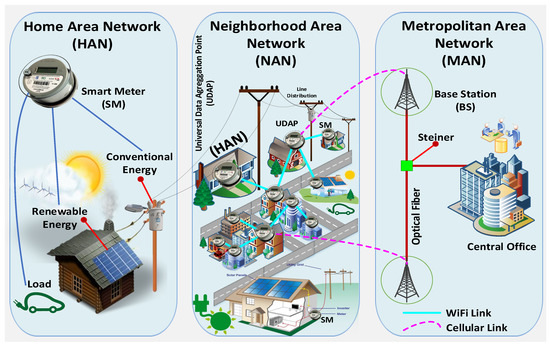
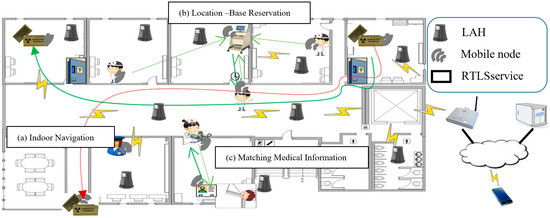
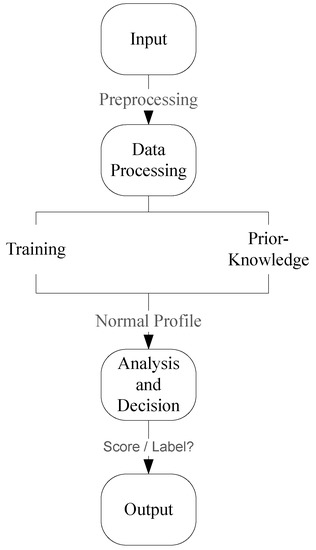
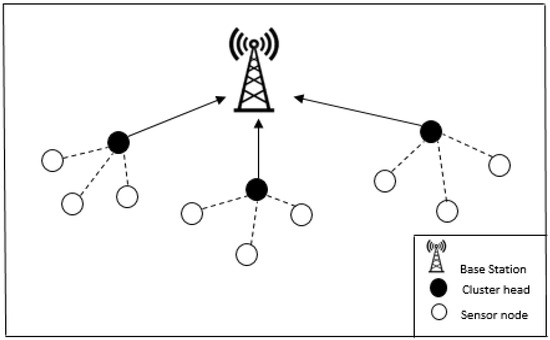
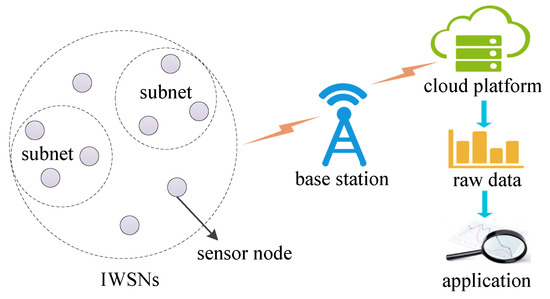
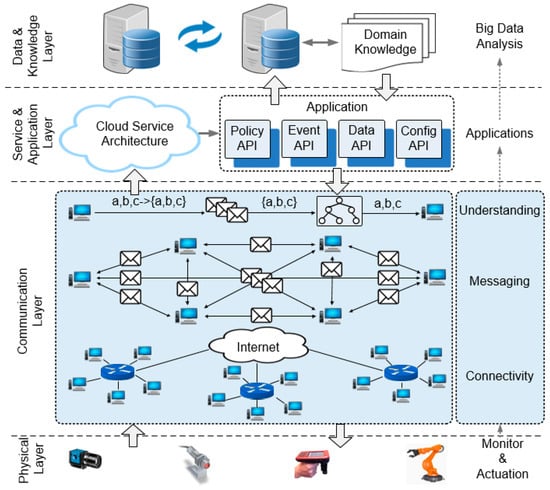
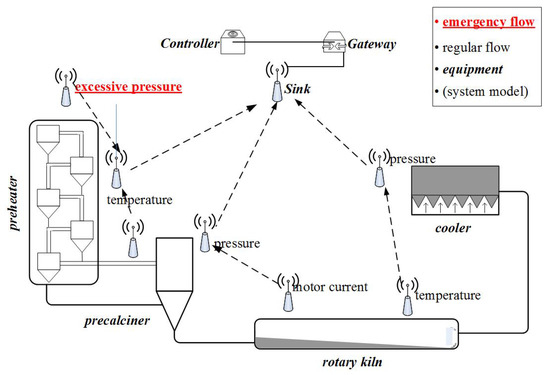
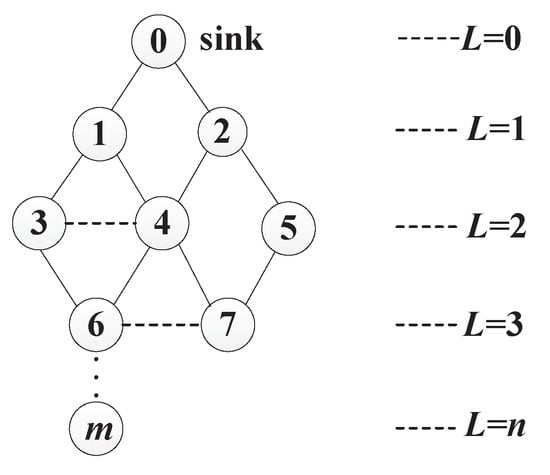
Smart Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (Closed)
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Sensor Networks".
Viewed by 155796Editors
2. School of Engineering, College of Science, University of Lincoln, Lincoln LN6 7TS, UK
Interests: Internet of Things; sensor networks; green computing; cloud and fog computing; fault diagnosis; wireless sensor networks; multimedia communication; middleware; security
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: wireless sensor networks
Interests: wireless sensor networks; cloud computing; Internet of Things; big data; social networks; security
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
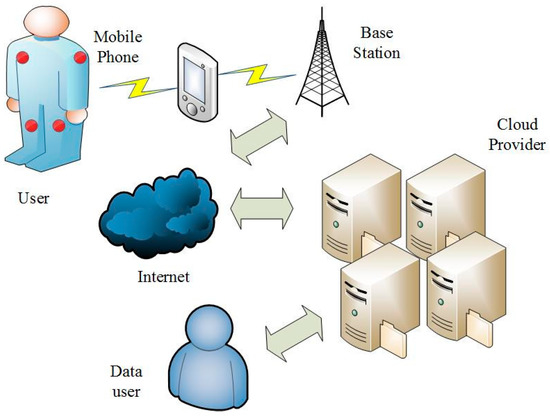
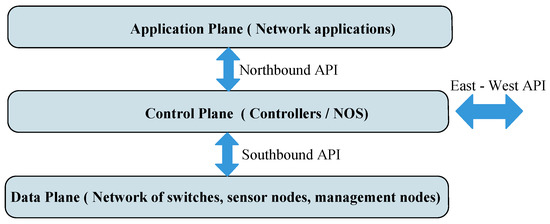
Researchers are in the pursuit of emerging technologies that enable human-centric or machine-centric networks to meet the evolving requirements (e.g., factory automation, fault diagnosis, fuel consumption monitoring, surveillance, etc.) in industries. Toward this goal, Smart Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (SIWSNs) are identified as an essential technology. Particularly, on the one hand, with SIWSNs, data sensing, gathering and communication are performed intelligently by all kinds of industrial wireless sensors (e.g., photoelectric sensor, ultrasonic sensor, gas sensor, video sensor, etc.). Thus, various industrial data can be exchanged and managed autonomously and efficiently. On the other hand, due to the ease of deployment and flexibility of SIWSNs, the inherent drawbacks of wired industrial networks can be well overcome.
However, to utilize SIWSNs in a robust manner, there are a lot of tough issues to be addressed (e.g., coverage, localization, middleware, energy efficiency, quality of service, security, etc.). Moreover, with the recent adoption of cloud computing and big data technologies in industries, new issues might be posed for SIWSNs.
Therefore, this Topical Collection aims to solicit high quality original technical or experimental papers which concern the current development or future challenge for SIWSNs. Review or survey papers will also be considered. Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
-
Wireless access for SIWSNs
-
Coverage for SIWSNs
-
Localization for SIWSNs
-
Data aggregation for SIWSNs
-
Data management for SIWSNs
-
Middleware for SIWSNs
-
Energy efficiency for SIWSNs
-
Quality of service for SIWSNs
-
Security for SIWSNs
-
Cloud computing for SIWSNs
-
Big data for SIWSNs
Prof. Dr. Lei Shu
Prof. Dr. Gerhard P. Hancke
Dr. Chunsheng Zhu
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
-
Industrial sensor networks
-
Smartness
-
Wireless
-
Robustness
-
Cloud computing
-
Big data