Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Marek Szopa
Prof. Dr. Marek Szopa
 Prof. Dr. Marek Szopa
Prof. Dr. Marek Szopa
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Operations Research, College of Informatics and Communication, University of Economics in Katowice, ul. Bogucicka 3, 40-287 Katowice, Poland
Interests: quantum economics; quantum games; quantum communication
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Quantum mechanics is one of the most prolific theories of all time. Despite the many controversies it has aroused since its conception, its predictions have been confirmed experimentally with incredible accuracy. It has also been used in a variety of fields, such as quantum economics (a very promising novel field of its application), quantum computation, quantum information science, quantum electronics, quantum cosmology, and quantum chemistry.
This EC aims to include relevant entries and invite more scholars to contribute to related entries on the Encyclopedia platform. It’s free of charge and each submission will undergo a formal peer review process.
Prof. Dr. Marek Szopa
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Encyclopedia is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1000 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- quantum mechanics
- quantum economics
- quantum computation
- quantum information science
- quantum electronics
- quantum cosmology
- quantum chemistry
Published Papers (3 papers)
Open AccessEntry
Wavefunction Collapse Broadens Molecular Spectrum
by
Peter Lebedev-Stepanov
Viewed by 1672
Definition
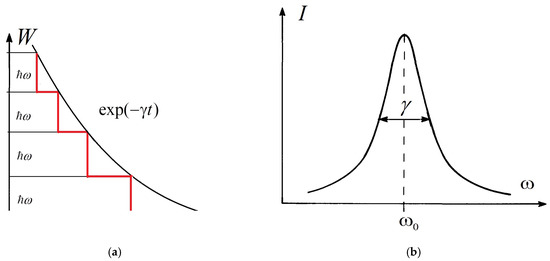
Spectral lines in the optical spectra of atoms, molecules, and other quantum systems are characterized by a range of frequencies
or a range of wavelengths
, where
c is the speed of light. Such a
[...] Read more.
Spectral lines in the optical spectra of atoms, molecules, and other quantum systems are characterized by a range of frequencies
or a range of wavelengths
, where
c is the speed of light. Such a frequency or wavelength range is called the width of the spectral lines (linewidth). It is influenced by many specific factors. Thermal motion of the molecules results in broadening of the lines as a result of the Doppler effect (thermal broadening) and by their collisions (pressure broadening). The electric fields of neighboring molecules lead to Stark broadening. The linewidth to be considered here is the so-called parametric broadening (PB) of spectral lines in the optical spectrum. PB can be considered the fundamental type of broadening of the electronic vibrational–rotational (rovibronic) transitions in a molecule, which is the direct manifestation of the basic concept of the collapse of a wavefunction that is postulated by the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. Thus, that concept appears to be not only valid but is also useful for predicting physically observable phenomena.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEntry
Undecidability and Quantum Mechanics
by
Canio Noce and Alfonso Romano
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2447
Definition
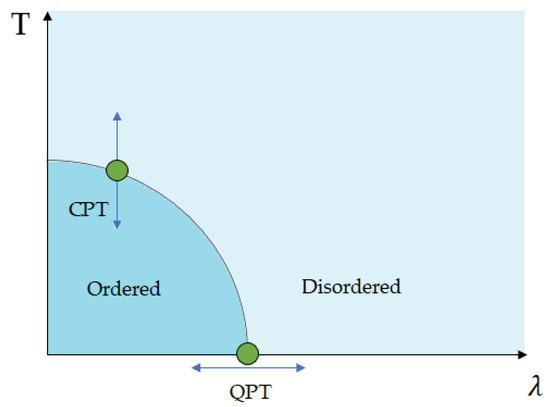
Recently, great attention has been devoted to the problem of the undecidability of specific questions in quantum mechanics. In this context, it has been shown that the problem of the existence of a spectral gap, i.e., energy difference between the ground state and
[...] Read more.
Recently, great attention has been devoted to the problem of the undecidability of specific questions in quantum mechanics. In this context, it has been shown that the problem of the existence of a spectral gap, i.e., energy difference between the ground state and the first excited state, is algorithmically undecidable. Using this result herein proves that the existence of a quantum phase transition, as inferred from specific microscopic approaches, is an undecidable problem, too. Indeed, some methods, usually adopted to study quantum phase transitions, rely on the existence of a spectral gap. Since there exists no algorithm to determine whether an arbitrary quantum model is gapped or gapless, and there exist models for which the presence or absence of a spectral gap is independent of the axioms of mathematics, it infers that the existence of quantum phase transitions is an undecidable problem.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEntry
Foundations of Quantum Mechanics
by
Salim Yasmineh
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3742
Definition
Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism that models the dynamics of physical objects. It deals with the elementary constituents of matter (atoms, subatomic and elementary particles) and of radiation. It is very accurate in predicting observable physical phenomena, but has many puzzling properties.
[...] Read more.
Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism that models the dynamics of physical objects. It deals with the elementary constituents of matter (atoms, subatomic and elementary particles) and of radiation. It is very accurate in predicting observable physical phenomena, but has many puzzling properties. The foundations of quantum mechanics are a domain in which physics and philosophy concur in attempting to find a fundamental physical theory that explains the puzzling features of quantum mechanics, while remaining consistent with its mathematical formalism. Several theories have been proposed for different interpretations of quantum mechanics. However, there is no consensus regarding any of these theories.
Full article