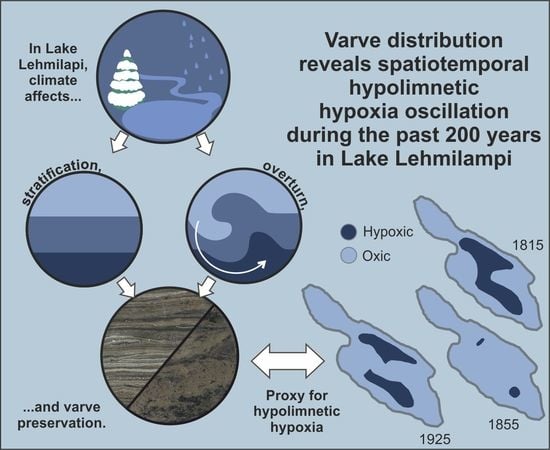
Varve Distribution Reveals Spatiotemporal Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations During the Past 200 Years in Lake Lehmilampi, Eastern Finland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Coring and Sample Preparation
3.2. Varve Analysis
- Varves are present in incident light microscopy images or X-ray images.
- Varves exhibit both a clastic spring lamina and a biogenic growing season lamina with clear differences in color or brightness.
- Varves have a sharp contact between preceding organic and subsequent clastic lamina.
- Varve structure without a sharp contact between preceding organic and subsequent clastic lamina is identified.
- Laminae are disturbed or laterally discontinuous. Such sections sometimes consist of several subsequent varves.
- Sediment is massive
- No laminated structure is identified.
3.3. Dating and Core Correlation
3.4. Modeling the Hypoxic Water Volume
3.5. Meteorological and Diatom Data
3.6. Statistical Analyses
4. Results
4.1. Varve Characteristics
4.2. Dating and Core Correlation
4.3. Changes in Varve Distribution and Hypoxic Water Volume
4.4. Climate and Varve Thickness Correlations with Hypoxia Volume
4.5. Diatom Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatiotemporal Changes in Varves and Hypolimnetic Hypoxia
5.2. Potential Forcing Factors behind Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, R.J. Overview of hypoxia around the world. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulch, H.M.; Schindler, D.W.; Turner, M.A.; Findlay, D.L.; Paterson, M.J.; Vinebrook, R.D. Effects of warming on benthic communities in a boreal lake: Implications of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1377–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsodendris, A.; Brauer, A.; Zacharias, I.; Putyrskaya, V.; Klemt, E.; Sangiorgi, F.; Pross, J. Ecosystem response to human-and climate-induced environmental stress on an anoxic coastal lagoon (Etoliko, Greece) since 1930 AD. J. Paleolimnol. 2015, 53, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.A.; Carpenter, R. Economic valuation of freshwater ecosystem services in The United States: 1971–1997. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 772–783. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution in Phosphorus Limitation in Lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Bryant, L.D.; Matzinger, A.; Wüest, A. Hypolimnetic oxygen depletion in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9964–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.; Janssen, F.; Aleynik, D.; Bange, H.W.; Boltacheva, N.; Çagatay, M.N.; Dale, A.W.; Etiope, G.; Erdem, Z.; Geraga, M.; et al. Investigating hypoxia in aquatic environments: Diverse approaches to addressing a complex phenomenon. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1215–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R. Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: Bistability and soil phosphorus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10002–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deutsch, C.; Brix, H.; Ito, T.; Frenzel, H.; Thompson, L. Climate-Forced Variability of Ocean Hypoxia. Science 2011, 333, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.M. Impact of secular climate change on the thermal structure of a large temperate central European lake. Clim. Chang. 2003, 57, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, W.M.; Smol, J.P. An introduction to physical and geochemical methods used in paleolimnology. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments. Vol. 1, Basin Analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zolitschka, B.; Francus, P.; Ojala, A.E.; Schimmelmann, A. Varves in lake sediments—A review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 117, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolitschka, B.; Enters, D. Lacustrine sediments. In Encyclopedia of Paleoclimatology and Ancient Environments; Gornitz, V., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf, C.; Sturm, M.; Hausmann, S. Natural environmental changes and human impact reflected in sediments of a high alpine lake in Switzerland. J. Paleolimnol. 2003, 30, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyllmann, W. Lithological and geochemical record of anthropogenic changes in recent sediments of a small and shallow lake (Lake Pusty Staw, northern Poland). J. Paleolimnol. 