Feature Paper Collection in Applied System Innovation
(Closed)
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Feature Paper Collection of Applied System Innovation will be published in Applied System Innovation (ISSN 2571-5577), and is dedicated to the publication and discussion of research articles, letters, reviews, and communications on all aspects of integrated engineering and technology that provide insights and address challenges in systems. Contributions will focus on the fundamentals and application of industries and engineering and will emphasize the potential of the covered subjects in addressing these important societal challenges. We welcome reviews and outstanding articles to this Feature Paper Collection in order to improve the current knowledge on Applied System Innovation.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Prof. Dr. Christos Douligeris
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied System Innovation is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (23 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Performance Assessment and Modeling of Routing Protocol in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Using Statistical Design of Experiments Methodology: A Comprehensive Study
by
Souad Ajjaj, Souad El Houssaini, Mustapha Hain and Mohammed-Alamine El Houssaini
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3053
Abstract
The performance assessment of routing protocols in vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs) plays a critical role in testing the efficiency of the routing algorithms before deployment in real conditions. This research introduces the statistical design of experiments (DOE) methodology as an innovative alternative
[...] Read more.
The performance assessment of routing protocols in vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs) plays a critical role in testing the efficiency of the routing algorithms before deployment in real conditions. This research introduces the statistical design of experiments (DOE) methodology as an innovative alternative to the one factor at a time (OFAT) approach for the assessment and the modeling of VANET routing protocol performance. In this paper, three design of experiments methods are applied, namely the two-level full factorial method, the Plackett–Burman method and the Taguchi method, and their outcomes are comprehensively compared. The present work considers a case study involving four factors namely: node density, number of connections, black hole and worm hole attacks. Their effects on four measured outputs called responses are simultaneously evaluated: throughput, packet loss ratio, average end-to-end delay and routing overhead of the AODV routing protocol. Further, regression models using the least squares method are generated. First, we compare the main effects of factors resulted from the three DOE methods. Second, we perform analysis of variance (ANOVA) to explore the statistical significance and compare the percentage contributions of each factor. Third, the goodness of fit of regression models is assessed using the adjusted R-squared measure and the fitting plots of measured versus predicted responses. VANET simulations are implemented using the network simulator (NS-3) and the simulator of urban mobility (SUMO). The findings reveal that the design of experiments methodology offers powerful mathematical, graphical and statistical techniques for analyzing and modeling the performance of VANET routing protocols with high accuracy and low costs. The three methods give equivalent results in terms of the main effect and ANOVA analysis. Nonetheless, the Taguchi models show higher predictive accuracy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
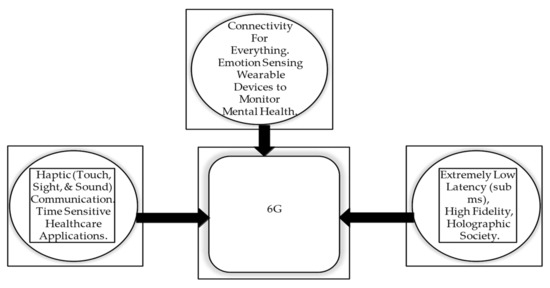
6G Enabled Tactile Internet and Cognitive Internet of Healthcare Everything: Towards a Theoretical Framework
by
Prafulla Kumar Padhi and Fernando Charrua-Santos
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 4335
Abstract
Digital era deficiencies traditionally exist in healthcare applications because of the unbalanced distribution of medical resources, especially in rural areas globally. Cognitive data intelligence, which constitute the integration of cognitive computing, massive data analytics, and tiny artificial intelligence, especially tiny machine learning, can
[...] Read more.
Digital era deficiencies traditionally exist in healthcare applications because of the unbalanced distribution of medical resources, especially in rural areas globally. Cognitive data intelligence, which constitute the integration of cognitive computing, massive data analytics, and tiny artificial intelligence, especially tiny machine learning, can be used to palpate a patient’s health status, physiologically and psychologically transforming the current healthcare system. To remotely detect patients’ emotional state of diagnosing diseases, the integration of 6G enabled Tactile Internet, cognitive data intelligence, and Internet of Healthcare Everything is proposed to form the 6GCIoHE system that aims at achieving global ubiquitous accessibility, extremely low latency, high reliability, and elevated performance in cognitive healthcare in real time to ensure patients receive prompt treatment, especially for the haptic actions. Judiciously, a model-driven methodology is proffered to facilitate the 6GCIoHE system design and development that adopts different refinement levels to incorporate the cognitive healthcare requirements through the interactions of semantic management, process management, cognitive intelligence capabilities, and knowledge sources. Based on the 6GCIoHE system architecture, applications, and challenges, the aim of this study was accomplished by developing a novel theoretical framework to captivate further research within the cognitive healthcare field.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
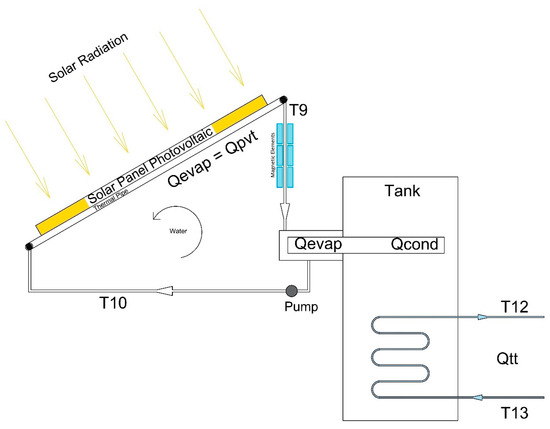
Impact of the Magnetic Field on the Performance of Heat Pipes Driven by a Photovoltaic–Thermal Panel with Nanofluids
by
Samuel Sami
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2817
Abstract
A two-dimensional dynamic heat transfer and fluid flow model was developed to describe the behavior of photovoltaic cells and the performance of a hybrid solar collector photovoltaic–thermal solar panel system. The system was assessed under different magnetic field Gauss forces. Nanofluids were used
[...] Read more.
A two-dimensional dynamic heat transfer and fluid flow model was developed to describe the behavior of photovoltaic cells and the performance of a hybrid solar collector photovoltaic–thermal solar panel system. The system was assessed under different magnetic field Gauss forces. Nanofluids were used to drive the heat pipes in a thermal panel under different conditions, such as levels of solar irradiance and different boundary conditions. The model was developed based on the equations of the dynamic conservation of mass and energy, coupled with the heat transfer relationships and thermodynamic properties, in addition to the material properties under different magnetic Gauss forces. Comparisons were made with the literature data to validate the predictive model. The model reliably predicted the key parameters under different nanofluid conditions and magnetic fields, and compared well with the existing data on the subject.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Influence of Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering toward Sustainable Development—A Systematic Literature Review
by
Bilal Manzoor, Idris Othman, Serdar Durdyev, Syuhaida Ismail and Mohammad Hussaini Wahab
Cited by 50 | Viewed by 21035
Abstract
The widespread use of artificial intelligence (AI) in civil engineering has provided civil engineers with various benefits and opportunities, including a rich data collection, sustainable assessment, and productivity. The trend of construction is diverted toward sustainability with the aid of digital technologies. In
[...] Read more.
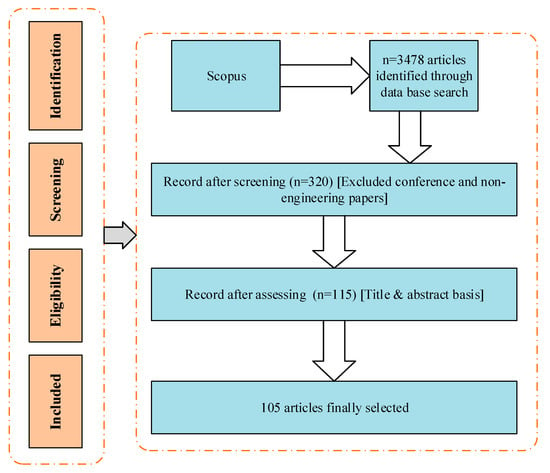
The widespread use of artificial intelligence (AI) in civil engineering has provided civil engineers with various benefits and opportunities, including a rich data collection, sustainable assessment, and productivity. The trend of construction is diverted toward sustainability with the aid of digital technologies. In this regard, this paper presents a systematic literature review (SLR) in order to explore the influence of AI in civil engineering toward sustainable development. In addition, SLR was carried out by using academic publications from Scopus (i.e., 3478 publications). Furthermore, screening is carried out, and eventually, 105 research publications in the field of AI were selected. Keywords were searched through Boolean operation “Artificial Intelligence” OR “Machine intelligence” OR “Machine Learning” OR “Computational intelligence” OR “Computer vision” OR “Expert systems” OR “Neural networks” AND “Civil Engineering” OR “Construction Engineering” OR “Sustainable Development” OR “Sustainability”. According to the findings, it was revealed that the trend of publications received its high intention of researchers in 2020, the most important contribution of publications on AI toward sustainability by the
Automation in Construction, the United States has the major influence among all the other countries, the main features of civil engineering toward sustainability are interconnectivity, functionality, unpredictability, and individuality. This research adds to the body of knowledge in civil engineering by visualizing and comprehending trends and patterns, as well as defining major research goals, journals, and countries. In addition, a theoretical framework has been proposed in light of the results for prospective researchers and scholars.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
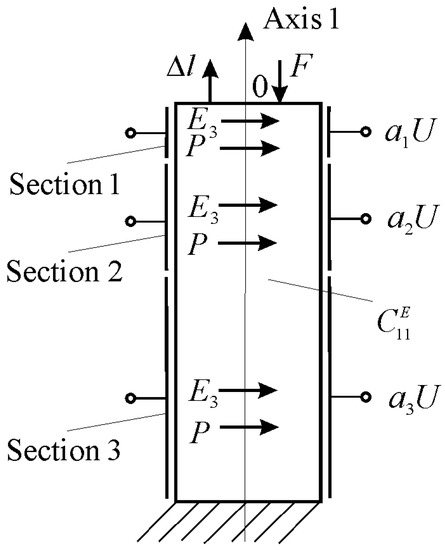
Coded Control of a Sectional Electroelastic Engine for Nanomechatronics Systems
by
Sergey M. Afonin
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 11431
Abstract
This work determines the coded control of a sectional electroelastic engine at the elastic–inertial load for nanomechatronics systems. The expressions of the mechanical and adjustment characteristics of a sectional electroelastic engine are obtained using the equations of the electroelasticity and the mechanical load.
[...] Read more.
This work determines the coded control of a sectional electroelastic engine at the elastic–inertial load for nanomechatronics systems. The expressions of the mechanical and adjustment characteristics of a sectional electroelastic engine are obtained using the equations of the electroelasticity and the mechanical load. A sectional electroelastic engine is applied for coded control of nanodisplacement as a digital-to-analog converter. The transfer function and the transient characteristics of a sectional electroelastic engine at elastic–inertial load are received for nanomechatronics systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
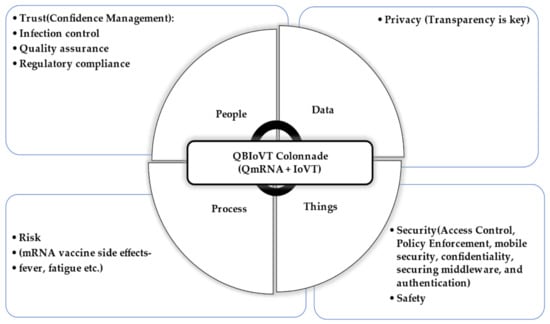
Quantum Biotech and Internet of Virus Things: Towards a Theoretical Framework
by
Prafulla Kumar Padhi and Feranando Charrua-Santos
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 9175
Abstract
Quantumization, the process of converting information into quantum (qubit) format, is a key enabler for propelling a new and distinct infrastructure in the pharmaceutical space. Quantum messenger RNA (QmRNA) technology, an indispensable constituent of quantum biotech (QB), is a compelling alternative to conventional
[...] Read more.
Quantumization, the process of converting information into quantum (qubit) format, is a key enabler for propelling a new and distinct infrastructure in the pharmaceutical space. Quantum messenger RNA (QmRNA) technology, an indispensable constituent of quantum biotech (QB), is a compelling alternative to conventional vaccine methods because of its capacity for rapid development, high efficacy, and low-cost manufacturing to combat infectious diseases. Internet of Virus Things (IoVT), a biological version of Internet of Things (IoT), comprises applications to fight against pandemics and provides effective vaccine administration. The integration of QB and IoVT constitutes the QBIoVT system to advance the prospect of QmRNA vaccine discovery within a few days. This research disseminates the QBIoVT system paradigm, including architectural aspects, priority areas, challenges, applications, and QmRNA research engine design to accelerate QmRNA vaccines discovery. A comprehensive review of the literature was accomplished, and a context-centered methodology was applied to the QBIoVT paradigm forensic investigations to impel QmRNA vaccine discovery. Based on the above rumination, the principal motive for this study was to develop a novel QBIoVT theoretical framework which has not been produced through earlier theories. The proposed framework shall inspire future QBIoVT system research activities to improve pandemics detection and protection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
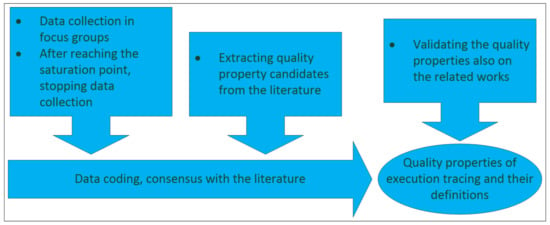
Quality Properties of Execution Tracing, an Empirical Study
by
Tamas Galli, Francisco Chiclana and Francois Siewe
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3792
Abstract
The quality of execution tracing impacts the time to a great extent to locate errors in software components; moreover, execution tracing is the most suitable tool, in the majority of the cases, for doing postmortem analysis of failures in the field. Nevertheless, software
[...] Read more.
The quality of execution tracing impacts the time to a great extent to locate errors in software components; moreover, execution tracing is the most suitable tool, in the majority of the cases, for doing postmortem analysis of failures in the field. Nevertheless, software product quality models do not adequately consider execution tracing quality at present neither do they define the quality properties of this important entity in an acceptable manner. Defining these quality properties would be the first step towards creating a quality model for execution tracing. The current research fills this gap by identifying and defining the variables, i.e., the quality properties, on the basis of which the quality of execution tracing can be judged. The present study analyses the experiences of software professionals in focus groups at multinational companies, and also scrutinises the literature to elicit the mentioned quality properties. Moreover, the present study also contributes to knowledge with the combination of methods while computing the saturation point for determining the number of the necessary focus groups. Furthermore, to pay special attention to validity, in addition to the the indicators of qualitative research: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability, the authors also considered content, construct, internal and external validity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
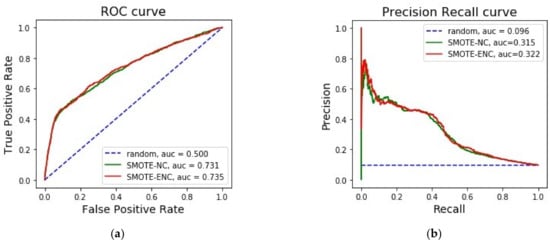
SMOTE-ENC: A Novel SMOTE-Based Method to Generate Synthetic Data for Nominal and Continuous Features
by
Mimi Mukherjee and Matloob Khushi
Cited by 66 | Viewed by 9121
Abstract
Real-world datasets are heavily skewed where some classes are significantly outnumbered by the other classes. In these situations, machine learning algorithms fail to achieve substantial efficacy while predicting these underrepresented instances. To solve this problem, many variations of synthetic minority oversampling methods (SMOTE)
[...] Read more.
Real-world datasets are heavily skewed where some classes are significantly outnumbered by the other classes. In these situations, machine learning algorithms fail to achieve substantial efficacy while predicting these underrepresented instances. To solve this problem, many variations of synthetic minority oversampling methods (SMOTE) have been proposed to balance datasets which deal with continuous features. However, for datasets with both nominal and continuous features, SMOTE-NC is the only SMOTE-based oversampling technique to balance the data. In this paper, we present a novel minority oversampling method, SMOTE-ENC (SMOTE—Encoded Nominal and Continuous), in which nominal features are encoded as numeric values and the difference between two such numeric values reflects the amount of change of association with the minority class. Our experiments show that classification models using the SMOTE-ENC method offer better prediction than models using SMOTE-NC when the dataset has a substantial number of nominal features and also when there is some association between the categorical features and the target class. Additionally, our proposed method addressed one of the major limitations of the SMOTE-NC algorithm. SMOTE-NC can be applied only on mixed datasets that have features consisting of both continuous and nominal features and cannot function if all the features of the dataset are nominal. Our novel method has been generalized to be applied to both mixed datasets and nominal-only datasets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
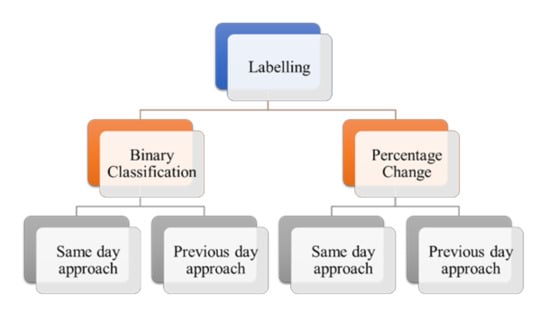
Text Mining of Stocktwits Data for Predicting Stock Prices
by
Mukul Jaggi, Priyanka Mandal, Shreya Narang, Usman Naseem and Matloob Khushi
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 12504
Abstract
Stock price prediction can be made more efficient by considering the price fluctuations and understanding people’s sentiments. A limited number of models understand financial jargon or have labelled datasets concerning stock price change. To overcome this challenge, we introduced FinALBERT, an ALBERT based
[...] Read more.
Stock price prediction can be made more efficient by considering the price fluctuations and understanding people’s sentiments. A limited number of models understand financial jargon or have labelled datasets concerning stock price change. To overcome this challenge, we introduced FinALBERT, an ALBERT based model trained to handle financial domain text classification tasks by labelling Stocktwits text data based on stock price change. We collected Stocktwits data for over ten years for 25 different companies, including the major five FAANG (Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google). These datasets were labelled with three labelling techniques based on stock price changes. Our proposed model FinALBERT is fine-tuned with these labels to achieve optimal results. We experimented with the labelled dataset by training it on traditional machine learning, BERT, and FinBERT models, which helped us understand how these labels behaved with different model architectures. Our labelling method’s competitive advantage is that it can help analyse the historical data effectively, and the mathematical function can be easily customised to predict stock movement.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
A Survey of Forex and Stock Price Prediction Using Deep Learning
by
Zexin Hu, Yiqi Zhao and Matloob Khushi
Cited by 179 | Viewed by 37017
Abstract
Predictions of stock and foreign exchange (Forex) have always been a hot and profitable area of study. Deep learning applications have been proven to yield better accuracy and return in the field of financial prediction and forecasting. In this survey, we selected papers
[...] Read more.
Predictions of stock and foreign exchange (Forex) have always been a hot and profitable area of study. Deep learning applications have been proven to yield better accuracy and return in the field of financial prediction and forecasting. In this survey, we selected papers from the Digital Bibliography & Library Project (DBLP) database for comparison and analysis. We classified papers according to different deep learning methods, which included Convolutional neural network (CNN); Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM); Deep neural network (DNN); Recurrent Neural Network (RNN); Reinforcement Learning; and other deep learning methods such as Hybrid Attention Networks (HAN), self-paced learning mechanism (NLP), and Wavenet. Furthermore, this paper reviews the dataset, variable, model, and results of each article. The survey used presents the results through the most used performance metrics: Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Square Error (MSE), accuracy, Sharpe ratio, and return rate. We identified that recent models combining LSTM with other methods, for example, DNN, are widely researched. Reinforcement learning and other deep learning methods yielded great returns and performances. We conclude that, in recent years, the trend of using deep-learning-based methods for financial modeling is rising exponentially.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
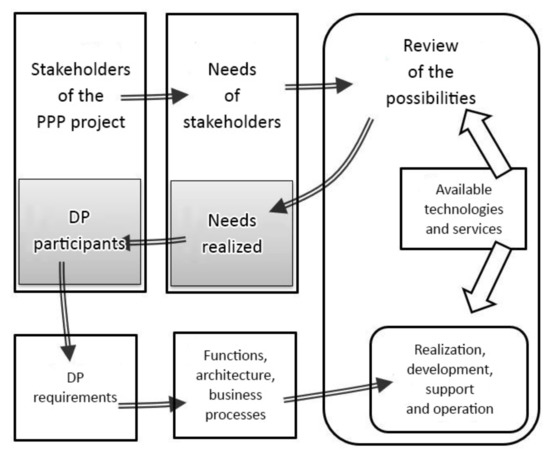
Systems Engineering Methodology for Designing Digital Public–Private Partnership Platforms
by
Igor Nikolaevich Glukhikh, Liudmila Anatolevna Tolstolesova and Otabek Anzor ugli Arzikulov
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3508
Abstract
The modern approach to realization of large, expensive projects with long payback periods in various sectors of infrastructure often involves combining the financial resources of public authorities and the private sector through a public–private partnership (PPP) mechanism. The PPP mechanism has a high
[...] Read more.
The modern approach to realization of large, expensive projects with long payback periods in various sectors of infrastructure often involves combining the financial resources of public authorities and the private sector through a public–private partnership (PPP) mechanism. The PPP mechanism has a high potential for attracting investments and facilitating other conditions necessary for the project. At the same time, the project participants need a third-party coordination platform that is objective and able to organize their dialog on equal terms. The authors of this article, for these purposes, consider the capabilities of digital platforms (DP). Digital platforms are able to unite many project participants in a single information field and provide them with the necessary services. Given the potential multitude of participants in such a system, there arises the question of meeting their basic needs to create mutually beneficial conditions during the implementation of projects. Thus, there is a need for flexible DPs. Flexibility can be achieved by using systems engineering (SE) approaches during the design of the DP. The practice of interaction with stakeholders in the framework of systems engineering allows the determination of the basic needs and areas of activity of the participants. The results of this practice will form the basis for the functional and physical design of the future DPs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Digitalization of Public Services—An Input Output Logit Analysis
by
Shahzadah Nayyar Jehan and Mudalige Uthpala Indeelinie Alahakoon
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4122
Abstract
In 2000, Sri Lanka designed an ambitious plan for the introduction of information and communication technology (ICT) in most government functions and in the public service delivery (PSD) system in the country. This process started in the early 2000s and gained momentum with
[...] Read more.
In 2000, Sri Lanka designed an ambitious plan for the introduction of information and communication technology (ICT) in most government functions and in the public service delivery (PSD) system in the country. This process started in the early 2000s and gained momentum with several local and internationally funded initiatives. A systematic innovation concept was incorporated within the ICT regime, which ensured bottom-up learning for a smooth transformation from paper to digitized PSD systems. Towards this end, the Information Communication Technology Agency (ICTA) and Lanka Government Network (LGN) were established. ICT incorporation covered the operations of most government agencies and departments to improve governance and PSD. We analyzed the efficiency of the ICT regime to understand its impact on public service employee output as well as on services to the public. We collected service delivery data from both the employees and their clients using a Likert-scale questionnaire. The questionnaire enquired about the utility of the ICT regime introduced in various departments and ministries (DMs) of the Sri Lankan government. This paper analyzes the overall and relative effectiveness of the ICT regime in terms of the inputs incurred and the outcomes realized. First, we calculated the Cronbach’s alpha to test the robustness of the data. Second, we applied ordinal logistics analysis to understand the interrelations among various measures (inputs) and their impacts (outcomes). Finally, we conducted specificity, sensitivity, and predictive value analysis to assess the accuracy of the investigative model. Our findings suggest a positive correlation between the inputs and the outcomes of the ICT regime introduced to digitalize PSD. Our results further indicate that although the inputs and the outcomes are positively corelated, this correlation is not sufficiently strong, and the ICT implementation measures need further emphasis to demonstrate any significant impact on user confidence in this regime.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
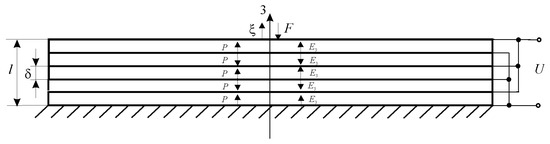
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Control of a Multilayer Electroelastic Engine with a Longitudinal Piezoeffect for Nanomechatronics Systems
by
Sergey M. Afonin
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 13923
Abstract
A electroelastic engine with a longitudinal piezoeffect is widely used in nanotechnology for nanomanipulators, laser systems, nanopumps, and scanning microscopy. For these nanomechatronics systems, the transition between individual positions of the systems in the shortest possible time is relevant. It is relevant to
[...] Read more.
A electroelastic engine with a longitudinal piezoeffect is widely used in nanotechnology for nanomanipulators, laser systems, nanopumps, and scanning microscopy. For these nanomechatronics systems, the transition between individual positions of the systems in the shortest possible time is relevant. It is relevant to solve the problem of optimizing the nanopositioning control system with a minimum control time. This work determines the optimal control of a multilayer electroelastic engine with a longitudinal piezoeffect and minimal control time for an optimal nanomechatronics system. The expressions of the control function and switching line are obtained with using the Pontryagin maximum principle for the optimal control system of the multilayer electroelastic engine at a longitudinal piezoeffect with an ordinary second-order differential equation of system. In this optimal nanomechatronics system, the control function takes only two values and changes once.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
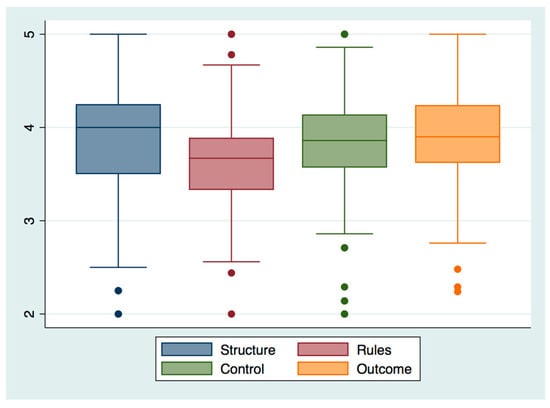
Open AccessArticle
Systematic Innovation Based BPR Regime—A Factors Analysis
by
Shahzadah Nayyar Jehan and Vishakha Wijeratne Elapatha
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2796
Abstract
Sri Lankan public services have a lingering colonial legacy, and there have been several efforts since the country’s independence to break away from the restraints of the past to align them with modern times and expectations. The drive for modernization of public services
[...] Read more.
Sri Lankan public services have a lingering colonial legacy, and there have been several efforts since the country’s independence to break away from the restraints of the past to align them with modern times and expectations. The drive for modernization of public services passed through several phases of experimentation without much success in the past. A significant attempt at the modernization of public services was made in the first decade of this millennium; we now notice substantial changes in public service delivery (PSD) in the country. In this paper, we assess the impact of an inside-outside-inside (IOI)-based open system innovation-related business process reengineering (BPR) regime adapted for reforms in the organization and the delivery of public services in the country. We carried out an input and output analysis of the BPR regime, adopted by various departments and ministries of the government of Sri Lanka to improve the PSD infrastructure. A broad-based ground survey on a five-point Likert scale was carried out, and performance data were collected. We collected a total of 290 responses—each questionnaire was composed of 40 questions regarding the inputs and the outputs of the regime’s implementation. Applying an ordered multivariate logistic regression model, we have attempted to estimate correlations amongst inputs, results, and overall perception of success or failure of the BPR regime across 29 departments and ministries (D&M). We have tabulated summary statistics and regression results to assess the relative significance of various regime inputs and their impact on the corresponding outcomes. The outcomes suggest that while all inputs and outputs are significantly correlated, some inputs have a more significant effect on the results expected from the BPR regime. We have used original data acquired through a survey carried out directly through the PSD organizations in the country, and this study is the first of its kind in this regard. We expect this study will be of high utility to the personnel engaged in the planning and implementation of PSD through systematic innovation and BPR, not only in Sri Lanka but also for many other professionals and researchers who are engaged in designing and execution of similar service improvements and reengineering strategies in different countries around the world.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Agent-Based Modeling of Rumor Propagation Using Expected Integrated Mean Squared Error Optimal Design
by
Shih-Hsien Tseng and Tien Son Nguyen
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4966
Abstract
In the “Age of the Internet”, fake news and rumor-mongering have emerged as some of the most critical factors that affect our online social lives. For example, in the workplace, rumor spreading runs rampant during times when employees may be plagued with uncertainty
[...] Read more.
In the “Age of the Internet”, fake news and rumor-mongering have emerged as some of the most critical factors that affect our online social lives. For example, in the workplace, rumor spreading runs rampant during times when employees may be plagued with uncertainty about the nature and consequences of major changes. Positive information should be widely propagated as much as possible; however, we must limit the spread of rumors in an effort to reduce their inherently harmful effects. The purpose of this research is to explain the mechanisms for controlling rumors and suggest an approach for dispelling the rumor effect in the workplace. In this study, we will present a simple simulation framework of agent-based modeling and apply Social Impact Theory to explain rumor propagation within social networks. Based on our results, we have found that organizations can significantly reduce the spread of the rumors by improving the workplace environment and instituting counseling for those in management positions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Metamodels Resulting from Two Different Geometry Morphing Approaches Are Suitable to Direct the Modification of Structure-Born Noise Transfer in the Digital Design Phase
by
Timo von Wysocki, Michael Leupolz and Frank Gauterin
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4167
Abstract
Noise vibration and harshness (NVH) development often takes place in the later development phases. Shifting the optimization to the early digital development phase enables more parameters to participate in the optimization and leads to a more holistic development process. Digital NVH development often
[...] Read more.
Noise vibration and harshness (NVH) development often takes place in the later development phases. Shifting the optimization to the early digital development phase enables more parameters to participate in the optimization and leads to a more holistic development process. Digital NVH development often modifies system and component frequency response functions (FRFs) using finite element (FE) simulation. Currently, the often manual process of creating new FE models for modified designs makes a systematic evaluation of many designs difficult and time-consuming. In this paper, we take on these difficulties and use both a Direct Morphing approach and a Box Morphing approach to automatically adopt the first existing FE models to modified designs. We use the generated simulation results to fit metamodels describing the correlation between geometrical parameters and characteristic FRF values. These metamodels provide an easy and fast to use tool for designers to consider NVH demands. In a simulation example, we demonstrate the capabilities by modifying the kinematic hard points of a vehicle suspension and using them to modify the noise transfer sensitivity. We show that the metamodels can lead the digital design process to intuitively and specifically reduce characteristic component FRF values by changing the location of the component hard points.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
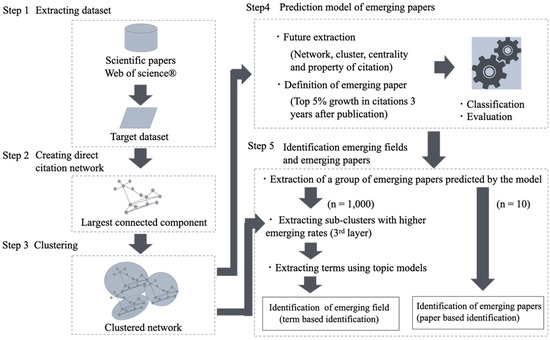
Emerging Scientific Field Detection Using Citation Networks and Topic Models—A Case Study of the Nanocarbon Field
by
Hajime Sasaki, Bunshi Fugetsu and Ichiro Sakata
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3960
Abstract
In fields with high science linkage, such as the nanocarbon field, trends in academic papers are particularly important for identifying future technological trends. The use of the number of citations allows us to predict the qualitative trends on a paper-by-paper basis. At the
[...] Read more.
In fields with high science linkage, such as the nanocarbon field, trends in academic papers are particularly important for identifying future technological trends. The use of the number of citations allows us to predict the qualitative trends on a paper-by-paper basis. At the same time, it is necessary to be able to comprehensively discuss both qualitative and quantitative aspects in the subject area. This study aimed to detect emerging areas in the nanocarbon field using network models and topic models. It was possible to not only construct a model that exceeded an 86.2%
F1 measure but also to focus on an area that could not be detected by the prediction model. This was accomplished by focusing on paper units, such as the research on the chemical synthesis of zigzag single-walled carbon nanotubes. Thus, it is possible to obtain knowledge that contributes to diversified R&D strategies and innovation policies by considering the emergence of new fields from multiple perspectives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
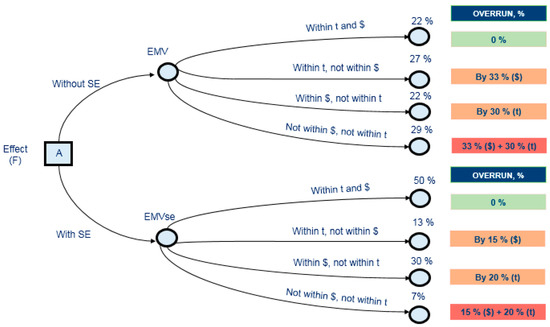
Evaluating the Cost Efficiency of Systems Engineering in Oil and Gas Projects
by
Igor Nikolaevich Glukhikh, Artyom Fedorovich Mozhchil, Mikhail Olegovich Pisarev, Otabek Anzor ugli Arzykulov and Kristina Zakharovna Nonieva
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 4322
Abstract
Studies of systems engineering applications have revealed that systems engineering (SE) has a high potential for transferring economically inefficient oil and gas projects into a profitable zone due to preserving the value created at the concept stage right up to the implementation stage.
[...] Read more.
Studies of systems engineering applications have revealed that systems engineering (SE) has a high potential for transferring economically inefficient oil and gas projects into a profitable zone due to preserving the value created at the concept stage right up to the implementation stage. To implement any project, including an organizational one, the company must have an economic justification for innovation. Studies into the global experience of assessing SE efficiency based on projects of various types have revealed the lack of a universal assessment method; however, individual studies have potential to be used in developing a method for quantifying the value of SE in oil and gas projects. Considering this fact, we developed our own method and prototype to assess the economic effect from the introduction of SE into oil and gas projects. The method is based on a decision tree used to calculate the Net Present Value considering the probability of projects’ success and failure in terms of budget and deadlines. This allowed us to predict the effect from introducing SE to an oil company’s capital project. The results obtained demonstrated the model’s performance capability and its possible applications in project resource planning stages.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
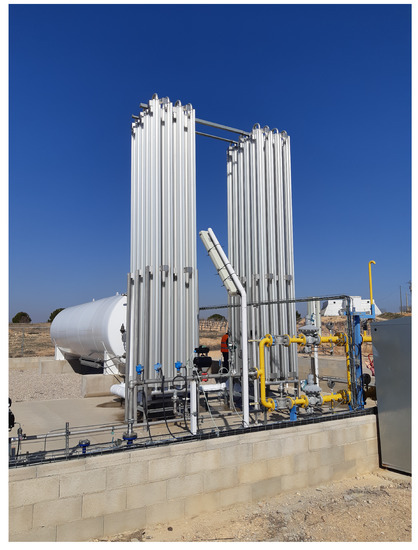
Sensor-Data-Driven Prognosis Approach of Liquefied Natural Gas Satellite Plant
by
Antoni Escobet, Teresa Escobet, Joseba Quevedo and Adoración Molina
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3356
Abstract
This paper proposes a sensor-data-driven prognosis approach for the predictive maintenance of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) satellite plant. By using data analytics of sensors installed in the satellite plants, it is possible to predict the remaining time to refill the tank of
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a sensor-data-driven prognosis approach for the predictive maintenance of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) satellite plant. By using data analytics of sensors installed in the satellite plants, it is possible to predict the remaining time to refill the tank of the remote plants. In the proposed approach, the first task of data validation and correction is presented in order to transform raw data into reliable validated data. Then, the second task presents two methods for the prognosis of gas consumption in real time and the forecast of remaining time to refill the tank of the plant. The obtained results with real satellite plants showed good performance for direct implementation in a predictive maintenance plan.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
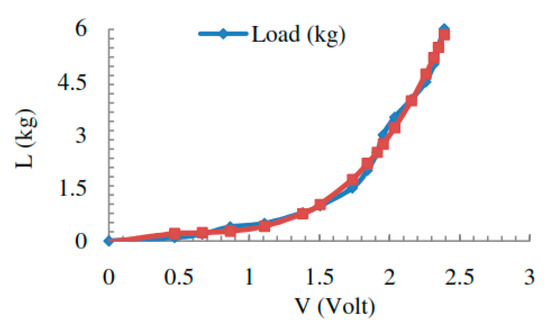
A Simple Foot Plantar Pressure Measurement Platform System Using Force-Sensing Resistors
by
Dwi Basuki Wibowo, Agus Suprihanto, Wahyu Caesarendra, Slamet Khoeron, Adam Glowacz and Muhammad Irfan
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5476
Abstract
Generally, there are two types of working style, i.e., some people work in sitting conditions, and the remaining work mostly in a standing position. For people working in a standing position, they can spend hours in a day doing their work standing. These
[...] Read more.
Generally, there are two types of working style, i.e., some people work in sitting conditions, and the remaining work mostly in a standing position. For people working in a standing position, they can spend hours in a day doing their work standing. These people do not realize that it can cause medical issues, especially for the feet, namely biometric problems. In addition, several doctors in Indonesia are already aware of this issue and state that the biometric problems faced by those kinds of people can be predicted from the load distribution on the foot. However, the tool used by the doctors in Indonesia to measure biometric problems is not a digital tool. Therefore it is very difficult to measure and predict the biometric problems quantitatively. This study aims to develop a low-cost static load measuring device using force-sensing resistor (FSR) sensors. The measuring instrument is designed in the form of a pressure plate platform which consist of 30 FSR 402 sensors. The sensors are placed right underneath the display area of the foot, 15 sensors on the soles of the left and right feet. Ten students from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Diponegoro University (five men and five women) were asked to stand on the platform. Each subject also measured foot length (FL) to estimate shoe size, foot area contact (FAC) for validation between genders, and foot type using the digital footprint tools. From the results of measurements obtained for the left foot in the medial mid foot area, i.e., in sensors 5 and 7, not exposed to the load, on almost all subjects except subject number 3 with a load of 0.196 kg on sensor 7. The highest average load occurs in the heel area i.e., sensor 1 measured 0.713 kg and the smallest average load occurs in the five sensors, with 0 kg. A static load gauge that is designed to be used to measure each leg area for subjects with a shoe size of 40–42 with low price to be held in hospital-orthopedic hospitals and biomechanical research centers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
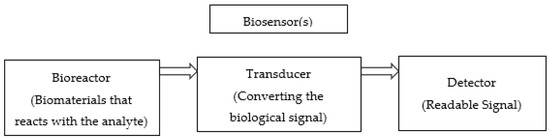
A Brief Description of Cyclic Voltammetry Transducer-Based Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor Using Synthesized Graphene Electrodes
by
Mohamed Husien Fahmy Taha, Hager Ashraf and Wahyu Caesarendra
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 10824
Abstract
The essential disadvantages of conventional glucose enzymatic biosensors such as high fabrication cost, poor stability of enzymes, pH value-dependent, and dedicated limitations, have been increasing the attraction of non-enzymatic glucose sensors research. Beneficially, patients with diabetes could use this type of sensor as
[...] Read more.
The essential disadvantages of conventional glucose enzymatic biosensors such as high fabrication cost, poor stability of enzymes, pH value-dependent, and dedicated limitations, have been increasing the attraction of non-enzymatic glucose sensors research. Beneficially, patients with diabetes could use this type of sensor as a fourth-generation of glucose sensors with a very low cost and high performance. We demonstrate the most common acceptable transducer for a non-enzymatic glucose biosensor with a brief description of how it works. The review describes the utilization of graphene and its composites as new materials for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose biosensors. The electrochemical properties of graphene and the electrochemical characterization using the cyclic voltammetry (CV) technique of electrocatalysis electrodes towards glucose oxidation have been summarized. A recent synthesis method of the graphene-based electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensors have been introduced along with this study. Finally, the electrochemical properties such as linearity, sensitivity, and the limit of detection (LOD) for each sensor are introduced with a comparison with each other to figure out their strengths and weaknesses.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Extending the Applicability of Newton’s Algorithm with Projections for Solving Generalized Equations
by
Michael I. Argyros, Gus I. Argyros, Ioannis K. Argyros, Samundra Regmi and Santhosh George
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2707
Abstract
A new technique is developed to extend the convergence ball of Newton’s algorithm with projections for solving generalized equations with constraints on the multidimensional Euclidean space. This goal is achieved by locating a more precise region than in earlier studies containing the solution
[...] Read more.
A new technique is developed to extend the convergence ball of Newton’s algorithm with projections for solving generalized equations with constraints on the multidimensional Euclidean space. This goal is achieved by locating a more precise region than in earlier studies containing the solution on which the Lipschitz constants are smaller than the ones used in previous studies. These advances are obtained without additional conditions. This technique can be used to extend the usage of other iterative algorithms. Numerical experiments are used to demonstrate the superiority of the new results.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
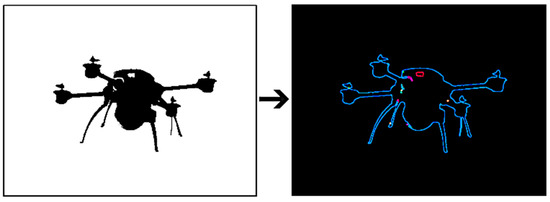
Automated Detection of Multi-Rotor UAVs Using a Machine-Learning Approach
by
Šimon Grác, Peter Beňo, František Duchoň, Martin Dekan and Michal Tölgyessy
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 5340
Abstract
The objective of this article is to propose and verify a reliable detection mechanism of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Such a task needs to be solved in many areas such as in the protection of vulnerable buildings or in the protection of
[...] Read more.
The objective of this article is to propose and verify a reliable detection mechanism of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Such a task needs to be solved in many areas such as in the protection of vulnerable buildings or in the protection of privacy. Our system was firstly realized by standard computer vision methods using the Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF (ORB) feature detector. Due to the low success rate achieved in real-world conditions, the machine-learning approach was used as an alternative detection mechanism. The “Common Objects in Context dataset” was used as a predefined dataset and it was extended by 1000 samples of UAVs from the SafeShore dataset. The effectiveness and the reliability of our system are proven by four basic experiments—drone in a static image and videos which are displaying a drone in the sky, multiple drones in one image, and a drone with another flying object in the sky. The successful detection rate achieved was 97.3% in optimal conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures