Recent Advances in Organocatalysis
(Closed)
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Raquel P. Herrera
Prof. Dr. Raquel P. Herrera
 Prof. Dr. Raquel P. Herrera
Prof. Dr. Raquel P. Herrera
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Laboratorio de Organocatálisis Asimétrica, Departamento de Química Orgánica, Instituto de Síntesis Química y Catálisis Homogénea (ISQCH) CSIC-Universidad de Zaragoza, C/Pedro Cerbuna 12, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain
Interests: asymmetric catalysis; biological properties; cinchona; computational calculations; hydrogen bond; mechanistic studies; natural products; organic synthesis; phase transfer catalysts; squaramides; (thio)ureas
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The field of organocatalysis has been experiencing an impressive growth in the last decade, and has attracted increasing the interest of researchers due to its broad spectrum of possibilities of activation. This growth has been reflected in the very large number of impressive results achieved with the development of new organocatalytic systems, as well as new and interesting applications. This amazing field of research covers different kind of organocatalysts, such as chiral secondary amines, thioureas, chiral phosphoric acids, squaramides, cinchona alkaloids, or phase transfer catalysts, as the more prominent ones. All of them provide efficient and environmentally friendly access to enantiomerically enriched compounds, including many drugs and bioactive natural products. In this Collection, we want to compile some of the last results reached in each family of organocatalysts by experts in the field.
Prof. Dr. Raquel P. Herrera
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- organocatalyst
- enamine catalysis
- iminium catalysis
- phase transfer catalysis
- H-bond catalysis
- organocatalysis
- organocatalytic asymmetric reactions
- thioureas
- secondary amines
- cinchona alkaloids
- quaternary ammonium salt
Published Papers (26 papers)
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Asymmetric Synthesis of Pyrrolidine-Based Organocatalysts and Their Application: A 15-Year Update
by
Arianna Quintavalla, Davide Carboni and Marco Lombardo
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4901
Abstract
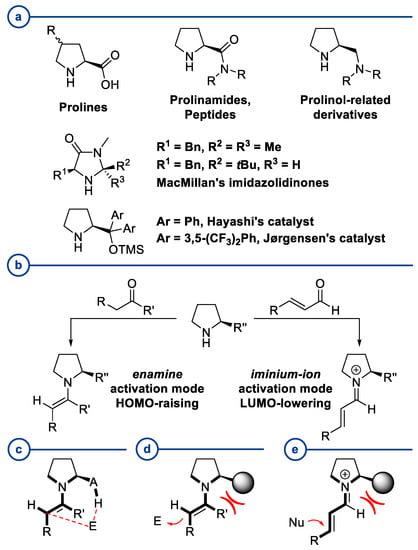
In 1971, chemists from Hoffmann-La Roche and Schering AG independently discovered a new asymmetric intramolecular aldol reaction catalyzed by the natural amino acid proline, a transformation now known as the Hajos–Parrish–Eder–Sauer–Wiechert reaction. These remarkable results remained forgotten until List and Barbas reported in
[...] Read more.
In 1971, chemists from Hoffmann-La Roche and Schering AG independently discovered a new asymmetric intramolecular aldol reaction catalyzed by the natural amino acid proline, a transformation now known as the Hajos–Parrish–Eder–Sauer–Wiechert reaction. These remarkable results remained forgotten until List and Barbas reported in 2000 that L-proline was also able to catalyze intermolecular aldol reactions with non-negligible enantioselectivities. In the same year, MacMillan reported on asymmetric Diels–Alder cycloadditions which were efficiently catalyzed by imidazolidinones deriving from natural amino acids. These two seminal reports marked the birth of modern asymmetric organocatalysis. A further important breakthrough in this field happened in 2005, when Jørgensen and Hayashi independently proposed the use of diarylprolinol silyl ethers for the asymmetric functionalization of aldehydes. During the last 20 years, asymmetric organocatalysis has emerged as a very powerful tool for the facile construction of complex molecular architectures. Along the way, a deeper knowledge of organocatalytic reaction mechanisms has been acquired, allowing for the fine-tuning of the structures of privileged catalysts or proposing completely new molecular entities that are able to efficiently catalyze these transformations. This review highlights the most recent advances in the asymmetric synthesis of organocatalysts deriving from or related to proline, starting from 2008.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
The Activating Effect of Strong Acid for Pd-Catalyzed Directed C–H Activation by Concerted Metalation-Deprotonation Mechanism
by
Heming Jiang and Tian-Yu Sun
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3618
Abstract
A computational study on the origin of the activating effect for Pd-catalyzed directed C–H activation by the concerted metalation-deprotonation (CMD) mechanism is conducted. DFT calculations indicate that strong acids can make Pd catalysts coordinate with directing groups (DGs) of the substrates more strongly
[...] Read more.
