Featured Reviews of Algorithms
(Closed)
A topical collection in Algorithms (ISSN 1999-4893).
Viewed by 22563
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Arun Kumar Sangaiah
Prof. Dr. Arun Kumar Sangaiah
 Prof. Dr. Arun Kumar Sangaiah
Prof. Dr. Arun Kumar Sangaiah
grade
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan and Vellore Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu 632014, India
Interests: wireless sensor networks; Internet of Things; edge computing; computational intelligence
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Xingjuan Cai
Dr. Xingjuan Cai
 Dr. Xingjuan Cai
Dr. Xingjuan Cai
grade
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Complex System and Computational Intelligence Laboratory, TaiYuan University of Science and Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
Interests: feature extraction; feedforward neural nets; image classification; invasive software; learning (artificial intelligence)
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection aims to collect high-quality review papers that highlight the most recent advances on the theory, design, analysis, and implementation of algorithms. We encourage researchers from related fields within the journal’s scope to contribute review papers highlighting the latest developments in their research fields. Reviews provide comprehensive in-depth overviews with no length restrictions, whereas topical reviews focus on a concise and precise “at-a-glance” summary of novel developments in the field. Moreover, the viewpoint of experts should guide the readers through the vast literature and indicate the right direction along which research should move in the near future.
Prof. Dr. Arun Kumar Sangaiah
Dr. Xingjuan Cai
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Algorithms is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- algorithms in biology, chemistry, physics
- approximation algorithms
- combinatorial optimization
- mathematical programming
- operations research
- discrete mathematics and graph theory
- computational geometry
- differential equations
- image processing with applications
- machine learning
- Markov chains and simulation
- metaheuristics and matheuristics
- numerical analysis
- parametrized algorithms
- production planning, scheduling, transport, and timetabling
- quantum algorithms
Published Papers (4 papers)
Open AccessReview
Algorithms in Tomography and Related Inverse Problems—A Review
by
Styliani Tassiopoulou, Georgia Koukiou and Vassilis Anastassopoulos
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2576
Abstract
In the ever-evolving landscape of tomographic imaging algorithms, this literature review explores a diverse array of themes shaping the field’s progress. It encompasses foundational principles, special innovative approaches, tomographic implementation algorithms, and applications of tomography in medicine, natural sciences, remote sensing, and seismology.
[...] Read more.
In the ever-evolving landscape of tomographic imaging algorithms, this literature review explores a diverse array of themes shaping the field’s progress. It encompasses foundational principles, special innovative approaches, tomographic implementation algorithms, and applications of tomography in medicine, natural sciences, remote sensing, and seismology. This choice is to show off the diversity of tomographic applications and simultaneously the new trends in tomography in recent years. Accordingly, the evaluation of backprojection methods for breast tomographic reconstruction is highlighted. After that, multi-slice fusion takes center stage, promising real-time insights into dynamic processes and advanced diagnosis. Computational efficiency, especially in methods for accelerating tomographic reconstruction algorithms on commodity PC graphics hardware, is also presented. In geophysics, a deep learning-based approach to ground-penetrating radar (GPR) data inversion propels us into the future of geological and environmental sciences. We venture into Earth sciences with global seismic tomography: the inverse problem and beyond, understanding the Earth’s subsurface through advanced inverse problem solutions and pushing boundaries. Lastly, optical coherence tomography is reviewed in basic applications for revealing tiny biological tissue structures. This review presents the main categories of applications of tomography, providing a deep insight into the methods and algorithms that have been developed so far so that the reader who wants to deal with the subject is fully informed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
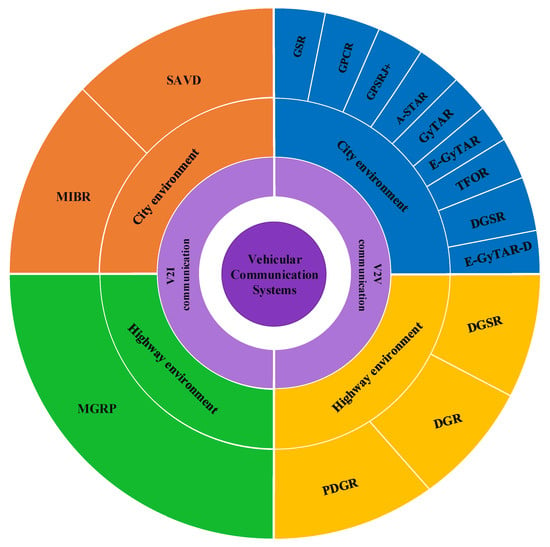
Investigating Routing in the VANET Network: Review and Classification of Approaches
by
Arun Kumar Sangaiah, Amir Javadpour, Chung-Chian Hsu, Anandakumar Haldorai and Ahmad Zeynivand
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2758
Abstract
Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANETs) need methods to control traffic caused by a high volume of traffic during day and night, the interaction of vehicles, and pedestrians, vehicle collisions, increasing travel delays, and energy issues. Routing is one of the most critical problems
[...] Read more.
Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANETs) need methods to control traffic caused by a high volume of traffic during day and night, the interaction of vehicles, and pedestrians, vehicle collisions, increasing travel delays, and energy issues. Routing is one of the most critical problems in VANET. One of the machine learning categories is reinforcement learning (RL), which uses RL algorithms to find a more optimal path. According to the feedback they get from the environment, these methods can affect the system through learning from previous actions and reactions. This paper provides a comprehensive review of various methods such as reinforcement learning, deep reinforcement learning, and fuzzy learning in the traffic network, to obtain the best method for finding optimal routing in the VANET network. In fact, this paper deals with the advantages, disadvantages and performance of the methods introduced. Finally, we categorize the investigated methods and suggest the proper performance of each of them.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
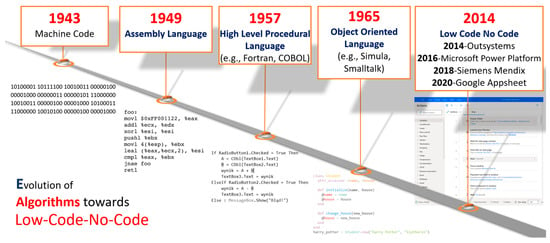
Algorithms in Low-Code-No-Code for Research Applications: A Practical Review
by
Fahim Sufi
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 11679
Abstract
Algorithms have evolved from machine code to low-code-no-code (LCNC) in the past 20 years. Observing the growth of LCNC-based algorithm development, the CEO of GitHub mentioned that the future of coding is no coding at all. This paper systematically reviewed several of the
[...] Read more.
Algorithms have evolved from machine code to low-code-no-code (LCNC) in the past 20 years. Observing the growth of LCNC-based algorithm development, the CEO of GitHub mentioned that the future of coding is no coding at all. This paper systematically reviewed several of the recent studies using mainstream LCNC platforms to understand the area of research, the LCNC platforms used within these studies, and the features of LCNC used for solving individual research questions. We identified 23 research works using LCNC platforms, such as SetXRM, the vf-OS platform, Aure-BPM, CRISP-DM, and Microsoft Power Platform (MPP). About 61% of these existing studies resorted to MPP as their primary choice. The critical research problems solved by these research works were within the area of global news analysis, social media analysis, landslides, tornadoes, COVID-19, digitization of process, manufacturing, logistics, and software/app development. The main reasons identified for solving research problems with LCNC algorithms were as follows: (1) obtaining research data from multiple sources in complete automation; (2) generating artificial intelligence-driven insights without having to manually code them. In the course of describing this review, this paper also demonstrates a practical approach to implement a cyber-attack monitoring algorithm with the most popular LCNC platform.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Synergic Approach of Deep Learning towards Digital Additive Manufacturing: A Review
by
Ayush Pratap, Neha Sardana, Sapdo Utomo, John Ayeelyan, P. Karthikeyan and Pao-Ann Hsiung
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4195
Abstract
Deep learning and additive manufacturing have progressed together in the previous couple of decades. Despite being one of the most promising technologies, they have several flaws that a collaborative effort may address. However, digital manufacturing has established itself in the current industrial revolution
[...] Read more.
Deep learning and additive manufacturing have progressed together in the previous couple of decades. Despite being one of the most promising technologies, they have several flaws that a collaborative effort may address. However, digital manufacturing has established itself in the current industrial revolution and it has slowed down quality control and inspection due to the different defects linked with it. Industry 4.0, the most recent industrial revolution, emphasizes the integration of intelligent production systems and current information technologies. As a result, deep learning has received a lot of attention and has been shown to be quite effective at understanding image data. This review aims to provide a cutting-edge deep learning application of the AM approach and application. This article also addresses the current issues of data privacy and security and potential solutions to provide a more significant dimension to future studies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures