Synthesis of Hematite Nanodiscs from Natural Laterites and Investigating Their Adsorption Capability of Removing Ni2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
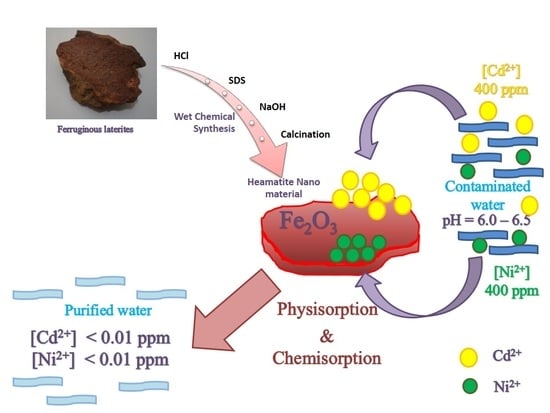
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Hematite Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Nitrogen Adsorption Studies
2.5. Calculations of Surface Properties
2.6. Adsorption Studies
2.6.1. Preparation of Stock Metal Ion Solutions
2.6.2. pH Optimization
2.6.3. Mass Optimization
2.6.4. Kinetic Study
2.6.5. Equilibrium Studies
2.6.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Hematite Nanoparticles
3.2. Characterization of Synthesized Hematite Nanoparticles
3.3. Nitrogen Adsorption Studies
3.4. Heavy Metal Sorption
3.5. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm Studies
3.6. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
3.7. pH Optimization
3.8. Mass Optimization
3.9. Kinetics Studies
3.10. Adsorption Mechanisms
3.11. Possible Applications of This Adsorption Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Alhoshan, M.; Dass, L.A.; Ali, F.A.A.; Muthumareeswaran, M.R.; Mishra, U.; Ansari, M.A. Removal of heavy metal ions using a carboxylated graphene oxide-incorporated polyphenlsulfone nanofiltration membrane. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, O.E.A.; Reiad, N.A.; ElShafei, M.M. A study of the removal characteristics of heavy metals from wastewater by low-cost adsorbents. J. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halawaa, R.A.E.; Zabin, S.A. Removal efficiency of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn from polluted water using dithiocarbamate ligands. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.S.; Hu, J.S.; Liang, H.P.; Cao, A.M.; Song, W.G.; Wan, L.J. Self-Assembled 3D Flowerlike Iron Oxide Nanostructures and Their Application in Water Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, M.; Sarkar, M.; Malik, M.A.; Xu, S.; Li, Q.; Mandal, S. Iron Oxide NPs Facilitated a Smart Building Composite for HeavyMetal Removal and Dye Degradation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisi, S.D.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 4, pp. 327–398. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, K.S.; Ardejani, F.D.; Badii, K.; Olya, M.E. Preparation and characterization of novel nanomineral for the removal of several heavy metals from aqueous solution: Batch and continuous systems. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3108–S3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chodak, A.D.; Baszczyk, U. The Impact of Nickel on Human Health. J. Elementol. 2008, 13, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment. EXS 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y. Mechanistic Insight into Disinfection Using Ferrate(VI). Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dave, P.N.; Chopda, L.V. Application of Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Stoller, M.; Wang, T.; Bao, Y.; Hao, H. An Overview of Nanomaterials for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.T.; Alazba, A.A.; Manzoor, U. A Review of Removal of Pollutants from Water/Wastewater Using Different Types of Nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velez, E.; Campillo, G.E.; Morales, G.; Hincapie, C.; Osorio, J.; Arnache, O.; Uribe, J.I.; Jaramillo, F. Mercury removal in wastewater by iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 687, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismadji, S.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ayucitra, A. Natural Clay Minerals as EnvironmentalCleaning Agents. Clay Mater. Environ. Remediat. 2015, 8, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Navaratne, A.; Priyantha, N.; Kulasooriya, T.P.K. Removal of Heavy Metal Ionsusing Rice Husk and Brick Clay as Adsorbents–Dynamic Conditions. IJEE 2013, 6, 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, C.; Priyantha, N. Chemical modification of thermally treated peat for removal of heavy metals in effluents. Symp. Proc. Int. Symp. Water Qual. Hum. Health 2012, 4, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Kadu, M.S.; Pandhurnekar, C.P.; Muthreja, I.L. Kinetics Study on the Adsorption of Ni2+ Ions onto Fly Ash. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2015, 50, 601–610. [Google Scholar]
