Space Applications
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Xiaolin Han
Dr. Xiaolin Han
 Dr. Xiaolin Han
Dr. Xiaolin Han
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Electronic Engineering, Institute for Ocean Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Interests: image fusion; spectral super-resolution; remote sensing information processing
 Dr. Feng Wang
Dr. Feng Wang
 Dr. Feng Wang
Dr. Feng Wang
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100094, China
Interests: SAR imaging; satellite imaging processing; digital surface model (DSM); digital elevation model (DEM)
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In recent times, more and more satellites and spacecraft are sent to space under different space-related projects, such the Star-link Project, China Lunar Exploration Project, and Tiangong Space Station. These projects have greatly advanced the development of space applications. Therefore, to exchange novel space application technologies, it is necessary to open a long-term topic, i.e., space applications, in this journal.
The aim of this Topical Collection on “Space Applications” is to give researchers the opportunity to provide new trends, recent achievements, and research directions as well as to present their current work on space applications.
Potential topics of interest for this Topical Collection include (but are not limited to) the following areas:
- Space-borne image processing;
- On-orbit artificial intelligence;
- Spacecraft prognostic and health management;
- Space-borne sensors;
- Space communications and navigation
- Spacecraft system design
Prof. Dr. Qizhi Xu
Dr. Xiaojian Yi
Dr. Mingjin Zhang
Dr. Jin Zheng
Dr. Xiaolin Han
Dr. Feng Wang
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- space-borne image processing
- space-borne artificial intelligence
- spacecraft prognostic and health management
- space-borne sensors
- space communications and navigation
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Mission Reliability Modeling and Analysis Methods for Reconfigurable Ship Electronic Information Systems
by
Xiaotong Fang, Xuan Wang, Lingling Feng, Jiapeng Zuo and Shulin Liu
Viewed by 486
Abstract
With the increasing intensity of ship missions, the mission reliability requirements of various ship systems are getting higher. Especially the new reconfigurable ship electronic information systems, which have the characteristics of resource sharing and reuse, function reconfiguration on demand, software and hardware loose
[...] Read more.
With the increasing intensity of ship missions, the mission reliability requirements of various ship systems are getting higher. Especially the new reconfigurable ship electronic information systems, which have the characteristics of resource sharing and reuse, function reconfiguration on demand, software and hardware loose coupling, and business integration, etc., is difficult to be taken into account by traditional reliability design and analysis methods. Therefore, it is imperative to design a reliability modeling and analysis method with careful consideration and strong applicability. Taking the new reconfigurable ship electronic information system as the research subject, this paper firstly adopts the architecture analysis and design language (AADL) to establish a reliability model from three perspectives, namely, system structure, system behavior, and failure impact; then, a model of mission reliability allocation under multiple constraints is developed and solved using the hybrid algorithm of Slime Mode Optimization Differential Evolution (SMA-DE) based on the optimal allocation model of reliability; next, a method for analyzing the mission reliability of ship electronic information systems based on the Goal Oriented (GO) method is proposed, and based on the state probability algorithm therein, a correction algorithm oriented to the co-causal failure modes is derived to realize the quantitative calculation of the mission reliability of ship electronic information systems; finally, an application validation was performed in conjunction with a typical ship electronic information system task. The results show that the method proposed in this study can successfully achieve the mission reliability allocation as well as quantitative analysis of reconfigurable ship electronic information systems under multi-mission requirements.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Clutter Intelligent Suppression Method Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
by
Yi Cheng, Junjie Su, Chunbo Xiu and Jiaxin Liu
Viewed by 593
Abstract
In the complex clutter background, the clutter center frequency is not fixed, and the spectral width is wide, which leads to the performance degradation of the traditional adaptive clutter suppression method. Therefore, an adaptive clutter intelligent suppression method based on deep reinforcement learning
[...] Read more.
