Non-Solvent- and Temperature-Induced Phase Separations of Polylaurolactam Solutions in Benzyl Alcohol as Methods for Producing Microfiltration Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- By immersion of a polymer solution in a bath with a non-solvent (a precipitant), where the membrane is formed due to the mass exchange of solvent and non-solvent [45,46,47]. The enrichment of the polymer solution with the non-solvent causes precipitation of the polymer, forming a membrane with a typically asymmetric structure that includes a dense surface layer (a skin) and a highly porous inner layer [48].
- By evaporating a solvent from a three-component solution that also contains a polymer and a small percentage of a non-solvent that is less volatile than the solvent. When heated, the solvent evaporates faster, and the system undergoes phase separation with the formation of a porous structure due to the gradual increase in the concentration of non-solvent [49].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Obtaining Porous Films
2.3. Methods
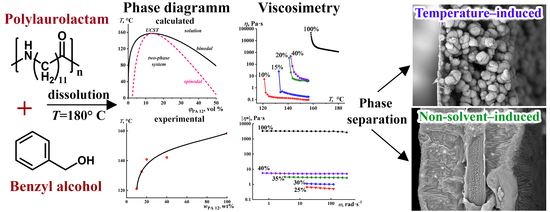
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical PA12/BA Miscibility
3.2. Viscosimetry of PA12/BA Solutions
3.3. Morphology of the PA12 Films
3.4. PA12 Porous Films as Microfiltration Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takht Ravanchi, M.; Kaghazchi, T.; Kargari, A. Application of Membrane Separation Processes in Petrochemical Industry: A Review. Desalination 2009, 235, 199–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Drioli, E. Membrane Engineering: Latest Advancements in Gas Separation and Pre-Treatment Processes, Petrochemical Industry and Refinery, and Future Perspectives in Emerging Applications. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 206, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pangarkar, B.L.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Sapkal, V.S.; Sapkal, R.S. Review of Membrane Distillation Process for Water Purification. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2959–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane Gas Separation: A Review/State of the Art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Gas Separation Membrane Materials and Structures. In Gas Separation Membranes: Polymeric and Inorganic; Ismail, A.F., Chandra Khulbe, K., Matsuura, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 37–192. ISBN 978-3-319-01095-3. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.S.; Popa, E.G.; Gomes, M.E.; Cerqueira, M.; Marques, A.P.; Caridade, S.G.; Teixeira, P.; Sousa, C.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. An Investigation of the Potential Application of Chitosan/Aloe-Based Membranes for Regenerative Medicine. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6790–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, R. Concise Review: Fetal Membranes in Regenerative Medicine: New Tricks from an Old Dog? Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. A Critical Review of Recent Advances in Hemodialysis Membranes Hemocompatibility and Guidelines for Future Development. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lim, S.K.; Abidin, M.N.Z.; Ismail, A.F. A Review of Commercial Developments and Recent Laboratory Research of Dialyzers and Membranes for Hemodialysis Application. Membranes 2021, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, D.; Kumar, M.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Vasanth, D. Separation of Bacteria Kocuria Rhizophila from Fermentation Broth by Cross-Flow Microfiltration Using Inexpensive Tubular Ceramic Membrane. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5767–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Cross-Flow Microfiltration of Glycerol Fermentation Broths with Citrobacter Freundii. Membranes 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced Functional Polymer Membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.S.; Kumakiri, I.; Nair, B.N.; Alsyouri, H. Microporous Inorganic Membranes. Sep. Purif. Methods 2002, 31, 229–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, H. Inorganic Membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dlamini, D.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Pendergast, M.T.M.; Wong, M.C.Y.; Mamba, B.B.; Freger, V.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Hoek, E.M.V. A Critical Review of Transport through Osmotic Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnau, I.; Freeman, B.D. Formation and Modification of Polymeric Membranes: Overview. In Membrane Formation and Modification; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 744, pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-0-8412-3604-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cot, L.; Ayral, A.; Durand, J.; Guizard, C.; Hovnanian, N.; Julbe, A.; Larbot, A. Inorganic Membranes and Solid State Sciences. Solid State Sci. 2000, 2, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A Review of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Fouling and Control Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Comparison of Polypropylene and Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes Applied for Separation of 1,3-PD Fermentation Broths and Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Yeast Suspensions. Membranes 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, M.T.; Barbeau, B.; Basu, O.D. Comparisons of NOM Fouling and Cleaning of Ceramic and Polymeric Membranes during Water Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Di, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J. Flexible Inorganic Nanofibrous Membranes with Hierarchical Porosity for Efficient Water Purification. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4378–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.K.; McKay, G.; Buekenhoudt, A.; Al Sulaiti, H.; Motmans, F.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M. Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination. Materials 2018, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Ultrafine Fibrous Cellulose Membranes from Electrospinning of Cellulose Acetate. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukma, F.M.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z. Cellulose Membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Makarova, V.V.; Anokhina, T.S.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Brantseva, T.V.; Volkov, A.V.; Antonov, S.V. Diffusion and Phase Separation at the Morphology Formation of Cellulose Membranes by Regeneration from N-Methylmorpholine N-Oxide Solutions. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolnicki, A.M.; Fisher, R.J.; Harrah, T.P.; Kaplan, D.L. Permeability of Bacterial Cellulose Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Jin, H.-J. Antimicrobial Properties of Hydrated Cellulose Membranes with Silver Nanoparticles. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.R.; O’Neill, H.M.; Malyvanh, V.P.; Lee, I.; Woodward, J. Palladium-Bacterial Cellulose Membranes for Fuel Cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barud, H.S.; Barrios, C.; Regiani, T.; Marques, R.F.C.; Verelst, M.; Dexpert-Ghys, J.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. Self-Supported Silver Nanoparticles Containing Bacterial Cellulose Membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ford, D.M.; Qian, X.; Cervellere, M.R.; Millett, P.C.; Wang, X. A Review on Models and Simulations of Membrane Formation via Phase Inversion Processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Ince, J.S.; Economy, J. Preparation of Nanofiltration Membranes from Polyacrylonitrile Ultrafiltration Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharnagl, N.; Buschatz, H. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Membranes for Ultra- and Microfiltration. Desalination 2001, 139, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xue, J.; Ran, F.; Sun, S. Modification of Polyethersulfone Membranes—A Review of Methods. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 76–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Kim, Y.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, Y.S. Membrane Formation by Water Vapor Induced Phase Inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part I: Production Techniques with Polysulfone and Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride). Polymers 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part II: Production Techniques with Polyethylene, Polydimethylsiloxane, Polypropylene, Polyimide, and Polytetrafluoroethylene. Polymers 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stucki, M.; Loepfe, M.; Stark, W.J. Porous Polymer Membranes by Hard Templating—A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerle, K.; Strathmann, H. Analysis of the Structure-Determining Process of Phase Inversion Membranes. Desalination 1990, 79, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Makarova, V.V.; Anokhina, T.S.; Volkov, A.V.; Antonov, S.V. Effect of Coagulating Agent Viscosity on the Kinetics of Formation, Morphology, and Transport Properties of Cellulose Nanofiltration Membranes. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2017, 59, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-P.; Lin, D.-J.; Shih, C.-H.; Dwan, A.-H.; Gryte, C.C. PVDF Membrane Formation by Diffusion-Induced Phase Separation-Morphology Prediction Based on Phase Behavior and Mass Transfer Modeling. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozelle, L.; Cadotte, J.E.; Corneliussen, R.D.; Erickson, E.E.; Cobian, K.E.; Kopp, C.V., Jr. Phase Inversion Membranes. In Encyclopedia of Separation Science; Mulder, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 3331–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Perepechkin, L.P. Methods for Obtaining Polymeric Membranes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1988, 57, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjabian, M.; Abetz, V. Advanced Porous Polymer Membranes from Self-Assembling Block Copolymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 102, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Recent Advances in Preparation and Morphology Control of Polymeric Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokhina, T.S.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Ilyin, S.O.; Volkov, A.V.; Antonov, S.V. The Effect of the Nature of a Coagulant on the Nanofiltration Properties of Cellulose Membranes Formed from Solutions in Ionic Media. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2020, 2, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.; Khoshnamvand, M.; Číhal, P.; Dendisová, M.; Randová, A.; Bouša, D.; Shaliutina-Kolešová, A.; Sofer, Z.; Friess, K. Fabrication of a PVDF Membrane with Tailored Morphology and Properties via Exploring and Computing Its Ternary Phase Diagram for Wastewater Treatment and Gas Separation Applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 40373–40383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervin, R.; Ghosh, P.; Basavaraj, M.G. Tailoring Pore Distribution in Polymer Films via Evaporation Induced Phase Separation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15593–15605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuyama, H.; Teramoto, M.; Nakatani, R.; Maki, T. Membrane Formation via Phase Separation Induced by Penetration of Nonsolvent from Vapor Phase. II. Membrane Morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Bouyer, D. A Review on Polymeric Membranes and Hydrogels Prepared by Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Process. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 568–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Thermally Induced Phase Separation and Electrospinning Methods for Emerging Membrane Applications: A Review. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; di Nicolo, E.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the Non-Solvent Induced Phase Separation (NIPS) Effect during the Fabrication of Microporous PVDF Membranes via Thermally Induced Phase Separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Anokhina, T.S.; Ilyin, S.O.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Makarova, V.V.; Antonov, S.V.; Volkov, A.V. Phase Separation of Polymethylpentene Solutions for Producing Microfiltration Membranes. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2020, 62, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lu, D.; Harris, T.A.L.; Escobar, I.C. Polymers and Solvents Used in Membrane Fabrication: A Review Focusing on Sustainable Membrane Development. Membranes 2021, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kinzer, K.E.; Tseng, H.S. Microporous Membrane Formation via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. I. Solid-Liquid Phase Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kim, S.S.; Kinzer, K.E. Microporous Membrane Formation via Thermally-Induced Phase Separation. II. Liquid—Liquid Phase Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasman, T.; Baptista, D.; van Riet, S.; Truckenmüller, R.K.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Rottier, R.J.; Stamatialis, D.; Poot, A.A. Development of Porous and Flexible PTMC Membranes for In Vitro Organ Models Fabricated by Evaporation-Induced Phase Separation. Membranes 2020, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.; Weinman, S.T. A Review on the Synthesis of Fully Aromatic Polyamide Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Desalination 2021, 502, 114939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Controlling the Formation of Porous Polyketone Membranes via a Cross-Linkable Alginate Additive for Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes for Membrane Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5710–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-L.; Xiao, C.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.-Y. Design of Super-Hydrophobic Microporous Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Anokhina, T.S.; Ilyin, S.O.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Antonov, S.V.; Volkov, A.V. Fabrication of Microfiltration Membranes from Polyisobutylene/Polymethylpentene Blends. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.; Ignatenko, V.; Anokhina, T.; Bakhtin, D.; Kostyuk, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Antonov, S.; Volkov, A. Formation of Microfiltration Membranes from PMP/PIB Blends: Effect of PIB Molecular Weight on Membrane Properties. Membranes 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; McCutcheon, J.R. Hydrophilic Nylon 6,6 Nanofibers Supported Thin Film Composite Membranes for Engineered Osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 457, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bui, N.-N.; Meyering, M.T.; Hamlin, T.J.; McCutcheon, J.R. Novel Hydrophilic Nylon 6,6 Microfiltration Membrane Supported Thin Film Composite Membranes for Engineered Osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Hao, X.M.; Guo, Y.F.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.M. Study on the Acid Resistant Properties of Bio-Based Nylon 56 Fiber Compared with the Fiber of Nylon 6 and Nylon 66. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1048, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, L.; Basilissi, L.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Zini, E.; Di Silvestro, G.; Scandola, M. Bio-Based Polyamide 11: Synthesis, Rheology and Solid-State Properties of Star Structures. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Jeon, H.; Nadarajan, S.P.; Chung, T.; Yoo, H.-W.; Kim, B.-G.; Patil, M.D.; Yun, H. Biosynthesis of the Nylon 12 Monomer, ω-Aminododecanoic Acid with Novel CYP153A, AlkJ, and ω-TA Enzymes. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Effect of the Electrospinning Process on Polymer Crystallization Chain Conformation in Nylon-6 and Nylon-12. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, L.J.; Yu, H.H. Fermi Resonance in the Infrared Spectra of Nylon-11. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1992, 30, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lánská, B.; Bohdanecký, M.; Šebenda, J.; Tuzar, Z. Dilute Solutions of Nylon 12—II. Relationship between Intrinsic Viscosity and Molecular Weight. Eur. Polym. J. 1978, 14, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B. Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Benzyl Alcohol, Benzoic Acid, and Sodium Benzoate. Int. J. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerike, P.; Gode, P. The Biodegradability and Inhibitory Threshold Concentration of Some Disinfectants. Chemosphere 1990, 21, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Flavourings (FAF); Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Engel, K.-H.; Fowler, P.; Fürst, P.; Gürtler, R.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Husøy, T.; et al. Re-Evaluation of Benzyl Alcohol (E 1519) as Food Additive. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, L.; Martin, S. Benzyl Alcohol as an Alternative Local Anesthetic. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 33, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macht, D.I.; Nelson, D.E. On the Antiseptic Action of Benzyl Alcohol. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1918, 16, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinking, T.L.; Villar, M.E.; Vicaria, M.; Eyerdam, D.H.; Paquet, D.; Mertz-Rivera, K.; Rivera, H.F.; Hiriart, J.; Reyna, S. The Clinical Trials Supporting Benzyl Alcohol Lotion 5% (UlesfiaTM): A Safe and Effective Topical Treatment for Head Lice (Pediculosis Humanus Capitis). Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Benzyl Alcohol, Benzoic Acid and Its Salts, and Benzyl Benzoate. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 5S–30S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uragami, T.; Maekawa, K.; Sugihara, M. Studies on Syntheses and Permeabilities of Special Polymer Membranes. 21. Permeabilities of Alcohols and Hydrocarbons through Nylon 12 Membranes. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1980, 87, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Maekawa, K.; Sugihara, M. Studies on Syntheses and Permeabilities of Special Polymer Membranes. XIV. Permeation Characteristics of Modified Nylon 12 Membranes. Desalination 1978, 27, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.V.; Billovits, G.F.; Koreltz, M.S.; Dooley, J.; Chiou, N.-R. Inducing Surface Porosity in Aqueous-Quenched, Microporous Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 Films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Beltsios, K.; Cheng, L.-P. Formation of Bicontinuous, Hydrophobic Nylon 12 Membranes via Cold-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation for Membrane Distillation Application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and Adhesive Properties of Nanocomposite Bitumen Binders Based on Hydrophilic or Hydrophobic Silica and Modified with Bio-Oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L. The Thermodynamics of High Polymer Solutions. IV. Phase Equilibria in the Ternary System: Polymer—Liquid 1—Liquid 2. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 17, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigbaum, W.R.; Carpenter, D.K. Phase Equilibria in Polymer–Liquid 1–Liquid 2 Systems. J. Polym. Sci. 1954, 14, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Simple Calculation of Phase Diagrams for Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation in Solutions of Two Macromolecular Solute Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, M.; Edwards, S.F.; Edwards, S.F. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1988; ISBN 978-0-19-852033-7. [Google Scholar]
- Touris, A.; Turcios, A.; Mintz, E.; Pulugurtha, S.R.; Thor, P.; Jolly, M.; Jalgaonkar, U. Effect of Molecular Weight and Hydration on the Tensile Properties of Polyamide 12. Results Mater. 2020, 8, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejmady, P.; van Breemen, L.C.A.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Anderson, P.D.; Cardinaels, R. Laser Sintering of PA12 Particles Studied by In-Situ Optical, Thermal and X-ray Characterization. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 52, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-429-12752-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kallio, K.J.; Hedenqvist, M.S. Ageing Properties of Polyamide-12 Pipes Exposed to Fuels with and without Ethanol. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerbower, A.; Wu, P.L.; Martin, A. Expanded Solubility Parameter Approach I: Naphthalene and Benzoic Acid in Individual Solvents. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macknight, W.J.; Karasz, F.E. Polymer Blends. Compr. Polym. Sci. Suppl. 1989, 7, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S. The Limitations of Using Flory-Huggins Equation for the States of Solutions during Asymmetric Hollow-Fiber Formation. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 126, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Yadykova, A.Y.; Makarova, V.V.; Yashchenko, V.S.; Matveenko, Y.V. Sulfonated Polyoxadiazole Synthesis and Processing into Ion-Conducting Films. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Venault, A.; Lai, J.-Y. Fundamentals of Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 13–56. ISBN 978-0-12-821876-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Karkhanechi, H.; Rajabzadeh, S. Polymeric Membrane Fabrication via Thermally Induced Phase Separation (TIPS) Method. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 57–83. ISBN 978-0-12-821876-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbacheva, S.N.; Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and Tribological Properties of Low-Temperature Greases Based on Cellulose Acetate Butyrate Gel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, K.; Deckers, J.; Boury, S.; Neirinck, B.; Kruth, J.-P.; Vleugels, J. Preparation and Indirect Selective Laser Sintering of Alumina/PA Microspheres. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H. Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method. Polymers 2021, 13, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbacheva, S.N.; Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. A Novel Method for Producing Cellulose Nanoparticles and Their Possible Application as Thickeners for Biodegradable Low-Temperature Greases. Cellulose 2021, 28, 10203–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnian, P.; D’Amore, A. Fabrication of High-Performance CNT Reinforced Polymer Composite for Additive Manufacturing by Phase Inversion Technique. Polymers 2021, 13, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokhina, T.S.; Ilyin, S.O.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Antonov, S.V.; Volkov, A.V. Formation of Porous Films with Hydrophobic Surface from a Blend of Polymers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2019, 61, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Polymer Content | 40% PA12 | 40% PA12 | 30% PA12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase separation | temperature induced | non-solvent induced | non-solvent induced |
| φ, % | 9.1 | 12.4 | 22.8 |
| θ, ° | 87 ± 10 | 73 ± 1 | 71 ± 4 |
| Pwater, kg/m2hbar | 2.1 | 142 | 69.9 |
| Pdispersion, kg/m2hbar | 4.7 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| R240nm, % | 58.4 | 98.9 | 99.6 |
| τ, MPa | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilyina, S.O.; Anokhina, T.S.; Ilyin, S.O. Non-Solvent- and Temperature-Induced Phase Separations of Polylaurolactam Solutions in Benzyl Alcohol as Methods for Producing Microfiltration Membranes. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010010
Ilyina SO, Anokhina TS, Ilyin SO. Non-Solvent- and Temperature-Induced Phase Separations of Polylaurolactam Solutions in Benzyl Alcohol as Methods for Producing Microfiltration Membranes. Colloids and Interfaces. 2023; 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlyina, Svetlana O., Tatyana S. Anokhina, and Sergey O. Ilyin. 2023. "Non-Solvent- and Temperature-Induced Phase Separations of Polylaurolactam Solutions in Benzyl Alcohol as Methods for Producing Microfiltration Membranes" Colloids and Interfaces 7, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010010
APA StyleIlyina, S. O., Anokhina, T. S., & Ilyin, S. O. (2023). Non-Solvent- and Temperature-Induced Phase Separations of Polylaurolactam Solutions in Benzyl Alcohol as Methods for Producing Microfiltration Membranes. Colloids and Interfaces, 7(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010010