Survey of Cryptographic Topics
A topical collection in Cryptography (ISSN 2410-387X).
Viewed by 39648
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Josef Pieprzyk
Prof. Dr. Josef Pieprzyk
 Prof. Dr. Josef Pieprzyk
Prof. Dr. Josef Pieprzyk
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
1. Data61, CSIRO (The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation), Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia
2. Insitute of Computer Science, Polish Academy of Science, 02-668 Warszawa, Poland
Interests: algorithms and complexity; cryptography; information security; security of computer networks
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The aim of this collection is to collect high-quality survey papers on topics related to cryptography.
Overviews of the current state of cryptographic research activities are invited. They may target a specific field or area of cryptography. They may focus on: (1) identification of research gaps and future research directions; (2) ethical/social aspects of cryptography and their impact on human rights and social coherence; and (3) cryptographic practice, implementation, and standardisation. Needless to say, all submissions are subject to a normal review process.
Prof. Dr. Josef Pieprzyk
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cryptography is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (6 papers)
Open AccessReview
A Survey on Complexity Measures for Pseudo-Random Sequences
by
Chunlei Li
Viewed by 1288
Abstract
Since the introduction of the Kolmogorov complexity of binary sequences in the 1960s, there have been significant advancements on the topic of complexity measures for randomness assessment, which are of fundamental importance in theoretical computer science and of practical interest in cryptography. This
[...] Read more.
Since the introduction of the Kolmogorov complexity of binary sequences in the 1960s, there have been significant advancements on the topic of complexity measures for randomness assessment, which are of fundamental importance in theoretical computer science and of practical interest in cryptography. This survey reviews notable research from the past four decades on the linear, quadratic and maximum-order complexities of pseudo-random sequences, and their relations with Lempel–Ziv complexity, expansion complexity, 2-adic complexity and correlation measures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Random Number Generators: Principles and Applications
by
Anastasios Bikos, Panagiotis E. Nastou, Georgios Petroudis and Yannis C. Stamatiou
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 5375
Abstract
In this paper, we present approaches to generating random numbers, along with potential applications. Rather than trying to provide extensive coverage of several techniques or algorithms that have appeared in the scientific literature, we focus on some representative approaches, presenting their workings and
[...] Read more.
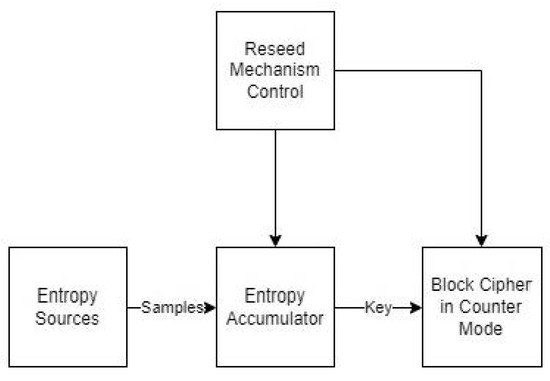
In this paper, we present approaches to generating random numbers, along with potential applications. Rather than trying to provide extensive coverage of several techniques or algorithms that have appeared in the scientific literature, we focus on some representative approaches, presenting their workings and properties in detail. Our goal is to delineate their strengths and weaknesses, as well as their potential application domains, so that the reader can judge what would be the best approach for the application at hand, possibly a combination of the available approaches. For instance, a physical source of randomness can be used for the initial seed; then, suitable preprocessing can enhance its randomness; then, the output of preprocessing can feed different types of generators, e.g., a linear congruential generator, a cryptographically secure one and one based on the combination of one-way hash functions and shared key cryptoalgorithms in various modes of operation. Then, if desired, the outputs of the different generators can be combined, giving the final random sequence. Moreover, we present a set of practical randomness tests that can be applied to the outputs of random number generators in order to assess their randomness characteristics. In order to demonstrate the importance of unpredictable random sequences, we present an application of cryptographically secure generators in domains where unpredictability is one of the major requirements, i.e., eLotteries and cryptographic key generation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Survey of Post-Quantum Cryptography: Start of a New Race
by
Duc-Thuan Dam, Thai-Ha Tran, Van-Phuc Hoang, Cong-Kha Pham and Trong-Thuc Hoang
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 16093
Abstract
Information security is a fundamental and urgent issue in the digital transformation era. Cryptographic techniques and digital signatures have been applied to protect and authenticate relevant information. However, with the advent of quantum computers and quantum algorithms, classical cryptographic techniques have been in
[...] Read more.
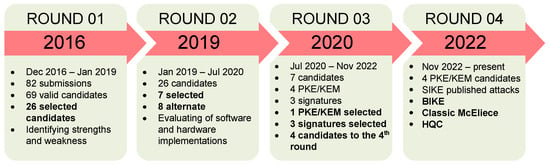
Information security is a fundamental and urgent issue in the digital transformation era. Cryptographic techniques and digital signatures have been applied to protect and authenticate relevant information. However, with the advent of quantum computers and quantum algorithms, classical cryptographic techniques have been in danger of collapsing because quantum computers can solve complex problems in polynomial time. Stemming from that risk, researchers worldwide have stepped up research on post-quantum algorithms to resist attack by quantum computers. In this review paper, we survey studies in recent years on post-quantum cryptography (PQC) and provide statistics on the number and content of publications, including a literature overview, detailed explanations of the most common methods so far, current implementation status, implementation comparisons, and discussion on future work. These studies focused on essential public cryptography techniques and digital signature schemes, and the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) launched a competition to select the best candidate for the expected standard. Recent studies have practically implemented the public key encryption/key encapsulation mechanism (PKE/KEM) and digital signature schemes on different hardware platforms and applied various optimization measures based on other criteria. Along with the increasing number of scientific publications, the recent trend of PQC research is increasingly evident and is the general trend in the cryptography industry. The movement opens up a promising avenue for researchers in public key cryptography and digital signatures, especially on algorithms selected by NIST.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Applications of Neural Network-Based AI in Cryptography
by
Abderrahmane Nitaj and Tajjeeddine Rachidi
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 10695
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a modern technology that allows plenty of advantages in daily life, such as predicting weather, finding directions, classifying images and videos, even automatically generating code, text, and videos. Other essential technologies such as blockchain and cybersecurity also benefit from
[...] Read more.
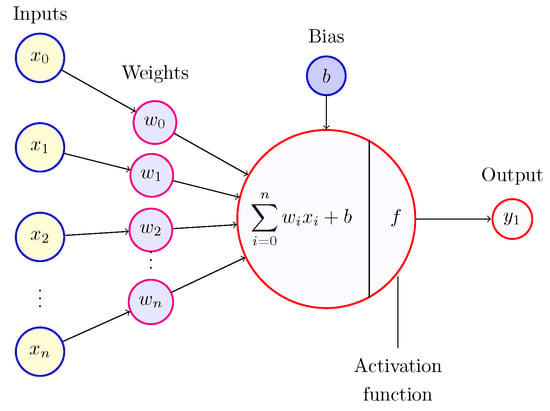
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a modern technology that allows plenty of advantages in daily life, such as predicting weather, finding directions, classifying images and videos, even automatically generating code, text, and videos. Other essential technologies such as blockchain and cybersecurity also benefit from AI. As a core component used in blockchain and cybersecurity, cryptography can benefit from AI in order to enhance the confidentiality and integrity of cyberspace. In this paper, we review the algorithms underlying four prominent cryptographic cryptosystems, namely the Advanced Encryption Standard, the Rivest–Shamir–Adleman, Learning with Errors, and the Ascon family of cryptographic algorithms for authenticated encryption. Where possible, we pinpoint areas where AI can be used to help improve their security.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Anonymous Homomorphic IBE with Application to Anonymous Aggregation
by
Michael Clear and Hitesh Tewari
Viewed by 2045
Abstract
All anonymous identity-based encryption (IBE) schemes that are group homomorphic (to the best of our knowledge) require knowledge of the identity to compute the homomorphic operation. This paper is motivated by this open problem, namely to construct an anonymous group-homomorphic IBE scheme that
[...] Read more.
All anonymous identity-based encryption (IBE) schemes that are group homomorphic (to the best of our knowledge) require knowledge of the identity to compute the homomorphic operation. This paper is motivated by this open problem, namely to construct an anonymous group-homomorphic IBE scheme that does not sacrifice anonymity to perform homomorphic operations. Note that even when strong assumptions, such as indistinguishability obfuscation (iO), are permitted, no schemes are known. We succeed in solving this open problem by assuming iO and the hardness of the DBDH problem over rings (specifically,
for RSA modulus
N). We then use the existence of such a scheme to construct an IBE scheme with re-randomizable anonymous encryption keys, which we prove to be IND-ID-RCCA secure. Finally, we use our results to construct identity-based anonymous aggregation protocols.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Algebraic Cryptanalysis with MRHS Equations
by
Pavol Zajac
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2397
Abstract
In this work, we survey the existing research in the area of algebraic cryptanalysis based on Multiple Right-Hand Sides (MRHS) equations (MRHS cryptanalysis). MRHS equation is a formal inclusion that contains linear combinations of variables on the left-hand side, and a potential set
[...] Read more.
In this work, we survey the existing research in the area of algebraic cryptanalysis based on Multiple Right-Hand Sides (MRHS) equations (MRHS cryptanalysis). MRHS equation is a formal inclusion that contains linear combinations of variables on the left-hand side, and a potential set of values for these combinations on the right-hand side. We describe MRHS equation systems in detail, including the evolution of this representation. Then we provide an overview of the methods that can be used to solve MRHS equation systems. Finally, we explore the use of MRHS equation systems in algebraic cryptanalysis and survey existing experimental results.
Full article