In the complex clutter background, the clutter center frequency is not fixed, and the spectral width is wide, which leads to the performance degradation of the traditional adaptive clutter suppression method. Therefore, an adaptive clutter intelligent suppression method based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is proposed. Each range cell to be detected is regarded as an independent intelligence (agent) in the proposed method. The clutter environment is interactively learned using a deep learning (DL) process, and the filter parameter optimization is positively motivated by the reinforcement learning (RL) process to achieve the best clutter suppression effect. The suppression performance of the proposed method is tested on simulated and real data. The experimental results indicate that the filter notch designed by the proposed method is highly matched with the clutter compared with the existing adaptive clutter suppression methods. While suppressing the clutter, it has a higher amplitude-frequency response to signals at non-clutter frequencies, thus reducing the loss of the target signal and maximizing the output signal-to-clutter and noise rate (SCNR).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Objective Optimization for Complex Systems Considering Both Performance Optimality and Robustness
by
Yue Chen and Jian Shi
Viewed by 676
Abstract
As engineering systems become increasingly complex, performance requirements rise, and tolerance for design parameter variations becomes more crucial due to increased uncertainty. Tolerance to parameter variation can be measured by the volume of the solution space. A larger solution space implies a higher
[...] Read more.
As engineering systems become increasingly complex, performance requirements rise, and tolerance for design parameter variations becomes more crucial due to increased uncertainty. Tolerance to parameter variation can be measured by the volume of the solution space. A larger solution space implies a higher tolerance to parameter changes and thus greater robustness. The box-shaped solution space, represented by intervals with respect to each design parameter, has the advantage of showing which design parameters can be decoupled. Therefore, this paper proposes a new multi-objective optimization problem to optimize both the performance and volume of the box-shaped solution space simultaneously. Often, optimal performance and maximum volume are conflicting objectives, indicating a trade-off between performance and robustness. Furthermore, the
DIRECT-NSGA-II approach is proposed for solving this multi-objective optimization problem. The
DIRECT algorithm evaluates the minimum value of the performance function within the box-shaped solution space, while the NSGA-II algorithm identifies Pareto-optimal solution spaces. Finally, two case studies are implemented to illustrate the effectiveness of the
DIRECT-NSGA-II method. We can conclude that (I) the proposed
DIRECT-NSGA-II approach is suitable for black-box performance functions, (II) any point within the obtained solution space is a good design point, and (III) the proposed optimization problem considers both performance optimality and robustness, enabling the identification of a representative set of Pareto-optimal solution spaces that balance these two factors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
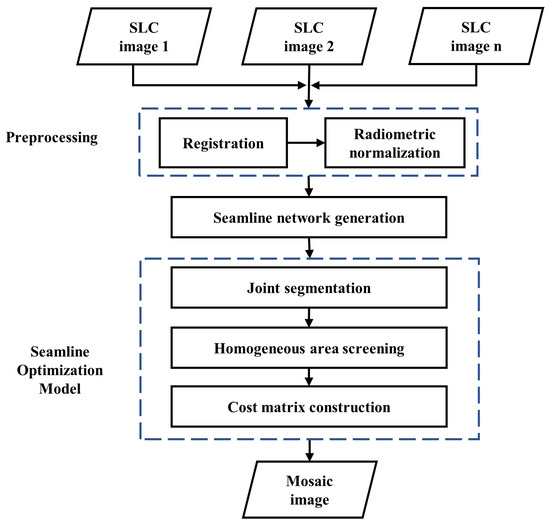
A Segmentation-Based Optimal Seamline Generation Method for SAR Image Mosaic
by
Rui Liu, Jingxing Zhu, Niangang Jiao, Yao Chen and Hongjian You
Viewed by 753
Abstract
In the mosaic creation of multiple high-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, achieving an optimal seamline in overlapping areas is crucial for seamless and visually satisfactory results. Many existing seamline generation methods are designed primarily for optical remote sensing images, but due to
[...] Read more.
In the mosaic creation of multiple high-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, achieving an optimal seamline in overlapping areas is crucial for seamless and visually satisfactory results. Many existing seamline generation methods are designed primarily for optical remote sensing images, but due to the differing characteristics of SAR images and optical images, applying these methods directly to SAR images poses challenges in finding the optimal seamline. In response, this paper proposes a segmentation-based optimal seamline generation (SOSG) method for SAR image mosaics. The SOSG method involves a multi-step process. First, SAR image joint segmentation is performed within the overlapping areas. Subsequently, homogeneous areas are identified based on the segmentation results. Following this, a pixel cost matrix is constructed, incorporating homogeneous areas and intensity differences. Finally, the minimum path cost from the starting pixel to the end pixel is computed using the Dijkstra algorithm to determine the optimal path. To assess the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are conducted using multiple SAR images from the Chinese Gaofen-3 01 satellite as datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method yields seamless mosaic images when compared to other methods, while delivering satisfactory outcomes. This indicates the potential of the proposed method in addressing the unique challenges posed by SAR images and enhancing the quality of SAR image mosaics.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Performance Evaluation Approach for Satellite Attitude Control System in Tracking Mode
by
Yanhua Zhang, Lei Yang, Yuehua Cheng and Kaixin Ying
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 935
Abstract
The study of satellite performance evaluation can reveal the ability of satellite systems to fulfil corresponding tasks in the space environment, and provide information support for the resource allocation and mission scheduling of in-orbit satellites. In this paper, we took the satellite attitude
[...] Read more.
The study of satellite performance evaluation can reveal the ability of satellite systems to fulfil corresponding tasks in the space environment, and provide information support for the resource allocation and mission scheduling of in-orbit satellites. In this paper, we took the satellite attitude control system in attitude tracking mode as the research object. In accordance with the system’s mission requirements, the control performance evaluation indicator set, characterized by a generalized grey number, is constructed to tackle the uncertainty and inadequacy of information contained in flight status data resulting from the complex space operating environment and sensor measurement noise. An improved principal component analysis method based on generalized grey number is proposed to solve the weight amplification caused by the correlation between performance indicators and realize the weight allocation of the indicators. Finally, the grey-target decision model is established to determine the weights of the performance indicators, and the performance evaluation model is established under the tracking mode. The feasibility of the grey-target decision-evaluation model based on the improved principal component is confirmed through comparative experiments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
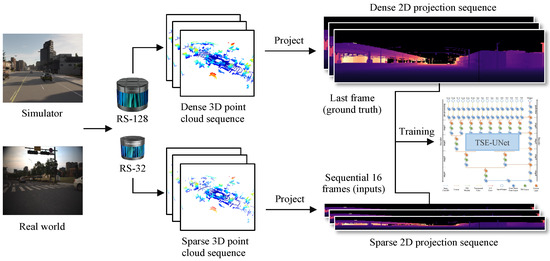
Open AccessArticle
TSE-UNet: Temporal and Spatial Feature-Enhanced Point Cloud Super-Resolution Model for Mechanical LiDAR
by
Lu Ren, Deyi Li, Zhenchao Ouyang and Zhibin Zhang
Viewed by 1222
Abstract
The mechanical LiDAR sensor is crucial in autonomous vehicles. After projecting a 3D point cloud onto a 2D plane and employing a deep learning model for computation, accurate environmental perception information can be supplied to autonomous vehicles. Nevertheless, the vertical angular resolution of
[...] Read more.
