All-Cellulose Composites Properties from Pre- and Post-Consumer Denim Wastes: Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
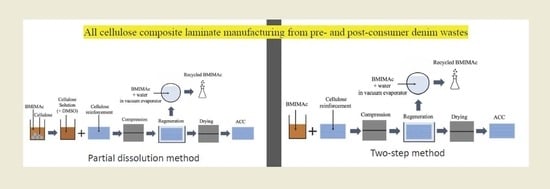
2.2.2. Composite Laminate Manufacturing
Partial Dissolution/One-Step Method
Two-Step Method
2.2.3. Recycling of [BMIM][Ac]
2.2.4. Characterization
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Recycling of Ionic Liquid
3.2. Mechanical Properties of ACCs
3.2.1. Influence of Recycling of Ionic Liquid
3.2.2. Influence of Manufacturing Method
3.2.3. Influence of Material
3.2.4. Influence of Method and Material
3.2.5. Influence of DMSO
3.3. Microscopic Analysis
3.4. Void Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Motamed, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Naebe, M. Death by waste: Fashion and textile circular economy case. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Militky, J. 10-Denim and consumers’ phase of life cycle. In Sustainability in Denim; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Recycled Fibres. In Sustainable Innovations in Recycled Textiles; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sandin, G.; Peters, G.M. Environmental impact of textile reuse and recycling—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykeabkaew, N.; Nishino, T.; Peijs, T. All-cellulose composites of regenerated cellulose fibres by surface selective dissolution. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrott, W.; Paul, R. 20-Environmental impacts of denim manufacture. In Denim; Paul, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 563–580. [Google Scholar]
- Levi Strauss & Co. The Life Cycle of a Jean Understanding the Environmental Impact of a Pair of Levi’s®501®Jeans; Levi Strauss & Co.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luiken, A.; Bouwhuis, G. 18-Recovery and recycling of denim waste. In Denim; Paul, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 527–540. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S. Denim Recycling. In Textiles and Clothing Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 79–125. [Google Scholar]
- Temmink, R.; Baghaei, B.; Skrifvars, M. Development of biocomposites from denim waste and thermoset bio-resins for structural applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 106, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Matsuda, I.; Hirao, K. All-Cellulose Composite. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 7683–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Niu, Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Rheological properties of cellulose/ionic liquid/dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solutions. Polymer 2012, 53, 2524–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratten, N.A. The precise measurement of the density of small samples. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon-Batenburg, L.M.J.; Kroon, J. The crystal and molecular structures of cellulose I and II. Glycoconj. J. 1997, 14, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Takano, K.; Nakamae, K. Elastic modulus of the crystalline regions of cellulose polymorphs. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1995, 33, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T.; Bickerton, S.; Müssig, J.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Flexural and impact properties of all-cellulose composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 88, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaei, B.; Compiet, S.; Skrifvars, M. Mechanical properties of all-cellulose composites from end-of-life textiles. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaei, B.; Skrifvars, M. All-Cellulose Composites: A Review of Recent Studies on Structure, Properties and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Keckes, J.; Plackner, J.; Liebner, F.; Englund, K.; Laborie, M.-P. All-cellulose composites prepared from flax and lyocell fibres compared to epoxy–matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Method | Solvent/Solution | Fiber Content (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO1 | One-step | [BMIM][Ac] | - |
| CO2 | Two-step | [BMIM][Ac] + CO | 94 |
| CO3 | Two-step | [BMIM][Ac] + CO + DMSO | 87 |
| BCO1 | One-step | [BMIM][Ac] | - |
| BCO2 | Two-step | [BMIM][Ac] + CO | 90 |
| BCO3 | Two-step | [BMIM][Ac] + CO + DMSO | 87 |
| RILCO | One-step | Recycled [BMIM][Ac] | - |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (Pa) | Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-step method | CO1 | 110 | 0.25, 0.50 | 60 |
| BCO1 | 110 | 0.25 | 60 | |
| RILCO | 110 | 0.25 | 60 | |
| Two-step method | CO2 | 110 | 0.125–0.375 | 60 |
| CO3 | 110 | 0.050–0.125 | 30 | |
| BCO2 | 110 | 0.050–0.125 | 30, 50 | |
| BCO3 | 110 | 0.050–0.125 | 30 |
| Sample | Strength (MPa) | E-Modulus (GPa) | Impact Strength (kJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO1 | 42.7 (16.6) | 6.0 (0.7) | 39.8 (5.6) |
| CO2 | 29.5 (16.8) | 2.1 (0.5) | 33.1 (7.2) |
| CO3 | 55.8 (5.7) | 4.1 (1.3) | 22.4 (4.5) |
| BCO1 | 53.5 (5.7) | 4.8 (1.6) | 62.4 (13.1) |
| BCO2 | 39.2 (13.3) | 5.7 (0.2) | 42.0 (8.1) |
| BCO3 | 49.5 (6.9) | 4.5 (0.8) | 34.1 (6.2) |
| RIL CO | 29.1 (6.8) | 4.7 (0.4) | 40.1 (4.5) |
| Sample | Measured Density [g/cm3] | Void Content [%] |
|---|---|---|
| CO1 | 1.43 | 7.45 |
| CO2 | 1.43 | 7.00 |
| CO3 | 1.40 | 8.89 |
| BCO1 | 1.40 | 9.15 |
| BCO2 | 1.40 | 8.79 |
| BCO3 | 1.41 | 8.37 |
| RILCO | 1.36 | 11.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baghaei, B.; Johansson, B.; Skrifvars, M.; Kadi, N. All-Cellulose Composites Properties from Pre- and Post-Consumer Denim Wastes: Comparative Study. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6050130
Baghaei B, Johansson B, Skrifvars M, Kadi N. All-Cellulose Composites Properties from Pre- and Post-Consumer Denim Wastes: Comparative Study. Journal of Composites Science. 2022; 6(5):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6050130
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaghaei, Behnaz, Belinda Johansson, Mikael Skrifvars, and Nawar Kadi. 2022. "All-Cellulose Composites Properties from Pre- and Post-Consumer Denim Wastes: Comparative Study" Journal of Composites Science 6, no. 5: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6050130
APA StyleBaghaei, B., Johansson, B., Skrifvars, M., & Kadi, N. (2022). All-Cellulose Composites Properties from Pre- and Post-Consumer Denim Wastes: Comparative Study. Journal of Composites Science, 6(5), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6050130