoda) fed on different microalgal diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanda, E.; Drillet, G.; Huang, C.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Højgaard, J.K.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Hansen, B.W. An analysis of how to improve production of copepods as live feed from tropical Taiwanese outdoor aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.W., Jr.; Ahlstrom, E.H.; Moser, H.G. Early Life History Stages of Fishes and Their Characters. In Early Life History Stages of Fishes and Their Characters; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wittenrich, M.L.; Turingan, R.G.; Creswell, R.L. Spawning, early development and first feeding in the gobiid fish Priolepis nocturna. Aquaculture 2017, 270, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimma, H.; Tsujigado, A. Some biochemical quality of bred scorpaenoid fish, Sebastiscus marmoratus, and activities of their larvae. Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquac. 1981, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Snedecor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shiobara, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Reproductive behavior, development of eggs and larvae of the gobiid fish, Valenciennea bella, reared in the aquarium. J. Fac. Mar. Sci. Technol. Tokai Univ. 1995, 39, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Reavis, R.H. The natural history of a monogamous coral-reef fish, Valenciennea strigata (Gobiidae): 2. Behavior, mate fidelity and reproductive success. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 49, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herler, J. Microhabitats and ecomorphology of coral-and coral rock-associated gobiid fish (Teleostei: Gobiidae) in the northern Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2007, 28, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shei, M.R.P.; Miranda-Filho, K.C.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Sampaio, L.A. Production of juvenile barber goby Elacatinus figaro in captivity: Developing technology to reduce fishing pressure on an endangered species. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2010, 3, E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, M.E.; Tsuzuki, M.Y.; Ribeiro, F.F.; Medeiros, R.C.; Silva, I.D. Reproduction, early development and larviculture of the barber goby, Elacatinus figaro (Sazima, Moura & Rosa 1997). Aquac. Res. 2009, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, R.J. The embryology of the neon goby, Gobiosoma oceanops. Copeia 1972, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunobe, T.; Nakazono, A. Embryonic development and larvae of genus Eviota (Pisces:Gobiidae) Ⅰ. Eviota abax and E. storthynx. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 1987, 31, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Shiobara, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Development eggs and early larvae of the gobiid fish, Trimma grammistes. J. Fac. Mar. Sci. Technol. Tokai Univ. 1994, 38, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Baensch, H.A.; Debelius, H. Meerwasser Atlas; Mergus Verlag GmbH: Melle, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, A.K.; Bok, A.W. Frequency and periodicity of spawning in the clownfish Amphiprion akallopisos under aquarium conditions. Aquar. Sci. Conserv. 2001, 3, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yonemori, A.; Fujiwara, K.; Shinomiya, A. Semi-lunar spawning cycle and mating tactics in the marine goby Asterropteryx semipunctata. Ichthyol. Res. 2009, 56, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunobe, T.; Nakazono, A. Alternative mating tactics in the gobiid fish, Eviota prasina. Ichthyol. Res. 1999, 46, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Van Tassell, J.L.; Patzner, R.A. Aspects of spawning behaviour in five gobiids of the genus Coryphopterus (Pisces: Gobiidae) in the Caribbean Sea. Open J. Fish. 2009, 2, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, C.A.; Gothreaux, C.T.; Green, C.C. Effects of temperature and salinity during incubation on hatching and yolk utilization of Gulf killifish Fundulus grandis embryos. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J. The growth of fish: III. The effect of temperature on the development of the eggs of Salmo fario. J. Exp. Biol. 1928, 6, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, A.; Gallardo, W.G.; Assavaaree, M.; Kotani, T.; De Araújo, A.B. Live food production in Japan: Recent progress and future aspects. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, P.; Munk, P.; Janekarn, V. Contrasting feeding patterns among species of fish larvae from the tropical Andaman Sea. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirota, A. Studies on the mouth size of fish larvae. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1970, 36, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côrtes, G.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. Effect of different live food on survival and growth of first feeding barber goby, Elacatinus figaro (Sazima, Moura & Rosa 1997) larvae. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva-Souza, M.F.; Sugai, J.K.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. Anticipation of Artemia sp. supply in the larviculture of the barber goby Elacatinus figaro (Gobiidae: Teleostei) influenced growth, metamorphosis and alkaline protease activity. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 43, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushiake, K.; Fujimoto, H.; Shimma, H. A trial of evaluation of activity in yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata larvae. Suisanzoshoku 1993, 41, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushiake, K.; Sekiya, S. A trial of evaluation of activity in striped jack, Pseudocaranx dentex larvae. Suisanzoshoku 1993, 41, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, G.; Lu, W. Ontogenesis from embryo to juvenile and salinity tolerance of Japanese devil stinger Inimicus japonicus during early life stage. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burt, J.M.; Hinch, S.G.; Patterson, D.A. The importance of parentage in assessing temperature effects on fish early life history: A review of the experimental literature. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 21, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, R.C.; Ikebata, S.P.; Araújo-Silva, S.L.; Manhães, J.V.A.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. Thermal influence on the embryonic development and hatching rate of the flameback pygmy angelfish Centropyge aurantonotus eggs. Zygote 2020, 28, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeuf, G.; Payan, P. How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, A.D.; Watanabe, W.O.; Montgomery, F.P.; Rezek, T.C.; Shafer, T.H.; Morris, J.A. Effects of salinity and temperature on the growth, survival, whole body osmolality, and expression of Na+/K+ ATPase mRNA in red porgy (Pagrus pagrus) larvae. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandler, A.; Anav, F.A.; Choshniak, I. The effect of salinity on growth rate, survival and swimbladder inflation in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata, larvae. Aquaculture 1995, 135, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiter, R.H.; Tonozuka, T. Early Life History of Marine Fishes. In Pictorial Guide to Indonesian Reef Fishes. Part 3. Jawfishes—Sunfishes, Opistognathidae—Molidae; Zoonetics: Melbourne, Australia, 2001; pp. 623–893. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia-López, V.; Kiewek-Martıńez, M.; Maldonado-Garcıá, M. Effects of temperature and salinity on artificially reproduced eggs and larvae of the leopard grouper Mycteroperca rosacea. Aquaculture 2004, 237, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Lee, P.S.; Cheng, M.J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Chen, W.Y. Artificial propagation of palette surgeonfish (Paracanthurus hepatus). J. Taiwan Fish. Res. 2013, 21, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaneesh, K.V.; Devi, K.N.; Kumar, T.A.; Balasubramanian, T.; Tissera, K. Breeding, embryonic development and salinity tolerance of Skunk clownfish Amphiprion akallopisos. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2012, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, B.S.; Kendall, A.W., Jr. Early Life History of Marine Fishes. In Rearing and Culture of Marine Fishes; Miller, B.S., Nummela, S., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 244–257. [Google Scholar]










| Developmental Stage | Duration Time (h:min pf) | Key Morphological Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Zygote | 00:00 | 1-cell stage; cytoplasm streamed toward animal pole to form the blastodisc |
| Cleavage | 00:07 | 2-cell stage; 1st cleavage, dividing the blastodisc into 2 blastomeres |
| 00:10 | 4-cell stage; 2nd cleavage | |
| 00:36 | 8-cell stage; 3rd cleavage | |
| 00:39 | 16-cell stage; 4th cleavage | |
| 00:48 | 32-cell stage; 5th cleavage | |
| 01:16 | 64-cell stage; 6th cleavage | |
| Blastula | 03:42 | High-cell stage; the blastomeres reduced in size |
| Gastrula | 28:48 | 60% epiboly completion |
| 31:46 | 90% epiboly completion | |
| Segmentation | 32:34 | 1-somite stage; first somite furrow |
| 34:23 | 6-somite stage; optic vesicles appeared | |
| 36:43 | 16-somite stage; the tail bud lifts off the yolk | |
| 37:59 | 26-somite stage; the lens placode appeared | |
| Pharyngula | 68:04 | High-pec; the pectoral fin bud’s height was approximately equal to the width of its base |
| Hatching | 80:13 | Pec-fin stage; the pectoral fin now had a flat flange |
| 81:26 | Hatching; larva is free from the membrane |
| Developmental Stage | Duration Time (dph) | Key Morphological Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Larval | ||
| Pre-flexion | 0 | Larva was free from the membrane; 24–26 (9–10 + 15–16) somites; one yolk sac; gas bladder appeared; 1.96 ± 0.01 mm total length (TL; mean ± SEM) |
| 1 | Mouth and anus opened; 1.99 ± 0.02 mm TL | |
| 2 | Yolk was completely absorbed; 8–9 obvious melanophores scattered along the ventrolateral area of trunk; 2.15 ± 0.01 mm TL | |
| 10 | The melanophores along the ventrolateral area of trunk spread and increased; 2.90 ± 0.07 mm TL | |
| Flexion | 15 | The hypural bones formed; 3.56 ± 0.02 mm TL |
| Post-flexion | 20 | The hypural bones assumed a vertical position; 6.06 ± 0.14 mm TL |
| 25 | The 1st dorsal fin appeared; 8.79 ± 0.10 mm TL | |
| Juvenile | 30 | The fin ray counts attained an adult complement; 12.11 ± 0.48 mm TL |
| 35 | A distinct melanophore spot appeared at the base of the caudal fin; 4–5 black vertical bands appeared on the trunk; 14.69 ± 0.84 mm TL | |
| 41 | The body color changed from transparent to light green; 22.07 ± 0.88 mm TL | |
| 52 | The trunk turned from light green into dark brown; several red streaks spread over the head, dorsal, and anal fin; 47.24 ± 1.89 mm TL |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Reference | Spawning Substrate | Rearing Temperature (°C) | Photoperiod (Light:Dark) | Spawning Time | Spawning Interval (Days) | Clutch Size (Eggs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblygobius phalaena | White-barred goby | Present study | Tank wall | 20.0–32.6 | 12:12 | 12:00–14:00 | 8–34 | 11,022–95,858 |
| Cryptocentrus cinctus | Yellow prawn-goby | [15] | PVC pipes | 27–29 | – | – | 16–120 | – |
| Elacatinus colini | Belize sponge goby | [17] | PVC pipes | 27–28 | 14:10 | – | 6.1–9.5 | 19–388 |
| Elacatinus figaro | Barber goby | [54] | Bivalve shells | 26.0 | 13:11 | 7:00–10:00 | 9.1–13.3 | 430–1020 |
| [55] | PVC pipes and bivalve shells | 23.5–26.9 | 11:13 | 07:00–10:00 | 9.14–13.34 | 140–700 | ||
| Elacatinus lori | Linesnout goby | [17] | PVC pipes | 27–28 | 14:10 | – | – | 564–1763 |
| Elacatinus oceanops | Neon goby | [56] | Bivalve shells | 28 | 8:16 | – | – | 300–450 |
| Elacatinus puncticulatus | Panamic redhead goby | [18] | PVC pipes | 25.2–26.5 | 8:16 | 15:00–15:30 | 7–10 | 45–240 |
| Elacatinus evelynae | Sharknose goby | [11] | PVC pipes | 25 | 13:11 | 10:00–11:00 | – | 200–250 |
| Eviota abax | Sand-table dwarf goby | [57] | PVC pipes | 24–27 | – | – | – | 250–350 |
| Eviota storthynx | Storthynx dwarf goby | [57] | PVC pipes | 24–27 | – | – | – | 200–250 |
| Istigobius ornatus | Ornate goby | [16] | Artificial caves | 25.2–29.2 | 12:12 | 08:00–12:00 | 2–17 | 264–10,214 |
| Lythrypnus dalli | Catalina Goby | [13] | PVC pipes | 14.4–22.2 | 14:10 | 08:00–12:00 | 9.4 | 396–1055 |
| Priolepis nocturna | Blackbarred reef goby | [48] | Ceramic tiles | 30.0 | – | – | – | 268–3121 |
| Trimma grammistes | Black-striped pygmy goby | [58] | Gravel tiles | 24.5–28.0 | – | – | – | – |
| Valenciennea bella | Bella goby | [51] | Gravel tiles | 25.2–26.6 | – | – | 11–24 | 25,459 |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Reference | Egg Size (L × W, mm) | Incubation Temperature (°C) | Incubation Time | TL at Hatching (mm) | Yolk Sac Absorbed (TL/dph) | Transformation into Juvenile (TL/dph) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblygobius phalaena | White-barred goby | Present study | 1.21–1.44 × 0.40–0.47 | 26.1–27.9 | 81 h 26 min | 1.91–2.03 | 2.09–2.25/2 | 9.95–13.47/30 |
| Cryptocentrus cinctus | yellow prawn-goby | [15] | 1.64–1.68 × 0.55 | 27–29 | 107 h 33 min | 2.36–2.42 | –/– | –/– |
| Elacatinus colini | Belize sponge goby | [17] | – | 27–28 | 144–168 h | 3.28–3.74 NL | 3.5 NL/1 | –/38 |
| Elacatinus figaro | Barber goby | [55] | 2.1 × 0.7 | 25 | 168 h | 3.00 | –/3 | –/– |
| [54] | 1.71–1.91 × 0.58–0.64 | 26.0 | 168 h | 3.08–3.22 | –/2 | –/– | ||
| Elacatinus lori | Linesnout goby | [17] | 2.49–2.59 × 0.44–0.88 | 27–28 | 192–216 h | 3.49–3.89 NL | 3.5 NL/1 | –/28 |
| Elacatinus oceanops | Neon goby | [56] | 1 × 0.8 | 28 | 150–160 h | 4.00 | –/– | –/– |
| Elacatinus puncticulatus | Panamic redhead goby | [18] | 0.4–0.7 D | 25.2–26.5 | 168–169.5 h | 2.55–3.55 | –/5 | –/– |
| Elacatinus evelynae | Sharknose goby | [11] | – | 25 | 168 h | – | –/– | –/30–40 |
| Eviota abax | Sand-table dwarf goby | [57] | 1.16–1.19 × 0.37–0.42 | 24–27 | 129 h | 2.60–2.80 | 2.9–3.0/1 | –/– |
| Eviota storthynx | Storthynx dwarf goby | [57] | 1.19–1.31 × 0.37–0.42 | 24–27 | 110 h | 1.90–2.10 | 2.0–2.2/3 | –/– |
| Istigobius ornatus | Ornate goby | [16] | 1.31–1.54 × 0.46–0.50 | 27.0–28.0 | 84 h | 1.78–2.28 | 2.42–2.52/1 | 7.78–7.80/30 |
| Lythrypnus dalli | Catalina Goby | [13] | 1.86–1.89 × 0.46 | 14.4–22.2 | 96–247.2 h | 3.0 | –/– | –/40 |
| Priolepis nocturna | Blackbarred reef goby | [48] | 0.75–0.90 × 0.49–0.52 | 30.0 | 121 h | 1.85–1.93 | 1.90/1 | –/– |
| Trimma grammistes | Black-striped pygmy goby | [58] | 0.65–0.71 × 0.45–0.50 | 26 | 68 h | 1.80–2.20 | 2.05/2 | –/– |
| Valenciennea bella | Bella goby | [51] | 1.00–1.20 × 0.45–0.50 | 25.2–26.6 | 61 h | 1.65 | 1.94/2 | –/– |
| Valenciennea strigata | Blueband goby | [14] | 1.0–1.1 × 0.29–0.30 | 26.8–28.6 | 56 h 30 min | 0.8–1.4 | –/– | –/– |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Reference | Higher Larval Hatching | Higher Larval Survival | Higher SAI | Lower Deformity | Recommended Larval Rearing Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pelagic spawner | |||||||
| Centropyge aurantonotus | Flameback pygmy angelfish | [75] | T: 24–28 °C | – | – | – | – |
| Cirrhitichthys falco | Dwarf hawkfish | [35] | T: 26–32 °C S: 27–30 ppt | T: 24–32 °C S: 24–30 ppt | T: 26 °C S: 24–30 ppt | T: 24–26 °C S: 27–33 ppt | T: 26 °C S: 27–30 ppt |
| Halichoeres melanurus | Melanurus wrasse | [36] | T: 28 °C | T: 25–28 °C | – | – | T: 25 °C |
| Labroides dimidiatus | Bluestreak cleaner wrasse | [34] | T: 26.1 °C S: 30–35 ppt | T: 27–32 °C S: 33 ppt | – | T: 22–27°C S: 30–33 ppt | T: 27 °C S: 33 ppt |
| Paracanthurus hepatus | Blue tang | [81] | S: 30 ppt | – | – | – | S: 30 ppt |
| Platax teira | Longfin batfish | [33] | T: 26.5–27.4 °C | – | – | – | T: 27 °C |
| Demersal spawner | |||||||
| Amblygobius phalaena | White-barred goby | Present study | – | T: 21–27 °C S: 24–36 ppt | T: 21–27 °C S: 30 ppt | – | T: 21–27 °C S: 30 ppt |
| Amphiprion clarkii | Yellowtail clownfish | [39] | – | S: 15–20 ppt | S: 15 ppt | – | S: 15–20 ppt |
| [40] | – | T: 23–29 °C | – | – | – | ||
| Amphiprion ocellaris | False clownfish | [38] | T: 29–30 °C | – | – | – | T: 29 °C |
| Istigobius ornatus | Ornate goby | [16] | – | T: 24–32 °C S: 10–30 ppt | T: 28 °C S: 10–30 ppt | – | T: 28 °C S: 10–30 ppt |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, P.-S.; Ho, S.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H. Captive Reproductive Behavior, Spawning, and Early Development of White-Barred Goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) and Examined Larval Survival and Viability at Different Water Temperatures and Salinities. Fishes 2023, 8, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070364
Chiu P-S, Ho S-W, Huang C-H, Lee Y-C, Lin Y-H. Captive Reproductive Behavior, Spawning, and Early Development of White-Barred Goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) and Examined Larval Survival and Viability at Different Water Temperatures and Salinities. Fishes. 2023; 8(7):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070364
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Pei-Sheng, Shine-Wei Ho, Cheng-Hsuan Huang, Yen-Chun Lee, and Yu-Hung Lin. 2023. "Captive Reproductive Behavior, Spawning, and Early Development of White-Barred Goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) and Examined Larval Survival and Viability at Different Water Temperatures and Salinities" Fishes 8, no. 7: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070364
APA StyleChiu, P. -S., Ho, S. -W., Huang, C. -H., Lee, Y. -C., & Lin, Y. -H. (2023). Captive Reproductive Behavior, Spawning, and Early Development of White-Barred Goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) and Examined Larval Survival and Viability at Different Water Temperatures and Salinities. Fishes, 8(7), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070364