Matrix Effectors and Cancer
(Closed)
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Nikos Karamanos
Prof. Dr. Nikos Karamanos
 Prof. Dr. Nikos Karamanos
Prof. Dr. Nikos Karamanos
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Biochemistry, Biochemical Analysis and Matrix Pathobiochemistry Research Group, Laboratory of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, University of Patras, 26500 Patras, Greece
Interests: matrix biology; molecular mechanisms in breast cancer progression; proteoglycans; glycosaminoglycans; metalloproteinases
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Zoi Piperigkou
Dr. Zoi Piperigkou
 Dr. Zoi Piperigkou
Dr. Zoi Piperigkou
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Biochemistry, Biochemical Analysis & Matrix Pathobiology Research Group, Laboratory of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, University of Patras, 26110 Patras, Greece
Interests: extracellular matrix; cell signaling; estrogen receptors; proteoglycans; breast cancer biomarkers; molecular targeting
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Extracellular matrices (ECMs) are highly dynamic three-dimensional structural meshworks composed of macromolecules, such as proteoglycans/glycosaminoglycans (PGs/GAGs), collagens, laminins, elastin, glycoproteins and proteinases. Matrix macromolecules are characterized by high structural complexity and heterogeneity. They form complex networks through which they dynamically communicate with cells, thus serving as critical regulators of several homeostatic and pathological processes, such as cancer. ECM molecular composition varies among the tissue of origin and it undergoes significant remodeling during cancer progression. The elucidation of the mechanistic aspects governing matrix assembly and cell–matrix interactions is of critical importance to discover matrix-mediated cancer pathobiology and novel therapeutic approaches. The aim of this Collection of Cancers is to highlight the emerging roles of effective matrix macromolecules, including matrix metalloproteinases, proteoglycans, specific types of collagens and matrix (glyco)proteins that play key roles in cancer development and aggressiveness.
Prof. Dr. Nikos Karamanos
Dr. Zoi Piperigkou
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- extracellular matrix
- cancer pathobiology
- metalloproteinases
- matrix remodeling
- proteoglycans
- collagen
- matrix (glyco)proteins
- molecular targeting
Published Papers (27 papers)
Open AccessReview
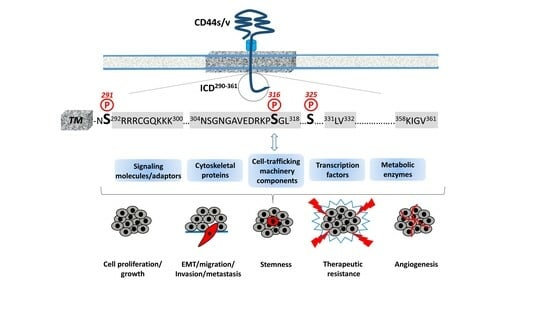
CD44 Intracellular Domain: A Long Tale of a Short Tail
by
Spyros S. Skandalis
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2922
Abstract
CD44 is a single-chain transmembrane receptor that exists in multiple forms due to alternative mRNA splicing and post-translational modifications. CD44 is the main cell surface receptor of hyaluronan as well as other extracellular matrix molecules, cytokines, and growth factors that play important roles
[...] Read more.
CD44 is a single-chain transmembrane receptor that exists in multiple forms due to alternative mRNA splicing and post-translational modifications. CD44 is the main cell surface receptor of hyaluronan as well as other extracellular matrix molecules, cytokines, and growth factors that play important roles in physiological processes (such as hematopoiesis and lymphocyte homing) and the progression of various diseases, the predominant one being cancer. Currently, CD44 is an established cancer stem cell marker in several tumors, implying a central functional role in tumor biology. The present review aims to highlight the contribution of the CD44 short cytoplasmic tail, which is devoid of any enzymatic activity, in the extraordinary functional diversity of the receptor. The interactions of CD44 with cytoskeletal proteins through specific structural motifs within its intracellular domain drives cytoskeleton rearrangements and affects the distribution of organelles and transport of molecules. Moreover, the CD44 intracellular domain specifically interacts with various cytoplasmic effectors regulating cell-trafficking machinery, signal transduction pathways, the transcriptome, and vital cell metabolic pathways. Understanding the cell type- and context-specificity of these interactions may unravel the high complexity of CD44 functions and lead to novel improved therapeutic interventions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Effects of Hyaluronan on Breast Cancer Aggressiveness
by
Arianna Parnigoni, Paola Moretto, Manuela Viola, Evgenia Karousou, Alberto Passi and Davide Vigetti
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2251
Abstract
The expression of the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in breast cancer cells is critical for determining tumor aggressiveness and targeting therapies. The presence of such receptors allows for the use of antagonists that
[...] Read more.
The expression of the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in breast cancer cells is critical for determining tumor aggressiveness and targeting therapies. The presence of such receptors allows for the use of antagonists that effectively reduce breast cancer growth and dissemination. However, the absence of such receptors in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) reduces the possibility of targeted therapy, making these tumors very aggressive with a poor outcome. Cancers are not solely composed of tumor cells, but also include several types of infiltrating cells, such as fibroblasts, macrophages, and other immune cells that have critical functions in regulating cancer cell behaviors. In addition to these cells, the extracellular matrix (ECM) has become an important player in many aspects of breast cancer biology, including cell growth, motility, metabolism, and chemoresistance. Hyaluronan (HA) is a key ECM component that promotes cell proliferation and migration in several malignancies. Notably, HA accumulation in the tumor stroma is a negative prognostic factor in breast cancer. HA metabolism depends on the fine balance between HA synthesis by HA synthases and degradation yielded by hyaluronidases. All the different cell types present in the tumor can release HA in the ECM, and in this review, we will describe the role of HA and HA metabolism in different breast cancer subtypes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Landscape of Small Leucine-Rich Proteoglycan Impact on Cancer Pathogenesis with a Focus on Biglycan and Lumican
by
Aikaterini Berdiaki, Eirini-Maria Giatagana, George Tzanakakis and Dragana Nikitovic
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2701
Abstract
Cancer development is a multifactorial procedure that involves changes in the cell microenvironment and specific modulations in cell functions. A tumor microenvironment contains tumor cells, non-malignant cells, blood vessels, cells of the immune system, stromal cells, and the extracellular matrix (ECM). The small
[...] Read more.