2005, 33, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sullivan, P.E. Annually-laminated lake sediments and the study of Quaternary environmental changes—A review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1983, 1, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguet-Covex, C.; Arnaud, F.; Poulenard, J.; Enters, D.; Reyss, J.L.; Millet, L.; Lazzaroto, J.; Vidal, O. Sedimentological and geochemical records of past trophic state and hypolimnetic anoxia in large, hard-water Lake Bourget, French Alps. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 43, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Arnaud, F.; Dorioz, J.M.; Giguet Covex, C.; Frossard, V.; Sabatier, P.; Millet, L.; Reyss, J.L.; Tachikawa, K.; Bard, E.; et al. A spatiotemporal investigation of varved sediments highlights the dynamics of hypolimnetic hypoxia in a large hard-water lake over the last 150 years. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, A.E.K.; Francus, P.; Zolitschka, B.; Besonen, M.; Lamoureux, S.F. Characteristics of sedimentary varve chronologies—A review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 43, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylmann, W.; Zolitschka, B.; Enters, D.; Ohlendorf, C. Laminated lake sediments in northeast Poland: Distribution, preconditions for formation and potential for paleoenvironmental investigation. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, A.E.; Saarinen, T.; Salonen, V.P. Preconditions for the formation of annually laminated lake sediments in southern and central Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2000, 5, 243–255. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.J.; Höök, T.O.; Ludsin, S.A.; Pothoven, S.A.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Brandt, S.B. Effects of hypolimnetic hypoxia on foraging and distributions of Lake Erie yellow perch. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 381, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarnisto, M. Annually laminated lake sediments. In Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology; Berglund, B.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New Jersey, USA, 1986; pp. 343–370. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, J.P.; Normandeau, A.; Francus, P.; Taranu, Z.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Lapointe, F.; Jautzy, J.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Dorioz, J.M.; Schimmelmann, A.; et al. Urban point sources of nutrients were the leading cause for the historical spread of hypoxia across European lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12655–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kienel, U.; Dulski, P.; Ott, F.; Lorenz, S.; Brauer, A. Recently induced anoxia leading to the preservation of seasonal laminae in two NE-German lakes. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J. Suomen Vesistöjen Jääolot. Finnish Environment, 751; Finnish Environment Institute Reports; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2005; (In Finnish, Summary “Ice Conditions in Lakes and Rivers in Finland” in English); Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/handle/10138/40687 (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Korhonen, J. Long-term changes in lake ice cover in Finland. Nord. Hydrol. 2006, 37, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertta Database. Available online: https://www.syke.fi/en-US/Open_information (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Korhonen, J. Suomen Vesistöjen Virtaaman ja Vedenkorkeuden Vaihtelut. Finnish Environment 45; Finnish Environment Institute Reports; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2007; Finnish Environment Institute Reports; (In Finnish, Summary “Discharge and water level variations in lakes and rivers in Finland” in English); Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/handle/10138/38428 (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Pirinen, P.; Simola, H.; Aalto, J.; Kaukoranta, J.P.; Karlsson, P.; Ruuhela, R. Tilastoja Suomen Ilmastosta 1981–2010; Finnish Environment Institute Reports; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2012; Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/handle/10138/35880 (accessed on 7 March 2019).
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Weather Data Download Service. Available online: https://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/download-observations#!/ (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Soininen, A. The Colonization of Northern Savo in the 15th and 16th Centuries. In Historiallisia Tutkimuksia LVIII. Suomen Historiallinen Seura; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 1961; (In Finnish, summary in English); Available online: https://www.sgr.fi/sust/sust265/sust265_korpela.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2018).
- Korpela, J. Migratory Lapps and the population explosion of Eastern Finns: The early colonization of Eastern Finland reconsidered. In Proceedings of the Networks, Interaction and Emerging Identities in Fennoscandia and Beyond, Finno-Ugrian Society Conference, Tromsø, Norway, 13–16 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Taavitsainen, J.P.; Simola, H.; Grönlund, E. Cultivation history beyond the periphery: Early agriculture in the North European boreal forest. J. World Prehist. 1998, 12, 199–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, A.; Gaillard, M.J.; Peltola, P.; Mazier, F.; Bergbäck, B.; Saarinen, T. Effects of land use and climate change on erosion intensity and sediment geochemistry at Lake Lehmilampi, Finland. Holocene 2013, 23, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soininen, A. Old Traditional Agriculture in Finland in the 18th and 19th Centuries. In Historiallisia Tutkimuksia 96. Suomen Historiallinen Seura; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 1974; (In Finnish, summary in English); Available online: http://www.doria.fi/handle/10024/167610 (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- Simola, H.; Arvola, L. Lakes of Northern Europe. In The Lakes Handbook Volume 2: Lake Restoration and Rehabilitation; O’Sullivan, P.E., Reynolds, C.S., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 117–158. [Google Scholar]
- Turunen, J. Development of Finnish peatland area and carbon storage 1950–2000. Boreal Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Maankamara e DigiKP. Digital Map Database. Available online: http://gtkdata.gtk.fi/maankamara/ (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Haltia-Hovi, E.; Saarinen, T.; Kukkonen, M. A 2000-year record of solar forcing on varved lake sediment in eastern Finland. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A.; Lallier-Vergès, E. Lacustrine sedimentary organic matter records of Late Quaternary paleoclimates. J. Paleolimnol. 1999, 21, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Heyer, C.; Kalff, J. Organic matter mineralization rates in sediments: A within—And among-lake study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Hu, F.S.; Devol, A.H.; Hartnett, H.E.; Tsamakis, E.; Keil, R.G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation; a test for selective degradation under oxic conditions. Am. J. Sci. 1999, 299, 529–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobek, S.; Durisch-Kaiser, E.; Zurbrügg, R.; Wongfun, N.; Wessels, M.; Pasche, N.; Wehrli, B. Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haltia-Hovi, E.; Nowaczyk, N.; Saarinen, T.; Plessen, B. Magnetic properties and environmental changes recorded in Lake Lehmilampi (Finland) during the Holocene. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I.; Hansson, H. The HTH sediment corer. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I. Improved methods for sampling, photographing and varve-counting of varved lake sediments. Boreas 1981, 10, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, T.; Wenho, H. Minijääsormi sekä muita uusia ja vanhoja ideoita järvisedimentin talvikairaukseen. In Proceedings of the Congress Abstract Book, Geologian Tutkijapäivät, Turku, Finland, 14–15 March 2005; pp. 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux, S.F. Embedding unfrozen lake sediments for thin section preparation. J. Paleolimnol. 1994, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiljander, M.; Ojala, A.; Saarinen, T.; Snowball, I. Documentation of the physical properties of annually laminated (varved) sediments at a sub-annual to decadal resolution for environmental interpretation. Quat. Int. 2002, 88, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnish Environment Institute 2014. Downloadable Spatial Datasets. Catchment Areas. Available online: https://www.syke.fi/en-US/Open_information/Spatial_datasets (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- National Land Survey of Finland 2017. Topographic Database. Available online: https://tiedostopalvelu.maanmittauslaitos.fi/tp/kartta?lang=en. (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Finnish Environment Institute 2018. Corine Land Cover. Available online: https://www.syke.fi/en-US/Open_information/Spatial_datasets. (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Geological Survey of Finland 2015. Superficial Deposits. Available online: https: //hakku.gtk.fi/en/locations/search. (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- National Land Survey of Finland. Paituli Spatial Data Download Service. Available online: www.csc.fi/paituli (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- NORDKLIM Dataset (NKDS) v2 2015. Available online: http://blog.fmi.fi/nordmet/node/214 (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Battarbee, R.W.; Jones, V.J.; Flower, R.J.; Cameron, N.G.; Bennion, H.; Carvalho, L.; Juggins, S. Diatoms. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Smol, J.P., Birks, H.J.B., Last, W.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 155–202. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae, Teil: Naviculaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettle, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Fischer: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Band 2/1. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae, Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettle, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1988; Band 2/2. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae, Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettle, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Fisher: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1991; Band 2/3. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae, Teil: Achnanthaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettle, H., Gartner, G., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Fisher: Stuttgart, Germany; Jena, Germany, 1991; Band 2/4. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, S.P. Algal Attributes: An Autecological Classification of Algal Taxa Collected by the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. In US Geological Survey Data Series 329; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding, S.A.; Lubinski, D.J.; Potapova, M. Diatoms of the United States. 2008. Available online: http://westerndiatoms.colorado.edu. (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M.; AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. 2018. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 24 October 2018).
- Grimm, E. TILIA and TILIAGRAPH Pollen Diagramming Program; Illinois State Museum: Springfield, IL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and Cano Draw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination; Version 4.5; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tammelin, M.; Kauppila, T.; Viitasalo, M. Factors controlling recent diatom assemblages across a steep local nutrient gradient in central-eastern Finland. Hydrobiologia 2017, 799, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juggins, S. C2 Version 1.5 User Guide, Software for Ecological and Palaeoecological Data Analysis and Visualization; University of Newcastle: Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Juggins, S. Weighted averaging partial least squares regression (WA-PLS): An improved method for reconstructing environmental variables from species assemblages. Hydrobiologia 1993, 269, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Francus, P.; Normandeau, A.; Lapointe, F.; Perga, M.E.; Ojala, A.; Schimmelmann, A.; Zolitschka, B. Global spread of hypoxia in freshwater ecosystems during the last three centuries is caused by rising local human pressure. Glob. Chan. Biol. 2016, 22, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, N.; Gaillard, J.F.; Packman, A.I. Interplay between flow and bioturbation enhances metal efflux from low-permeability sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.S.; Miller, M.F. Benthic invertebrate activity in lakes: Linking present and historical bioturbation patterns. Aquat. Biol. 2008, 2, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savrda, C.E. Taphonomy of trace fossils. In Trace Fossils: Concepts, Problems, Prospects; Miller, W., III, Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, A. Ecologic interpretation of deep-sea trace fossil communities. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1991, 85, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.A.; Jeppesen, E. The role of palaeolimnology in assessing eutrophication and its impact on lakes. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 49, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühland, K.M.; Paterson, A.M.; Smol, J.P. Lake diatom responses to warming: Reviewing the evidence. J. Paleolimnol. 2015, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissman, C.E.H.; Williamson, C.E.; Rose, K.C.; Saros, J.E. Response of phytoplankton in an alpine lake to inputs of dissolved organic matter through nutrient enrichment and trophic forcing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, C.E.; Anderson, N.J.; Haworth, E. Aulacoseira subarctica: Taxonomy, physiology, ecology and palaeoecology. Eur. J. Phycol. 2003, 38, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoermer, E.F.; Kreis, R.G., Jr.; Sicko-Goad, L. A Systematic, Quantitative, and Ecological Comparison of Melosira Islandica, O. Müll. with M. Granulata (EHR.) Ralfs from the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 1981, 7, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, A.E.; Alenius, T. 10 000 years of interannual sedimentation recorded in the Lake Nautajärvi (Finland) clastic–organic varves. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 219, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, A.E.K.; Kosonen, E.; Weckström, J.; Korkonen, S.; Korhola, A. Seasonal formation of clastic-biogenic varves: The potential for palaeoenvironmental interpretations. GFF 2013, 135, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarni, S.; Lensu, A.; Tammelin, M.; Haltia, E.; Saarinen, T. Winter climate signal in boreal clastic-biogenic varves: A comprehensive analysis of three varved records from 1890 to 1990 AD with meteorological and hydrological data from Eastern Finland. GFF 2017, 139, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehrer, B.; Schultze, M. Stratification of lakes. Rev. Geophys. 2008, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassiljev, J. The simulated response of lakes to changes in annual and seasonal precipitation: Implication for Holocene lake-level changes in northern Europe. Clim. Dyn. 1998, 14, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavapuro, M.; Lipponen, A.; Artimo, A.; Katko, T.S. Groundwater sustainability indicators: Testing with Finnish data. Boreal Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 381–402. [Google Scholar]








| Core | Core Type | Sampling Point/Transect | Water Depth (m) | Sediment Types | Core Length (cm) | Core | Core Type | Sampling Point/Transect | Water Depth (m) | Sediment Types | Core Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL1 | FC | NB | 10.80 | a | 32 | LL18 | PC | AB transect | 9.90 | a,b,c | 140 |
| LL2 | PC | NB | 10.80 | a | 142 | LL19 | FC | AB transect | 10.30 | a,b,c | 29 |
| LL3 | FC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 26 | LL20 | PC | AB transect | 10.30 | a,b,c | 152 |
| LL4 | PC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 147 | LL21 | FC | AB transect | 10.60 | a,b,c | 32 |
| LL5 | FC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 30 | LL22 | PC | AB transect | 10.60 | a,b,c | 140 |
| LL6 | PC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 152 | LL23 | FC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 27 |
| LL7 | FC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 33 | LL24 | PC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 142 |
| LL8 | PC | AB transect | 10.80 | a | 162 | LL25 | FC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 37 |
| LL9 | FC | AB transect | 10.50 | a,b | 21 | LL26 | PC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 166 |
| LL10 | PC | AB transect | 10.50 | a,b | 167 | LL27 | FC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 32 |
| LL11 | FC | AB transect | 9.58 | a,b,c | 17 | LL28 | PC | AB transect | 10.75 | a | 146 |
| LL12 | PC | AB transect | 9.58 | a,b,c | 149 | LL29 | FC | BC transect | 10.40 | a,b | 27 |
| LL13 | FC | AB transect | 7.20 | a,b,c | 24 | LL30 | FC | BC transect | 10.30 | a,b,c | 33 |
| LL14 | PC | AB transect | 7.20 | a,b,c | 158 | LL31 | FC | BC transect | 9.90 | a,b,c | 24 |
| LL15 | FC | AB transect | 6.53 | c | 25 | LL32 | FC | BC transect | 9.10 | a,b,c | 30 |
| LL16 | PC | AB transect | 6.53 | c | 162 | LL33 | FC | BC transect | 8.68 | a,b,c | 28 |
| LL17 | FC | AB transect | 9.90 | a,b,c | 27 | LLS2 | FC | SB | 11.60 | a | 32 |
| Core | Water Depth (m) | Varve Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| LL1-LL7 | 10.80 | 100 |
| LL23-LL27 | 10.75 | 100 |
| LL21 | 10.60 | 69 |
| LL9 | 10.50 | 68 |
| LL29 | 10.40 | 35 |
| LL19 | 10.30 | 27 |
| LL30 | 10.30 | 22 |
| LL17 | 9.90 | 12 |
| LL31 | 9.90 | 11 |
| LL11 | 9.58 | 8 |
| LL32 | 9.10 | 6 |
| LL33 | 8.68 | 5 |
| LL13 | 7.20 | 1 |
| LL15 | 6.53 | 0 |
| Hypoxia Period | Duration (Years) | Duration (from-to) | Median Hypoxia Volume (m3) | Range of Variation of Hypoxia Volume (m3) | Median Hypoxia Volume per Lake Volume (%) | Maximum Hypoxia Volume per Lake Volume (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 20 | 1994–2014 | 2255 | 787–34599 | 0.240 | 3.727 |
| 6 | 9 | 1971–1980 | 1638 | 1638–7648 | 0.180 | 0.823 |
| 5 | 1 | 1943 | 428 | 428–428 | 0.046 | 0.046 |
| 4 | 16 | 1905–1921 | 1638 | 1638–34599 | 0.180 | 3.727 |
| 3 | 11 | 1881–1892 | 428 | 428–787 | 0.046 | 0.085 |
| 2 | 5 | 1852–1857 | 787 | 787–787 | 0.084 | 0.085 |
| 1 | 27 | 1815–1842 | 1638 | 1638–53304 | 0.180 | 5.740 |
| Variable | Period | n | ρ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual temperature | 1890–1997 | 107 | 0.36 | 0.06 |
| Annual precipitation | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.05 | 0.63 |
| Winter temperature * | 1890–1997 | 107 | 0.56 | <0.01 |
| Winter precipitation | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.06 | 0.22 |
| Days of snow cover * | 1957–1997 | 40 | −0.38 | 0.03 |
| Spring temperature | 1890–1997 | 107 | 0.27 | <0.01 |
| March temperature * | 1890–1997 | 107 | 0.39 | <0.01 |
| Spring precipitation | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.11 | 0.27 |
| Summer temperature | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.26 | 0.01 |
| Summer precipitation | 1890–1997 | 107 | 0.26 | <0.01 |
| Autumn temperature | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.23 | 0.02 |
| November temperature * | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.47 | <0.01 |
| Autumn precipitation * | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.36 | <0.01 |
| October precipitation * | 1890–1997 | 107 | −0.56 | <0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salminen, S.; Saarni, S.; Tammelin, M.; Fukumoto, Y.; Saarinen, T. Varve Distribution Reveals Spatiotemporal Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations During the Past 200 Years in Lake Lehmilampi, Eastern Finland. Quaternary 2019, 2, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat2020020
Salminen S, Saarni S, Tammelin M, Fukumoto Y, Saarinen T. Varve Distribution Reveals Spatiotemporal Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations During the Past 200 Years in Lake Lehmilampi, Eastern Finland. Quaternary. 2019; 2(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalminen, Sarianna, Saija Saarni, Mira Tammelin, Yu Fukumoto, and Timo Saarinen. 2019. "Varve Distribution Reveals Spatiotemporal Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations During the Past 200 Years in Lake Lehmilampi, Eastern Finland" Quaternary 2, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat2020020
APA StyleSalminen, S., Saarni, S., Tammelin, M., Fukumoto, Y., & Saarinen, T. (2019). Varve Distribution Reveals Spatiotemporal Hypolimnetic Hypoxia Oscillations During the Past 200 Years in Lake Lehmilampi, Eastern Finland. Quaternary, 2(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat2020020