The mechanical LiDAR sensor is crucial in autonomous vehicles. After projecting a 3D point cloud onto a 2D plane and employing a deep learning model for computation, accurate environmental perception information can be supplied to autonomous vehicles. Nevertheless, the vertical angular resolution of inexpensive multi-beam LiDAR is limited, constraining the perceptual and mobility range of mobile entities. To address this problem, we propose a point cloud super-resolution model in this paper. This model enhances the density of sparse point clouds acquired by LiDAR, consequently offering more precise environmental information for autonomous vehicles. Firstly, we collect two datasets for point cloud super-resolution, encompassing CARLA32-128in simulated environments and Ruby32-128 in real-world scenarios. Secondly, we propose a novel temporal and spatial feature-enhanced point cloud super-resolution model. This model leverages temporal feature attention aggregation modules and spatial feature enhancement modules to fully exploit point cloud features from adjacent timestamps, enhancing super-resolution accuracy. Ultimately, we validate the effectiveness of the proposed method through comparison experiments, ablation studies, and qualitative visualization experiments conducted on the CARLA32-128 and Ruby32-128 datasets. Notably, our method achieves a PSNR of 27.52 on CARLA32-128 and a PSNR of 24.82 on Ruby32-128, both of which are better than previous methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
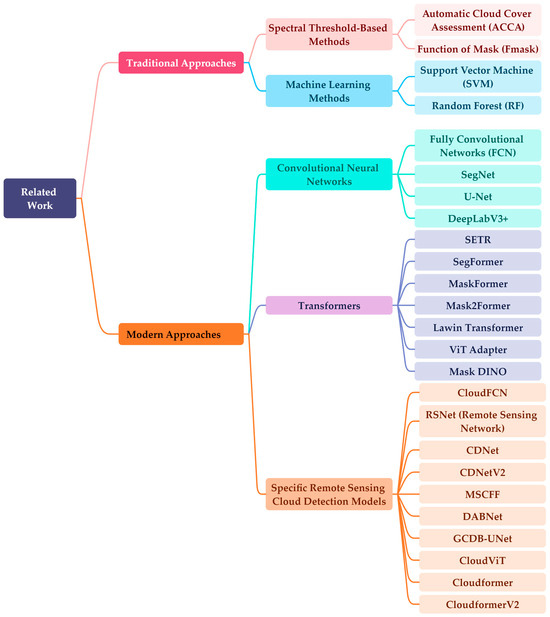
Open AccessArticle
CloudformerV3: Multi-Scale Adapter and Multi-Level Large Window Attention for Cloud Detection
by
Zheng Zhang, Shuyang Tan and Yongsheng Zhou
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1049
Abstract
Cloud detection in remote sensing images is a crucial preprocessing step that efficiently identifies and extracts cloud-covered areas within the images, ensuring the precision and reliability of subsequent analyses and applications. Given the diversity of clouds and the intricacies of the surface, distinguishing
[...] Read more.
Cloud detection in remote sensing images is a crucial preprocessing step that efficiently identifies and extracts cloud-covered areas within the images, ensuring the precision and reliability of subsequent analyses and applications. Given the diversity of clouds and the intricacies of the surface, distinguishing the boundaries between thin clouds and the underlying surface is a major challenge in cloud detection. To address these challenges, an advanced cloud detection method, CloudformerV3, is presented in this paper. The proposed method employs a multi-scale adapter to incorporate dark and bright channel prior information into the model’s backbone, enhancing the model’s ability to capture prior information and multi-scale details from remote sensing images. Additionally, multi-level large window attention is utilized, enabling high-resolution feature maps and low-resolution feature maps to mutually focus and subsequently merge during the resolution recovery phase. This facilitates the establishment of connections between different levels of feature maps and offers comprehensive contextual information for the model’s decoder. The experimental results on the GF1_WHU dataset illustrate that the method proposed in this paper achieves MIoU of 92.89%, while achieving higher detection accuracy compared to state-of-the-art cloud detection models. Specifically, in comparison to Cloudformer, our method demonstrates a 1.11% improvement, while compared to CloudformerV2, there is a 0.37% increase. Furthermore, enhanced detection performance is achieved along cloud edges and concerning thin clouds, showcasing the efficacy of the proposed method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Prediction-to-Prediction Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution Network under a Multi-Level Supervision Paradigm
by
Jian Guo, Mingkai Li, Qingjie Zhao and Qizhi Xu
Viewed by 997
Abstract
Super-resolution enhances the spatial resolution of remote sensing images, yielding clearer data for diverse satellite applications. However, existing methods often lose true detail and produce pseudo-detail in reconstructed images due to an insufficient number of ground truth images for supervision. To address this
[...] Read more.
