Assessment of Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the Environment: Occurrence, Detection, Removal and Toxicity
A special issue of Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This special issue belongs to the section "Environmental Sciences".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 30 December 2024 | Viewed by 782
Special Issue Editors
Interests: high-resolution mass spectrometry; contaminants of emerging concern; toxicity assessment
Interests: Inflammation; chronic disorders; anti-inflammatory; pharmaceuticals; cosmetics; natural bioactives; bioassays; toxicity; antitoxicity; valorization of agri-food by-products; emerging contaminants; quality of urban and semi-urban rivers’ and/or lakes’ and/or surface and/or sea waters; freshwater and marine organisms; fish; marine fungi; microalgae; macroalgae; seaweeds; plants; Lemnea
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
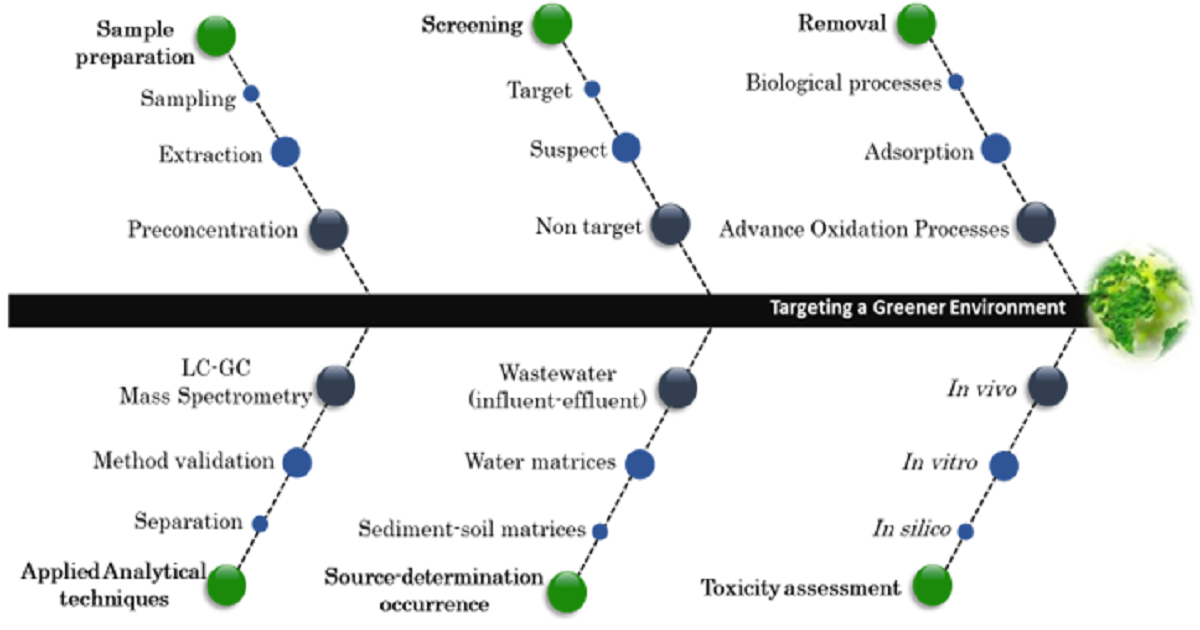
The term “contaminants of emerging concern” definitely incorporates categories of a sheer number of compounds, such as the overwhelming group of pharmaceutical and personal care products, drugs of abuse, perfluorinated compounds, organophosphate flame retardants, etc., all of which are consumed exponentially throughout the years and many of them have been monitored as a complex multiphase mixture in aquatic environments worldwide. The fact that many contaminants are not removed completely in wastewater treatment plants and are introduced in receiving water is a remaining global challenge. After their release to the environment, their concentrations do not remain unaffected; thus, the effluent wastewater is considered their major contributor in aquatic compartments which can engender possible detrimental effects to non-target organisms.
This Special Issue aims to promote research in six major areas based on the above. Emphasis will be given to research with the most up-to dated sample pretreatment techniques. Special attention will be given to studies with state-of-the-art validated multi-residue methods. The third objective concerns the suspect and non-target screening through high-resolution mass spectrometry. Determining the target compounds, their transformation products, and their removal efficiency will further enhance the general picture. Finally, studies with toxicity assessment via in silico, in vitro, and in vivo bioassays are also welcome.
All contributions to this Special Issue will improve our knowledge in these fields.
Dr. Anna Ofrydopoulou
Dr. Alexandros Tsoupras
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- contaminants of emerging concern
- high-resolution mass spectrometry
- toxicity assessment
- removal
- non-target screening
- occurrence
- sample pretreatment
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.






