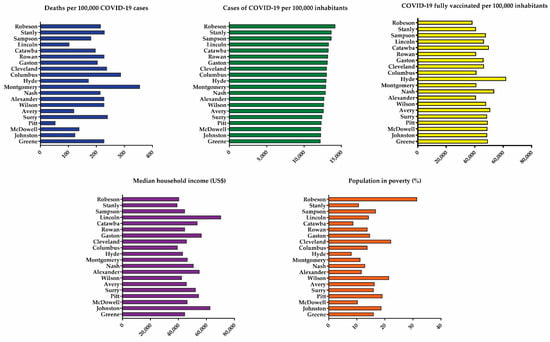
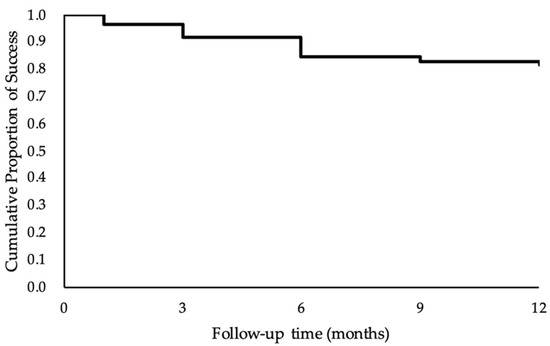
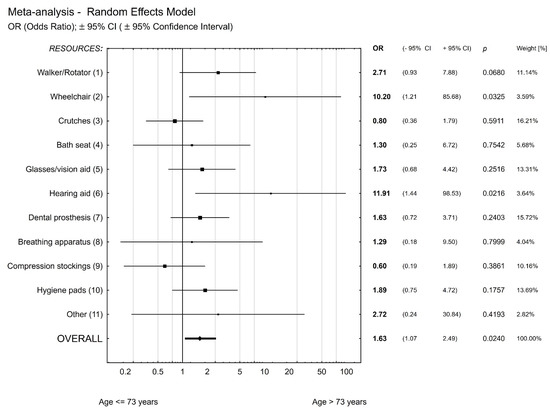
The Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Services
A topical collection in Healthcare (ISSN 2227-9032). This collection belongs to the section "Coronaviruses (CoV) and COVID-19 Pandemic".
Viewed by 138843Editors
2. Unit of Hygiene, Epidemiology and Public Health, ASL Pescara, 65100 Pescara, Italy
Interests: epidemiology; public health; non-communicable diseases; health services research; outcomes research; vaccines
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: epidemiology; public health; health services research; preventive medicine; vaccine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: epidemiology; public health; non-communicable diseases; health services research; occupational medicine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
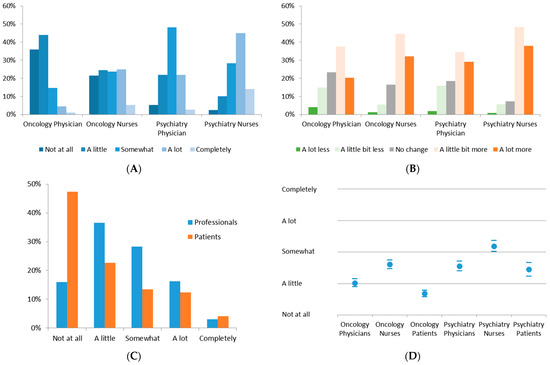
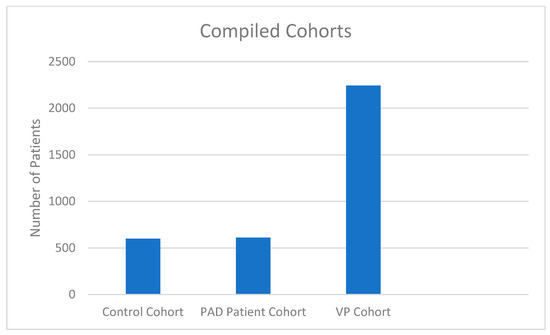
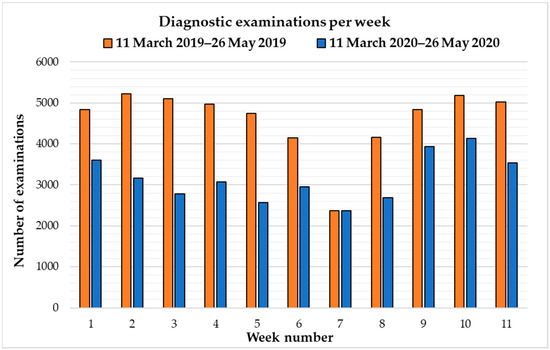
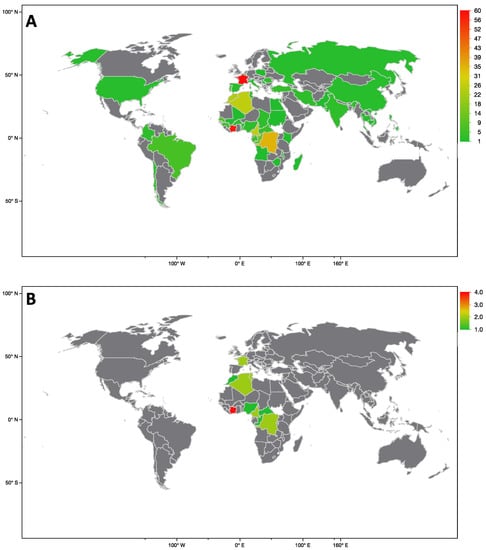
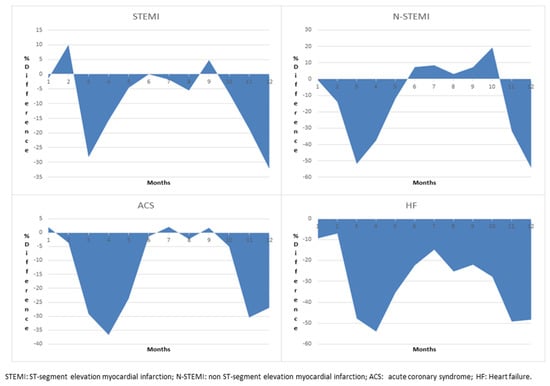
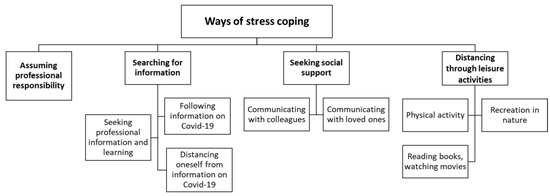
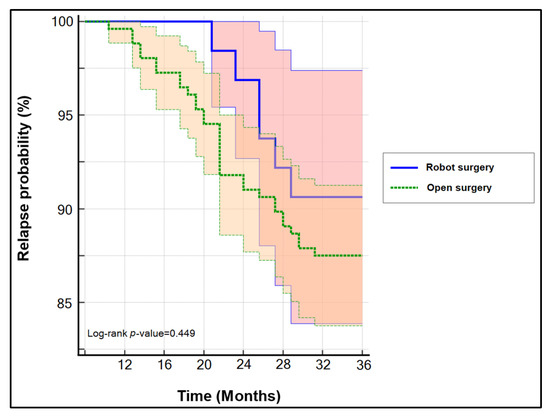
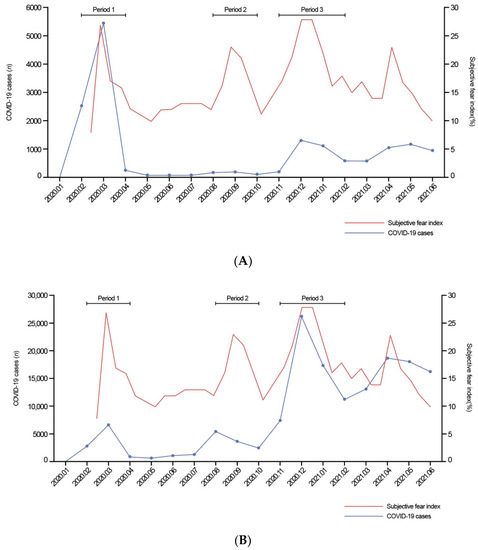
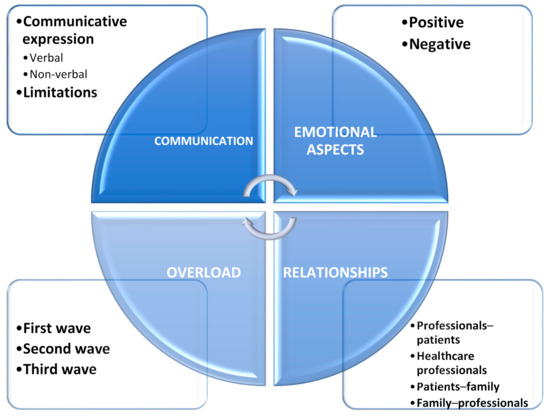
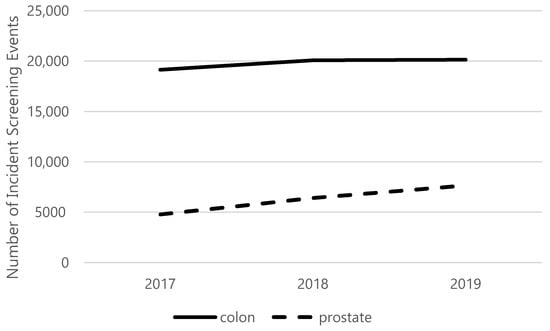
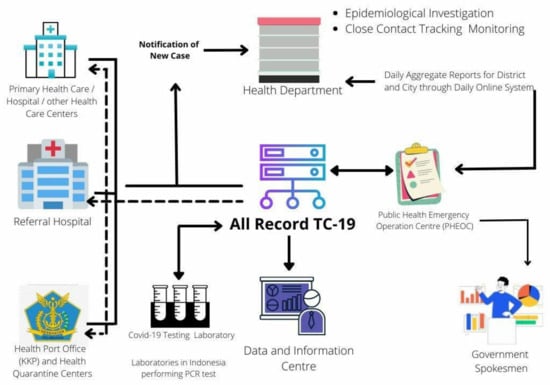
COVID-19 pandemic heavly impacted health services across all countries: the increase in morbidity and mortality due to Sars-Cov-2 infection caused an important consumption in hospital resourches. This situation in paraller influenced healthcare services, in particular about hospital admissions and visits unrelated to COVID-19 itself. There is emerging evidence from many countries that there are variations in healthcare utilization patterns due to COVID-19. In particular, ambulatory services switched to tele-medicine and several elective admissions were postponed. Given that COVID-19 is a fluctuating circumstance, many elective procedures have continued to be delayed as COVID-19 cases increase and virtual care remains a large component for many outpatient practices. Despite the reduction in outpatient service and elective surgeries, patients would presumably still require inpatient management for their acute and chronic medical conditions requiring admission through the emergency department, and the impact of the emergency measures on overall hospital use is uncertain. Because of that, an increase in emergency department acces for ambulatory care sensitive condition would be expected. This Special Issue aims to summarize the latest research that analyzed the impact of COVID19 on health services. In particular, papers that examine trends in hospital admissions during the pandemic, the impact of COVID19 on chronic conditions and ambulatory care sensitive conditions, and the effect of preventive strategies to improve hospital care in patients with and without COVID-19. Papers which examine the epidemiology of COVID-19 hospitalization, primary care, out-hospital management of the disease, the impact of COVID-19 on other diseases, and the economic burden of COVID-19 will also be considered.
Dr. Giuseppe Di MartinoProf. Dr. Tommaso Staniscia
Dr. Fabrizio Cedrone
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Healthcare is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- COVID19
- Hospitalization
- Healthcare
- hospital care
- hospital management
- healthcare services
- quality
- sustainability
- patient safety
- pandemic response
- public health
- health systems