A computational study on the origin of the activating effect for Pd-catalyzed directed C–H activation by the concerted metalation-deprotonation (CMD) mechanism is conducted. DFT calculations indicate that strong acids can make Pd catalysts coordinate with directing groups (DGs) of the substrates more strongly and lower the C–H activation energy barrier. For the CMD mechanism, the electrophilicity of the Pd center and the basicity of the corresponding acid ligand for deprotonating the C–H bond are vital to the overall C–H activation energy barrier. Furthermore, this rule might disclose the role of some additives for C–H activation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
New Mesoporous Silica-Supported Organocatalysts Based on (2S)-(1,2,4-Triazol-3-yl)-Proline: Efficient, Reusable, and Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction
by
Omar Sánchez-Antonio, Kevin A. Romero-Sedglach, Erika C. Vázquez-Orta and Eusebio Juaristi
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3236
Abstract
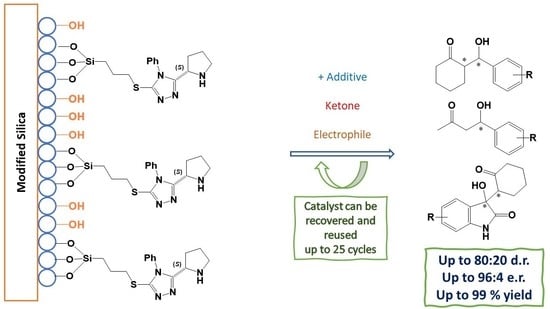
Novel organocatalytic systems based on the recently developed (
S)-proline derivative (2
S)-[5-(benzylthio)-4-phenyl-(1,2,4-triazol)-3-yl]-pyrrolidine supported on mesoporous silica were prepared and their efficiency was assessed in the asymmetric aldol reaction. These materials were fully characterized by FT-IR, MS, XRD, and SEM microscopy,
[...] Read more.
Novel organocatalytic systems based on the recently developed (
S)-proline derivative (2
S)-[5-(benzylthio)-4-phenyl-(1,2,4-triazol)-3-yl]-pyrrolidine supported on mesoporous silica were prepared and their efficiency was assessed in the asymmetric aldol reaction. These materials were fully characterized by FT-IR, MS, XRD, and SEM microscopy, gathering relevant information regarding composition, morphology, and organocatalyst distribution in the doped silica. Careful optimization of the reaction conditions required for their application as catalysts in asymmetric aldol reactions between ketones and aldehydes afforded the anticipated aldol products with excellent yields and moderate diastereo- and enantioselectivities. The recommended experimental protocol is simple, fast, and efficient providing the enantioenriched aldol product, usually without the need of a special work-up or purification protocol. This approach constitutes a remarkable improvement in the field of heterogeneous (
S)-proline-based organocatalysis; in particular, the solid-phase silica-bonded catalytic systems described herein allow for a substantial reduction in solvent usage. Furthermore, the supported system described here can be recovered, reactivated, and reused several times with limited loss in catalytic efficiency relative to freshly synthesized organocatalysts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Enantioselective Synthesis of Chromanones Bearing an α,α-Disubstituted α-Amino Acid Moiety via Decarboxylative Michael Reaction
by
Jan Bojanowski, Lesław Sieroń and Anna Albrecht
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3879
Abstract
In this manuscript, a novel, decarboxylative Michael reaction between α-substituted azlactones and chromone-3-carboxylic acids is described. The reaction proceeds in a sequence Michael addition followed by decarboxylative deprotonation, and it results in the formation of chromanones bearing an azlactone structural unit. The possibility
[...] Read more.
In this manuscript, a novel, decarboxylative Michael reaction between α-substituted azlactones and chromone-3-carboxylic acids is described. The reaction proceeds in a sequence Michael addition followed by decarboxylative deprotonation, and it results in the formation of chromanones bearing an azlactone structural unit. The possibility of transforming an azlactone moiety into a protected α,α-disubstituted α-amino acid derivative is also demonstrated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Chiral Diol-Based Organocatalysts in Enantioselective Reactions
by
Truong N. Nguyen, Po-An Chen, Krit Setthakarn and Jeremy A. May
Cited by 36 | Viewed by 10729
Abstract
Organocatalysis has emerged as a powerful synthetic tool in organic chemistry in the last few decades. Among various classes of organocatalysis, chiral diol-based scaffolds, such as BINOLs, VANOLs, and tartaric acid derivatives, have been widely used to induce enantioselectivity due to the ability
[...] Read more.
Organocatalysis has emerged as a powerful synthetic tool in organic chemistry in the last few decades. Among various classes of organocatalysis, chiral diol-based scaffolds, such as BINOLs, VANOLs, and tartaric acid derivatives, have been widely used to induce enantioselectivity due to the ability of the hydroxyls to coordinate with the Lewis acidic sites of reagents or substrates and create a chiral environment for the transformation. In this review, we will discuss the applications of these diol-based catalysts in different types of reactions, including the scopes of reactions and the modes of catalyst activation. In general, the axially chiral aryl diol BINOL and VANOL derivatives serve as the most competent catalyst for most examples, but examples of exclusive success using other scaffolds, herein, suggests that they should not be overlooked. Lastly, the examples, to date, are mainly from tartrate and biaryl diol catalysts, suggesting that innovation may be available from new diol scaffolds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of Both Enantiomers of Chiral Phenylalanine Derivatives Catalyzed by Cinchona Alkaloid Quaternary Ammonium Salts as Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysts
by
Lei Jin, Shuai Zhao and Xin Chen
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5507
Abstract
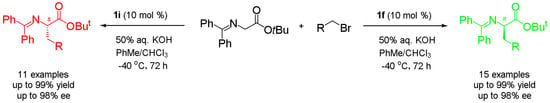
A practical synthesis of both enantiomers of unnatural phenylalanine derivatives by using two pseudoenantiomeric phase transfer catalysts is described. Through asymmetric α-alkylation of glycine Schiff base with substituted benzyl bromides and 1-(bromomethyl)naphthalene under the catalysis of
O-allyl-
N-(9-anthracenmethyl) cinchoninium bromide (
[...] Read more.
A practical synthesis of both enantiomers of unnatural phenylalanine derivatives by using two pseudoenantiomeric phase transfer catalysts is described. Through asymmetric α-alkylation of glycine Schiff base with substituted benzyl bromides and 1-(bromomethyl)naphthalene under the catalysis of
O-allyl-
N-(9-anthracenmethyl) cinchoninium bromide (
1f) and
O-allyl-
N-(9-anthracenylmethyl)cinchonidium bromide (
1i), respectively, a series of both (
R)- and (
S)-enantiomers of unnatural α-amino acid derivatives were obtained in excellent yields and enantioselectivity. The synthetic method is simple and scalable, and the stereochemistry of the products is fully predictable and controlled: the cinchonine-type phase transfer catalyst
1f resulted in (
R)-α-amino acid derivatives, and the cinchonidine-type phase transfer catalyst
1i afforded (
S)-α-amino acid derivatives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Organocatalyzed Synthesis of [3.2.1] Bicyclooctanes
by
Ignacio E. Tobal, Alejandro M. Roncero, Narciso M. Garrido, Isidro S. Marcos and David Díez
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 5810
Abstract
Organocatalysis constitutes one of the main research areas in organic chemistry from the last two decades. This chemistry has been applied to the synthesis of many natural products and structures in a manner that reduces the residues and so the ecological impact. In
[...] Read more.
Organocatalysis constitutes one of the main research areas in organic chemistry from the last two decades. This chemistry has been applied to the synthesis of many natural products and structures in a manner that reduces the residues and so the ecological impact. In this review, we consider the work that has been done for the synthesis of bicyclo[3.2.1]octane framework. This structure is present in many natural products with very important biological activities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Organocatalyzed Domino C–C Bond-Forming Reactions
by
Cleo S. Evans and Lindsey O. Davis
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 6257
Abstract
Reactions that form a C–C bond make up a foundational pillar of synthetic organic chemistry. In addition, organocatalysis has emerged as an easy, environmentally-friendly way to promote this type of bond formation. Since around 2000, organocatalysts have been used in a variety of
[...] Read more.
Reactions that form a C–C bond make up a foundational pillar of synthetic organic chemistry. In addition, organocatalysis has emerged as an easy, environmentally-friendly way to promote this type of bond formation. Since around 2000, organocatalysts have been used in a variety of C–C bond-forming reactions including Michael and aldol additions, Mannich-type reactions, and Diels–Alder reactions, to name a few. Many of these methodologies have been refined and further developed to include cascade and domino processes. This review will focus on recent advances in this area with an emphasis on methodologies having applications in the synthesis of biologically-significant compounds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Novel Chiral Bis-Phosphoramides as Organocatalysts for Tetrachlorosilane-Mediated Reactions
by
Sergio Rossi, Marco Ziliani, Rita Annunziata and Maurizio Benaglia
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 5039
Abstract
The formation of novel chiral bidentate phosphoroamides structures able to promote Lewis base-catalyzed Lewis acid-mediated reactions was investigated. Two different classes of phosphoroamides were synthetized: the first class presents a phthalic acid/primary diamine moiety, designed with the aim to perform a self-assembly recognition
[...] Read more.
The formation of novel chiral bidentate phosphoroamides structures able to promote Lewis base-catalyzed Lewis acid-mediated reactions was investigated. Two different classes of phosphoroamides were synthetized: the first class presents a phthalic acid/primary diamine moiety, designed with the aim to perform a self-assembly recognition process through hydrogen bonds; the second one is characterized by the presence of two phosphoroamides as side arms connected to a central pyridine unit, able to chelate SiCl
4 in a 2:1 adduct. These species were tested as organocatalysts in the stereoselective allylation of benzaldehyde and a few other aromatic aldehydes with allyl tributyltin in the presence of SiCl
4 with good results. NMR studies confirm that only pyridine-based phosphoroamides effectively coordinate tetrachlorosilane and may lead to the generation of a self-assembled entity that would act as a promoter of the reaction. Although further work is necessary to clarify and confirm the formation of the hypothesized adduct, the study lays the foundation for the design and the synthesis of chiral supramolecular organocatalysts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Non-Covalent Organocatalyzed Domino Reactions Involving Oxindoles: Recent Advances
by
Tecla Gasperi, Martina Miceli, Jean-Marc Campagne and Renata Marcia de Figueiredo
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 6858
Abstract
The ubiquitous presence of spirooxindole architectures with several functionalities and stereogenic centers in bioactive molecules has been appealing for the development of novel methodologies seeking their preparation in high yields and selectivities. Expansion and refinement in the field of asymmetric organocatalysis have made
[...] Read more.
The ubiquitous presence of spirooxindole architectures with several functionalities and stereogenic centers in bioactive molecules has been appealing for the development of novel methodologies seeking their preparation in high yields and selectivities. Expansion and refinement in the field of asymmetric organocatalysis have made possible the development of straightforward strategies that address these two requisites. In this review, we illustrate the current state-of-the-art in the field of spirooxindole synthesis through the use of non-covalent organocatalysis. We aim to provide a concise overview of very recent methods that allow to the isolation of unique, densely and diversified spirocyclic oxindole derivatives with high structural diversity via the use of cascade, tandem and domino processes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
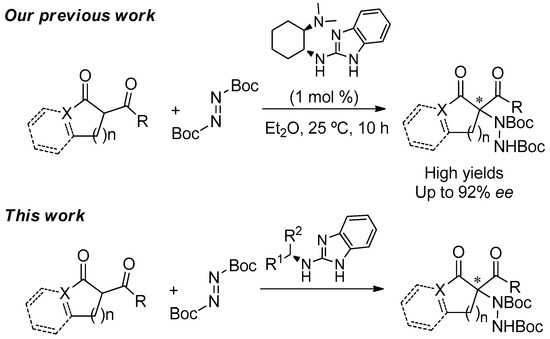
Readily Available Chiral Benzimidazoles-Derived Guanidines as Organocatalysts in the Asymmetric α-Amination of 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds
by
Llorenç Benavent, Francesco Puccetti, Alejandro Baeza and Melania Gómez-Martínez
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6131
Abstract
The synthesis and the evaluation as organocatalysts of new chiral guanidines derived from benzimidazoles in the enantioselective α-amination of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds using di-
t-butylazodicarboxylate as aminating agent is herein disclosed. The catalysts are readily synthesized through the reaction of 2-chlorobezimidazole and a
[...] Read more.
The synthesis and the evaluation as organocatalysts of new chiral guanidines derived from benzimidazoles in the enantioselective α-amination of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds using di-
t-butylazodicarboxylate as aminating agent is herein disclosed. The catalysts are readily synthesized through the reaction of 2-chlorobezimidazole and a chiral amine in moderate-to-good yields. Among all of them, those derived from (
R)-1-phenylethan-1-amine (
1) and (
S)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethan-1-amine (
3) turned out to be the most efficient for such asymmetric transformation, rendering good-to-high yields and moderate-to-good enantioselectivities for the amination products.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Asymmetric Michael Addition Organocatalyzed by α,β-Dipeptides under Solvent-Free Reaction Conditions
by
C. Gabriela Avila-Ortiz, Lenin Díaz-Corona, Erika Jiménez-González and Eusebio Juaristi
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 7231
Abstract
The application of six novel α,β-dipeptides as chiral organocatalysts in the asymmetric Michael addition reaction between enolizable aldehydes and
N-arylmaleimides or nitroolefins is described. With
N-arylmaleimides as substrates, the best results were achieved with dipeptide
2 as a catalyst in the
[...] Read more.
The application of six novel α,β-dipeptides as chiral organocatalysts in the asymmetric Michael addition reaction between enolizable aldehydes and
N-arylmaleimides or nitroolefins is described. With
N-arylmaleimides as substrates, the best results were achieved with dipeptide
2 as a catalyst in the presence of aq. NaOH. Whereas dipeptides
4 and
6 in conjunction with 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) and thiourea as a hydrogen bond donor proved to be highly efficient organocatalytic systems in the enantioselective reaction between isobutyraldehyde and various nitroolefins.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Expedient Organocatalytic Syntheses of 4-Substituted Pyrazolidines and Isoxazolidines
by
Tarek Yousfi, Alysha Elliott, Messiad Hanane, Rachid Merdes and Albert Moyano
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 5637
Abstract
The efficient organocatalytic synthesis of heterocyclic systems of biological relevance is a subject of growing interest. We have found that the pyrrolidine/benzoic acid-catalyzed reaction of α-substituted propenals such as methacrolein, 2-benzylpropenal and 2-(
n-hexyl)propenal with activated hydrazines takes place in very good
[...] Read more.
The efficient organocatalytic synthesis of heterocyclic systems of biological relevance is a subject of growing interest. We have found that the pyrrolidine/benzoic acid-catalyzed reaction of α-substituted propenals such as methacrolein, 2-benzylpropenal and 2-(
n-hexyl)propenal with activated hydrazines takes place in very good yields (83%–99.6%) under very mild conditions to afford 4-substituted pyrazolidin-3-ols (as diastereomer mixtures); subsequent oxidation with PCC affords the corresponding-4-substituted-3-pyrazolidinones in essentially quantitative yields. In a similar way, 4-substituted isoxazolidinones are obtained with
N-Cbz-hydroxylamine as a reagent. The use of chiral diarylprolinol trimethylsilyl ethers as catalysts allows the synthesis of several of these compounds in optically active form, in some cases with excellent enantioselectivity (up to 96:4 er). A preliminary evaluation of the biological activity shows that some of these compounds exhibit interesting antibacterial and antifungal activities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
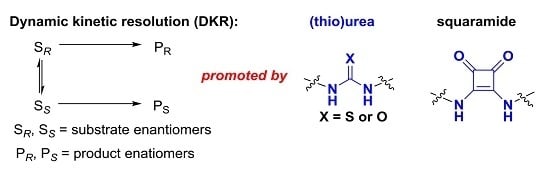
Recent Advances in Dynamic Kinetic Resolution by Chiral Bifunctional (Thio)urea- and Squaramide-Based Organocatalysts
by
Pan Li, Xinquan Hu, Xiu-Qin Dong and Xumu Zhang
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 9614
Abstract
The organocatalysis-based dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) process has proved to be a powerful strategy for the construction of chiral compounds. In this feature review, we summarized recent progress on the DKR process, which was promoted by chiral bifunctional (thio)urea and squaramide catalysis via
[...] Read more.
The organocatalysis-based dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) process has proved to be a powerful strategy for the construction of chiral compounds. In this feature review, we summarized recent progress on the DKR process, which was promoted by chiral bifunctional (thio)urea and squaramide catalysis via hydrogen-bonding interactions between substrates and catalysts. A wide range of asymmetric reactions involving DKR, such as asymmetric alcoholysis of azlactones, asymmetric Michael–Michael cascade reaction, and enantioselective selenocyclization, are reviewed and demonstrate the efficiency of this strategy. The (thio)urea and squaramide catalysts with dual activation would be efficient for more unmet challenges in dynamic kinetic resolution.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
TBD- or PS-TBD-Catalyzed One-Pot Synthesis of Cyanohydrin Carbonates and Cyanohydrin Acetates from Carbonyl Compounds
by
Satoru Matsukawa, Junya Kimura and Miki Yoshioka
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 6634
Abstract
Cyanation reactions of carbonyl compounds with methyl cyanoformate or acetyl cyanide catalyzed by 5 mol % of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4,4,0]dec-5-ene (TBD) were examined. Using methyl cyanoformate, the corresponding cyanohydrin carbonates were readily obtained in high yield for aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes and ketones. Similar results
[...] Read more.
Cyanation reactions of carbonyl compounds with methyl cyanoformate or acetyl cyanide catalyzed by 5 mol % of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4,4,0]dec-5-ene (TBD) were examined. Using methyl cyanoformate, the corresponding cyanohydrin carbonates were readily obtained in high yield for aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes and ketones. Similar results were obtained when acetyl cyanide was used as the cyanide source. The polymer-supported catalyst, PS-TBD, also acted as a good catalyst for this reaction. PS-TBD was easily recovered and reused with minimal activity loss.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Organocatalyzed Intramolecular Carbonyl-Ene Reactions
by
Heidi A. Dahlmann, Amanda J. McKinney, Maria P. Santos and Lindsey O. Davis
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5867
Abstract
An organocatalyzed intramolecular carbonyl-ene reaction was developed to produce carbocyclic and heterocyclic 5- and 6-membered rings from a citronellal-derived trifluoroketone and a variety of aldehydes. A phosphoramide derivative was found to promote the cyclization of the trifluoroketone, whereas a less acidic phosphoric acid
[...] Read more.
An organocatalyzed intramolecular carbonyl-ene reaction was developed to produce carbocyclic and heterocyclic 5- and 6-membered rings from a citronellal-derived trifluoroketone and a variety of aldehydes. A phosphoramide derivative was found to promote the cyclization of the trifluoroketone, whereas a less acidic phosphoric acid proved to be a superior catalyst for the aldehyde substrates.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
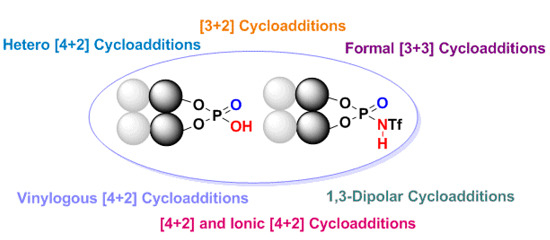
Open AccessReview
Enantioselective Cycloaddition Reactions Catalyzed by BINOL-Derived Phosphoric Acids and N-Triflyl Phosphoramides: Recent Advances
by
Felix E. Held, Dominik Grau and Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 10323
Abstract
Over the last several years there has been a huge increase in the development and applications of new efficient organocatalysts for enantioselective pericyclic reactions, which represent one of the most powerful types of organic transformations. Among these processes are cycloaddition reactions (e.g., [3+2];
[...] Read more.
Over the last several years there has been a huge increase in the development and applications of new efficient organocatalysts for enantioselective pericyclic reactions, which represent one of the most powerful types of organic transformations. Among these processes are cycloaddition reactions (e.g., [3+2]; formal [3+3]; [4+2]; vinylogous [4+2] and 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions), which belong to the most utilized reactions in organic synthesis of complex nitrogen- and oxygen-containing heterocyclic molecules. This review presents the breakthrough realized in this field using chiral BINOL-derived phosphoric acids and
N-triflyl phosphoramide organocatalysts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
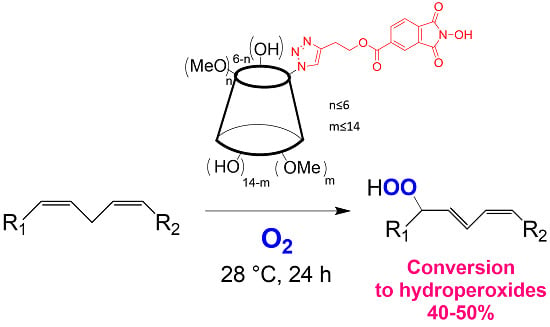
Functionalization of Cyclodextrins with N-Hydroxyphthalimide Moiety: A New Class of Supramolecular Pro-Oxidant Organocatalysts
by
Lucio Melone, Manuel Petroselli, Nadia Pastori and Carlo Punta
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 6599
Abstract
N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) is an organocatalyst for free-radical processes able to promote the aerobic oxidation of a wide range of organic substrates. In particular, NHPI can catalyze the hydroperoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). This property could be of interest for biological applications.
[...] Read more.
N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) is an organocatalyst for free-radical processes able to promote the aerobic oxidation of a wide range of organic substrates. In particular, NHPI can catalyze the hydroperoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). This property could be of interest for biological applications. This work reports the synthesis of two β-cyclodextrin derivatives (
CD5 and
CD6) having a different degree of methylation and bearing a NHPI moiety. These compounds, having different solubility in water, have been successfully tested for the hydroperoxidation of methyl linoleate, chosen as the PUFA model molecule.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
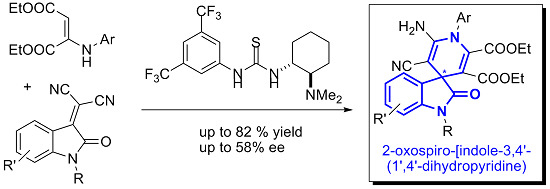
Open AccessCommunication
New Organocatalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Highly Substituted Chiral 2-Oxospiro-[indole-3,4′- (1′,4′-dihydropyridine)] Derivatives
by
Fernando Auria-Luna, Eugenia Marqués-López, Somayeh Mohammadi, Roghayeh Heiran and Raquel P. Herrera
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 9785
Abstract
Herein, we report our preliminary results concerning the first promising asymmetric synthesis of highly functionalized 2-oxospiro-[indole-3,4′-(1′,4′-dihydropyridine)] via the reaction of an enamine with isatylidene malononitrile derivatives in the presence of a chiral base organocatalyst. The moderate, but promising, enantioselectivity observed (30%–58% ee (enantiomeric
[...] Read more.
Herein, we report our preliminary results concerning the first promising asymmetric synthesis of highly functionalized 2-oxospiro-[indole-3,4′-(1′,4′-dihydropyridine)] via the reaction of an enamine with isatylidene malononitrile derivatives in the presence of a chiral base organocatalyst. The moderate, but promising, enantioselectivity observed (30%–58% ee (enantiomeric excess)) opens the door to a new area of research for the asymmetric construction of these appealing spirooxindole skeletons, whose enantioselective syntheses are still very limited.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Experimental and Theoretical Studies in Hydrogen-Bonding Organocatalysis
by
Matej Žabka and Radovan Šebesta
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 12164
Abstract
Chiral thioureas and squaramides are among the most prominent hydrogen-bond bifunctional organocatalysts now extensively used for various transformations, including aldol, Michael, Mannich and Diels-Alder reactions. More importantly, the experimental and computational study of the mode of activation has begun to attract considerable attention.
[...] Read more.
Chiral thioureas and squaramides are among the most prominent hydrogen-bond bifunctional organocatalysts now extensively used for various transformations, including aldol, Michael, Mannich and Diels-Alder reactions. More importantly, the experimental and computational study of the mode of activation has begun to attract considerable attention. Various experimental, spectroscopic and calculation methods are now frequently used, often as an integrated approach, to establish the reaction mechanism, the mode of activation or explain the stereochemical outcome of the reaction. This article comprises several case studies, sorted according to the method used in their study. The aim of this review is to give the investigators an overview of the methods currently utilized for mechanistic investigations in hydrogen-bonding organocatalysis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
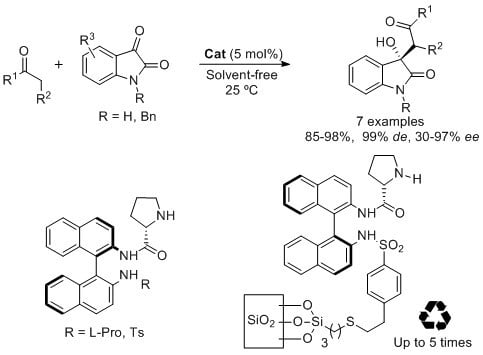
Open AccessArticle
Enantioselective Solvent-Free Synthesis of 3-Alkyl-3-hydroxy-2-oxoindoles Catalyzed by Binam-Prolinamides
by
Abraham Bañn-Caballero, Jesús Flores-Ferrándiz, Gabriela Guillena and Carmen Nájera
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 7195
Abstract
BINAM-prolinamides are very efficient catalyst for the synthesis of non-protected and
N-benzyl isatin derivatives by using an aldol reaction between ketones and isatins under solvent-free conditions. The results in terms of diastereo- and enantioselectivities are good, up to 99%
de and 97%
[...] Read more.
BINAM-prolinamides are very efficient catalyst for the synthesis of non-protected and
N-benzyl isatin derivatives by using an aldol reaction between ketones and isatins under solvent-free conditions. The results in terms of diastereo- and enantioselectivities are good, up to 99%
de and 97%
ee, and higher to those previously reported in the literature under similar reaction conditions. A high variation of the results is observed depending on the structure of the isatin and the ketone used in the process. While 90% of
ee and 97%
ee, respectively, is obtained by using (
Ra)-BINAM-l-(bis)prolinamide as catalyst in the addition of cyclohexanone and α-methoxyacetone to free isatin, 90%
ee is achieved for the reaction between
N-benzyl isatin and acetone using
N-tosyl BINAM-l-prolinamide as catalyst. This reaction is also carried out using a silica BINAM-l-prolinamide supported catalyst under solvent-free conditions, which can be reused up to five times giving similar results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Emergence of Quinone Methides in Asymmetric Organocatalysis
by
Lorenzo Caruana, Mariafrancesca Fochi and Luca Bernardi
Cited by 292 | Viewed by 15979
Abstract
Quinone methides (QMs) are highly reactive compounds that have been defined as “elusive” intermediates, or even as a “synthetic enigma” in organic chemistry. Indeed, there were just a handful of examples of their utilization in catalytic asymmetric settings until some years ago. This
[...] Read more.
Quinone methides (QMs) are highly reactive compounds that have been defined as “elusive” intermediates, or even as a “synthetic enigma” in organic chemistry. Indeed, there were just a handful of examples of their utilization in catalytic asymmetric settings until some years ago. This review collects organocatalytic asymmetric reactions that employ QMs as substrates and intermediates, from the early examples, mostly based on stabilized QMs bearing specific substitution patterns, to more recent contributions, which have dramatically expanded the scope of QM chemistry. In fact, it was only very recently that the generation of QMs
in situ through strategies compatible with organocatalytic methodologies has been realized. This tactic has finally opened the gate to the full exploitation of these unstable intermediates, leading to a series of remarkable disclosures. Several types of synthetically powerful asymmetric addition and cycloaddition reactions, applicable to a broad range of QMs, are now available.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
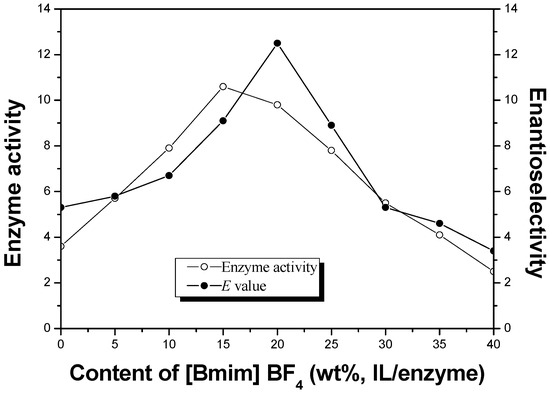
Microwave-Assisted Resolution of α-Lipoic Acid Catalyzed by an Ionic Liquid Co-Lyophilized Lipase
by
Ning Liu, Lei Wang, Zhi Wang, Liyan Jiang, Zhuofu Wu, Hong Yue and Xiaona Xie
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 6444
Abstract
The combination of the ionic liquid co-lyophilized lipase and microwave irradiation was used to improve enzyme performance in enantioselective esterification of α-lipoic acid. Effects of various reaction conditions on enzyme activity and enantioselectivity were investigated. Under optimal condition, the highest enantioselectivity (
E
[...] Read more.
The combination of the ionic liquid co-lyophilized lipase and microwave irradiation was used to improve enzyme performance in enantioselective esterification of α-lipoic acid. Effects of various reaction conditions on enzyme activity and enantioselectivity were investigated. Under optimal condition, the highest enantioselectivity (
E = 41.2) was observed with a high enzyme activity (178.1 μmol/h/mg) when using the ionic liquid co-lyophilized lipase with microwave assistance. Furthermore, the ionic liquid co-lyophilized lipase exhibited excellent reusability under low power microwave.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
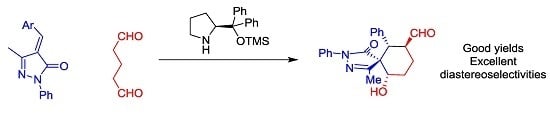
Open AccessCommunication
Highly Diastereoselective Synthesis of Spiropyrazolones
by
Victor Ceban, Temitope O. Olomola, Marta Meazza and Ramon Rios
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 6618
Abstract
We report a highly diastereoselective synthesis of spiropyrazolones catalyzed by secondary amines. The reported Michael-Aldol cascade reaction affords the desired spiropyrazolones bearing four chiral centers as a single diastereomer in excellent yields.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
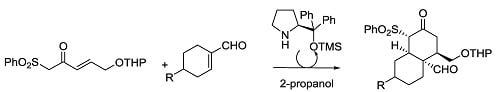
Open AccessArticle
Enantioselective Synthesis of cis-Decalins Using Organocatalysis and Sulfonyl Nazarov Reagents
by
Javier Peña, Gastón Silveira-Dorta, Rosalina F. Moro, Narciso M. Garrido, Isidro S. Marcos, Francisca Sanz and David Díez
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 9159
Abstract
The first organocatalytic synthesis of
cis-decalins using sulfonyl Nazarov reagents is reported. The Jørgensen’s catalyst directs this highly enantioselective synthesis using different cyclohexenal derivatives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
DNA-Catalyzed Henry Reaction in Pure Water and the Striking Influence of Organic Buffer Systems
by
Marleen Häring, Maria M. Pérez-Madrigal, Dennis Kühbeck, Asja Pettignano, Françoise Quignard and David Díaz Díaz
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 10097
Abstract
In this manuscript we report a critical evaluation of the ability of natural DNA to mediate the nitroaldol (Henry) reaction at physiological temperature in pure water. Under these conditions, no background reaction took place (
i.e., control experiment without DNA). Both heteroaromatic
[...] Read more.
In this manuscript we report a critical evaluation of the ability of natural DNA to mediate the nitroaldol (Henry) reaction at physiological temperature in pure water. Under these conditions, no background reaction took place (
i.e., control experiment without DNA). Both heteroaromatic aldehydes (e.g., 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde) and aromatic aldehydes bearing strong or moderate electron-withdrawing groups reacted satisfactorily with nitromethane obeying first order kinetics and affording the corresponding β-nitroalcohols in good yields within 24 h. In contrast, aliphatic aldehydes and aromatic aldehydes having electron-donating groups either did not react or were poorly converted. Moreover, we discovered that a number of metal-free organic buffers efficiently promote the Henry reaction when they were used as reaction media without adding external catalysts. This constitutes an important observation because the influence of organic buffers in chemical processes has been traditionally underestimated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures