Thermodynamic and Thermo-Economic Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Laura Vanoli
Prof. Dr. Laura Vanoli
 Prof. Dr. Laura Vanoli
Prof. Dr. Laura Vanoli
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Dipartimento di Ingegneria, Università degli Studi di Napoli “Parthenope”, Centro Direzionale, Isola C4, 80143 Naples, Italy
Interests: thermodynamic and thermo-economic analysis of advanced energy systems; energy saving; renewable energy sources; dynamic modeling of energy conversion systems; innovative energy conversion systems; energy planning; thermo-fluid-dynamic measurements
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Francesco Calise
Prof. Dr. Francesco Calise
 Prof. Dr. Francesco Calise
Prof. Dr. Francesco Calise
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Naples Federico II, 80125 Naples, Italy
Interests: fuel cells; advanced optimization techniques; solar thermal systems; concentrating photovoltaic/thermal photovoltaic systems; energy saving in buildings; solar heating and cooling; organic Rankine cycles; geothermal energy; dynamic simulations of energy systems; renewable polygeneration systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue in
Energies: Simulation of Polygeneration Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Solar Cooling and Heating
Special Issue in
Energies: Integration of Renewable Technologies in Water, Electricity, Heating and Cooling Networks
Special Issue in
Energies: Solar Cooling and Heating 2018
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from SDEWES 2017: The 12th Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from SDEWES 2018 Conferences on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Renewable Energy Systems 2019
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from 3rd International Conference on the Sustainable Energy and Environmental Development (SEED 2019)
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from SDEWES 2019 conferences on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Integrated Solar Thermal Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2020 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water, and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Sustainability: Sustainability of Smart Energy Grids: Pathway for Achieving a Green Smart Energy Grid
Special Issue in
Thermo: Smart Energy Networks: Thermal Balancing and Managing Issues
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2021 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Sustainability: Sustainable and Secure Energy Conversion Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2022 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water, and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Energies: Integrated Solar Thermal Systems II
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2023 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water, and Environment Systems
Special Issue in
Sustainability: Sustainability of Smart Energy Networks: Pathway for Achieving a Green Smart Energy Network—2nd Edition
Special Issue in
Energies: Power-to-X Technologies: Pioneering the Future of Sustainable Energy Conversion and Storage
Special Issue in
Energies: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2024 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems
Topics:
Clean Energy Technologies and Assessment
 Dr. Adriano Macaluso
Dr. Adriano Macaluso
 Dr. Adriano Macaluso
Dr. Adriano Macaluso
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Engineering Department, University of Naples “Parthenope”, Centro Direzionale, Isola C4, 80143 Naples, Italy
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection aims to include the most recent studies on energy conversion systems powered by renewable sources, considering conventional and innovative technologies. One of the keys to global energy conversion lies in the synergistic integration and simultaneous exploitation of multiple renewable sources: in this perspective, special attention is given to the so-called "hybrid" systems. Another crucial aspect of the future energy conversion systems is the possibility of simultaneously producing different energy and materials vectors, therefore special attention is also paid to polygenerative systems, to the practice of "load sharing" and to the “green communities".
As regards the polygenerative systems, special attention is paid to two aspects:
- systems whose energy and material products consist not only in electricity, heat and cold, but also in products deriving from energy-intensive processes of public utility such as the waste water and sludge treatment process, water desalination, biomass and sludge drying process, urban waste treatments and disposal;
- control and management strategy. The analysis of energy conversion systems should include the market context; the definition of the cost formation process and the identification of an optimum of the operations are fundamental to understand how the technology or the integration of the proposed technologies can represent a viable way. From this point of view, the thermo-economic analysis and optimization - with special regard to the exergoeconomics - is the most advanced thermodynamic diagnosis tool for this purpose.
Prof. Dr. Laura Vanoli
Prof. Dr. Francesco Calise
Dr. Adriano Macaluso
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Renewables
- Hybrid renewables systems
- Thermoeconomic analysis
- Exergoeconomic optimization
- Polygeneration
- Smart energy system
- Smart and resilient communities
- Control and management strategies
- Circular economy
Published Papers (8 papers)
Open AccessArticle
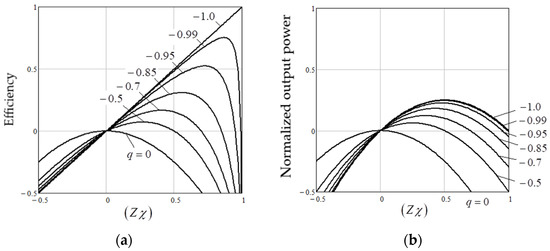
A Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamic Approach for Analysis of Power Conversion Efficiency in the Wind Energy System
by
Ihor Shchur, Marek Lis and Yurii Biletskyi
Viewed by 1157
Abstract
This article proposes an approach and develops an appropriate method of applying linear non-equilibrium thermodynamics to analyze energy processes, in particular using the example of the wind energy conversion system (WECS) with a directly connected vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) and vector-controlled permanent
[...] Read more.