- Igwe, J.C.; Abia, A.A. Adsorption isotherm studies of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions bioremediation from aqueous solution using unmodified and EDTA-modified maize cob. Eclet. Quim. 2007, 32, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senevirathne, H.M.M.S.; Bandara, J.M.R.S. Cadmium and other heavy metal removal from contaminated drinking and irrigation water. Symp. Proc. Int. Symp. Water Qual. Hum. Health 2012, 4, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesinghe, W.P.S.L.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Peiris, T.A.N.; Rajapakse, R.M.G.; Wijayantha, K.G.U.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Premachandra, T.N.; Herath, H.M.T.U.; Rajapakse, R.P.V.J. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous hydroxyapatite with non-cytotoxicity and heavy metal adsorption capacity. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10271–10278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.A.; Kassim, K.A.; Nur, H.; Yunus, N.Z.M. Strength of lime-cement stabilized tropical lateritic clay contaminated by heavy metals. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 19, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latifi, N.; Marto, A.; Eisazadeh, A. Structural Characteristics of Laterite Soil Treated by SH-85 and TX-85 (Non-Traditional) Stabilizers. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 18, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Maignien, R. Review of research on laterites. UNESCO 1966, 26-77, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, M.A.; Jaafar, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alfadul, S.M. New Route for Preparation and Characterization of Magnetite Nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 4, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, M.K.; Pionern, E.; Issa, T.B.; Singh, P. Arsenic Adsorption on Goethite Nanoparticles Produced through Hydrazine sulfate Assisted Synthesis Method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangami, S.; Manu, B. Synthesis of green iron nanoparticles using laterite and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of herbicide Ametryn in water. Environ. Tech. Innov. 2017, 8, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.M.S.N.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Palihawadana, T.C.; Chandrakumara, G.T.D.; De Silva, R.T.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Nalin de Silva, K.M.; Amaratunga, G.A.J. Facile and low-cost synthesis of pure hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles from naturally occurring laterites and their superior adsorption capability towards acid-dyes. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21249–21257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brasileiro, I.L.O.; Madeira, V.S.; de Souza, C.P.; Lopes-Moriyama, A.L.; Ramalho, M.L.R.A.; Araujo, A.D. Development of α-Fe2O3/Nb2O5 photocatalysts by a Pechini sol-gel route: Structural, morphological and optical influence. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 015043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayananda, K.E.D.Y.T.; Gunawardhana, B.P.N.; Dissanayake, D.M.S.N.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Rajapakse, R.M.G.; Nalin de Silva, K.M.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A. Low Cost, Novel Synthesis Methods of Heamatite Nanoparticles from Sri Lankan Iron Rich Laterites. Book Abstr. 4th ICNSNT 2017, 66, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarathna, L.; Bandara, A.; Ng, W.J.; Weerasooriya, R. Fluoride adsorption on γ−Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.A.; Hu, J.; Engates, K.E.; Shipley, H.J. Adsortion and Desorption of Bivalent Metals to Hematite Nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.; Vilanova, A.; Lopes, T.; Andrade, L.; Mendes, A. Extremely stable bare heamatite photoanode for solar water splitting. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivula, K.; Zboril, R.; Formal, F.L.; Robert, R.; Weidenkaff, A.; Tucek, J.; Frydrych, J.; Gratzel, M. Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting with Mesoporous Heamatite Prepared by a Solution-Based Colloidal Approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7436–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, A.; Lassoued, M.S.; Dkhil, B.; Ammar, S.; Gadri, A. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles under visible irradiation. J. Mater. Sci.Mater. Electron. 2018, 10, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirita, M.; Grozescu, I. Fe2O3–Nanoparticles, Physical Properties and Their Photochemical And Photoelectrochemical Applications. Chem. Bull. POLITEHNICA 2009, 54, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Basavegowda, N.; Mishra, K.; Lee, Y.R. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic applications of heamatite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles as reusable nanocatalyst. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.A.; Deshmukh, T.B.; Deshmukh, R.V.; Patil, D.D.; Chavan, U.J. Electrochemical super capacitive performance of Heamatite α-Fe2O3 thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis from non-aqueous medium. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 616, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.Q.; Piao, X.; Zhang, Q. Hydrothermal evolution, optical and electrochemical properties of hierarchical porous heamatite nanoarchitectures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanga, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.Y. Selective removals of heavy metals (Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+) from wastewater by gelation with alginate for effective metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, M.S.; de Silva, R.M.; de Silva, K.M.N. Synthesis, characterization, and application of nano hydroxyapatite and nanocomposite of hydroxyapatite with granular actvated carbon for the removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solutions. J. App. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Agarwal, K.; Singh, A.K.; Polke, B.G.; Raha, K.C. Characterization of γ- and α-Fe2O3 nano powders synthesized by emulsion precipitation-calcination route and rheological behaviour of α-Fe2O3. IJEST 2010, 2, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lassoued, A.; Dkhil, B.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, A.U.; Vithanage, M.; Weerasooriya, R.; Dissanayake, C.B. Surface complexation of nickel on iron and aluminum oxides: A comparative study with single and dual site clays. Colloids Surf. A. 2012, 405, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S. Modeling of Experimental Adsorption Isotherm Data. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2016, 7, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Han, G.; Yang, H.; Lin, G.; Xu, R. Investigation on Magnetic Properties of Heamtite Superstructures with Controlled Microstructures. ASEAN J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 8, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Tng, L.; Lim, T.; Choo, M.; Zhang, J.; Tan, H.R.; Bai, S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Octadecahedral Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles: An Epitaxial Growth from Goethite (α-FeOOH). J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 10903–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Daniele, V.; Passacantando, M.; D’Orazio, F. Nano-sized Fe(III) oxide particles starting from an innovative and eco-friendly synthesis method. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Application of Large Pore MCM-41 Molecular sieves to improve pore size analysis using nitrogen adsorption measurements. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6267–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.K.; Rhadfi, T.; Mckay, G.; Al-marri, M.; Abdala, A.; Hilal, N.; Hussien, M.A. Enhancing oil removal from water using ferric oxide nanoparticles doped carbon nanotubes adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 293, 90–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Kavipriya, M.; Karthika, C.; Radhika, M.; Vennilamani, N.; Pattabhi, S. Utilization of Various Agricultural Wastes for Activated Carbon Preparation and Application for the Removal of Dyes and Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.T.; Ooi, S.T.; Lee, C.K. Removal of chromium(VI) from solution by coconut husk and palm pressed fibres. Environ. Technol. 1993, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, C.; Kadanapitiye, M.S.; Dudarko, O.; Huang, S.D.; Jaroniec, M. Adsorption of Lead ions from Aqeous Phase on Mesoporous Silica with P-Containing Pendant Groups. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23144–23152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.M.; Karthik, C.; Saratale, R.G.; Kumar, S.S.; Prabakar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biological approaches to tackle heavy metal pollution: A survey of literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Sreekumari, S.S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from industrial effluents using activated carbon derived from waste coconut buttons. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuquo, E.D.; Martin, A.D.; Nzerem, P. Evaluation of Cd(II) Ion Removal from Aqeous Solution by a Low-Cost Adsorbent Prepared from White Yam (Dioscorea rotundata) Waste using Batch Sorption. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osinska, M. Removal of lead(II), copper(II), cobalt(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqeous solutions using carbon gels. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.H.; Ding, J.; Luan, Z.; Wang, S. Adsorption of Cadmium (II) From Aqeous Solution by Surface Oxidized Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2003, 41, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Vatta, P.; Kaur, M. Carbon Nanotubes: A Review Article. IJRASET 2018, 6, 5075–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Chemical Composition | Values (%) | Engineering and Physical Properties | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.55 | pH | 5.35 |
| Al2O3 | 24.31 | Specific gravity | 2.69 |
| Fe2O3 | 29.40 | External surface area (m2 g−1) | 42.0 |
| Na2O | 0.07 | Maximum dry density (mg m−3) | 1.31 |
| K2O | 0.11 | Optimum moisture content (%) | 34.0 |
| P2O5 | 16.71 | Unconfined compressive strength (kPa) | 270.0 |
| SO3 | 3.98 | - | - |
| CO2 | 3.65 | - | - |
| Element | Composition/% | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Fe | 97.17 |
| (2) | Al | 0.32 |
| (3) | Na | 0.05 |
| (4) | V | 0.02 |
| Content | Particle Diameter (nm) | MLC (cc STP/g) | Vsp (cc/g) | Vmi (cc/g) | SBET (m2/g) | Wmax nm | Vt (cc/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematite NP | 37.5 | 2.53 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 11.03 | 2.5/20.2 | 0.04 |
| Initial Concentration/ppm | RE% of Ni2+ | RE% of Cd2+ |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 80.50 ± 0.04 | 95.95 ± 0.08 |
| 200 | 72.41 ± 0.07 | 94.29 ± 0.08 |
| 300 | 50.58 ± 0.02 | 92.89 ± 0.05 |
| 400 | 43.93 ± 0.07 | 91.21 ± 0.02 |
| Ion | Qm/mg g−1 | KL/L mg−1 | Regression (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2+ | 62.50 ± 0.05 | (4.07 × 10−2) ± 0.07 | 0.98 |
| Cd2+ | 200.00 ± 0.08 | (4.10 × 10−2) ± 0.05 | 0.97 |
| C0 (Ppm) | RL for Ni2+ | RL for Cd2+ |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.197 | 0.196 |
| 200 | 0.109 | 0.109 |
| 300 | 0.076 | 0.075 |
| 400 | 0.058 | 0.058 |
| Ion | 1/n | KF | Regression (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2+ | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 12.30 ± 0.15 | 0.80 |
| Cd2+ | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 12.93 ± 0.48 | 0.99 |
| Adsorbent | Heavy Metal Ion | Maximum Adsorption Capacity/mg g−1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activated carbon | Ni(II) | 400.0 | [14,60,61,62] |
| Cd(II) | 178.5 | ||
| CNT * modified with hydroxyquinoline | Ni(II) | 4.2 | [63] |
| CNT * | Cd(II) | 10.9 | [64] |
| Laterite derived-hematite nanoparticles | Ni(II) | 62.5 | Current study |
| Cd(II) | 200.0 | Current study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunawardhana, B.P.N.; Gunathilake, C.A.; Dayananda, K.E.D.Y.T.; Dissanayake, D.M.S.N.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Kalpage, C.S.; Rathnayake, R.M.L.D.; Rajapakse, R.M.G.; Manchanda, A.S.; Etampawala, T.N.B.; et al. Synthesis of Hematite Nanodiscs from Natural Laterites and Investigating Their Adsorption Capability of Removing Ni2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020057
Gunawardhana BPN, Gunathilake CA, Dayananda KEDYT, Dissanayake DMSN, Mantilaka MMMGPG, Kalpage CS, Rathnayake RMLD, Rajapakse RMG, Manchanda AS, Etampawala TNB, et al. Synthesis of Hematite Nanodiscs from Natural Laterites and Investigating Their Adsorption Capability of Removing Ni2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020057
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunawardhana, B. P. N., C. A. Gunathilake, K. E. D. Y. T. Dayananda, D. M. S. N. Dissanayake, M. M. M. G. P. G. Mantilaka, C. S. Kalpage, R. M. L. D. Rathnayake, R. M. G. Rajapakse, A. S. Manchanda, Thusitha N. B. Etampawala, and et al. 2020. "Synthesis of Hematite Nanodiscs from Natural Laterites and Investigating Their Adsorption Capability of Removing Ni2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020057
APA StyleGunawardhana, B. P. N., Gunathilake, C. A., Dayananda, K. E. D. Y. T., Dissanayake, D. M. S. N., Mantilaka, M. M. M. G. P. G., Kalpage, C. S., Rathnayake, R. M. L. D., Rajapakse, R. M. G., Manchanda, A. S., Etampawala, T. N. B., Weerasekara, B. G. N. D., Fernando, P. N. K., & Dassanayake, R. S. (2020). Synthesis of Hematite Nanodiscs from Natural Laterites and Investigating Their Adsorption Capability of Removing Ni2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Composites Science, 4(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020057