Land Use Optimisation
A special issue of Land (ISSN 2073-445X). This special issue belongs to the section "Land Planning and Landscape Architecture".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (19 April 2022) | Viewed by 47965
Special Issue Editor
Interests: spatial analysis; geocomputation; GIS; land cover; land use; spatial data analytics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Land use describes the socioeconomic activity that takes place on land. It is distinct from land cover (although they are frequently rolled together) because value of some kind is attached to the land. This value was historically related to some kind of food or fibre production but now includes many different goods and services with wider societal value—commonly called ecosystem services (ESs)—as well as support for climate-related objectives such as biofuels.
Land use optimisation is used to support and inform land use decision making. There are two key considerations. First, land use decision making drives many of the processes that directly impact on our everyday lives. These include local-scale decisions about which food crops to grow, new building developments, natural flood management strategies, enhancing biodiversity, producing biomass and biofuels, as well as carbon sequestration. Second, land use decisions made now will also shape and have implications for our collective lives in the future. They will, for example, not only determine levels of food security locally and support regional emission targets, but also drive climate change at coarser scales.
Additionally, these start to hint at the complexity of land use optimisation or allocation (what to put where, what to do where). This aims to determine the spatial composition and configuration of land use that “best” satisfies some objective or combination of objectives. Objectives of course will vary depending on (a) the scale of decision making (for example, from field to farm holding to sub-catchment to region), (b) the underlying suitability or gradients for different uses, and (c) the value placed on those activities by society (see Figure 1).
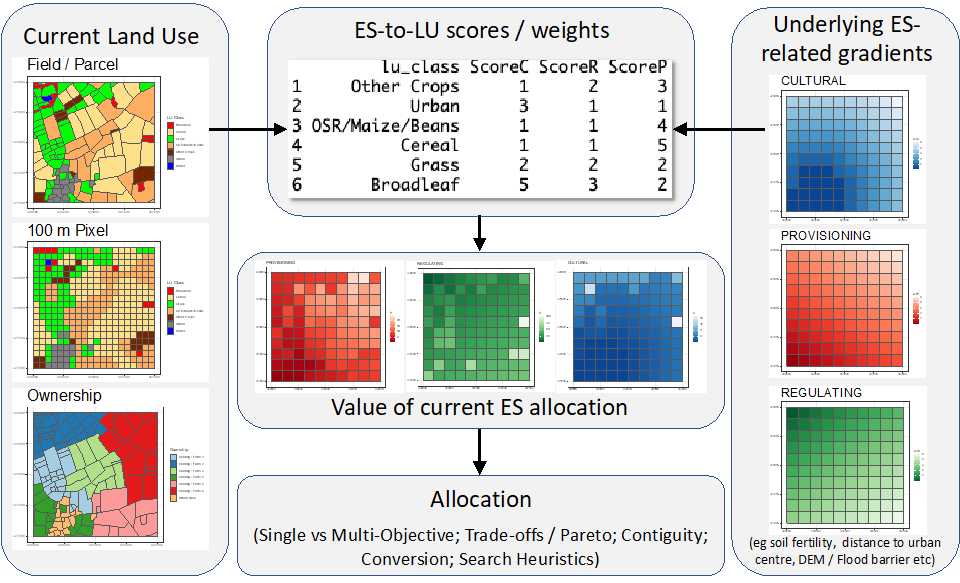
Figure 1. An example of the land use optimisation process: values are placed on different ecosystem services (ESs), and these interact with underlying suitability to generate values to be optimised.
For this Special Issue, we invite papers focusing on any aspect of land use optimisation, and we particularly welcome contributions examining the following topics:
- Informing land use decision making to support complex and interacting policy objectives;
- Handling divergent and potentially contradictory land use decision-making objectives;
- Developing methods for handling the inherent uncertainty in land use optimisation (from scales of representation to ES scoring and weighting in multiobjective evaluation functions);
- Exploring the impacts of scale on optimisation, from spatial data with different granularities and scales to evaluations of the impact of the Ecological Fallacy or the modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) (OpenShaw 1984) on aggregated data used in allocation;
- Modelling future land use compositions in a changing world (e.g., related to market and climate);
- Considering how to incorporate values for other aspects of the problem (e.g., contiguity, conversion costs, and spatial aspects into optimisations);
- Supporting multiobjective and multiscale landscape decisions;
- Determining whether (quick) “good enough” solutions can be used to replace (slow) optimal ones.
Submissions can be grounded in any area related to land use optimisation (from novel allocation methods to land use decision making), can examine different scales of the problem (from field to global), and can be focused on any of the related thematic areas (e.g., agriculture, food, biofuel, carbon sequestration, development, cultural ecosystem services, flood protection) as well as their interactions.
References
Openshaw S (1984) CATMOG 38: the modifiable areal unit problem. In: Norwich: geo-abstracts – see https://www.qmrg.org.uk/catmog/index.html
Prof. Dr. Alexis Comber
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Land is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.