This article proposes an approach and develops an appropriate method of applying linear non-equilibrium thermodynamics to analyze energy processes, in particular using the example of the wind energy conversion system (WECS) with a directly connected vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) and vector-controlled permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG). The main steps of the proposed approach are the description of the component subsystems as universal linear or linearized energy converters (ECs), which are characterized by several dimensionless parameters, the main one of which is the degree of coupling between their input and output. According to their value, as well as justified efficiency criteria, the optimal operating points of each ECs can be easily found. Such an approach makes it possible to abstract from physical laws of a different nature and equally assess the work of each of the subsystems. The next step is a connection of the received ECs. As shown in the paper, for the most common cascade connection of ECs, there are the best conditions for their connection, under which the newly formed equivalent EC can have maximum efficiency. This opens up an opportunity to analyze the influence of already real parameters of cascaded interconnected subsystems on the quality of their connection and justify specific solutions that would not have been seen without this approach. For example, in this study, from all parameters of the PMSG, only the selection of the optimal rated inductance of the armature winding made it possible to improve the quality of the connection of the PMSG with a specific VAWT and approximate the efficiency of the entire WECS to the maximum possible, especially in medium and high winds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
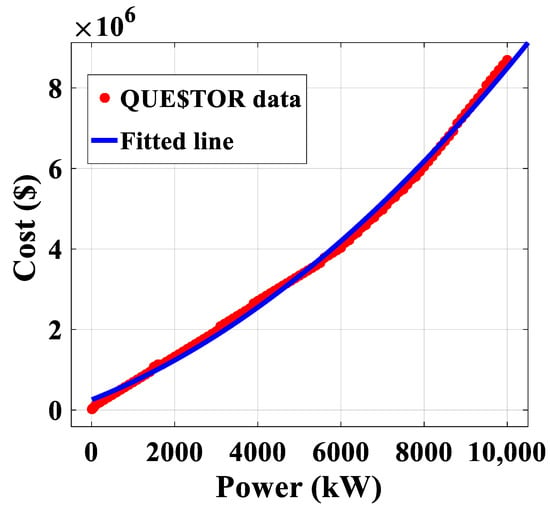
Development of Cost Correlations for the Economic Assessment of Power Plant Equipment
by
Moein Shamoushaki, Pouriya H. Niknam, Lorenzo Talluri, Giampaolo Manfrida and Daniele Fiaschi
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 7243
Abstract
A comprehensive cost correlation analysis was conducted based on available cost correlations, and new equipment cost correlation models were proposed based on QUE$TOR modeling. Cost correlations for various types of equipment such as pumps, compressors, heat exchangers, air coolers, and pressure vessels were
[...] Read more.
A comprehensive cost correlation analysis was conducted based on available cost correlations, and new equipment cost correlation models were proposed based on QUE$TOR modeling. Cost correlations for various types of equipment such as pumps, compressors, heat exchangers, air coolers, and pressure vessels were generated on the basis of extracted cost data. The models were derived on the basis of robust multivariable regression with the aim of minimizing the residuals by using the genetic algorithm. The proposed compressor models for both centrifugal and reciprocating types showed that the Turton cost estimation for carbon steel compressor and Matche’s and Mhhe’s data were compatible with the generated model. According to the results, the cost trend in the Turton correlation for carbon steel had a somewhat lower estimation than these correlations. Further, the cost trend of the Turton correlation for carbon steel pressure vessels was close to the presented model trend for both bullet and sphere types. The Turton cost trend for U-tube shell-and-tube heat exchangers with carbon steel shell and stainless steel tube was close to the proposed heat exchanger model. Furthermore, the Turton cost trend for the flat-plate heat exchanger using carbon steel was similar to the proposed model with a slight difference.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
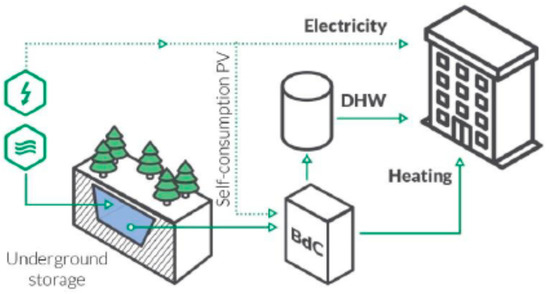
Exergy Assessment and Thermo-Economic Analysis of Hybrid Solar Systems with Seasonal Storage and Heat Pump Coupling in the Social Housing Sector in Zaragoza
by
Amaya Martínez-Gracia, Sergio Usón, Mª Teresa Pintanel, Javier Uche, Ángel A. Bayod-Rújula and Alejandro Del Amo
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2355
Abstract
A real case study of an energy system based on a Solar Assisted Heat Pump (SAHP) fed by hybrid photovoltaic-thermal solar panels (PVT) and seasonal storage (SS) is presented in this paper. Exergy and exergy cost analyses are proposed as complementary methods for
[...] Read more.
A real case study of an energy system based on a Solar Assisted Heat Pump (SAHP) fed by hybrid photovoltaic-thermal solar panels (PVT) and seasonal storage (SS) is presented in this paper. Exergy and exergy cost analyses are proposed as complementary methods for the assessment and better understanding of the efficiency of this cogeneration solar configuration. The system performance takes advantage of storage heat in summer, when the solar resource is high in Spain, and is then later consumed during the cold winter (heating season). The building is devoted to social housing, and it is currently under construction. The assessment is based on simulations developed using TRNSYS, a dynamic simulation software for energy systems. Results show that the unit exergy cost of the solar field is around 6. The cost of the seasonal storage is higher, about 13, and its formation is affected both by its own irreversibility and by the irreversibility of the PVT solar field. The cost of the heat delivered by the heat pump is around 15, being affected by all the upstream units and even by the grid. Besides, the analysis points out strategies for improving the system efficiency, such as increasing the size of the storage tank or improving the control strategy of the boiler.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
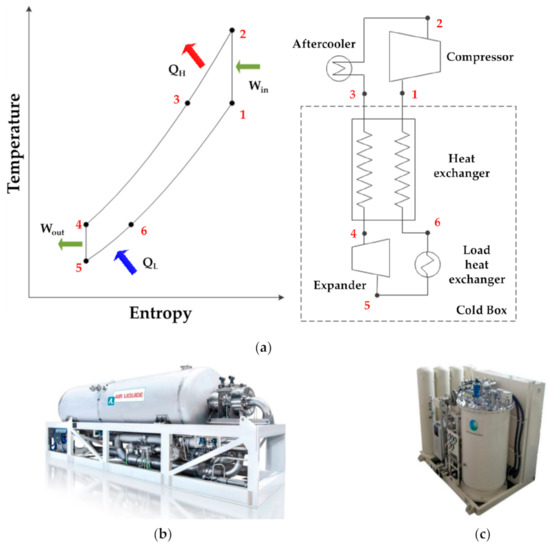
Design and Performance Test of 2 kW Class Reverse Brayton Cryogenic System
by
Keuntae Lee, Deuk-Yong Koh, Junseok Ko, Hankil Yeom, Chang-Hyo Son and Jung-In Yoon
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3777
Abstract
With the increased commercialization of high-temperature superconducting (HTS) power cables cooled using liquid nitrogen and the use of liquefied natural gas as fuel, the need for large-capacity reverse Brayton cryogenic systems is gradually increasing. In this paper, the thermodynamic design of a reverse
[...] Read more.
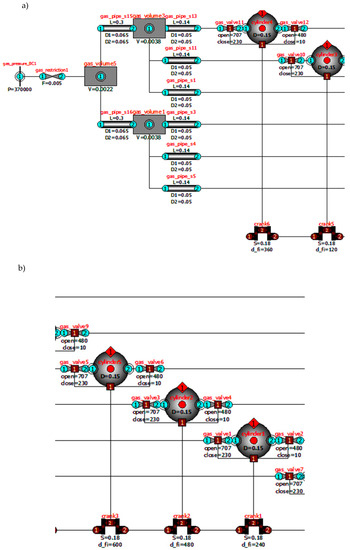
With the increased commercialization of high-temperature superconducting (HTS) power cables cooled using liquid nitrogen and the use of liquefied natural gas as fuel, the need for large-capacity reverse Brayton cryogenic systems is gradually increasing. In this paper, the thermodynamic design of a reverse Brayton cryogenic system with a cooling capacity of the 2 kW class at 77 K using neon as a refrigerant is described. Unlike conventional reverse Brayton systems, the proposed system uses a cryogenic turbo-expander, scroll compressor, and plate-type heat exchanger. The performance test conducted on the fabricated system is also described. The isentropic efficiency of the cryogenic turbo-expander was measured to be 86%, which is higher than the design specification. The effectiveness of the heat exchanger and the flow rate and operating pressure of the refrigerant were found to be lower than the design specifications. Consequently, the refrigeration capacity of the fabricated reverse Brayton cryogenic system was measured to be 1.23 kW at 77 K. In the future, we expect to achieve the targeted refrigeration capacity through further improvements. In addition, the faster commercialization of HTS power cables and more efficient storage of liquefied natural gas will be realized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mathematical Model of Thermodynamic Processes in the Intake Manifold of a Diesel Engine with Fuel and Water Injection
by
Vladimir Bondar, Sergei Aliukov, Andrey Malozemov and Arkaprava Das
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2884
Abstract
The article presents the results of a study aimed at creating a mathematical model of thermodynamic processes in the intake manifold of a forced diesel engine, taking into account the features of simultaneous injection of fuel and water into the collector. In the
[...] Read more.
The article presents the results of a study aimed at creating a mathematical model of thermodynamic processes in the intake manifold of a forced diesel engine, taking into account the features of simultaneous injection of fuel and water into the collector. In the course of the study, the tasks of developing a mathematical model were solved, it was implemented in the existing software for component simulation “Internal combustion engine research and development” (ICE RnD), created using the Modelica language, and verification was undertaken using the results of bench tests of diesel engines with injection fuel and water into the intake manifold. The mathematical model is based on a system of equations for the energy and mass balances of gases and includes detailed mathematical submodels of the processes of simultaneous evaporation of fuel and water in the intake manifold; it takes into account the effect of the evaporation of fuel and water on the parameters of the gas state in the intake manifold; it takes into account the influence of the state parameters of the working fluid in the intake manifold on the physical characteristics of fuel and water; it meets the principles of component modeling, since it does not contain parameters that are not related to the simulated component; it describes the process of simultaneous transfer of vapors and non-evaporated liquids between components; and it does not include empirical relationships requiring data on the dynamics of fuel evaporation under reference conditions. According to the results of a full-scale experiment, the adequacy of the mathematical model developed was confirmed. This model can be used to determine the rational design parameters of the fuel and water injection system, the adjusting parameters of the forced diesel engine that provide the required power, and economic indicators, taking into account the limitations on the magnitude of the mechanical and thermal loads of its parts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermodynamic Optimization of a Waste Heat Power System under Economic Constraint
by
Liya Ren, Jianyu Liu and Huaixin Wang
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2431
Abstract
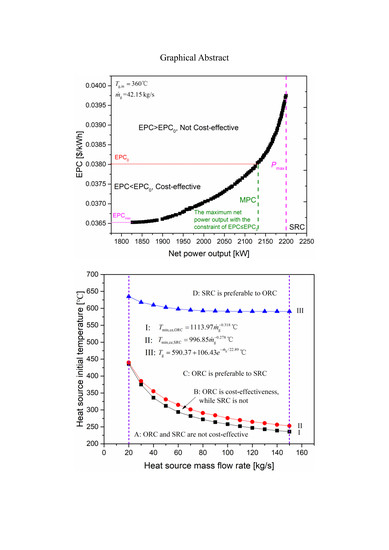
A novel thermo-economic performance indicator for a waste heat power system, namely, MPC, is proposed in this study, which denotes the maximum net power output with the constraint of
EPC ≤ EPC
0, where
EPC is the electricity production cost of the
[...] Read more.
A novel thermo-economic performance indicator for a waste heat power system, namely, MPC, is proposed in this study, which denotes the maximum net power output with the constraint of
EPC ≤ EPC
0, where
EPC is the electricity production cost of the system and EPC
0 refers to the
EPC of conventional fossil fuel power plants. The organic and steam Rankine cycle (ORC, SRC) systems driven by the flue gas are optimized to maximize the net power output with the constraint of
EPC ≤ EPC
0 by using the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (NSGA-II). The optimization process entails the design of the heat exchangers, the instantaneous calculation of the turbine efficiency, and the system cost estimation based on the Aspen Process Economic Analyzer. Six organic fluids, n-butane, R245fa, n-pentane, cyclo-pentane, MM (Hexamethyldisiloxane), and toluene, are considered for the ORC system. Results indicate that the MPC of the ORC system using cyclo-pentane is 39.7% higher than that of the SRC system under the waste heat source from a cement plant with an initial temperature of 360 °C and mass flow rate of 42.15 kg/s. The precondition of the application of the waste heat power system is
EPC ≤ EPC
0, and the minimum heat source temperatures to satisfy this condition for ORC and SRC systems are obtained. Finally, the selection map of ORC versus SRC based on their thermo-economic performance in terms of the heat source conditions is provided.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Thermodynamic Consistency of the Richardson–Duhmann Model for Thermionic Converters
by
Antonio Martí
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2436
Abstract
In this work, we develop the general theory for analyzing the thermodynamic consistency of the Richardson–Duhmann model for vacuum thermionic energy converters. In addition to the electron fluxes from emitter to collector and vice versa, we calculate the energy and entropy fluxes associated
[...] Read more.
In this work, we develop the general theory for analyzing the thermodynamic consistency of the Richardson–Duhmann model for vacuum thermionic energy converters. In addition to the electron fluxes from emitter to collector and vice versa, we calculate the energy and entropy fluxes associated to them. The calculation of the entropy fluxes is what allows us to conclude that the model is consistent by verifying that both at the emitter and at the collector the entropy generation rate is positive. In the process, we review the Richardson–Duhmann model in order to assure that the assumptions we make for calculating the energy and entropy fluxes are consistent. We also generalize the Richardson–Duhmann model in order to consider Fermi–Dirac statistics.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy, Exergy and Economic Analyses of a Combined Heating and Power System with Turbine-Driving Fans and Pumps in Northeast China
by
Ximei Li, Jianmin Gao, Yaning Zhang, Yu Zhang, Qian Du, Shaohua Wu and Yukun Qin
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 2740
Abstract
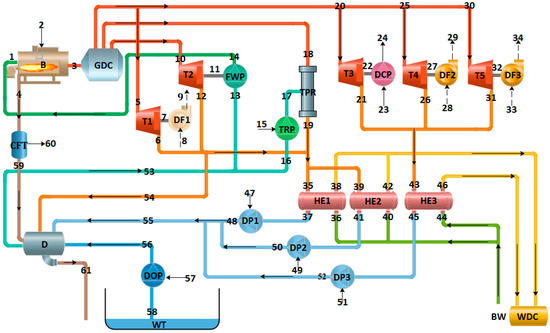
The combined heating and power (CHP) system with turbine-driving fans and pumps is more efficient and economical in meeting heat demand in cold areas, however, there are no detailed studies that investigate its thermodynamic performance, improvement possibilities and economy. In this paper, the
[...] Read more.
The combined heating and power (CHP) system with turbine-driving fans and pumps is more efficient and economical in meeting heat demand in cold areas, however, there are no detailed studies that investigate its thermodynamic performance, improvement possibilities and economy. In this paper, the energy, exergy and economic analysis of a CHP system with turbine-driving fans and pumps operated in Northeast China were conducted to provide insights into improvement options. It is revealed that the boiler is the main source of exergy destruction, followed by the steam-water heat exchangers (SWHE), temperature and pressure reducer (TPR), turbines, and deaerator. The energy and exergy efficiencies of the system are 89.72% and 10.07%, while the boiler’s are 84.89% and 30.04%. The thermodynamic performance of the boiler and turbines are compared with other studies, and the inefficiencies of major components are analyzed and some advice for further improvement is given. As the reference state changes, the main conclusions stay the same. The turbine-driving mode saves an electricity cost of 16,654.08 yuan on 15 December 2018. The effect of electricity price and on-grid price on the saved daily electricity cost is investigated and it proves that the turbine-driving mode is more economical in China.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Exergy assessment and thermo-economic analysis of hybrid solar systems with seasonal storage and heat pump coupling in the social housing sector in Zaragoza
Authors: Amaya Martínez-Gracia
Affiliation: CIRCE Institute, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Zaragoza, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain
Submit your paper and select the Journal “Energies” and the Topical Collection “Thermodynamic and Thermo-Economic Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems” via: https://susy.mdpi.com/user/manuscripts/upload?journal=energies. Please contact the Guest Editor or the journal editor ([email protected]) for any queries.