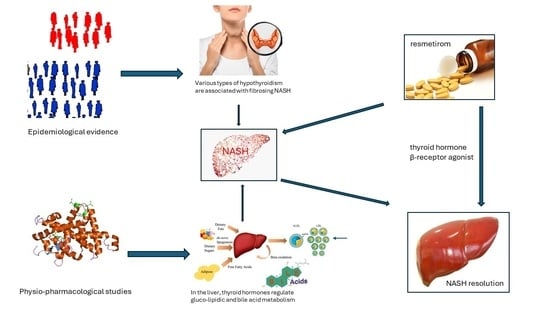
Resmetirom: Finally, the Light at the End of the NASH Tunnel?
1. Introduction
2. What Has NASH to Do with Thyroid?
3. Safety and Efficacy of Resmetirom
4. Conclusions and Research Agenda
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludwig, J.; Viggiano, T.R.; McGill, D.B.; Oh, B.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1980, 55, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ratziu, V.; Friedman, S.L. Why Do So Many Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Trials Fail? Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NASH drug treatment development: Challenges and lessons. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juluri, R.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Olson, J.; Unalp, A.; Van Natta, M.L.; Cummings, O.W.; Tonascia, J.; Chalasani, N. Generalizability of the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network histologic scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, G.; Bansal, M.B. Resmetirom: An Orally Administered, Smallmolecule, Liver-directed, β-selective THR Agonist for the Treatment of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. touchREV Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Leoni, S.; Alswat, K.A.; Fouad, Y. History of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Caldwell, S.H. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Summary of an AASLD Single Topic Conference. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1202–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J.; Luyckx, F.H.; Esser, N.; Lamproye, A.; Delwaide, J.; Paquot, N. Stéatohépatite non alcoolique (NASH): Un modèle d’inflammation métabolique («métaflammation») [Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A model of metabolic inflammation («metaflammation»)]. Rev. Med. Liege 2022, 77, 316–322. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Mantovani, A.; Targher, G.; Bril, F. Endpoints in NASH Clinical Trials: Are We Blind in One Eye? Metabolites 2024, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Lonardo, A. The independent predictors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and its individual histological features.: Insulin resistance, serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and serum total cholesterol are a clue to pathogenesis and candidate targets for treatment. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Carani, C.; Carulli, N.; Loria, P. ‘Endocrine NAFLD’ a hormonocentric perspective of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, P.; Carulli, L.; Bertolotti, M.; Lonardo, A. Endocrine and liver interaction: The role of endocrine pathways in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandino, G.; Kaspari, R.R.; Spadaro, O.; Reyna-Neyra, A.; Perry, R.J.; Cardone, R.; Kibbey, R.G.; Shulman, G.I.; Dixit, V.D.; Carrasco, N. Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD is driven by intra- and extrahepatic mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9172–E9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD: Evidence for a distinct disease entity? Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebe, R.; Esposito, I.; Bock, H.H.; Vom Dahl, S.; Stindt, J.; Baumann, U.; Luedde, T.; Keitel, V. Diagnosis and management of secondary causes of steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1455–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, A.L.; Tavaglione, F.; Romeo, S.; Charlton, M. Endocrine aspects of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Beyond insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1524–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Bonora, E.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Targher, G. Association Between Primary Hypothyroidism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Han, B.; Qi, X. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with thyroid function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.; Joo, S.K.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Ahmed, A. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Low-Normal Thyroid Function Are Associated with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahadini, A.A.D.; Rahadina, A. Association between hypothyroidism and liver fibrosis risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 8, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvari, M.; Valenzuela-Vallejo, L.; Axarloglou, E.; Verrastro, O.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Mingrone, G.; George, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Thyroid function, adipokines and mitokines in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: A multi-centre biopsy-based observational study. Liver Int. 2024. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, J.; Chen, Y.; Schöning, W.; Mai, K.; Tacke, F.; Spranger, J.; Köhrle, J.; Wirth, E.K. Hepatic Energy Metabolism under the Local Control of the Thyroid Hormone System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.; Kim, A.; Ni, B.; Celi, F.S. Thyroid hormone action and liver disease, a complex interplay. Hepatology 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Murúa-Beltrán Gall, S.; Uribe, M.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C. Understanding the Relationship between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Thyroid Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, E.K.; Puengel, T.; Spranger, J.; Tacke, F. Thyroid hormones as a disease modifier and therapeutic target in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 17, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, M. Burning hepatic fat: Therapeutic potential for liver-specific thyromimetics in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, E.E.; Finn, P.D.; Stebbins, J.W.; Hou, J.; Ito, B.R.; van Poelje, P.D.; Linemeyer, D.L.; Erion, M.D. Reduction of hepatic steatosis in rats and mice after treatment with a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor agonist. Hepatology 2009, 49, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Taub, R.A.; Barbone, J.M.; Harrison, S.A. Hepatic Fat Reduction Due to Resmetirom in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated With Improvement of Quality of Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1354–1361.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, L. Lipid lowering effects of iodothyronines: In vivo and in vitro studies on rat liver. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, K.E.; Chalasani, N. Should combination therapy be the paradigm for future nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical trials? Hepatology 2011, 54, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burra, P.; Zanetto, A.; Germani, G. Sex bias in clinical trials in gastroenterology and hepatology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G. Editorial: Resmetirom—A promising treatment option for NASH and liver fibrosis. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K. Selective Agonists of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta for the Treatment of NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lonardo, A. Resmetirom: Finally, the Light at the End of the NASH Tunnel? Livers 2024, 4, 138-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4010010
Lonardo A. Resmetirom: Finally, the Light at the End of the NASH Tunnel? Livers. 2024; 4(1):138-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLonardo, Amedeo. 2024. "Resmetirom: Finally, the Light at the End of the NASH Tunnel?" Livers 4, no. 1: 138-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4010010
APA StyleLonardo, A. (2024). Resmetirom: Finally, the Light at the End of the NASH Tunnel? Livers, 4(1), 138-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4010010