Cancer development is a multifactorial procedure that involves changes in the cell microenvironment and specific modulations in cell functions. A tumor microenvironment contains tumor cells, non-malignant cells, blood vessels, cells of the immune system, stromal cells, and the extracellular matrix (ECM). The small leucine-rich proteoglycans (SLRPs) are a family of nineteen proteoglycans, which are ubiquitously expressed among mammalian tissues and especially abundant in the ECM. SLRPs are divided into five canonical classes (classes I–III, containing fourteen members) and non-canonical classes (classes IV–V, including five members) based on their amino-acid structural sequence, chromosomal organization, and functional properties. Variations in both the protein core structure and glycosylation status lead to SLRP-specific interactions with cell membrane receptors, cytokines, growth factors, and structural ECM molecules. SLRPs have been implicated in the regulation of cancer growth, motility, and invasion, as well as in cancer-associated inflammation and autophagy, highlighting their crucial role in the processes of carcinogenesis. Except for the class I SLRP decorin, to which an anti-tumorigenic role has been attributed, other SLPRs’ roles have not been fully clarified. This review will focus on the functions of the class I and II SLRP members biglycan and lumican, which are correlated to various aspects of cancer development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
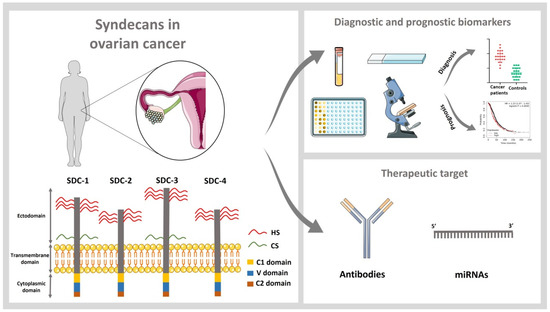
Role of Syndecans in Ovarian Cancer: New Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets
by
Julia Oto, Quang-Khoi Le, Sebastian D. Schäfer, Ludwig Kiesel, Josep Marí-Alexandre, Juan Gilabert-Estellés, Pilar Medina and Martin Götte
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2012
Abstract
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the eighth cancer both in prevalence and mortality in women and represents the deadliest female reproductive cancer. Due to generally vague symptoms, OC is frequently diagnosed only at a late and advanced stage, resulting in high mortality. The tumor
[...] Read more.
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the eighth cancer both in prevalence and mortality in women and represents the deadliest female reproductive cancer. Due to generally vague symptoms, OC is frequently diagnosed only at a late and advanced stage, resulting in high mortality. The tumor extracellular matrix and cellular matrix receptors play a key role in the pathogenesis of tumor progression. Syndecans are a family of four transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans (PG), including syndecan-1, -2, -3, and -4, which are dysregulated in a myriad of cancers, including OC. Many clinicopathological studies suggest that these proteins are promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for OC. Furthermore, functions of the syndecan family in the regulation of cellular processes make it an interesting pharmacological target for anticancer therapies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
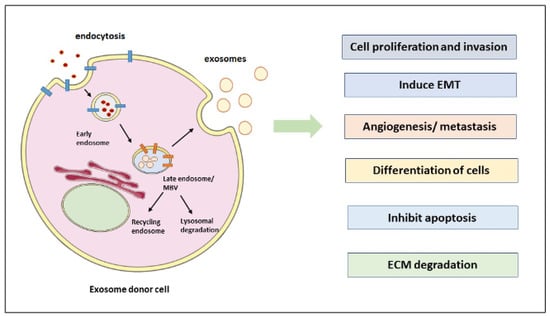
The Role of Exosomes in Epithelial–to-Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Functional Properties in Head and Neck Cancer
by
Nicholas S. Mastronikolis, Efthymios Kyrodimos, Despoina Spyropoulou, Alexander Delides, Evangelos Giotakis, Zoi Piperigkou and Nikos K. Karamanos
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3440
Abstract
Exosomes are nanosized vesicles that are produced in normal and cancer cells, promoting intracellular communication. In head and neck cancer (HNC), exosomes are involved in many undesirable events of cancer development and progression, including angiogenesis, tumor microenvironment (TME) remodeling, invasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT),
[...] Read more.
Exosomes are nanosized vesicles that are produced in normal and cancer cells, promoting intracellular communication. In head and neck cancer (HNC), exosomes are involved in many undesirable events of cancer development and progression, including angiogenesis, tumor microenvironment (TME) remodeling, invasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, and drug resistance. Exosomes are involved in altering the signaling pathways in recipient cells by the cargoes they carry. Proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids such as DNA fragments and RNAs (i.e., mRNAs, miRNAs, and long non-coding RNAs) are carried in the exosomes to promote cell communication. EMT is a critical cellular process in which epithelial cells are forced to become mesenchymal cells by the actions of SNAIL/SLUG, TWIST, and ZEB family transcription factors carried in exosomes that facilitate metastasis. In this critical review, we focused on exosome biogenesis, their cargoes, and their involvement in EMT induction and metastasis during HNC. Insights into exosome isolation and characterization, as well as their key role in ECM remodeling and degradation, are also presented and critically discussed. More importantly, this article addresses the role of exosomes in HNC and drug resistance induced in drug-sensitive cancer cells. In addition, exosomes have a great potential to be used as diagnostic and therapeutic tools. A better understanding on exosome biogenesis, composition, and functions in HNC will aid in developing novel therapeutic strategies to treat HNC, overcome therapy resistance, and avoid metastasis, which is a significant cause of cancer death.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditorial
Matrix Effectors and Cancer
by
Zoi Piperigkou and Nikos K. Karamanos
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2081
Abstract
Extracellular matrices (ECMs) are highly dynamic three-dimensional structural meshworks composed of macromolecules, such as proteoglycans/glycosaminoglycans (PGs/GAGs), collagens, laminins, elastin, (glyco)proteins, and matrix-degrading enzymes, such as proteases and glycosidases [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
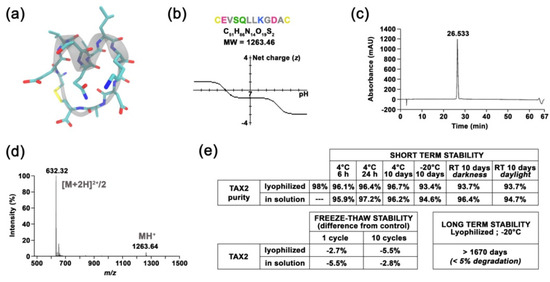
Targeting Ovarian Carcinoma with TSP-1:CD47 Antagonist TAX2 Activates Anti-Tumor Immunity
by
Albin Jeanne, Thomas Sarazin, Magalie Charlé, Catherine Moali, Caroline Fichel, Camille Boulagnon-Rombi, Maïté Callewaert, Marie-Christine Andry, Eric Diesis, Frédéric Delolme, Damien Rioult and Stéphane Dedieu
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 4509
Abstract
TAX2 peptide is a cyclic peptide that acts as an orthosteric antagonist for thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) interaction with CD47. TAX2 was first described for its anti-angiogenic activities and showed anti-cancer efficacy in numerous preclinical models. Here, we aimed at providing an extensive molecular characterization
[...] Read more.
TAX2 peptide is a cyclic peptide that acts as an orthosteric antagonist for thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) interaction with CD47. TAX2 was first described for its anti-angiogenic activities and showed anti-cancer efficacy in numerous preclinical models. Here, we aimed at providing an extensive molecular characterization of TAX2 mode of action, while evaluating its potential in ovarian cancer therapy. Multidisciplinary approaches were used to qualify a TAX2 drug candidate in terms of stability, solubility and potency. Then, efficacy studies, together with benchmark experiments, were performed in relevant mouse models of ovarian carcinoma. TAX2 peptide appears to be stable and soluble in clinically relevant solvents, while displaying a favorable safety profile. Moreover, clinical data mining allowed for the identification of TSP-1 as a relevant pharmacological target in ovarian cancer. In mice, TAX2 therapy inhibits ovarian tumor growth and metastatic dissemination, while activating anti-cancer adaptive immunity. Interestingly, TAX2 also synergizes when administered in combination with anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitiors. Altogether, our data expose TAX2 as an optimized candidate with advanced preclinical characterization. Using relevant syngeneic ovarian carcinoma models, we highlighted TAX2’s ability to convert poorly immunogenic tumors into ones displaying effective anti-tumor T-cell immunity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
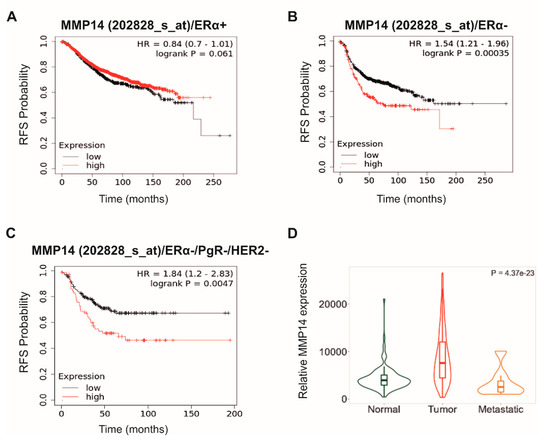
Open AccessArticle
Differential MMP-14 Targeting by Lumican-Derived Peptides Unraveled by In Silico Approach
by
Jonathan Dauvé, Nicolas Belloy, Romain Rivet, Nicolas Etique, Pierre Nizet, Katarzyna Pietraszek-Gremplewicz, Konstantina Karamanou, Manuel Dauchez, Laurent Ramont, Stéphane Brézillon and Stéphanie Baud
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3009
Abstract
Lumican, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) of the extracellular matrix (ECM), displays anti-tumor properties through its direct interaction with MMP-14. Lumican-derived peptides, such as lumcorin (17 amino acids) or L9M (10 amino acids), are able to inhibit the proteolytic activity of MMP-14 and
[...] Read more.
Lumican, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) of the extracellular matrix (ECM), displays anti-tumor properties through its direct interaction with MMP-14. Lumican-derived peptides, such as lumcorin (17 amino acids) or L9M (10 amino acids), are able to inhibit the proteolytic activity of MMP-14 and melanoma progression. This work aimed to visualize the interactions of lumican-derived peptides and MMP-14. Molecular modeling was used to characterize the interactions between lumican-derived peptides, such as lumcorin, L9M, and cyclic L9M (L9Mc, 12 amino acids), and MMP-14. The interaction of L9Mc with MMP-14 was preferential with the MT-Loop domain while lumcorin interacted more with the catalytic site. Key residues in the MMP-14 amino acid sequence were highlighted for the interaction between the inhibitory SLRP-derived peptides and MMP-14. In order to validate the in silico data, MMP-14 activity and migration assays were performed using murine B16F1 and human HT-144 melanoma cells. In contrast to the HT-144 melanoma cell line, L9Mc significantly inhibited the migration of B16F1 cells and the activity of MMP-14 but with less efficacy than lumican and lumcorin. L9Mc significantly inhibited the proliferation of B16F1 but not of HT-144 cells in vitro and primary melanoma tumor growth in vivo. Thus, the site of interaction between the domains of MMP-14 and lumcorin or L9Mc were different, which might explain the differences in the inhibitory effect of MMP-14 activity. Altogether, the biological assays validated the prediction of the in silico study. Possible and feasible improvements include molecular dynamics results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
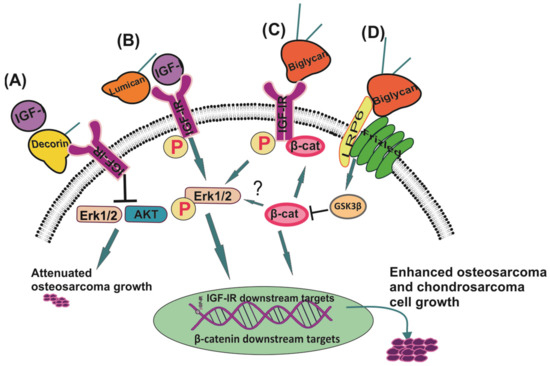
The Role of IGF/IGF-IR-Signaling and Extracellular Matrix Effectors in Bone Sarcoma Pathogenesis
by
George N. Tzanakakis, Eirini-Maria Giatagana, Aikaterini Berdiaki, Ioanna Spyridaki, Kyoko Hida, Monica Neagu, Aristidis M. Tsatsakis and Dragana Nikitovic
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 4158
Abstract
Bone sarcomas, mesenchymal origin tumors, represent a substantial group of varying neoplasms of a distinct entity. Bone sarcoma patients show a limited response or do not respond to chemotherapy. Notably, developing efficient chemotherapy approaches, dealing with chemoresistance, and preventing metastasis pose unmet challenges
[...] Read more.
Bone sarcomas, mesenchymal origin tumors, represent a substantial group of varying neoplasms of a distinct entity. Bone sarcoma patients show a limited response or do not respond to chemotherapy. Notably, developing efficient chemotherapy approaches, dealing with chemoresistance, and preventing metastasis pose unmet challenges in sarcoma therapy. Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 (IGF-1 and -2) and their respective receptors are a multifactorial system that significantly contributes to bone sarcoma pathogenesis. Whereas failures have been registered in creating novel targeted therapeutics aiming at the IGF pathway, new agent development should continue, evaluating combinatorial strategies for enhancing antitumor responses and better classifying the patients that could best benefit from these therapies. A plausible approach for developing a combinatorial strategy is to focus on the tumor microenvironment (TME) and processes executed therein. Herewith, we will discuss how the interplay between IGF-signaling and the TME constituents affects sarcomas’ basal functions and their response to therapy. This review highlights key studies focusing on IGF signaling in bone sarcomas, specifically studies underscoring novel properties that make this system an attractive therapeutic target and identifies new relationships that may be exploited. Potential direct and adjunct therapeutical implications of the extracellular matrix (ECM) effectors will also be summarized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Syndecan-1 Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through the Prognostically Relevant Tissue Factor Pathway and Additional Angiogenic Routes
by
Eyyad Nassar, Nourhan Hassan, Eslam A. El-Ghonaimy, Hebatallah Hassan, Mahmoud Salah Abdullah, Theresa V. Rottke, Ludwig Kiesel, Burkhard Greve, Sherif Abdelaziz Ibrahim and Martin Götte
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 3748
Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by increased angiogenesis, metastasis, and poor survival. Dysregulation of the cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan and signaling co-receptor Syndecan-1 is linked to poor prognosis. To study its role in angiogenesis, we silenced Syndecan-1 in TNBC cell lines
[...] Read more.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by increased angiogenesis, metastasis, and poor survival. Dysregulation of the cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan and signaling co-receptor Syndecan-1 is linked to poor prognosis. To study its role in angiogenesis, we silenced Syndecan-1 in TNBC cell lines using a 3D human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) co-culture system. Syndecan-1 siRNA depletion in SUM-149, MDA-MB-468, and MDA-MB-231 cells decreased HUVEC tubule network formation. Angiogenesis array revealed reduced VEGF-A and tissue factor (TF) in the Syndecan-1-silenced secretome. qPCR independently confirmed altered expression of
F3,
F7,
F2R/PAR1,
F2RL1/PAR2,
VEGF-A,
EDN1,
IGFBP1, and
IGFBP2 in SUM-149, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 cells. ELISA revealed reduced secreted endothelin-1 (SUM-149, MDA-MB-468) and TF (all cell lines) upon Syndecan-1 depletion, while TF pathway inhibitor treatment impaired angiogenesis. Survival analysis of 3951 patients demonstrated that high expression of
F3 and
F7 are associated with better relapse-free survival, whereas poor survival was observed in TNBC and p53 mutant basal breast cancer (
F3) and in ER-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer (
F2R, F2RL1). STRING protein network analysis revealed associations of Syndecan-1 with VEGF-A and IGFBP1, further associated with the TF and ET-1 pathways. Our study suggests that TNBC Syndecan-1 regulates angiogenesis via the TF and additional angiogenic pathways and marks its constituents as novel prognostic markers and therapeutic targets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
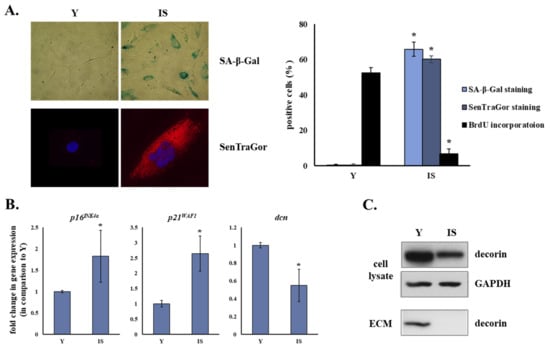
Down-Regulation of the Proteoglycan Decorin Fills in the Tumor-Promoting Phenotype of Ionizing Radiation-Induced Senescent Human Breast Stromal Fibroblasts
by
Eleni Mavrogonatou, Adamantia Papadopoulou, Asimina Fotopoulou, Stathis Tsimelis, Heba Bassiony, Andreas M. Yiacoumettis, Petros N. Panagiotou, Harris Pratsinis and Dimitris Kletsas
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3189
Abstract
Down-regulation of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan decorin in the stroma is considered a poor prognostic factor for breast cancer progression. Ionizing radiation, an established treatment for breast cancer, provokes the premature senescence of the adjacent to the tumor stromal fibroblasts. Here, we showed
[...] Read more.
Down-regulation of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan decorin in the stroma is considered a poor prognostic factor for breast cancer progression. Ionizing radiation, an established treatment for breast cancer, provokes the premature senescence of the adjacent to the tumor stromal fibroblasts. Here, we showed that senescent human breast stromal fibroblasts are characterized by the down-regulation of decorin at the mRNA and protein level, as well as by its decreased deposition in the pericellular extracellular matrix in vitro. Senescence-associated decorin down-regulation is a long-lasting process rather than an immediate response to γ-irradiation. Growth factors were demonstrated to participate in an autocrine manner in decorin down-regulation, with bFGF and VEGF being the critical mediators of the phenomenon. Autophagy inhibition by chloroquine reduced decorin mRNA levels, while autophagy activation using the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin enhanced decorin transcription. Interestingly, the secretome from a series of both untreated and irradiated human breast cancer cell lines with different molecular profiles inhibited decorin expression in young and senescent stromal fibroblasts, which was annulled by SU5402, a bFGF and VEGF inhibitor. The novel phenotypic trait of senescent human breast stromal fibroblasts revealed here is added to their already described cancer-promoting role via the formation of a tumor-permissive environment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Yin and Yang of Discoidin Domain Receptors (DDRs): Implications in Tumor Growth and Metastasis Development
by
Sandra Majo and Patrick Auguste
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 4925
Abstract
The tumor microenvironment is a complex structure composed of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and nontumoral cells (notably cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and immune cells). Collagens are the main components of the ECM and they are extensively remodeled during tumor progression. Some collagens are ligands
[...] Read more.
The tumor microenvironment is a complex structure composed of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and nontumoral cells (notably cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and immune cells). Collagens are the main components of the ECM and they are extensively remodeled during tumor progression. Some collagens are ligands for the discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases, DDR1 and DDR2. DDRs are involved in different stages of tumor development and metastasis formation. In this review, we present the different roles of DDRs in these processes and discuss controversial findings. We conclude by describing emerging DDR inhibitory strategies, which could be used as new alternatives for the treatment of patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Overexpression of Human Syndecan-1 Protects against the Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Mice
by
Andrea Reszegi, Katalin Karászi, Gábor Tóth, Kristóf Rada, Lóránd Váncza, Lilla Turiák, Zsuzsa Schaff, András Kiss, László Szilák, Gábor Szabó, Gábor Petővári, Anna Sebestyén, Katalin Dezső, Eszter Regős, Péter Tátrai, Kornélia Baghy and Ilona Kovalszky
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3898
Abstract
Although syndecan-1 (SDC1) is known to be dysregulated in various cancer types, its implication in tumorigenesis is poorly understood. Its effect may be detrimental or protective depending on the type of cancer. Our previous data suggest that SDC1 is protective against hepatocarcinogenesis. To
[...] Read more.
Although syndecan-1 (SDC1) is known to be dysregulated in various cancer types, its implication in tumorigenesis is poorly understood. Its effect may be detrimental or protective depending on the type of cancer. Our previous data suggest that SDC1 is protective against hepatocarcinogenesis. To further verify this notion, human SDC1 transgenic (hSDC1
+/+) mice were generated that expressed hSDC1 specifically in the liver under the control of the albumin promoter. Hepatocarcinogenesis was induced by a single dose of diethylnitrosamine (DEN) at an age of 15 days after birth, which resulted in tumors without cirrhosis in wild-type and hSDC1
+/+ mice. At the experimental endpoint, livers were examined macroscopically and histologically, as well as by immunohistochemistry, Western blot, receptor tyrosine kinase array, phosphoprotein array, and proteomic analysis. Liver-specific overexpression of hSDC1 resulted in an approximately six month delay in tumor formation via the promotion of SDC1 shedding, downregulation of lipid metabolism, inhibition of the mTOR and the β-catenin pathways, and activation of the Foxo1 and p53 transcription factors that lead to the upregulation of the cell cycle inhibitors p21 and p27. Furthermore, both of them are implicated in the regulation of intermediary metabolism. Proteomic analysis showed enhanced lipid metabolism, activation of motor proteins, and loss of mitochondrial electron transport proteins as promoters of cancer in wild-type tumors, inhibited in the hSDC1
+/+ livers. These complex mechanisms mimic the characteristics of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) induced human liver cancer successfully delayed by syndecan-1.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Key Matrix Remodeling Enzymes: Functions and Targeting in Cancer
by
Zoi Piperigkou, Konstantina Kyriakopoulou, Christos Koutsakis, Stylianos Mastronikolis and Nikos K. Karamanos
Cited by 67 | Viewed by 6346
Abstract
Tissue functionality and integrity demand continuous changes in distribution of major components in the extracellular matrices (ECMs) under normal conditions aiming tissue homeostasis. Major matrix degrading proteolytic enzymes are matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), plasminogen activators, atypical proteases such as intracellular cathepsins and glycolytic enzymes
[...] Read more.
Tissue functionality and integrity demand continuous changes in distribution of major components in the extracellular matrices (ECMs) under normal conditions aiming tissue homeostasis. Major matrix degrading proteolytic enzymes are matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), plasminogen activators, atypical proteases such as intracellular cathepsins and glycolytic enzymes including heparanase and hyaluronidases. Matrix proteases evoke epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and regulate ECM turnover under normal procedures as well as cancer cell phenotype, motility, invasion, autophagy, angiogenesis and exosome formation through vital signaling cascades. ECM remodeling is also achieved by glycolytic enzymes that are essential for cancer cell survival, proliferation and tumor progression. In this article, the types of major matrix remodeling enzymes, their effects in cancer initiation, propagation and progression as well as their pharmacological targeting and ongoing clinical trials are presented and critically discussed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Extracellular Small Leucine-Rich Proteoglycan Biglycan Is a Key Player in Gastric Cancer Aggressiveness
by
Filipe Pinto, Liliana Santos-Ferreira, Marta T. Pinto, Catarina Gomes and Celso A. Reis
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 3579
Abstract
Biglycan (
BGN gene), an extracellular proteoglycan, has been described to be associated with cancer aggressiveness. The purpose of this study was to clarify the clinical value of biglycan as a biomarker in multiple independent GC cohorts and determine the in vitro and
[...] Read more.
Biglycan (
BGN gene), an extracellular proteoglycan, has been described to be associated with cancer aggressiveness. The purpose of this study was to clarify the clinical value of biglycan as a biomarker in multiple independent GC cohorts and determine the in vitro and in vivo role of biglycan in GC malignant features. We found that
BGN is commonly over-expressed in all analyzed cohorts, being associated with disease relapse and poor prognosis in patients with advanced stages of disease. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that biglycan knock-out GC cells display major phenotypic changes with a lower cell survival, migration, and angiogenic potential when compared with biglycan expressing cells. Biglycan KO GC cells present increased levels of PARP1 and caspase-3 cleavage and a decreased expression of mesenchymal markers. Importantly, biglycan deficient GC cells that were supplemented with exogenous biglycan were able to restore biological features, such as survival, clonogenic and migratory capacities. Our in vitro and in vivo findings were validated in human GC samples, where
BGN expression was associated with several oncogenic gene signatures that were associated with apoptosis, cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. This study provided new insights on biglycan role in GC that should be taken in consideration as a key cellular regulator with major impact in tumor progression and patients’ clinical outcome.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
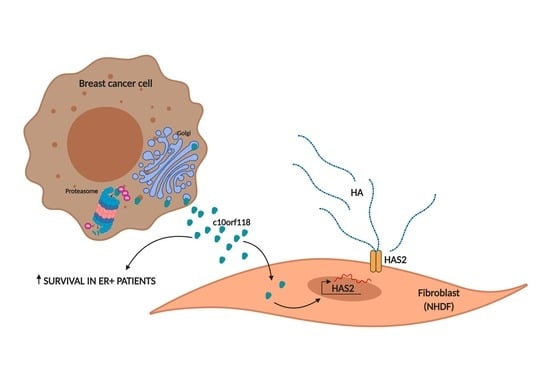
Open AccessArticle
The Secreted Protein C10orf118 Is a New Regulator of Hyaluronan Synthesis Involved in Tumour-Stroma Cross-Talk
by
Ilaria Caon, Maria Luisa D’Angelo, Barbara Bartolini, Elena Caravà, Arianna Parnigoni, Flavia Contino, Patrizia Cancemi, Paola Moretto, Nikos K. Karamanos, Alberto Passi, Davide Vigetti, Evgenia Karousou and Manuela Viola
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3009
Abstract
Interaction between cancer cells and their microenvironment is central in defining the fate of cancer development. Tumour cells secrete signals (cytokines, chemokines, growth factors) that modify the surrounding area, while the niche supplies structures and activities necessary for tumour maintenance and growth. Hyaluronan
[...] Read more.
Interaction between cancer cells and their microenvironment is central in defining the fate of cancer development. Tumour cells secrete signals (cytokines, chemokines, growth factors) that modify the surrounding area, while the niche supplies structures and activities necessary for tumour maintenance and growth. Hyaluronan (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan that constitute cancer cell niche and is known to influence tumour functions such as proliferation, migration and neoangiogenesis. The knowledge of the factors regulating HA synthesis and size is crucial in understanding the mechanisms sustaining tumour development. Here we show that a yet uncharacterized protein secreted by breast tumour cell lines, named c10orf118 (accession number NM_018017 in NCBI/BLAST, and Q7z3E2 according to the Uniprot identifier), with a predicted length of 898 amino acids, can induce the secretion of HA by stromal fibroblasts through the up-regulation of the hyaluronan synthase 2 gene (HAS2). Intracellularly, this protein is localized in the Golgi apparatus with a possible role in vesicle maturation and transport. The expression of c10orf118 was verified in breast cancer patient specimens and was found to be associated with the presence of estrogen receptor that characterizes a good patient survival. We suggest c10orf118 as a new player that influences the HA amount in breast cancer microenvironment and is associated with low aggressiveness of cancer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
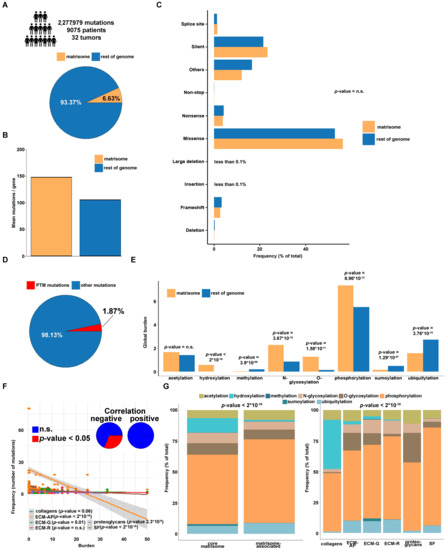
The Burden of Post-Translational Modification (PTM)—Disrupting Mutations in the Tumor Matrisome
by
Elisa Holstein, Annalena Dittmann, Anni Kääriäinen, Vilma Pesola, Jarkko Koivunen, Taina Pihlajaniemi, Alexandra Naba and Valerio Izzi
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5453
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the occurrence of mutations affecting post-translational modification (PTM) sites in matrisome genes across different tumor types, in light of their genomic and functional contexts and in comparison with the rest of the genome. Methods: This study spans 9075 tumor samples
[...] Read more.
Background: To evaluate the occurrence of mutations affecting post-translational modification (PTM) sites in matrisome genes across different tumor types, in light of their genomic and functional contexts and in comparison with the rest of the genome. Methods: This study spans 9075 tumor samples and 32 tumor types from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Pan-Cancer cohort and identifies 151,088 non-silent mutations in the coding regions of the matrisome, of which 1811 affecting known sites of hydroxylation, phosphorylation, N- and O-glycosylation, acetylation, ubiquitylation, sumoylation and methylation PTM. Results: PTM-disruptive mutations (PTM
mut) in the matrisome are less frequent than in the rest of the genome, seem independent of cell-of-origin patterns but show dependence on the nature of the matrisome protein affected and the background PTM types it generally harbors. Also, matrisome PTM
mut are often found among structural and functional protein regions and in proteins involved in homo- and heterotypic interactions, suggesting potential disruption of matrisome functions. Conclusions: Though quantitatively minoritarian in the spectrum of matrisome mutations, PTM
mut show distinctive features and damaging potential which might concur to deregulated structural, functional, and signaling networks in the tumor microenvironment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
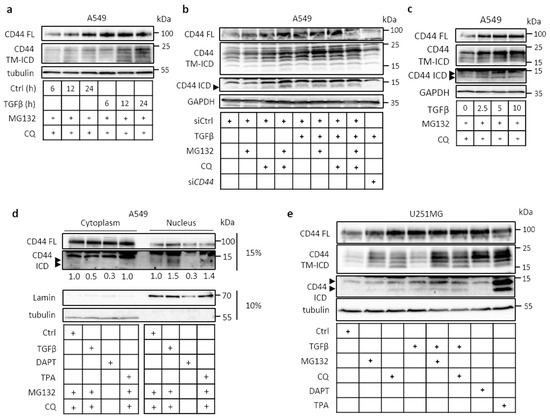
Open AccessArticle
TRAF4/6 Is Needed for CD44 Cleavage and Migration via RAC1 Activation
by
Constantinos Kolliopoulos, Athanasios Chatzopoulos, Spyros S. Skandalis, Carl-Henrik Heldin and Paraskevi Heldin
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3231
Abstract
The hyaluronan receptor CD44 can undergo proteolytic cleavage in two steps, leading to the release of its intracellular domain; this domain is translocated to the nucleus, where it affects the transcription of target genes. We report that CD44 cleavage in A549 lung cancer
[...] Read more.
The hyaluronan receptor CD44 can undergo proteolytic cleavage in two steps, leading to the release of its intracellular domain; this domain is translocated to the nucleus, where it affects the transcription of target genes. We report that CD44 cleavage in A549 lung cancer cells and other cells is promoted by transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) in a manner that is dependent on ubiquitin ligase tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 4 or 6 (TRAF4 or TRAF6, respectively). Stem-like A549 cells grown in spheres displayed increased TRAF4-dependent expression of CD44 variant isoforms, CD44 cleavage, and hyaluronan synthesis. Mechanistically, TRAF4 activated the small GTPase RAC1. CD44-dependent migration of A549 cells was inhibited by siRNA-mediated knockdown of TRAF4, which was rescued by the transfection of a constitutively active RAC1 mutant. Our findings support the notion that TRAF4/6 mediates pro-tumorigenic effects of CD44, and suggests that inhibitors of CD44 signaling via TRAF4/6 and RAC1 may be beneficial in the treatment of tumor patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
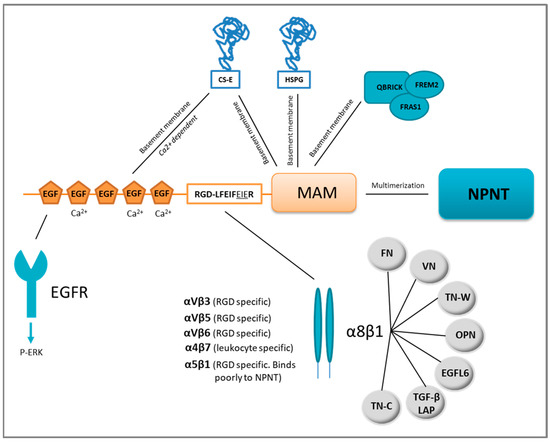
Open AccessReview
Nephronectin as a Matrix Effector in Cancer
by
Synnøve Norvoll Magnussen, Jimita Toraskar, Elin Hadler-Olsen, Tonje S. Steigedal and Gunbjørg Svineng
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3545
Abstract
The extracellular matrix protein nephronectin plays an important regulatory role during embryonic development, controlling renal organogenesis through integrin α8β1 association. Nephronectin has three main domains: five N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domains, a linker region harbouring two integrin-binding motifs (RGD and LFEIFEIER), and a
[...] Read more.
The extracellular matrix protein nephronectin plays an important regulatory role during embryonic development, controlling renal organogenesis through integrin α8β1 association. Nephronectin has three main domains: five N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domains, a linker region harbouring two integrin-binding motifs (RGD and LFEIFEIER), and a C-terminal MAM domain. In this review, we look into the domain-related functions of nephronectin, and tissue distribution and expression. During the last two decades it has become evident that nephronectin also plays a role during cancer progression and in particular metastasis. Nephronectin is overexpressed in both human and mouse breast cancer compared to normal breast tissue where the protein is absent. Cancer cells expressing elevated levels of nephronectin acquire increased ability to colonise distant organs. In particular, the enhancer-motif (LFEIFEIER) which is specific to the integrin α8β1 association induces viability via p38 MAPK and plays a role in colonization. Integrins have long been desired as therapeutic targets, where low efficiency and receptor redundancy have been major issues. Based on the summarised publications, the enhancer-motif of nephronectin could present a novel therapeutic target.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Collagen Type XI Alpha 1 (COL11A1): A Novel Biomarker and a Key Player in Cancer
by
Sameera Nallanthighal, James Patrick Heiserman and Dong-Joo Cheon
Cited by 59 | Viewed by 6016
Abstract
Collagen type XI alpha 1 (COL11A1), one of the three alpha chains of type XI collagen, is crucial for bone development and collagen fiber assembly. Interestingly, COL11A1 expression is increased in several cancers and high levels of COL11A1 are often associated with poor
[...] Read more.
Collagen type XI alpha 1 (COL11A1), one of the three alpha chains of type XI collagen, is crucial for bone development and collagen fiber assembly. Interestingly, COL11A1 expression is increased in several cancers and high levels of COL11A1 are often associated with poor survival, chemoresistance, and recurrence. This review will discuss the recent discoveries in the biological functions of COL11A1 in cancer. COL11A1 is predominantly expressed and secreted by a subset of cancer-associated fibroblasts, modulating tumor-stroma interaction and mechanical properties of extracellular matrix. COL11A1 also promotes cancer cell migration, metastasis, and therapy resistance by activating pro-survival pathways and modulating tumor metabolic phenotype. Several inhibitors that are currently being tested in clinical trials for cancer or used in clinic for other diseases, can be potentially used to target COL11A1 signaling. Collectively, this review underscores the role of COL11A1 as a promising biomarker and a key player in cancer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix
by
Vasiliki Zolota, Vasiliki Tzelepi, Zoi Piperigkou, Helen Kourea, Efthymia Papakonstantinou, Maria-Ioanna Argentou and Nikos K. Karamanos
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 5532
Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subgroup of breast cancer characterized by genomic complexity and therapeutic options limited to only standard chemotherapy. Although it has been suggested that stratifying TNBC patients by pathway-specific molecular alterations may predict benefit from specific therapeutic agents,
[...] Read more.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subgroup of breast cancer characterized by genomic complexity and therapeutic options limited to only standard chemotherapy. Although it has been suggested that stratifying TNBC patients by pathway-specific molecular alterations may predict benefit from specific therapeutic agents, application in routine clinical practice has not yet been established. There is a growing body of the literature supporting that epigenetic modifications comprised by DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling and non-coding RNAs play a fundamental role in TNBC pathogenesis. Extracellular matrix (ECM) is a highly dynamic 3D network of macromolecules with structural and cellular regulatory roles. Alterations in the expression of ECM components result in uncontrolled matrix remodeling, thus affecting its ability to regulate vital functions of cancer cells, including proliferation, migration, adhesion, invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Recent molecular data highlight the major role of tumor microenvironment and ECM alterations in TNBC and approaches for targeting tumor microenvironment have recently been recognized as potential therapeutic strategies. Notably, many of the ECM/EMT modifications in cancer are largely driven by epigenetic events, highlighting the pleiotropic effects of the epigenetic network in TNBC. This article presents and critically discusses the current knowledge on the epigenetic alterations correlated with TNBC pathogenesis, with emphasis on those associated with ECM/EMT modifications, their prognostic and predictive value and their use as therapeutic targets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Syndecan-1 Overexpressing Mesothelioma Cells Inhibit Proliferation, Wound Healing, and Tube Formation of Endothelial Cells
by
Joman Javadi, Ghazal Heidari-Hamedani, Angelika Schmalzl, Tünde Szatmári, Muzaffer Metintas, Pontus Aspenström, Anders Hjerpe and Katalin Dobra
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3545
Abstract
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive tumor of the serosal cavities. Angiogenesis is important for mesothelioma progression, but so far, anti-angiogenic agents have not improved patient survival. Our hypothesis is that better understanding of the regulation of angiogenesis in this tumor would largely
[...] Read more.
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive tumor of the serosal cavities. Angiogenesis is important for mesothelioma progression, but so far, anti-angiogenic agents have not improved patient survival. Our hypothesis is that better understanding of the regulation of angiogenesis in this tumor would largely improve the success of such a therapy. Syndecan-1 (SDC-1) is a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan that acts as a co-receptor in various cellular processes including angiogenesis. In MM, the expression of SDC-1 is generally low but when present, SDC-1 associates to epithelioid differentiation, inhibition of tumor cell migration and favorable prognosis, meanwhile SDC-1 decrease deteriorates the prognosis. In the present study, we studied the effect of SDC-1 overexpression and silencing on MM cells ability to secrete angiogenic factors and monitored the downstream effect of SDC-1 modulation on endothelial cells proliferation, wound healing, and tube formation. This was done by adding conditioned medium from SDC-1 transfected and SDC-1 silenced mesothelioma cells to endothelial cells. Moreover, we investigated the interplay and molecular functional changes in angiogenesis in a co-culture system and characterized the soluble angiogenesis-related factors secreted to the conditioned media. We demonstrated that SDC-1 over-expression inhibited the proliferation, wound healing, and tube formation of endothelial cells. This effect was mediated by a multitude of angiogenic factors comprising angiopoietin-1 (Fold change ± SD: 0.65 ± 0.07), FGF-4 (1.45 ± 0.04), HGF (1.33 ± 0.07), NRG1-β1 (1.35 ± 0.08), TSP-1 (0.8 ± 0.02), TIMP-1 (0.89 ± 0.01) and TGF-β1 (1.35 ± 0.01). SDC-1 silencing increased IL8 (1.33 ± 0.06), promoted wound closure, but did not influence the tube formation of endothelial cells. Pleural effusions from mesothelioma patients showed that Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) levels correlate to soluble SDC-1 levels and have prognostic value. In conclusion, SDC-1 over-expression affects the angiogenic factor secretion of mesothelioma cells and thereby inhibits endothelial cells proliferation, tube formation, and wound healing. VEGF could be used in prognostic evaluation of mesothelioma patients together with SDC-1.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Adhesome Network: Key Components Shaping the Tumour Stroma
by
Pinelopi A. Nikolopoulou, Maria A. Koufaki and Vassiliki Kostourou
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4638
Abstract
Beyond the conventional perception of solid tumours as mere masses of cancer cells, advanced cancer research focuses on the complex contributions of tumour-associated host cells that are known as “tumour microenvironment” (TME). It has been long appreciated that the tumour stroma, composed mainly
[...] Read more.
Beyond the conventional perception of solid tumours as mere masses of cancer cells, advanced cancer research focuses on the complex contributions of tumour-associated host cells that are known as “tumour microenvironment” (TME). It has been long appreciated that the tumour stroma, composed mainly of blood vessels, cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells, together with the extracellular matrix (ECM), define the tumour architecture and influence cancer cell properties. Besides soluble cues, that mediate the crosstalk between tumour and stroma cells, cell adhesion to ECM arises as a crucial determinant in cancer progression. In this review, we discuss how adhesome, the intracellular protein network formed at cell adhesions, regulate the TME and control malignancy. The role of adhesome extends beyond the physical attachment of cells to ECM and the regulation of cytoskeletal remodelling and acts as a signalling and mechanosensing hub, orchestrating cellular responses that shape the tumour milieu.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Interactome of Cancer-Related Lysyl Oxidase and Lysyl Oxidase-Like Proteins
by
Sylvain D. Vallet, Coline Berthollier, Romain Salza, Laurent Muller and Sylvie Ricard-Blum
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 3632
Abstract
The members of the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family are amine oxidases, which initiate the covalent cross-linking of the extracellular matrix (ECM), regulate ECM stiffness, and contribute to cancer progression. The aim of this study was to build the first draft of the interactome
[...] Read more.
The members of the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family are amine oxidases, which initiate the covalent cross-linking of the extracellular matrix (ECM), regulate ECM stiffness, and contribute to cancer progression. The aim of this study was to build the first draft of the interactome of the five members of the LOX family in order to determine its molecular functions, the biological and signaling pathways mediating these functions, the biological processes it is involved in, and if and how it is rewired in cancer. In vitro binding assays, based on surface plasmon resonance and bio-layer interferometry, combined with queries of interaction databases and interaction datasets, were used to retrieve interaction data. The interactome was then analyzed using computational tools. We identified 31 new interactions and 14 new partners of LOXL2, including the α5β1 integrin, and built an interactome comprising 320 proteins, 5 glycosaminoglycans, and 399 interactions. This network participates in ECM organization, degradation and cross-linking, cell-ECM interactions mediated by non-integrin and integrin receptors, protein folding and chaperone activity, organ and blood vessel development, cellular response to stress, and signal transduction. We showed that this network is rewired in colorectal carcinoma, leading to a switch from ECM organization to protein folding and chaperone activity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
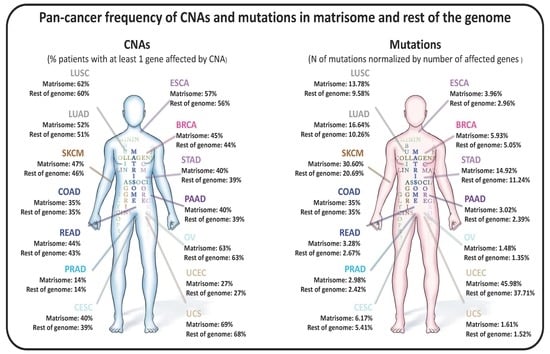
Open AccessArticle
Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Genomic Alterations and Mutations of the Matrisome
by
Valerio Izzi, Martin N. Davis and Alexandra Naba
Cited by 52 | Viewed by 7222
Abstract
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a master regulator of all cellular functions and a major component of the tumor microenvironment. We previously defined the “matrisome” as the ensemble of genes encoding ECM proteins and proteins modulating ECM structure or function. While compositional and
[...] Read more.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a master regulator of all cellular functions and a major component of the tumor microenvironment. We previously defined the “matrisome” as the ensemble of genes encoding ECM proteins and proteins modulating ECM structure or function. While compositional and biomechanical changes in the ECM regulate cancer progression, no study has investigated the genomic alterations of matrisome genes in cancers and their consequences. Here, mining The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data, we found that copy number alterations and mutations are frequent in matrisome genes, even more so than in the rest of the genome. We also found that these alterations are predicted to significantly impact gene expression and protein function. Moreover, we identified matrisome genes whose mutational burden is an independent predictor of survival. We propose that studying genomic alterations of matrisome genes will further our understanding of the roles of this compartment in cancer progression and will lead to the development of innovative therapeutic strategies targeting the ECM.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
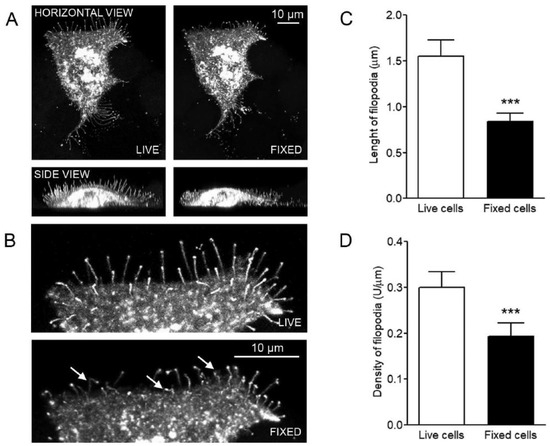
The Density and Length of Filopodia Associate with the Activity of Hyaluronan Synthesis in Tumor Cells
by
Heikki Kyykallio, Sanna Oikari, María Bueno Álvez, Carlos José Gallardo Dodd, Janne Capra and Kirsi Rilla
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5269
Abstract
Filopodia are multifunctional finger-like plasma membrane protrusions with bundles of actin filaments that exist in virtually all cell types. It has been known for some time that hyaluronan synthesis activity induces filopodial growth. However, because of technical challenges in the studies of these
[...] Read more.
Filopodia are multifunctional finger-like plasma membrane protrusions with bundles of actin filaments that exist in virtually all cell types. It has been known for some time that hyaluronan synthesis activity induces filopodial growth. However, because of technical challenges in the studies of these slender and fragile structures, no quantitative analyses have been performed so far to indicate their association with hyaluronan synthesis. In this work we comprehensively address the direct quantification of filopodial traits, covering for the first time length and density measurements in a series of human cancer cell lines with variable levels of hyaluronan synthesis. The synthesis and plasma membrane binding of hyaluronan were manipulated with hyaluronan synthase 3 (HAS3) and hyaluronan receptor CD44 overexpression, and treatments with mannose, 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU), and glucosamine. The results of this work show that the growth of filopodia was associated with the levels of hyaluronan synthesis but was not dependent on CD44 expression. The results confirm the hypothesis that abundance and length of filopodia in cancer cells is associated with the activity of hyaluronan synthesis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Non-Anticoagulant Heparan Sulfate from the Ascidian Phallusia nigra Prevents Colon Carcinoma Metastasis in Mice by Disrupting Platelet-Tumor Cell Interaction
by
Christiane F. S. Silva, Juliana M. Motta, Felipe C. O. B. Teixeira, Angélica M. Gomes, Eduardo Vilanova, Eliene O. Kozlowski, Lubor Borsig and Mauro S. G. Pavão
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2851
Abstract
Although metastasis is the primary cause of death in patients with malignant solid tumors, efficient anti-metastatic therapies are not clinically available currently. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans from marine sources have shown promising pharmacological effects, acting on different steps of the metastatic process. Oversulfated dermatan sulfates
[...] Read more.
Although metastasis is the primary cause of death in patients with malignant solid tumors, efficient anti-metastatic therapies are not clinically available currently. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans from marine sources have shown promising pharmacological effects, acting on different steps of the metastatic process. Oversulfated dermatan sulfates from ascidians are effective in preventing metastasis by inhibition of P-selectin, a platelet surface protein involved in the platelet-tumor cell emboli formation. We report in this work that the heparan sulfate isolated from the viscera of the ascidian
Phallusia nigra drastically attenuates metastases of colon carcinoma cells in mice. Our in vitro and in vivo assessments demonstrate that the
P. nigra glycan has very low anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities and a reduced hypotension potential, although it efficiently prevented metastasis. Therefore, it may be a promising candidate for the development of a novel anti-metastatic drug.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures