Interaction of Prokineticin Receptors with Accessory Proteins
Definition
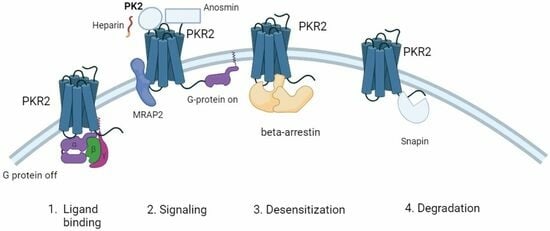
:1. Introduction
2. Proteins Mediating the Endoplasmic Reticulum Quality Control System
3. Proteins That Stabilize PKRs at the Cell Surface
4. Proteins That Modulate Ligand Binding of PKRs
5. Protein That Mediates Receptor Desensitization
6. Protein-Mediating Endocytosis of Receptors
7. Glycosaminoglycans and Their Interaction with Proteins
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, D.M.F.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Kobilka, B.K. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 2009, 459, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Oda, T.; Saito, T.; Hiyama, H.; Takasaki, J.; Kamohara, M.; Ohishi, T.; Matsushime, H.; Furuichi, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of prokineticin receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1579, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.C.; Bullock, C.M.; Ehlert, F.J.; Chen, J.-L.; Tian, H.; Zhou, Q.Y. Identification and Molecular Characterization of Two Closely Related G Protein-coupled Receptors Activated by Prokineticins/Endocrine Gland Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19276–19280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Takatsu, Y.; Terao, Y.; Kumano, S.; Ishibashi, Y.; Suenaga, M.; Abe, M.; Fukusumi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Shintani, Y.; et al. Isolation and identification of EG-VEGF/prokineticins as cognate ligands for two orphan G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, L.; Ferrara, N. The Prokineticins: Neuromodulators and Mediators of Inflammation and Myeloid Cell-Dependent. Angiogenesis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1055–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, R.; Maftei, D.; Fullone, M.R.; Miele, R. Identification and characterization of Prokineticin receptor 2 splicing TM4-7 variant and its modulation in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropeptides 2019, 73, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Bullock, C.M.; Knauer, D.J.; Ehlert, F.J.; Zhou, Q.Y. Identification of two prokineticin cDNAs: Recombinant proteins potently contract gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollay, C.; Wechselberger, C.; Mignogna, G.; Negri, L.; Melchiorri, P.; Barra, D.; Kreil, G. Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 374, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, H.; Pacaud, P.; Diochot, S.; Moinier, D.; Lazdunski, M. MIT (1), a black mamba toxin with a new and highly potent activity on intestinal contraction. FEBS Lett. 1999, 461, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; LeCouter, J.; Lin, R.; Peale, F. EG-VEGF and Bv8: A novel family of tissue-restricted angiogenic factors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1654, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCouter, J.; Kowalski, J.; Foster, J.; Hass, P.; Zhang, Z.; Dillard-Telm, L.; Frantz, G.; Rangell, L.; DeGuzman, L.; Keller, G.A.; et al. Identification of an angiogenic mitogen selective for endocrine gland endothelium. Nature 2001, 412, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Prokineticin-Receptor Network: Mechanisms of Regulation. Life 2022, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilek, A.; Engel, E.; Beier, D.; Lepperdinger, G. Murine Bv8 gene maps near a synteny breakpoint of mouse chromosome 6 and human 3p21. Gene 2000, 256, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kuei, C.; Sutton, S.; Wilson, S.; Yu, J.; Kamme, F.; Mazur, C.; Lovenberg, T.; Liu, C. Identification and pharmacological characterization of prokineticin 2 beta as a selective ligand for prokineticin receptor 1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, R.; Maftei, D.; Negri, L.; Fusco, I.; Miele, R. PK2β ligand, a splice variant of prokineticin 2, is able to modulate and drive signaling through PKR1 receptor. Neuropeptides 2018, 71, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, R.; Maftei, D.; Vincenzi, M.; Fullone, M.R.; Miele, R. Identification and Characterization of a New Splicing Variant of Prokineticin 2. Life 2022, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, A.; Winklmayr, M.; Lepperdinger, G.; Kreil, G. The AVIT protein family. Secreted cysteine-rich vertebrate proteins with diverse functions. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, J.; Samson, M. Cytokine properties of prokineticins. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 4014–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; LeCouter, J.; Kowalski, J.; Ferrara, N. Characterization of endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in adrenal cortex capillary endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8724–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. How and why do GPCRs dimerize? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufareva, I.; Salanga, C.L.; Handel, T.M. Chemokine and chemokine receptor structure and interactions: Implications for therapeutic strategies. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 93, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, C.; Dodé, C.; Fabre, L.; Teixeira, L.; Labesse, G.; Pin, J.P.; Hardelin, J.P.; Rondard, P. PROKR2 missense mutations associated with Kallmann syndrome impair receptor signalling activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullone, M.R.; Lattanzi, R.; Maftei, D.; Bonaccorsi, M.C.; Miele, R. Analysis of role of aromatic residues in extracellular loop 2 of Prokineticin receptor 2 in ligand binding probed with genetically encoded photo-crosslinkers. BBA Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, A.; Yarnitzky, T.; Wiener, A.; Meidan, R.; Niv, M.Y. Modeling of human prokineticin receptors: Interactions with novel small-molecule binders and potential off-target drugs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Non-Peptide Agonists and Antagonists of the Prokineticin Receptors. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 6323–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, A.; Brogi, S.; Urayama, K.; Nishi, T.; Kurose, H.; Tafi, A.; Ribeiro, N.; Désaubry, L.; Nebigil, C.G. Discovery and cardioprotective effects of the first non-Peptide agonists of the G protein-coupled prokineticin receptor-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, C.M.; Li, J.D.; Zhou, Q.Y. Structural Determinants Required for the Bioactivities of Prokineticins and Identification of Prokineticin Receptor Antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusal, K.G.; Tonelli, R.R.; Mattos, E.C.; Soares, C.O.; Genova, D.B.M.; Juliano, M.A.; Urias, U.; Alves, M.J.M. Prokineticin receptor identified by phage display is an entry receptor for Trypanosoma cruzi into mammalian cells. Parasitol Res. 2015, 114, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Versatile Role of Prokineticins and Prokineticin Receptors in Neuroinflammation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, R.; Severini, C.; Miele, R. Prokineticin 2 in cancer-related inflammation. Cancer Lett. 2022, 546, 215838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfati, J.; Dode, C.; Young, J. Kallmann syndrome caused bymutations in the PROK2 and PROKR2 genes: Pathophysiology and genotype-phenotype correlations. Front. Horm. Res. 2010, 39, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, F.; Wu, X.; Zhong, C.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.H.; Yao, J.; Blanchard, D.; Bais, C.; Peale, F.V.; van Bruggen, N.; et al. Bv8 regulates myeloid-cell-dependent tumour angiogenesis. Nature 2007, 450, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traboulsi, W.; Brouillet, S.; Sergent, F.; Boufettal, H.; Samouh, N.; Aboussaouira, T.; Hoffmann, P.; Feige, J.J.; Benharouga, M.; Alfaidy, N. Prokineticins in central and peripheral control of human reproduction. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 24, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, K.; Nagata, K. Protein folding and quality control in the ER. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a007526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.B.; Park, S.Y.; Park, K.; Kaiser, U.B. Trafficking-defective mutant PROKR2 cycles between endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi to attenuate endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2102248119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.N.; Ma, Y.T.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Li, J.D. Functional rescue of Kallmann syndrome-associated prokineticin receptor 2 (PKR2) mutants deficient in trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15518–15526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, J.V.; Bataveljic, A.; Patel, N.A.; Bewick, G.A.; Roy, D.; Campbell, D.; Greenwood, H.C.; Murphy, K.G.; Hameed, S.; Jethwa, P.H.; et al. Prokineticin 2 is a hypothalamic neuropeptide that potently inhibits food intake. Diabetes 2010, 59, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, K.; Gardiner, J.V.; Bewick, G.A.; Hostomska, K.; Patel, N.A.; Hussain, S.S.; Jayasena, C.N.; Ebling, F.J.; Jethwa, P.H.; Prosser, H.M.; et al. Peripheral administration of prokineticin 2 potently reduces food intake and body weight in mice via the brainstem. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkowski, C.; Vallet, J.; Dormishian, M.; Messaddeq, N.; Valet, P.; Boulberdaa, M.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Nebigil, C.G. Prokineticin receptor 1 as a novel suppressor of preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation to control obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, R.; Kindo, M.; Arora, H.; Boulberdaa, M.; Steenman, M.; Nebigil, C.G. Prokineticin receptor-1-dependent paracrine and autocrine pathways control cardiac tcf21 fibroblast progenitor cell transformation into adipocytes and vascular cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maftei, D.; Lattanzi, R.; Vincenzi, M.; Squillace, S.; Fullone, M.R.; Miele, R. The balance of concentration between Prokineticin 2β and Prokineticin 2 modulates the food intake by STAT3 signaling. BBA Adv. 2021, 1, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruien, N.N.; Smith, C.L. Emerging roles of melanocortin receptor accessory proteins (MRAP and MRAP2) in physiology and pathophysiology. Gene 2020, 757, 144949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaly, A.L.; Srisai, D.; Gardner, E.E.; Sebag, J.A. The Melanocortin Receptor Accessory Protein 2 promotes food intake through inhibition of the Prokineticin Receptor-1. eLife 2016, 5, e12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkle, P.M.; Sebag, J.A. Structure and function of the melanocortin2 receptor accessory protein (MRAP). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 300, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, M.; Ramachandrappa, S.; Joachim, M.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Nuthalapati, N.; Ramanathan, V.; Strochlic, D.E.; Ferket, P.; Linhart, K.; et al. Loss of Function of the Melanocortin 2 Receptor Accessory Protein 2 Is Associated with Mammalian Obesity. Science 2013, 341, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdinez, J.A.; Sebag, J.A. Role of N-Linked Glycosylation in PKR2 Trafficking and Signaling. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 730417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullone, M.R.; Maftei, D.; Vincenzi, M.; Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Identification of Regions Involved in the Physical Interaction between Melanocortin Receptor Accessory Protein 2 and Prokineticin Receptor 2. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, A.A.J.; Lee, A.A.; Sebag, J.A. Regions of MRAP2 required for the inhibition of orexin and prokineticin receptor signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullone, M.R.; Maftei, D.; Vincenzi, M.; Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Arginine 125 Is an Essential Residue for the Function of MRAP2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Belmonte, V.; Astillero-López, V.; Esteban, P.F. Anosmin 1 Interacts with the Prokineticin Receptor 2 In Vitro Indicating a Molecular Link Between Both Proteins in the Pathogenesis of Kallmann Syndrome. Protein Pept. Lett. 2016, 23, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcia-Belmonte, V.; Tercero-Díaz, M.; Barrasa-Martín, D.; Lopez de la Vieja, S.; Munoz-Lopez, M.; Esteban, P.F. Anosmin 1 N-terminal domains modulate prokineticin receptor 2 activation by prokineticin 2. Cell. Signal. 2022, 98, 110417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, C.; Kim, S.-H. Biological actions and interactions of anosmin 1. Front. Horm. Res. 2010, 39, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kemal Topaloglu, A.; Damla Kotan, L. Genetics of Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 29, 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hardelin, J.P.; Dodé, C. The complex genetics of Kallmann syndrome: KAL1, FGFR1, FGF8, PROKR2, PROK2; et al. Sex Dev. 2008, 2, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Leslie, F.M.; Zhou, Q.-Y. Expression of prokineticins and their receptors in the adult mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 498, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.-I.; Yamazaki, C.; Masumoto, K.H.; Nagano, M.; Naito, M.; Soga, T.; Hiyama, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Takasaki, J.; Kamohara, M.; et al. Abnormal development of the olfactory bulb and reproductive system in mice lacking prokineticin receptor PKR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4140–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.L.; Li, J.-D.; Cheng, M.Y.; Leslie, F.M.; Lee, A.G.; Zhou, Q.-Y. Dependence of olfactory bulb neurogenesis on prokineticin 2 signaling. Science 2005, 308, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Transduction of receptor signals by b-arrestins. Science 2005, 308, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; de Waal, P.W.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Van Eps, N.; Yin, Y.; Pal, K.; Goswami, D.; White, T.A.; et al. Identification of phosphorylation codes for arrestin recruitment by G protein-coupled receptors. Cell 2017, 170, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, I.; Ambrosio, C. Prokineticin receptors interact unselectively with several G protein subtypes but bind selectively to -arrestin 2. Cell. Signal. 2021, 83, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbai, Q.; Monnier, C.; Dodé, C.; Pin, J.-P.; Hardelin, J.-P.; Rondard, P. Biased signaling through G-protein-coupled PROKR2 receptors harboring missense mutations. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3734–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Liu, H.; Peng, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.-D. Mechanisms that underlie the internalization and extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 activation by PKR2 receptor. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, C.; Vaidya, F.U.; Waghela, B.N.; Jaiswara, P.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Rajendran, B.K.; Ranjan, K. Insights of Endocytosis Signaling in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilardi, J.M.; Mochida, S.; Sheng, Z.H. Snapin: A SNARE-associated protein implicated in synaptic transmission. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pluhackova, K.; Böckmann, R.A. The Multifaceted Role of SNARE Proteins in Membrane Fusion. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumiko Suzuki, F.; Shigeru Morishima, S.; Takashi Tanaka, T.; Ikunobu Muramatsu, I. Snapin, a New Regulator of Receptor Signaling, Augments 1a-Adrenoceptor-operatedCalcium Influx through TRPC6. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29563–29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, X.T.; Li, Y.D. Snapin interacts with G-protein coupled receptor PKR2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.S.; Mancera, R.L. The Structure of Glycosaminoglycans and their Interactions with Proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2008, 72, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCouter, J.; Ferrara, N. The role of EG-VEGF in the regulation of angiogenesis in endocrine glands. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2002, 67, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCouter, J.; Ferrara, N. EG-VEGF and the concept of tissue-specific angiogenic growth factors. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotliar, I.B.; Lorenzen, E.; Schwenk, J.M.; Hay, D.L.; Sakmar, T.P. Elucidating the Interactome of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Receptor Activity-Modifying Proteins. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiying Lu, H.; Qiaodan Zhou, Q.; He, J.; Jiang, Z.; Peng, C.; Tong, R.; Shi, J. Recent advances in the development of protein–protein interactions modulators: Mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 213. [Google Scholar]


| Interacting Protein | Functions | PKR2 Site of Interaction | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| BiP | ER quality control system | ND | [34] |
| gp78 | ER quality control system | ND | [34] |
| RER1 | ER quality control system | ND | [34] |
| MRAP2 | Down regulation of PKR s trafficking and signal transduction pathways | N-terminal region | [42,45,46,47,48] |
| Anosmin-1 | Modulation of PK2 binding on PKR2 | N-terminal regionExtracellular loop 2Extracellular loop 3 | [49,50] |
| beta-arrestin 2 | Desensibilization | ND | [59,60] |
| Snapin | Degradation | C-terminal region | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lattanzi, R.; Miele, R. Interaction of Prokineticin Receptors with Accessory Proteins. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 1498-1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3040107
Lattanzi R, Miele R. Interaction of Prokineticin Receptors with Accessory Proteins. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(4):1498-1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLattanzi, Roberta, and Rossella Miele. 2023. "Interaction of Prokineticin Receptors with Accessory Proteins" Encyclopedia 3, no. 4: 1498-1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3040107
APA StyleLattanzi, R., & Miele, R. (2023). Interaction of Prokineticin Receptors with Accessory Proteins. Encyclopedia, 3(4), 1498-1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3040107