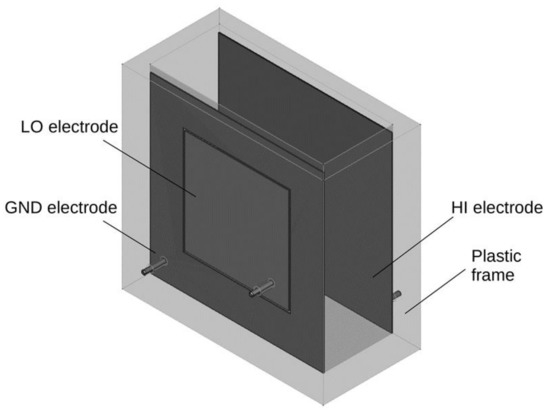
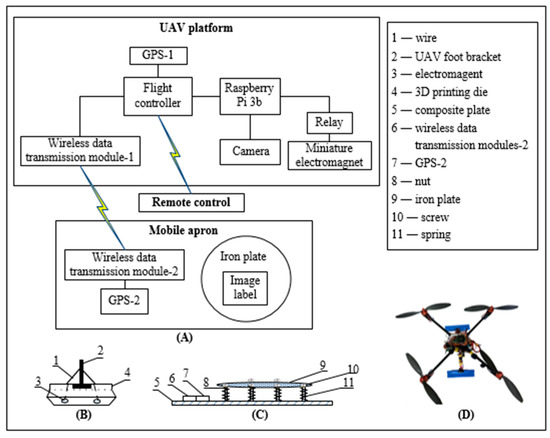
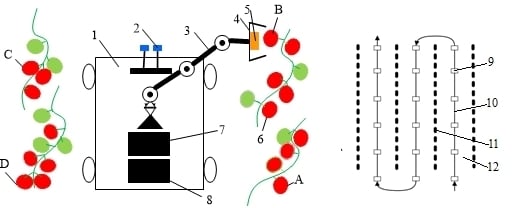
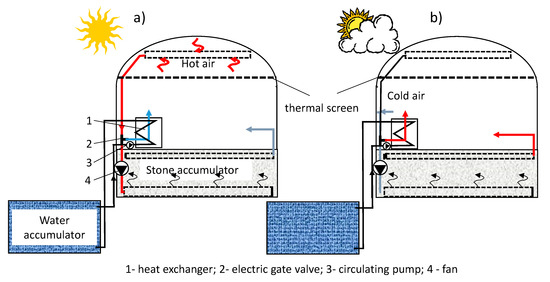
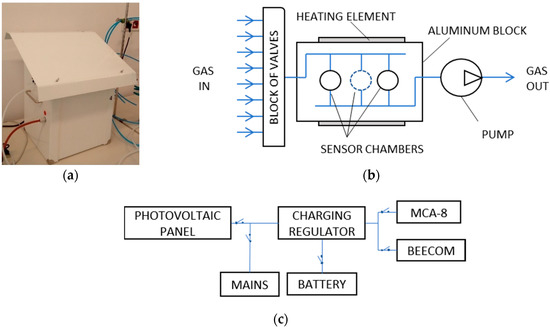
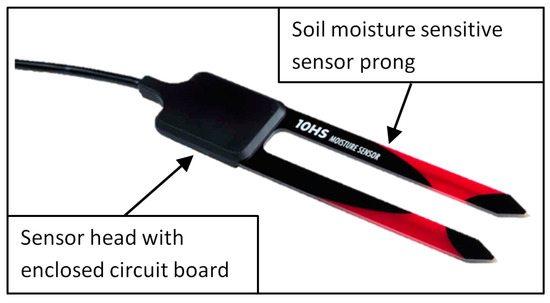
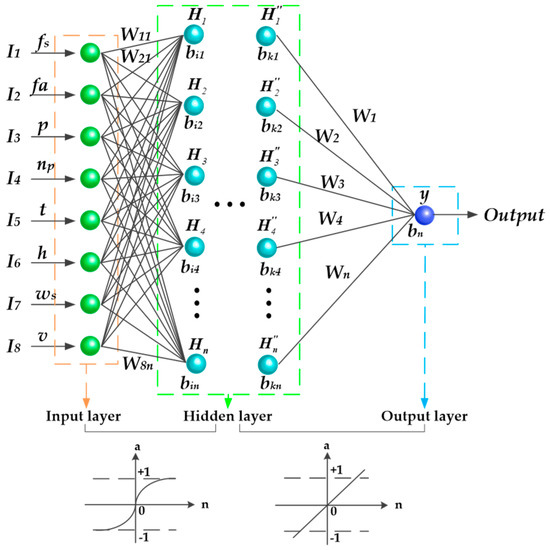
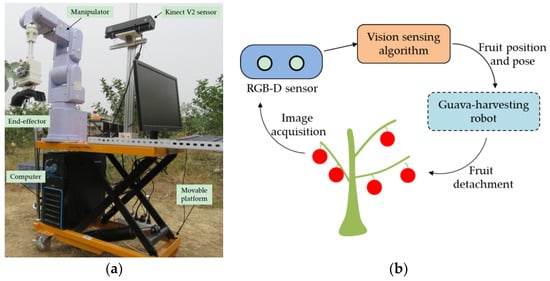
Sensors in Agriculture and Forestry
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Smart Agriculture".
Viewed by 308175Editor
Interests: computer vision; image processing; pattern recognition; 3D image reconstruction, spatio-temporal image change detection and tracking; fusion and registering from imaging sensors; superresolution from low-resolution image sensors
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Sensors and technologies involving sensors in agriculture and forestry play an important role today. In agriculture and silviculture, as a branch of forestry, the need for increasing the production and simultaneously the efforts for minimizing the environmental impact and for saving costs make the sensor systems the best allied tool. The use of sensors helps to exploit all available resources appropriately and to apply hazardous products moderately. When nutrients in the soil, humidity, solar radiation, density of weeds and all factors affecting the production are known, this gets better and the use of chemical products such as fertilizers, herbicides and other pollution products can be reduced considerably. These activities fall inside the emerging area known as Precision Agriculture. In forest management, which can be considered a branch of forestry, a lot of number of activities is oriented towards wood production or forest inventories with the aims of controlling parameters of interest such as diameter of trees, height, crown height, bark thickness and other variables, such as canopy, humidity, illumination, CO2 transformation, where the social acceptation is of interest.
The use of unmanned aerial or ground vehicles (UAVs and UGVs), equipped with a set of sensors, has experimented an important growing during the last years to carry out the tasks involved in the above processes and also for autonomous navigation on the specific agricultural and forestry environments. But also traditional crewed vehicles are sensorized conveniently with same purpose.
Additionally, during the post-production process, including transportation, storage, packing, selection, classification or distribution among others, the use of sensors is of vital importance for minimizing costs and negative environmental impact allowing saving energy or minimizing the application of chemical products.
A list of sensors covering the above topics, but are not limited, is the following: biological (including chemical and gas analyzers), water sensors, meteorological sensors, weed seekers, optical cameras, Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR), photometric sensors, soil respiration or moisture, photosynthesis sensors, Leaf Area index (LAI) sensors, range finders, Dendrometers, hygrometers.
This Topical Collection covers the following topics related to the above sensors:
- Sensors devices capabilities, materials and technologies
- Applications and problems addressed
- Sensors domain-oriented devices and methods used for processing the data sensed
Prof. Dr. Gonzalo Pajares Martinsanz
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Keywords
- sensors in agriculture and forestry
- precision agriculture
- sensors in agricultural and forestry production
- storage and distribution
- technologies
- material and methods
- sensors applications
- processing of sensed data