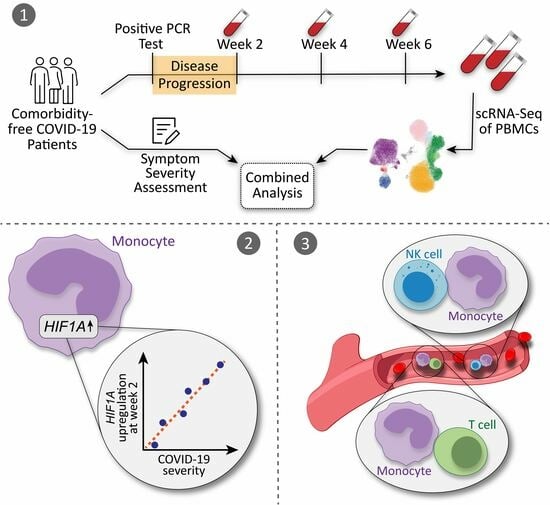
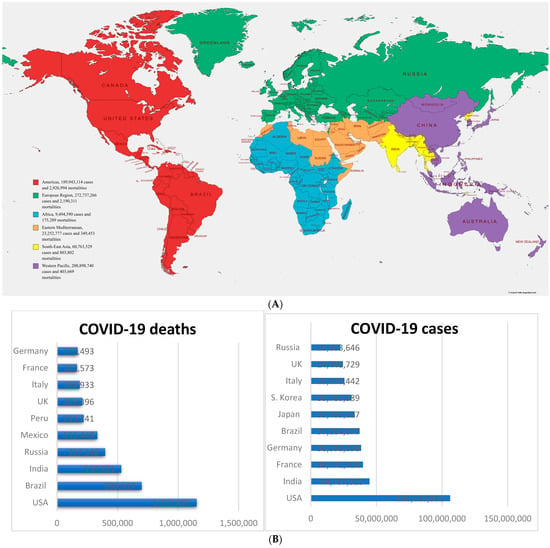
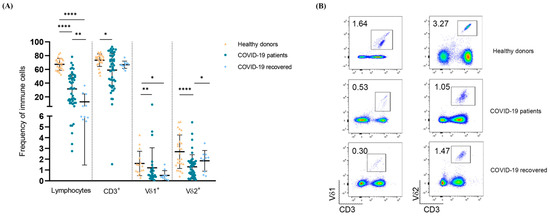
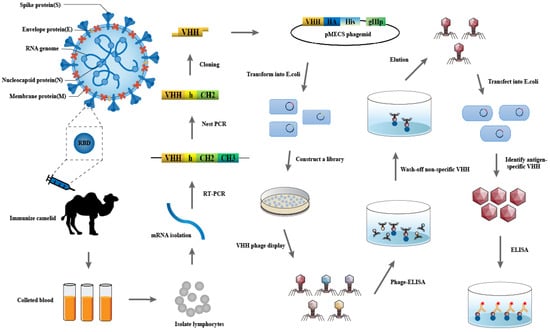
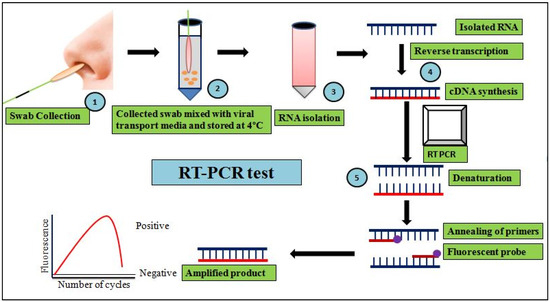
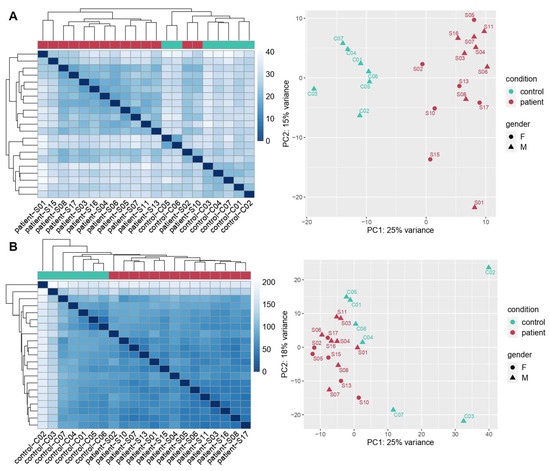
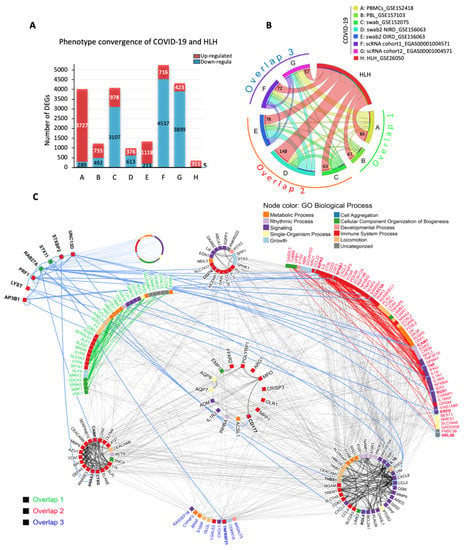
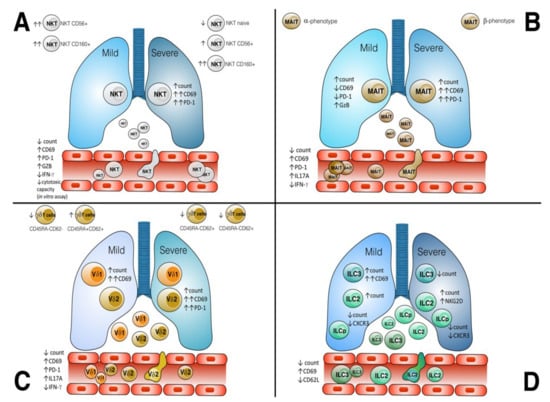
Cellular Immunology and COVID-19
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cellular Immunology".
Viewed by 161284Editor
Interests: primary immunodeficiencies; vaccines; anti-infectious immunity; mucosal immunity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
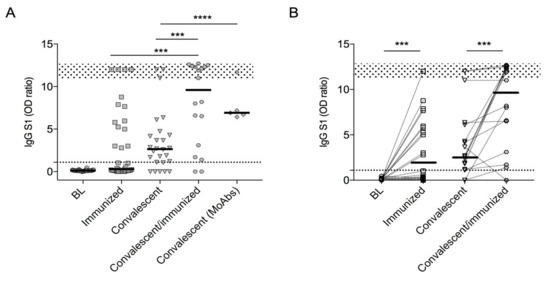
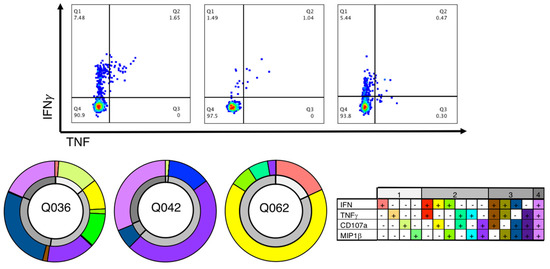
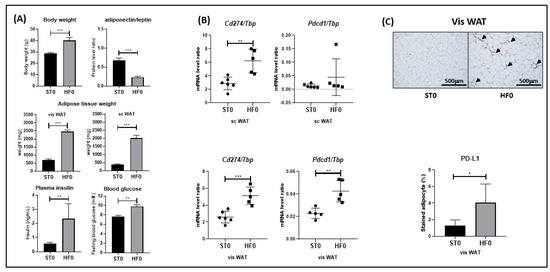
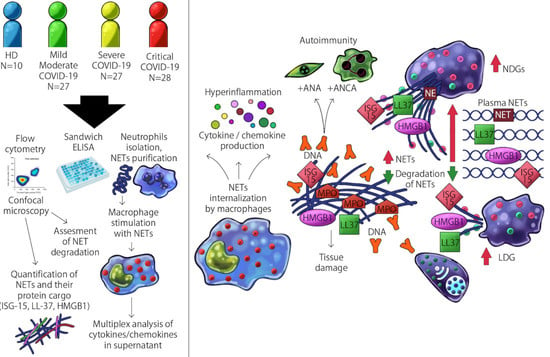
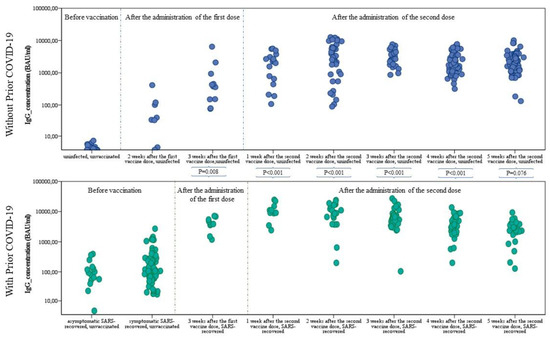
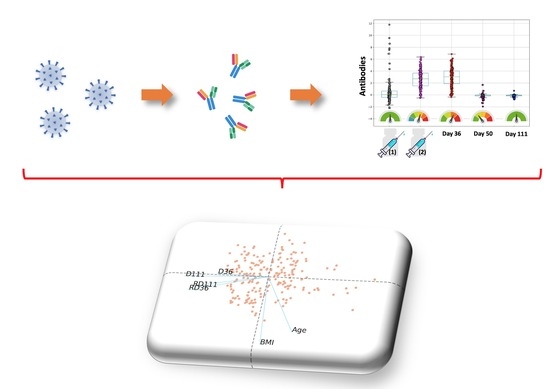
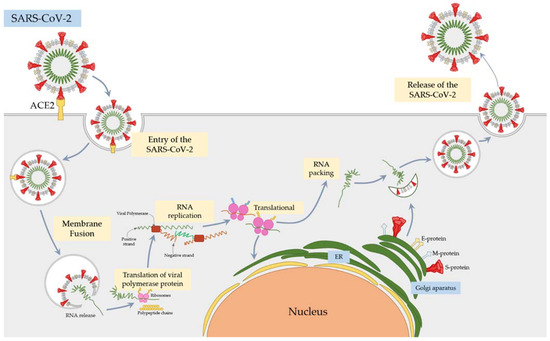
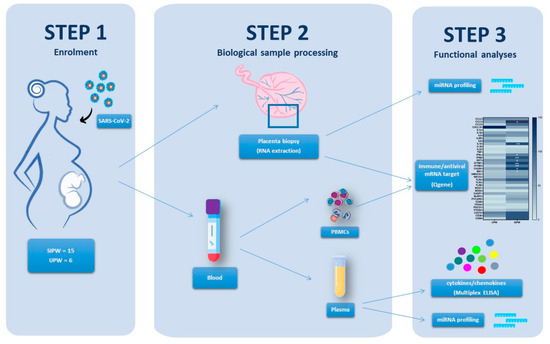
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic continues to spread and cause COVID-19 disease and death. Vaccination is the safest and most effective tool to achieve a protective response in most individuals. Effective vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 have been rapidly developed and are being administered with the aim of preventing COVID-19, stopping viral circulation, and terminating the pandemic. Cellular immune responses protect us from re-infection through their synergistic action. Immune cells migrate in response to chemokines to the inflamed tissue and reinforce protection by secreting antibodies locally. The aim of vaccination is to generate long-term immune memory by the pool of memory cells, including T cells, high-affinity memory B cells, and plasma cells, all able to prevent reinfection. Specificity and rapidity of action are the indispensable properties of protective immune memory. Differently from memory T cells, B cells have the ability to improve their specificity by repeated steps of somatic mutation and selection in the germinal centers. If the antibodies produced by MBCs and plasma cells have a high affinity for the pathogen, this is immediately eliminated.
Therefore, this Topical Collection will summarize the latest molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in SARS-Cov-2 short- and long-term protection
We look forward to your contributions.
Prof. Dr. Isabella Quinti
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- immunological memory
- COVID-19
- T and B lymphocytes