Inverse Proportionality of Thermal Conductivity and Complex Permittivity to Filler-Diameter in Epoxy Resin Composites with Silica
Abstract
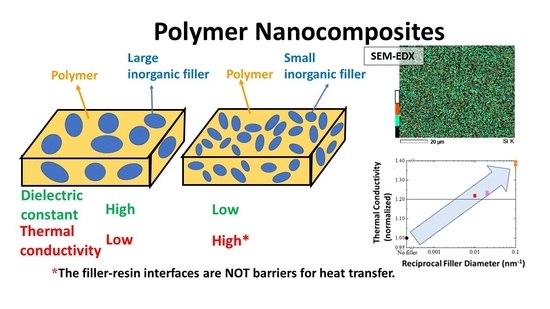
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohki, Y. 13 Permeability Control by Nano-Magnetic Fillers: Case Study. In Tailoring of Nanocomposite Dielectrics—From Fundamentals to Devices and Applications, 1st ed.; Tanaka, T., Vaughan, A.S., Eds.; Pan Stanford: Singapore, 2017; pp. 369–381. ISBN 978-981-4669-80-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ohki, Y. 3.3 Composites with High Permeability and High Dielectric Permittivity. In Advanced Nanodielectrics—Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Tanaka, T., Imai, T., Eds.; Pan Stanford: Singapore, 2017; pp. 110–117. ISBN 978-981-4745-02-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.K. Dielectric Polymer Nanocomposites, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-1590-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pleşa, I.; Noţingher, P.V.; Stancu, C.; Wiesbrock, F.; Schlög, S. Polyethylene nanocomposites for power cable insulations. Polymers 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Moon, K.; Wong, C.P. Glass Transition and Relaxation Behavior of Epoxy Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3849–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, J.; Ohki, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Tao, K. Dielectric properties of nanocomposites based on epoxy resin and HBP/plasma modified nanosilica. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, N.; Ohki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Imai, T.; Harada, M.; Ochi, M. Dielectric Properties of Epoxy/clay Nanocomposites—Effects of Curing Agent and Clay Dispersion Method. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2008, 15, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, N.; Sato, H.; Ohki, Y.; Tanaka, T. Effects of Nanofiller Loading on the Molecular Motion and Carrier Transport in Polyamide. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2009, 16, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Effect of Water Absorption on the Mechanical Properties of Nano-filler Reinforced Epoxy Nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, F.; Ohki, Y. Charge Transport and Electrode Polarization in Epoxy Resin at High Temperatures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Masuzaki, Y.; Tian, F.; Ohki, Y. Space Charge Formation and Charge Transport in Epoxy Resin at Varied Temperatures. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2015, 135, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghar, A.; Mabrouk, A.B.; Arous, M.; Boufi, S.; Kallel, A. Dielectric Properties of Nanocomposites Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) and Poly(styrene-co-2-ethyl hexylacrylate) Copolymer. Polymer 2017, 125, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurimoto, M.; Yoshida, S.; Umemoto, T.; Mabuchi, T.; Muto, H. Breakdown Strength of TiO2/Epoxy Nanocomposites Using Centrifugation Agglomerate Removal. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, T.; Yoshida, S.; Muto, H.; Kurimoto, M. Critical Agglomerate Size for Electrical Insulation Lifetime Extension of Epoxy/TiO2 Nanocomposite with a Void Defect. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama, K.; Iizuka, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Otake, Y.; Umemoto, T.; Mabuchi, T.; Muto, H. Electroluminescence of epoxy resin nanocomposite under AC high field. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Richland, WA, USA, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, E.; Iizuka, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Hirai, N.; Ohki, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Umemoto, T.; Muto, H. Filler-dependent Changes in Thermal, Dielectric, and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 16, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashizaka, N.; Kawasaki, K.; Yamashita, M.; Ebina, T.; Ishida, T.; Hattori, S. Electrical Insulating Resin Composition for Partial-Discharge Resistance. US Patent Application Publication US20180201804A1, 19 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzoe, T.; Kita, N.; Nishigaki, Y.; Abe, T.; Kubo, T.; Nakano, Y.; Kozako, M.; Hikita, M.; Fujimoto, N.; Hayashizaka, N.; et al. Dielectric and Insulation Properties of Polyimide-based Boehmite Nanocomposite Material. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Calgary, AB, Canada, 16–19 June 2019; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. Development of XLPE-insulated cable for high-voltage dc submarine transmission line (2) [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. Development of XLPE-insulated cable for high-voltage dc submarine transmission line (1) [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. World’s first dc 400-kV XLPE cable system [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2020, 36, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. A new 250-kV HVDC XLPE cable system in Japan [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2019, 35, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. Development of new nanocomposite-based enameled wire for inverter-fed motor coils [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y. Development of a high-performance casting method for solid-insulated switchgear [News from Japn]. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2010, 26, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshiba Achieves Cumulative Delivery of Solid-State Insulation Switchgear: 2000 Faces at the Fastest. Available online: https://newswitch.jp/p/28211 (accessed on 1 October 2021). (In Japanese).
- Mahrholz, T.; Strangle, J.; Sinapius, M. Quantitation of the reinforcement effect of silica nanoparticles in epoxy resins used in liquid composite moulding processes. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.U.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, J.M. Estimation of Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluid Using Experimental Effective Particle Volume. Exp. Heat Transf. 2006, 19, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Kozako, M.; Hikita, M.; Tanaka, T. Effects of Addition of Nano-scale Alumina and Silica Fillers on Thermal Conductivity and Dielectric Strength of Epoxy/Alumina Microcomposites. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid Dielectrics, Potsdam, Germany, 4–9 July 2010; pp. B2–B28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y.; Okubo, H.; Suzuoki, Y.; Hozumi, N. Yuudentai Genshoron (Phenomenological Theories of Dielectric Materials); IEE Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; p. 150. ISBN 978-4-88686-315-7. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Cho, T.J.; Xu, J.; Lee, D.; Yang, B.; Zachariah, M.R. Effect of nanoparticle clustering on the effective thermal conductivity of concentrated silica colloids. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 011406-1-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Kozako, M.; Fuse, N.; Ohki, Y. Proposal of a Multi-core Model for Polymer Nanocomposite Dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y.; Okada, M.; Fuse, N.; Iwai, K.; Mizuno, M.; Fukunaga, K. Terahertz Time-domain Spectroscopic Analysis of Molecular Behavior in Polyamide Nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Express 2008, 1, 122401-1–122401-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Hirai, N.; Ohki, Y. Space Charge Distribution in Epoxy/MgO Nanocomposites at Various Temperatures. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Hirai, N.; Ohki, Y.; Otake, Y.; Umemoto, T.; Muto, H. Effects of Interaction between Filler and Resin on the Glass Transition and Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites. IET Nanodielectr. 2019, 2, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Seki, T.; Hirai, N.; Ohki, Y. Terahertz absorption spectra of several polymer nanocomposites indicating polymer-filler interactions. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y.; Yanashima, R.; Azeyanagi, C.; Hirai, N. Several experimental results indicating filler/polymer interactions in polymer nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Dielectrics (ICD), Budapest, Hungary, 1–5 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermal Conductivity. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_conductivity (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Huang, C.; Qian, X.; Yang, R. Thermal conductivity of polymers and polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 132, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 74th ed.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1973; pp. 12–44. ISBN 0-8493-0474-1. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, J.; Ohki, Y.; Fuse, N.; Kozako, M.; Tanaka, T. Effects of nanofiller materials on the dielectric properties of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2013, 20, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulański, J.; Friedrich, K.; Boiteux, G.; Seytre, G. Evolution of ion mobility in cured epoxy-amine system as determined by time-of-flight method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Symbol | Diameter (nm) | Content (vol%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ● | Neat | |
| 2 | ■ | 100 | 10 |
| 3 | ⬟ | 50 | 10 |
| 4 | ⬢ | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | ◆ | 100 | 1 |
| 6 | ▲ | 100 | 5 |
| 7 | ▼ | 100 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohki, Y.; Hirai, N.; Umemoto, T.; Muto, H. Inverse Proportionality of Thermal Conductivity and Complex Permittivity to Filler-Diameter in Epoxy Resin Composites with Silica. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5100266
Ohki Y, Hirai N, Umemoto T, Muto H. Inverse Proportionality of Thermal Conductivity and Complex Permittivity to Filler-Diameter in Epoxy Resin Composites with Silica. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(10):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5100266
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhki, Yoshimichi, Naoshi Hirai, Takahiro Umemoto, and Hirotaka Muto. 2021. "Inverse Proportionality of Thermal Conductivity and Complex Permittivity to Filler-Diameter in Epoxy Resin Composites with Silica" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 10: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5100266
APA StyleOhki, Y., Hirai, N., Umemoto, T., & Muto, H. (2021). Inverse Proportionality of Thermal Conductivity and Complex Permittivity to Filler-Diameter in Epoxy Resin Composites with Silica. Journal of Composites Science, 5(10), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5100266