Super-resolution enhances the spatial resolution of remote sensing images, yielding clearer data for diverse satellite applications. However, existing methods often lose true detail and produce pseudo-detail in reconstructed images due to an insufficient number of ground truth images for supervision. To address this issue, a prediction-to-prediction super-resolution (P2P-SR) network under a multi-level supervision paradigm was proposed. First, a multi-level supervision network structure was proposed to increase the number of supervisions by introducing more ground truth images, which made the network always predict the next level based on the super-resolution reconstruction results of the previous level. Second, a super-resolution component combining a convolutional neural network and Transformer was designed with a flexible super-resolution scale factor to facilitate the construction of multi-level supervision networks. Finally, a method of dividing the super-resolution overall scale factor was proposed, enabling an investigation into the impact of diverse numbers of components and different scale factors of components on the performance of the multi-level supervision network. Additionally, a new remote sensing dataset containing worldwide scenes was also constructed for the super-resolution task in this paper. The experiment results on three datasets demonstrated that our P2P-SR network outperformed the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
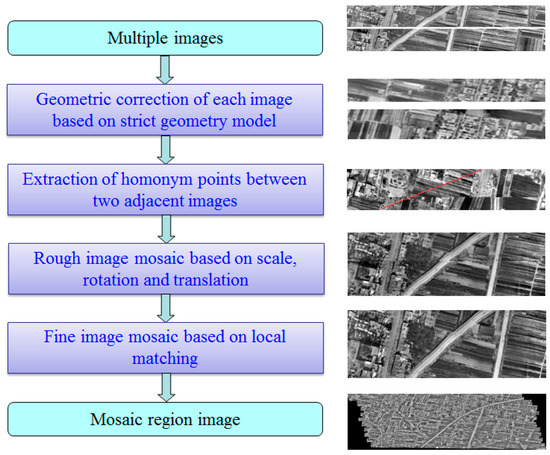
Open AccessArticle
Mosaicing Technology for Airborne Wide Field-of-View Infrared Image
by
Lei Dong, Fangjian Liu, Mingchao Han and Hongjian You
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1042
Abstract
Multi-detector parallel scanning is derived from the traditional airborne panorama camera, and it has a great lateral field of view. A wide field-of-view camera can be used to obtain an area of remote sensing image by whisk broom mood during the flight. The
[...] Read more.
Multi-detector parallel scanning is derived from the traditional airborne panorama camera, and it has a great lateral field of view. A wide field-of-view camera can be used to obtain an area of remote sensing image by whisk broom mood during the flight. The adjacent image during acquisition should cover the overlap region according to the flight path, and then the regional image can be generated by image processing. Complexity and difficulty are increased during the regional image processing due to some interference factors of aircraft in flight. The overlap of the acquired regional image is constantly variable. Depending on the analysis of the imaging geometric principle of a wide field-of-view scanning camera, this paper proposes the rigorous geometric model of geoposition. The infrared image mosaic technology is proposed according to the features of regional images through the SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) operator to extract the two best-matching point pairs in the adjacent overlap region. We realize the coarse registration of adjacent images according to image translation, rotation, and a scale model of image geometric transformation, and then the local fine stitching is realized using the normalized cross-correlation matching strategy. The regional mosaic experiment of aerial multi-detector parallel scanning infrared image is processed to verify the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed algorithm.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
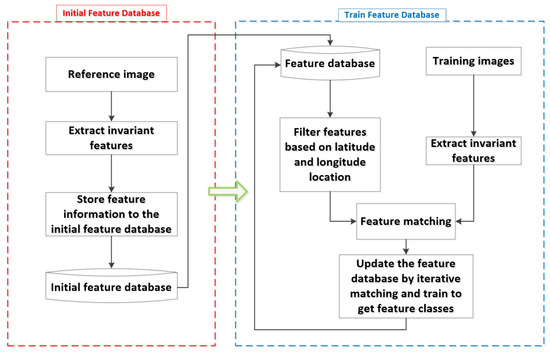
An Optical Remote Sensing Image Matching Method Based on the Simple and Stable Feature Database
by
Zilu Zhao, Hui Long and Hongjian You
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2122
Abstract
Satellite remote sensing has entered the era of big data due to the increase in the number of remote sensing satellites and imaging modes. This presents significant challenges for the processing of remote sensing systems and will result in extremely high real-time data
[...] Read more.
Satellite remote sensing has entered the era of big data due to the increase in the number of remote sensing satellites and imaging modes. This presents significant challenges for the processing of remote sensing systems and will result in extremely high real-time data processing requirements. The effective and reliable geometric positioning of remote sensing images is the foundation of remote sensing applications. In this paper, we propose an optical remote sensing image matching method based on a simple stable feature database. This method entails building the stable feature database, extracting local invariant features that are comparatively stable from remote sensing images using an iterative matching strategy, and storing useful information about the features. Without reference images, the feature database-based matching approach potentially saves storage space for reference data while increasing image processing speed. To evaluate the performance of the feature database matching method, we train the feature database with various local invariant feature algorithms on different time phases of Gaofen-2 (GF-2) images. Furthermore, we carried out matching comparison experiments with various satellite images to confirm the viability and stability of the feature database-based matching method. In comparison with direct matching using the classical feature algorithm, the feature database-based matching method in this paper can essentially improve the correct rate of feature point matching by more than
and reduce the matching time by more than
. This method improves the accuracy and timeliness of image matching, potentially solves the problem of large storage space occupied by the reference data, and has great potential for fast matching of optical remote sensing images.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
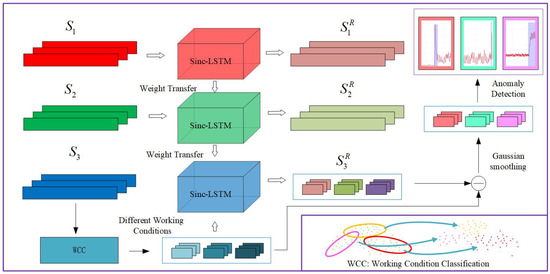
Anomaly Detection of Control Moment Gyroscope Based on Working Condition Classification and Transfer Learning
by
Kuan Zhang, Shuchen Wang, Saijin Wang and Qizhi Xu
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1761
Abstract
The process of human exploration of the universe has accelerated, and aerospace technology has developed rapidly. The health management and prognosis guarantee of spacecraft systems has become an important basic technology. However, with thousands of telemetry data channels and massive data scales, spacecraft
[...] Read more.
The process of human exploration of the universe has accelerated, and aerospace technology has developed rapidly. The health management and prognosis guarantee of spacecraft systems has become an important basic technology. However, with thousands of telemetry data channels and massive data scales, spacecraft systems are increasingly complex. The anomaly detection that relied on simple threshold judgment and expert manual annotation in the past is no longer applicable. In addition, the particularity of the anomaly detection task leads to the lack of fault data for training. Therefore, a data-driven deep transfer learning-based approach is needed for rapid analysis and accurate detection of large-scale data. The control moment gyroscope (CMG) is a significant inertial actuator in the process of large-scale, long-life spacecraft in-orbit operation and mission execution. Its anomaly detection plays a major role in the prevention and elimination of early failures. Based on the research of SincNet and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, this paper proposed a Sinc-LSTM neural network based on transfer learning and working condition classification for CMG anomaly detection. First, a two-stage pre-training method is proposed to alleviate the data imbalance, using the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) dataset and a satellite dataset from NASA. Second, the Sinc-LSTM network is designed to enhance the local fitting and long-period memory ability of the model for CMG time series data. Finally, a dynamic threshold judgment anomaly detection method based on working condition classification is designed to accommodate threshold changes for CMG full-cycle anomaly detection. The method is validated on the spacecraft CMG dataset.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
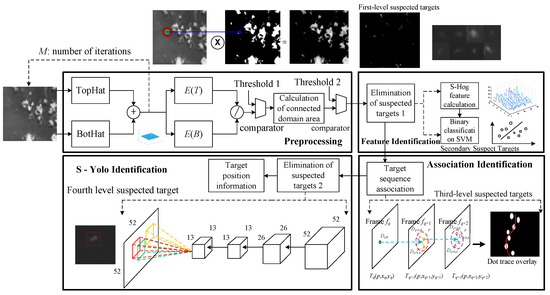
Real-Time Moving Ship Detection from Low-Resolution Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Sequence
by
Jiyang Yu, Dan Huang, Xiaolong Shi, Wenjie Li and Xianjie Wang
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 1609
Abstract
Optical remote sensing ship target detection has become an essential means of ocean supervision, coastal defense, and frontier defense. Accurate, effective, fast, and real-time remote sensing data processing is the critical technology in this field. This paper proposes a real-time detection algorithm for
[...] Read more.
Optical remote sensing ship target detection has become an essential means of ocean supervision, coastal defense, and frontier defense. Accurate, effective, fast, and real-time remote sensing data processing is the critical technology in this field. This paper proposes a real-time detection algorithm for moving targets in low-resolution wide-area remote sensing images, which includes four steps: pre-screening, simplified HOG feature identification, sequence correlation identification, and facilitated Yolo identification. It can effectively detect and track targets in low-resolution sequence data. Firstly, iterative morphological processing was used to improve the contrast of low-resolution ship target profile edge features compared with the sea surface background. Next, the target area after adaptive segmentation was used to eliminate false alarms. As a result, the invalid background information of extensive comprehensive data was quickly eliminated. Then, support vector machine classification of S-HOG feature was carried out for suspected targets, and interference such as islands and reefs, broken clouds, and waves were eliminated according to the shape characteristics of ship targets. The method of multi-frame data association and searching for adjacent target information between frames was adopted to eliminate the interference of static targets and broken clouds with similar contours. Finally, the sequential marks were further trained and learned, and further false alarm elimination was completed based on the clipped Yolo network. Compared with the traditional Yolo Tiny V2/V3 series network, this method had higher computational speed and better detection performance. The F1 number of detection results was increased by 3%, and the calculation time was reduced by 66%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improved Matching Algorithm with Anchor Argument for Rotate Target Detection
by
Kangkang Wang, Bowen Chen, Xianyun Wu and Yunsong Li
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1660
Abstract
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used in the task of object detection in remote sensing. Remote sensing targets can have arbitrary angles, and many anchor-base methods use a lot of anchors with different angles which cause efficiency and precision problems. To
[...] Read more.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used in the task of object detection in remote sensing. Remote sensing targets can have arbitrary angles, and many anchor-base methods use a lot of anchors with different angles which cause efficiency and precision problems. To solve the problem caused by too many anchors, this paper presents a novel matching algorithm in the matching stage of the rotating anchor and object, which determines a more accurate rotating region of interests (RRoIs) for target regression using the copies set for each oriented anchor. It makes use of the high recall rate brought by a large number of anchor boxes with different angles and avoids the computation brought by a large number of anchor boxes. We use the remote sensing datasets DOTA and HRSC2016 with rotation bounding boxes to evaluate our improved algorithm on Rotation RetinaNet and compare it with it. For the targets of high aspect ratios, such as large vehicles and ships, our method is superior to Rotation RetinaNet and achieves a better performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures