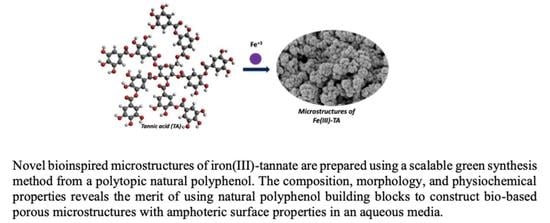
Green Synthesis of De Novo Bioinspired Porous Iron-Tannate Microstructures with Amphoteric Surface Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Procedure for the Preparation of Fe(III)-TA Microstructures
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Lead (Pb+2) Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Morphology and Surface Properties of Fe(III)-TA Microstructures
3.4. Thermal and Physiochemical Properties
3.5. Heavy Metal Adsorption Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, R.; Pal, A.; Rakshit, A.; Saha, B. Properties and applications of amphoteric surfactant: A concise review. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2021, 24, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eredyuk, V.; Alami, E.; Nydén, M.; Holmberg, K.; Peresypkin, A.V.; Menger, F.M. Micellization and Adsorption Properties of Novel Zwitterionic Surfactants. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5160–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Jin, J.; Ma, H.; Chen, J. Multifunctionalized mesoporous silica as an efficient reversed-phase/anion exchange mixed-mode sorbent for solid-phase extraction of four acidic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1527, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanals, N.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M. Mixed-mode ion-exchange polymeric sorbents in environmental analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Eiroa, A.; Canle, M.; Leroy-Cancellieri, V.; Cerdà, V. Solid-phase extraction of organic compounds: A critical review. Part II. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S.; Chimuka, L. Recent developments in selective materials for solid phase extraction. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houk, R.J.T.; Jacobs, B.W.; Gabaly, F.E.; Chang, N.N.; Talin, A.A.; Graham, D.D.; House, S.D.; Robertson, I.M.; Allendorf, M.D. Silver Cluster Formation, Dynamics, and Chemistry in Metal−Organic Frameworks. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3413–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water stability and adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriemma, M.; Piscitelli, A.; Pasquino, R.; Cerruti, P.; Malinconico, M.; Grizzuti, N. Blending poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) with tannic acid: Influence of a polyphenolic natural additive on the rheological and thermal behavior. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 63, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, D.P.; Boskou, G.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Polyphenolic content and in vitro antioxidant characteristics of wine industry and other agri-food solid waste extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutava, T.; Prouty, M.; Kommireddy, D.; Lvov, Y. pH Responsive Decomposable Layer-by-Layer Nanofilms and Capsules on the Basis of Tannic Acid. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel-Unal, I.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Hydrogen-Bonded Multilayers of a Neutral Polymer and a Polyphenol. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3962–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Feng, X.; Bu, Y.; Wu, D.; Jin, Z. Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation Based on Tannic Acid. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Liang, K.; Best, J.P.; van Koeverden, M.P.; Such, G.K.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science 2013, 341, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bing, W.; Huang, S.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Mussel Byssus-Like Reversible Metal-Chelated Supramolecular Complex Used for Dynamic Cellular Surface Engineering and Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Kempe, K.; Müllner, M.; Ejima, H.; Ju, Y.; van Koeverden, P.M.; Suma, T.; Braunger, J.A.; Leeming, M.G.; Abrahams, B.F.; et al. Surface-Confined Amorphous Films from Metal-Coordinated Simple Phenolic Ligands. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5825–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Björnmalm, M.; Suma, T.; Faria, M.; Ju, Y.; Kempe, K.; Müllner, M.; Ejima, H.; Stickland, A.D.; Caruso, F. Metal–Phenolic Supramolecular Gelation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13803–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Björnmalm, M.; Bertleff-Zieschang, N.; Besford, Q.; Mettu, S.; Suma, T.; Faria, M.; Caruso, F. Rust-Mediated Continuous Assembly of Metal–Phenolic Networks. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erwin, W.R.; Zarick, H.F.; Talbert, E.M.; Bardhan, R. Light trapping in mesoporous solar cells with plasmonic nanostructures. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1577–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Chemistry of Mesoporous Organosilica in Nanotechnology: Molecularly Organic–Inorganic Hybridization into Frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3235–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zharov, I. Large Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Templating with a Nonsurfactant Molecule, Tannic Acid. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhou, L.; Ma, L.; He, Y.; Gao, J. Improved Performance of Lipase Immobilized on Tannic Acid-Templated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 179, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Lei, H.; Han, Z.; Shi, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y. Dopamine functionalized tannic-acid-templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the efficient removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, S.; Moon, H.C.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Hong, S.-P.; Lee, B.S.; Kang, E.; Lee, J.; Ryu, D.H.; et al. Antimicrobial spray nanocoating of supramolecular Fe(III)-tannic acid metal-organic coordination complex: Applications to shoe insoles and fruits. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saowalak, K.; Titipun, T.; Somchai, T.; Chalermchai, P. Iron(III)-Tannic Molecular Nanoparticles Enhance Autophagy effect and T1 MRI Contrast in Liver Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krungchanuchat, S.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S.; Pilapong, C. Characterization and cellular studies of molecular nanoparticle of iron (III)-tannic complexes; toward a low cost magnetic resonance imaging agent. Biointerphases 2017, 12, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.-G.; Yoon, H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.-C. Polyphenol/FeIII Complex Coated Membranes Having Multifunctional Properties Prepared by a One-Step Fast Assembly. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, L.; Ren, J.; Wei, H.; Jia, L. Coating process and stability of metal-polyphenol film. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 484, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Ejima, H.; Cho, K.L.; Kempe, K.; Müllner, M.; Best, J.P.; Caruso, F. Coordination-Driven Multistep Assembly of Metal–Polyphenol Films and Capsules. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.T.; Furukawa, H.; Gándara, F.; Trickett, C.A.; Jeong, H.M.; Cordova, K.E.; Yaghi, O.M. Three-Dimensional Metal-Catecholate Frameworks and Their Ultrahigh Proton Conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15394–15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Antonietti, M.; Fechler, N. Self-Assembly of Metal Phenolic Mesocrystals and Morphosynthetic Transformation toward Hierarchically Porous Carbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8269–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Veith, G.M.; Dai, S. Soluble Porous Coordination Polymers by Mechanochemistry: From Metal-Containing Films/Membranes to Active Catalysts for Aerobic Oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Kong, B.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Q.; Tong, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.P.; Wang, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Metal–Polyphenol Coordination Crystals and Their Derived Metal/N-doped Carbon Composites for Oxygen Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 12658–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, J.; Ray, M. Iron-polyphenol nanocluster removes fluoride and methylene blue dye from water and promotes plant growth. SSRN 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsi, T.M. Synthesis of Nano-Titanium Tannate as an Adsorbent for Crystal Violet Dye, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherm Studies. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Synthesis and characterization of ferric tannate as a novel porous adsorptive-catalyst for notrogen removal from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40785–40791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P. Decontamination of Heavy Metals: Processes, Mechanisms, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnayake, H. CCDC 2108217: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination; The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC): Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]






| Elemental Transition Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Chemical and Oxidation State | Elemental Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Theoretical | |||
| C 1s | 284.1, 287.9 | C-C (sp3), O-C=O (sp2) | 45.79 | 46.28 |
| Fe 2p 2p3/2 & 2p1/2 | 701.9, 714.8, 729.9, 735.5, 723.6 | Fe+3, Fe+2 | 11.78 a/12.20 b | 11.96 |
| O 1s | 530.2, 531.0, 532.4 | Fe-O-C, C-O (sp3), C=O (sp2) | 39.24 a | 39.39 |
| H | - | - | 3.19 | 2.16 |
| pH of the Solution | Zeta Potential (eV) | |
|---|---|---|
| in Water | in Ethanol | |
| 2 | −2.0 | 8.0 |
| 4 | −20.9 | −4.5 |
| 6 | −22.4 | −19.0 |
| 7 | −45.0 | −23.8 |
| 10 | −35.2 | −8.4 |
| 12 | −33.8 | −10.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rathnayake, H.; Dawood, S.; Pathiraja, G.; Adrah, K.; Ayodele, O. Green Synthesis of De Novo Bioinspired Porous Iron-Tannate Microstructures with Amphoteric Surface Properties. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 3, 192-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020013
Rathnayake H, Dawood S, Pathiraja G, Adrah K, Ayodele O. Green Synthesis of De Novo Bioinspired Porous Iron-Tannate Microstructures with Amphoteric Surface Properties. Sustainable Chemistry. 2022; 3(2):192-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRathnayake, Hemali, Sheeba Dawood, Gayani Pathiraja, Kelvin Adrah, and Olubunmi Ayodele. 2022. "Green Synthesis of De Novo Bioinspired Porous Iron-Tannate Microstructures with Amphoteric Surface Properties" Sustainable Chemistry 3, no. 2: 192-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020013
APA StyleRathnayake, H., Dawood, S., Pathiraja, G., Adrah, K., & Ayodele, O. (2022). Green Synthesis of De Novo Bioinspired Porous Iron-Tannate Microstructures with Amphoteric Surface Properties. Sustainable Chemistry, 3(2), 192-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020013