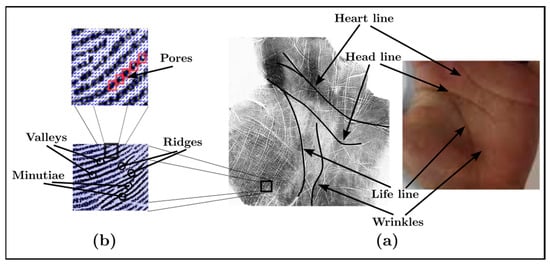
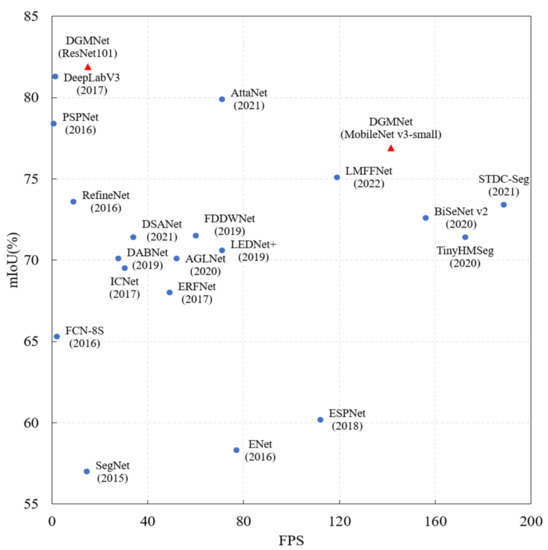
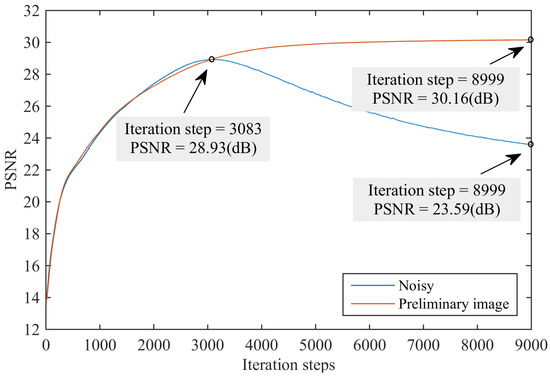
Advances in Image Processing, Analysis and Recognition Technology
A topical collection in Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This collection belongs to the section "Computing and Artificial Intelligence".
Viewed by 19959Editor
Interests: machine vision; computer vision; image processing; image recognition; biometrics; medical images analysis; shape description; binary images representation; fusion of various features representing an object of interest; content-based image retrieval; practical applications of image processing; analysis and recognition algorithms
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
For many decades, researchers have been trying to make computer analyses of images as effective as human vision. For this purpose, many algorithms and systems have been created so far. The whole process covers various stages, including image processing, representation and recognition. The results of this work have found many applications in computer-assisted areas of everyday life. They improve particular activities and provide useful tools, sometimes only for entertainment but quite often significantly for increasing safety. In fact, the practical implementation of image processing algorithms is particularly wide. Moreover, the rapid growth of computational complexity and computer efficiency has allowed for the development of more sophisticated and effective algorithms and tools. Although significant progress has been made so far, many issues still remain open, resulting in the need for the development of novel approaches.
The aim of this Topical Collection on “Advances in Image Processing, Analysis and Recognition Technology” is to give researchers the opportunity to provide new trends, latest achievements and research directions as well as to present their current work on the important problem of image processing, analysis and recognition.
Potential topics of interest for this Topical Collection include (but are not limited to) the following areas:
- Image acquisition;
- Image quality analysis;
- Image filtering, restoration and enhancement;
- Image segmentation;
- Biomedical image processing;
- Color image processing;
- Multispectral image processing;
- Hardware and architectures for image processing;
- Image databases;
- Image retrieval and indexing;
- Image compression;
- Low-level and high-level image description;
- Mathematical methods in image processing, analysis and representation;
- Artificial intelligence tools in image analysis;
- Pattern recognition algorithms applied for images;
- Digital watermarking;
- Digital photography;
- Practical applications of image processing, analysis and recognition algorithms in medicine, surveillance, biometrics, document analysis, multimedia, intelligent transportation systems, stereo vision, remote sensing, computer vision, robotics, etc.
Dr. Dariusz Frejlichowski
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- image processing
- image analysis
- image recognition
- computer vision