Board Members’ Collection Series: Clean Coal Extraction and Using
A topical collection in Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This collection belongs to the section "H: Geo-Energy".
Viewed by 13077
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Pavel A. Strizhak
Prof. Dr. Pavel A. Strizhak
 Prof. Dr. Pavel A. Strizhak
Prof. Dr. Pavel A. Strizhak
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Power Engineering National Research, Tomsk Polytechnic University, 634050 Tomsk, Russia
Interests: energy; fuels; ignition; combustion chemistry; environmental performance; gas emissions; waste-derived fuels; coal–water slurry; waste to energy; thermal engineering; mathematical modeling; heat and mass transfer
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Manoj Khandelwal
Dr. Manoj Khandelwal
 Dr. Manoj Khandelwal
Dr. Manoj Khandelwal
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Institute of Innovation, Science and Sustainability, Federation University Australia, Ballarat, VIC 3350, Australia
Interests: rock mechanics; rock blasting; soft computing; sustainable mining; environmental geotechnology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Every year, coal energy receives new impetus for development around the world, and the availability of solid fuels plays a decisive role. The key problems of coal energy include high concentrations of anthropogenic emissions during transportation and combustion and low efficiency of power plants. This Topical Collection invites papers with new scientific results in the field of improving the environmental indicators of mining, transport, processing and combustion of coal. Each of the stages of work with solid fuels are extremely important in terms of environmental indicators.
Prof. Dr. Pavel A. Strizhak
Dr. Manoj Khandelwal
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- coal energy
- green mining
- clean coal technology
- clean and low carbon
- intelligent mining
- coal mine transportation
Published Papers (9 papers)
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Key SDG7 Factors Shaping the Future of Clean Coal Technologies: Analysis of Trends and Prospects in Poland
by
Aurelia Rybak, Aleksandra Rybak, Jarosław Joostberens and Spas D. Kolev
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 847
Abstract
This article presents the results of an analysis aimed at verifying the relationship between the implementation of SDG Goal 7 and the use of clean coal technologies in Poland. Clean coal technologies in the United Nations plans will constitute a crucial element of
[...] Read more.
This article presents the results of an analysis aimed at verifying the relationship between the implementation of SDG Goal 7 and the use of clean coal technologies in Poland. Clean coal technologies in the United Nations plans will constitute a crucial element of the strategy for sustainable development in the energy context. They are intended to be one of the tools for building an energy system based on renewable energy sources, constituting a bridge that enables the transition of Poland’s energy system from coal to renewable energy sources. To identify whether this relationship exists, the Autoregressive Moving Average with Exogenous Input (ARMAX) model was used. The structure of the model, its correctness, and its accuracy were confirmed using information criteria; statistical tests such as Dickey-Fuller, Doornik-Hansen, Durbin-Watson, and Breusch-Pagan; and measures of prediction accuracy such as MAPE, MAE, and RMSE. The explanatory variables were the Objective 7 indicators adopted by Eurostat. Before being introduced to the ARMAX model, they were standardized using the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) indicator. The analysis made it possible to indicate which of the explanatory variables has the greatest impact on the development of clean coal technologies in Poland, to determine a synthetic CAGR measure for all the explanatory variables, and to compare the results obtained with the indicator determined by the United Nations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Impact of Additives on Gaseous Pollutants from the Combustion of Various Solid Fuels
by
Ewa Szatyłowicz and Anna Siemieniuk
Viewed by 763
Abstract
This article compares the emission of gaseous pollutants such as CO
2, CO, NO, SO
2, and HCl emissions from the combustion of the selected most popular solid fuels in a low-power boiler. The process was carried out under controlled conditions
[...] Read more.
This article compares the emission of gaseous pollutants such as CO
2, CO, NO, SO
2, and HCl emissions from the combustion of the selected most popular solid fuels in a low-power boiler. The process was carried out under controlled conditions on a laboratory stand equipped with a Moderator Unica Vento Eko 25 kW boiler. Solid fuels were selected for comparison, such as hard coal with granulation above 60 mm, hard coal with a granulation of 25–80 mm, hard coal with a granulation of 8–25 mm, wood pellets, and mixed firewood. The experiment was carried out in two stages. In stage 1, previously selected solid fuels were combusted under controlled repeatable conditions, while simultaneously measuring gaseous components in the exhaust gases in real time. On the other hand, the second stage involves the combustion of the same fuels under the same conditions with combustion additives that modify the combustion process in terms of reducing the emission of pollutants. At the same time, in the second stage, gaseous components in the exhaust gas were also measured in real time. The experiments carried out have shown that, in addition to the additive, a testing system should be used to assess the profitability and improve the efficiency of energy production and distribution after using a given additive for fuel combustion. Implementation of the use of solid fuel activators on a common scale should also entail research on the emission of dioxins and furans, which may be emitted in increased amounts under the influence of some components contained in combustion modifiers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Clean Coal Technologies in the Development of Renewable Energy Sources
by
Aurelia Rybak, Aleksandra Rybak and Jarosław Joostberens
Viewed by 676
Abstract
The article presents research on the synergistic impact of clean coal technologies and renewable energy sources on the energy mix in Poland. The main causes of problems that inhibit the development of renewable energy sources and ways to eliminate them are presented. A
[...] Read more.
The article presents research on the synergistic impact of clean coal technologies and renewable energy sources on the energy mix in Poland. The main causes of problems that inhibit the development of renewable energy sources and ways to eliminate them are presented. A factor that may undermine the development of renewable energy potential is access to critical raw materials such as rare earth elements. Clean coal technologies will make it possible to survive the transition period for coal-based energy mixes. The CCT solution described in this article will enable the acquisition of rare earth elements necessary for the development of renewable energy sources. The ability to meet the demand for REEs based on elements recovered from fly ash is examined. For this purpose, an analysis of wind electricity production capacities was carried out and a forecast until 2030 was created. A program was written using machine learning and the Gompretz sigmoid model. Based on the forecast, the level of demand for REEs was determined and compared with the supply obtained from fly ash. The authors propose an alternative source of REEs and analyze the relationship between demand and supply of this source.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Hydrogen Storage and Combustion for Blackout Protection of Mine Water Pumping Stations
by
Andrzej Chmiela, Paweł Wrona, Małgorzata Magdziarczyk, Ronghou Liu, Le Zhang and Adam Smolinski
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 890
Abstract
Global warming increases the risk of power outages. Mine water pumping stations pump approximately 100 million m
3 of water per year (2023). The cessation of mine water pumping would expose neighboring mines and lower lying areas to flooding. The pumping stations have
[...] Read more.
Global warming increases the risk of power outages. Mine water pumping stations pump approximately 100 million m
3 of water per year (2023). The cessation of mine water pumping would expose neighboring mines and lower lying areas to flooding. The pumping stations have some containment, but a prolonged shutdown could cause environmental problems. Remediation of the resulting damage would be costly and time-consuming. The combination of the problems of dewatering abandoned mines and storing energy in the form of hydrogen to ensure continuity of power supply to pumping stations has not been the subject of extensive scientific research. The purpose of this paper was to develop options for protecting mine water pumping stations against the “blackout” phenomenon and to assess their investment relevance. Six technically feasible options for the modernization of mine water pumping stations were designed and analyzed in the study. All pumping station modernization options include storage of the generated energy in the form of green hydrogen. For Q1 2024 conditions, the option with the partial retail sale of the produced hydrogen and the increased volume of produced water for treatment is recommended for implementation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Impact of Clean Coal Technologies on the Share of Coal in Poland’s Energy Mix
by
Aurelia Rybak, Aleksandra Rybak, Jarosław Joostberens, Joachim Pielot and Piotr Toś
Viewed by 1161
Abstract
This article presents research results on the share of coal in the energy mix and the impact of clean coal technologies on Poland’s energy mix. Two mathematical models were utilised: the Boltzmann sigmoidal curve and a supervised machine learning model that employs multiple
[...] Read more.
This article presents research results on the share of coal in the energy mix and the impact of clean coal technologies on Poland’s energy mix. Two mathematical models were utilised: the Boltzmann sigmoidal curve and a supervised machine learning model that employs multiple regressions. Eight explanatory variables were incorporated into the model, the influence of which on the explained variable was confirmed by Student’s
t-test. The constructed models were verified using ex post errors and the Durbin–Watson and Shapiro–Wilk statistical tests. It was observed that the share of coal in the mix decreased more dynamically after 2015 compared to previous years. Furthermore, a simulation was conducted using the machine learning model, which confirmed the hypothesis on the influence of clean coal technologies on the level of coal share in the Poland energy production structure. As shown by the analysis and simulation, coal could be maintained in the energy mixes of EU countries, and even if the negative aspects of using this fuel were limited—primarily the emission of harmful substances—its share could even increase. It was noted that this share could be higher by 22% assuming a return to the interest in CCT levels from before 2015 and the reduction in CO
2 emissions using membrane techniques proposed by the authors. Clean coal technologies would enable diversification of the energy mix, which is an important aspect of energy security. They would also enable the gradual introduction of renewable energy sources or other energy sources, which would facilitate the transition stage on the way to a sustainable energy mix.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
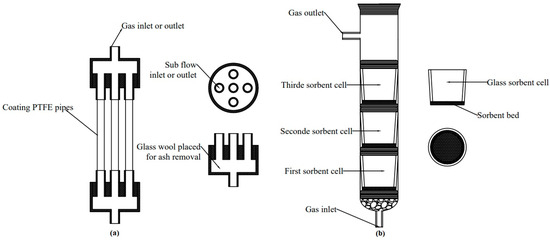
A Prototype Reactor Promoting the Hg(0) Capture in the Simulated Flue Gas from Small-Scale Boilers by Using Copper Oxide- and Copper Sulfide-Coated Teflon Pipes
by
Yinyou Deng, Jerzy Górecki, Katarzyna Szramowiat-Sala and Mariusz Macherzynski
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 961
Abstract
In this study, we designed a prototype reactor, the multiple pipes reactor (MPR), for Hg(0) capture, which can be applied in small-scale boilers. It was tested on a laboratory scale by comparing it with a fixed-bed type, the vertical glass reactor (VGR). In
[...] Read more.
In this study, we designed a prototype reactor, the multiple pipes reactor (MPR), for Hg(0) capture, which can be applied in small-scale boilers. It was tested on a laboratory scale by comparing it with a fixed-bed type, the vertical glass reactor (VGR). In total, 200 mg of CuO and CuS was applied as sorbent materials to reduce the concentration of Hg(0) from the simulated flue gas, in both VGR and MPR reactors. The mercury capture measurements were performed in the same laboratory system at 125 °C and a flow rate of 54 L/h. The contact time between the sorbents and simulated flue gas in the VGR was 0.035 s for both materials. In the case of the MPR, it was 0.44 s (CuO coating) and 0.63 s (CuS coating), depending on the coating area. The contact area inside the VGR was 5.31 cm
2, contrasting with the values of 13.19 cm
2 (CuO coating) and 18.84 cm
2 (CuS coating) in the MPRs. The average Hg(0) capture effectiveness of CuO (granulate) and CuS (granulate) was 51% and 67% in VGR, respectively. The MPR with CuO- and CuS-coating Teflon (PTFE) pipes promoted an average Hg(0) capture effectiveness reaching 65 (by 268%) and 94% (by 158%), respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Combustion Characteristics of Coal-Water Slurry Droplets in High-Temperature Air with the Addition of Syngas
by
Maxim Belonogov, Vadim Dorokhov, Dmitrii Glushkov, Daria Kuznechenkova and Daniil Romanov
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1966
Abstract
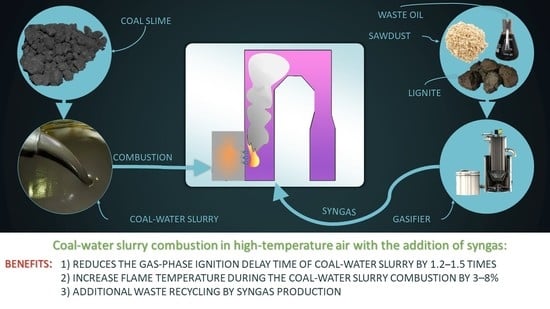
An experimental study of the ignition and combustion processes of coal-water slurry (CWS) droplets based on coal enrichment waste in a high-temperature oxidizer at 650–850 °C with a syngas addition was carried out. The fuel slurry was a mixture of finely dispersed solid
[...] Read more.
An experimental study of the ignition and combustion processes of coal-water slurry (CWS) droplets based on coal enrichment waste in a high-temperature oxidizer at 650–850 °C with a syngas addition was carried out. The fuel slurry was a mixture of finely dispersed solid combustible particles (coal sludge, 10–100 µm in size) and water. The syngas was a product of biomass pyrolysis and two waste-derived fuels in a laboratory gasifier. Composition of the syngas was controlled by a precision analytical gas analyzer. The feasibility of co-firing CWS with syngas was experimentally established. Under such conditions, the CWS droplets ignition process was intensified by 15–40%, compared to fuel combustion without the addition of syngas to the combustion chamber. The greatest positive effect was achieved by adding the gas obtained during the biomass pyrolysis. The ignition delay times of CWS droplets are 5.2–12.5 s versus 6.1–20.4 s (lower by 15–39%) when ignited in a high-temperature medium without adding syngas to the combustion chamber. Based on the results obtained, a concept for the practical implementation of the CWS combustion technology in a syngas-modified oxidizer medium is proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Secondary Atomization of Fuel Oil and Fuel Oil/Water Emulsion through Droplet-Droplet Collisions and Impingement on a Solid Wall
by
Anastasia Islamova, Pavel Tkachenko, Nikita Shlegel and Genii Kuznetsov
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2429
Abstract
This paper presents findings from an experimental study investigating the secondary atomization of liquid fuel droplets widely used in the heat and power industry exemplified by fuel oil and environmentally promising fuel oil/water emulsion. The scientific novelty comes from the comparative analysis of
[...] Read more.
This paper presents findings from an experimental study investigating the secondary atomization of liquid fuel droplets widely used in the heat and power industry exemplified by fuel oil and environmentally promising fuel oil/water emulsion. The scientific novelty comes from the comparative analysis of the critical conditions and integral characteristics of the secondary atomization of the liquid and composite fuels with the greatest potential for power plants. Here, we used two fuel atomization schemes: droplet–droplet collisions in a gas and droplets impinging on a heated solid wall. The temperature of the liquids under study was 80 °C. The velocities before collision ranged from 0.1 m/s to 7 m/s, while the initial droplet sizes varied from 0.3 mm to 2.7 mm. A copper substrate served as a solid wall; its temperature was varied from 20 °C to 300 °C. The main characteristics of droplet interaction were recorded by a high-speed camera. Regime maps were constructed using the experimental findings. It was established that the critical Weber number was several times lower when water and fuel oil droplets collided than during the collision of fuel oil droplets with 10 vol% of water. The secondary atomization of fuel oil/water emulsion droplets by their impingement on a heated solid wall was found to reduce the typical sizes of liquid fragments by a factor of 40–50. As shown in the paper, even highly viscous fuels can be effectively sprayed using primary and secondary droplet atomization schemes. It was established that the optimal temperature of the fuel oil to be supplied to the droplet collision zone is 80 °C, while the optimal substrate temperature for the atomization of fuel oil/water emulsion droplets approximates 300 °C.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Pool Fire Suppression Using CO2 Hydrate
by
Olga Gaidukova, Sergey Misyura, Igor Donskoy, Vladimir Morozov and Roman Volkov
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2337
Abstract
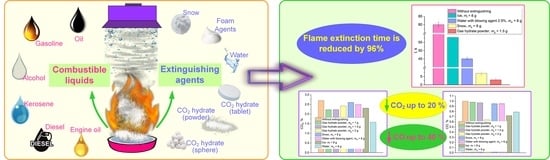
This paper presents experimental findings on heat and mass transfer, phase transitions, and chemical reactions during the interaction of CO
2 hydrate in powder granules and tablets with burning liquid fuels and oil. The experiments involved CO
2 hydrate tablets and spheres made
[...] Read more.
This paper presents experimental findings on heat and mass transfer, phase transitions, and chemical reactions during the interaction of CO
2 hydrate in powder granules and tablets with burning liquid fuels and oil. The experiments involved CO
2 hydrate tablets and spheres made of pressed granules. The fire containment and suppression times were established experimentally. Using the gas analysis data, we studied the effects of the mitigation of anthropogenic emissions from the combustion of liquids and their suppression by gas hydrates. We also compared the performance of water aerosol, foaming agent emulsion, snow, ice, and CO
2 hydrate samples as laboratory-scale fire suppressants. The paper further describes the numerical modeling of the CO
2 hydrate dissociation during liquid fuel combustion. The rapid carbon dioxide release is shown to prevent the oxidizer from the combustion zone. The suppression of a flame using powder with a granule size of 3 mm requires 20-times less carbon dioxide hydrate than in the case of pressed tablets. Effective conditions are identified for using CO
2 hydrates to extinguish fires involving flammable liquids and most common fuels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures