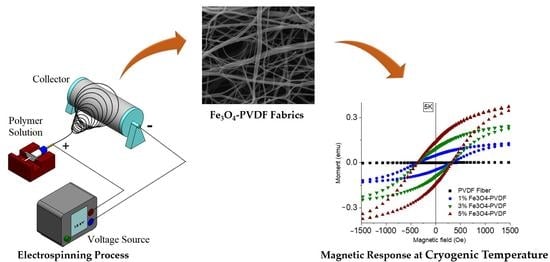
Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fe3O4-PVDF Fiber Mats
2.2. Nanofiber Mats Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.5. Piezoelectric Coefficient (d33) Test
3.6. Magnetization Test
3.7. Dynamic Mechanical Analyzer (DMA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, Y.; Long, Z.; Wan, X.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; He, Y. 3D carbon fiber mats/nano-Fe3O4 hybrid material with high electromagnetic shielding performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiscan, O.; Dumitru, I.; Postolache, P.; Tura, V.; Stancu, A. Electrospun PVC/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers for microwave absorption applications. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Kawabe, A.; Shinkai, M.; Kobayashi, T. Development of chitosan-conjugated magnetite for magnetic cell separation. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.-F.; Stiller, S.; Hoth, A.; Kaufner, L.; Pison, U.; Cartier, R. One-Pot Synthesis of PEGylated Ultrasmall Iron-Oxide Na-noparticles and Their In Vivo Evaluation as Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3132–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelliccione, M.; Jenkins, A.; Ovartchaiyapong, P.; Reetz, C.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Ni, N.; Jayich, A.C.B. Scanned probe imaging of nanoscale magnetism at cryogenic temperatures with a single-spin quantum sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abderrahmane, A.; Ko, P.J.; Okada, H.; Sato, S.-I.; Ohshima, T.; Sandhu, A. Proton irradiation enhancement of low-field negative magnetoresistance sensitivity of AlGaN/GaN-based magnetic sensor at cryogenic temperature. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, O.; Setua, D.; Chattopadhyay, S. A brief overview on ferrite (Fe3O4) based polymeric nanocomposites: Recent developments and challenges. J. Res. Updat. Polym. Sci. 2014, 3, 184. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Fan, J.; Lau, S. Thermal, mechanical, and dielectric properties of graphite reinforced poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Y. Preparation and electroactive properties of a PVDF/nano-TiO2 composite film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3831–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mohseni, M. Investigation of the electromagnetic microwaves absorption and piezoelectric properties of electrospun Fe3O4-GO/PVDF hybrid nanocomposites. Org. Electron. 2018, 59, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, S.; Miyata, S. Effects of crystal structure on piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of copoly(vinylidenefluoride-tetrafluoroethylene). J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.; Gunawan, H.; Sugondo, A.; Chiu, C.-W. A New Approach of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Poling Method for Higher Electric Response. Ferroelectrics 2013, 446, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; D’Souza, N.; Dahotre, N. Low-Cost Reliable Corrosion Sensors Using ZnO-PVDF Nanocomposite Textiles. Sensors 2021, 21, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; D’Souza, N.; Ho, Y.H.; Dahotre, N.; Mahbub, I. Embedded Corrosion Sensing with ZnO-PVDF Sensor Textiles. Sensors 2020, 20, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Sheikholeslami, T.F.; Behzadmehr, A. Investigation on the electrospun PVDF/NP-ZnO nanofibers for application in environmental energy harvesting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Chandra, A.; Praveen, G.; Snigdha, S.; Roy, S.; Agatemor, C.; Thomas, S.; Provaznik, I. Electrospinning over Solvent Casting: Tuning of Mechanical Properties of Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, P.; Lu, J.; Li, K.; Chen, X.; Dan, R. Research on hydrophobicity of electrospun Fe3O4/PVDF nanofiber membranes under different preparation conditions. Full Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2019, 28, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.S.; Bhat, D.K.; Santosh, M.S. Crystallinity, conductivity, and magnetic properties of PVDF-Fe3O4 composite films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 119, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, O.D.; Mandal, B.P.; Majeed, J.; Lawes, G.; Naik, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Inorganic–organic multiferroic hybrid films of Fe3O4 and PVDF with significant magneto-dielectric coupling. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3710–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, T.; Hemalatha, J. Ferroelectric and magnetic studies on unpoled (Polyvinylidine fluoride)/Fe3O4 magnetoelectric nanocomposite structures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 137, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-Q.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.-T.; Zhou, K.-M. The performance of the PVDF-Fe3O4 ultrafiltration membrane and the effect of a parallel magnetic field used during the membrane formation. Desalination 2012, 292, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, C.; Wu, Z. A Review of the Polymer for Cryogenic Application: Methods, Mechanisms and Perspectives. Polymers 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, S.; Lu, C.; Feng, M.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C. Micro-crack behavior of carbon fiber reinforced Fe3O4/graphene oxide modified epoxy composites for cryogenic application. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 108, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Polymethylmethacrylate/Fe3O4 composite nanofiber membranes with ultra-low dielectric permittivity. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 97, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorayani-Bafqi, M.S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M. Fabrication of composite PVDF-ZnO nanofiber mats by electrospinning for energy scavenging application with enhanced efficiency. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ouyang, C.; Jia, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Magnetic and optical properties of poly(vinylidene difluoride)/Fe3O4 nanocomposite prepared by coprecipitation approach. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Persi, L.; Scrosati, B. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 394, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, W.; Roos, J.; Brinkmann, D.; Capuano, F.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. Comparison of NMR and conductivity in (PEP)8LiClO4+γ-LiAlO2. Solid State Ion. 1992, 53, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.P.; Reddy, M.J. Sm2O3 composite PEO solid polymer electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2003, 115, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.; Steele, B. Effects of inert fillers on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of lithium salt-poly(ethylene oxide) polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1982, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, W.; Such, K.; Wyciślik, H.; Płocharski, J. Modifications of crystalline structure of PEO polymer electrolytes with ceramic additives. Solid State Ion. 1989, 36, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukitpaneenit, P.; Chung, T.-S. Molecular elucidation of morphology and mechanical properties of PVDF hollow fiber mem-branes from aspects of phase inversion, crystallization and rheology. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.J.; Thakur, A.K.; Subba-Rao, G.V.; Chowdari, B.V.R. Effect of glass—Ceramic filler on properties of polyethylene oxide–LiCF3SO3 complex. J. Power Sources 2003, 115, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Wu, Y.; Kan, E.; Fan, J. Breathable and Flexible Piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF Fibrous Nanogenerator for Wearable Ap-plications. Polymers 2018, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Yousefi, A.A. Analysis Method: FTIR studies of β-phase crystal formation in stretched PVDF films. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, S.; Kadlec, A. Piezoelectric and dielectric properties of nanoporous polyvinylidence fluoride (PVDF) films. Behav. Mech. Multifunct. Mater. Compos. 2016, 9800, 98000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, G.; Morales, M.D.P. Field Dependence of Blocking Temperature in Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Metastab. Nanocryst. Mater. 2004, 20–21, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sara-Majetich, T.W.; Mefford, O.T. Magnetic Nanoparticles. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demir, A.; Topkaya, R.; Baykal, A. Green synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with maltose: Its magnetic investigation. Polyhedron 2013, 65, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramajo, L.A.; Cristóbal, A.A.; Botta, P.M.; Porto-López, J.M.; Reboredo, M.M.; Castro, M.S. Dielectric and magnetic response of Fe3O4/epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Sha, Y.; Shevchenko, E. Effect of Polymer Removal on the Morphology and Phase of the Nanoparticles in All-Inorganic Heterostructures Synthesized via Two-Step Polymer Infiltration. Molecules 2021, 26, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sample | Tm (°C) | ∆H (J/g) | Corrected ∆H | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF Fiber | 160.12 | 26.40 | 26.40 | 25.14 |
| 1% Fe3O4-PVDF Fiber | 160.46 | 22.91 | 22.68 | 21.81 |
| 3% Fe3O4-PVDF Fiber | 160.35 | 15.07 | 14.62 | 14.35 |
| 5% Fe3O4-PVDF Fiber | 160.18 | 14.52 | 13.79 | 13.82 |
| Sample | F(β) | d33 (pC/N) |
|---|---|---|
| PVDF Pellet | 48.45 ± 3.43 | 5 ± 3 |
| PVDF Fiber | 81.16 ± 1.81 | 32 ± 1.73 |
| 1% Fe3O4-PVDF | 73.39 ± 1.24 | 28 ± 1 |
| 3% Fe3O4-PVDF | 71.69 ± 2.16 | 26 ± 1 |
| 5% Fe3O4-PVDF | 65.26 ± 3.39 | 20 ± 2.65 |
| Sample | PVDF | 1% Fe3O4-PVDF | 3% Fe3O4-PVDF | 5% Fe3O4-PVDF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| emu | emu/g | emu | emu/g | emu | emu/g | emu | emu/g | |
| 300 K | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.28 | 0.28 | 3.29 | 0.44 | 5.11 |
| 5 K | 0 | 0 | 0.17 | 1.45 | 0.33 | 3.88 | 0.51 | 5.93 |
| Sample | PVDF | 1% Fe3O4-PVDF | 3% Fe3O4-PVDF | 5% Fe3O4-PVDF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E Before magnetization test (MPa) | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 0.71 ± 0.01 |
| E After magnetization test (MPa) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.62± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chowdhury, T.; D’Souza, N.; Berman, D. Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications. Textiles 2021, 1, 227-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1020011
Chowdhury T, D’Souza N, Berman D. Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications. Textiles. 2021; 1(2):227-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleChowdhury, Tonoy, Nandika D’Souza, and Diana Berman. 2021. "Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications" Textiles 1, no. 2: 227-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1020011
APA StyleChowdhury, T., D’Souza, N., & Berman, D. (2021). Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications. Textiles, 1(2), 227-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1020011