On the Fragility of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Experimental Data
3.2. Fitting Procedures
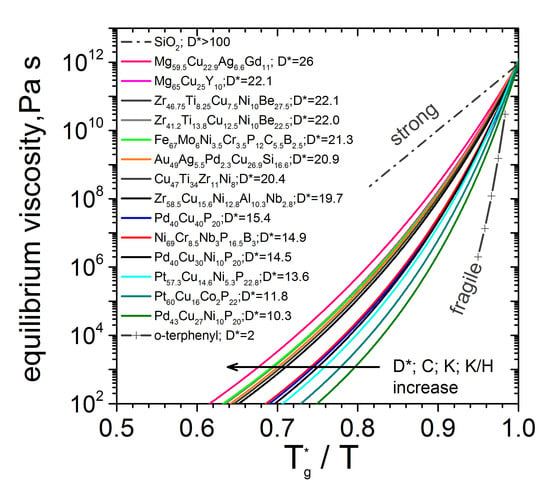
3.3. Kinetic Fragility
3.4. Thermodynamic Fragility
3.5. Connection between the Kinetic and the Thermodynamic Fragility
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Amorphous Zr-Al-Tm (Tm = Co, Ni, Cu) Alloys with Significant Supercooled Liquid Region of over 100-K. Mater. Trans. JIM 1991, 32, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Nakamura, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Masumoto, T. Mg-Cu-Y Bulk Amorphous Alloys with High Tensile Strength Produced by a High-Pressure Die Casting Method. Mater. Trans. JIM 1992, 33, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Johnson, W.L. Formation of Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 6514–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Johnson, W.L. Highly Processable Bulk Metallic Glass-forming alloys in the Pt–Co–Ni–Cu–P system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Lohwongwatana, B.; Johnson, W.L.; Peker, A. Gold based bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 2005–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Floyd, M.; Garrett, G.; Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L. Bulk Metallic Steel with High Glass Forming Ability. U.S. Patent 2015/0020929 A1, 22 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Na, J.H.; Demetriou, M.D.; Floyd, M.; Hoff, A.; Garrett, G.R.; Johnson, W.L. Compositional landscape for glass formation in metal alloys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9031–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peker, A.; Johnson, W.L. A highly processable metallic glass: Zr41.2Ti 13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glade, S.C.; Busch, R.; Lee, D.S.; Johnson, W.L.; Wunderlich, R.K.; Fecht, H.J.; Introduction, I. Thermodynamics of Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8, Zr52.5Cu17.9Ni14.6Al10Ti5 and Zr57Cu15.4Ni12.6Al10Nb5 bulk metallic glass forming alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 7242–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, C.C.; Schroers, J.; Johnson, W.L.; Rathz, T.J.; Hyers, R.W.; Rogers, J.R.; Robinson, M.B. Vitrification and determination of the crystallization time scales of the bulk-metallic-glass-forming liquid Zr58.5Nb2.8Cu15.6Ni12.8Al 10.3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Bulk Glass Formation and Crystallization of Zr-Ti Based Alloy. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, O.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R.; Eisenbart, M.; Klotz, U.E. Massivglasbildende Weißgoldlegierung. Patent DE202016004123 (U1), 12 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.L. Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys—Science and technology. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R. The thermophysical properties of bulk metallic glass-forming liquids. JOM 2000, 52, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Gallino, I. On the kinetic, thermodynamics and structure of bulk metallic glass forming liquids. JOM Spec. Issue Amorph. Alloy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Schroers, J.; Wang, W.H. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Bulk Metallic Glass. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Bakke, E.; Johnson, W.L. Viscosity of the supercooled liquid and relaxation at the glass transition of the Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 bulk metallic glass forming alloy. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallino, I.; Shah, M.B.; Busch, R. Enthalpy relaxation and its relation to the thermodynamics and crystallization of the Zr58.5Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3Nb2.8 bulk metallic glass-forming alloy. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, Z.; Busch, R. Equilibrium viscosity, enthalpy recovery and free volume relaxation in a Zr44Ti11Ni10Cu10Be25 bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4404–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtler, B.; Gross, O.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R. Thermo-physical characterization of the Fe67Mo6Ni3.5Cr3.5P12C5.5B2.5 bulk metallic glass forming alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 118, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, O.; Bochtler, B.; Stolpe, M.; Hechler, S.; Hembree, W.; Busch, R.; Gallino, I. The kinetic fragility of Pt-P- and Ni-P-based bulk glass-forming liquids and its thermodynamic and structural signature. Acta Mater. 2017, 132, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallino, I.; Cangialosi, D.; Evenson, Z.; Schmitt, L.; Hechler, S.; Stolpe, M.; Ruta, B. Activation energy spectrum for relaxation and polyamorphism in an ultra-viscous metallic glass former. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1706.03830. [Google Scholar]
- Angell, C.A. Formation of glasses from liquids and biopolymers. Science 1995, 267, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallino, I.; Schroers, J.; Busch, R. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the fragility of bulk metallic glass forming liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Gibbs, J.H. On the Temperature Dependence of Cooperative Relaxation Properties in Glass-Forming Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 43, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M. Viscous liquids and the glass transition: A potential energy barrier picture. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 3728–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.-M.; Angell, C.A. A thermodynamic connection to the fragility of glass-forming liquids. Nature 2001, 410, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, J.C.; Yue, Y.; Ellison, A.J.; Gupta, P.K.; Allan, D.C. Viscosity of glass-forming liquids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19780–19784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumis, G.G. Glass transition phenomenology and flexibility: An approach using the energy landscape formalism. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Thorpe, M.F. Constraint theory, vector percolation and glass formation. Solid State Commun. 1985, 53, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Mauro, J.C. Composition dependence of glass transition and fragility. I. A topological model incorporating temperature-dependent constraints. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenson, Z.; Raedersdorf, S.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R. Equilibrium viscosity of Zr-Cu-Ni-Al-Nb bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Yang, F.; Bednarcik, J.; Kaban, I.; Shuleshova, O.; Meyer, A.; Busch, R. Liquid–liquid transition in a strong bulk metallic glass-forming liquid. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolpe, M.; Jonas, I.; Wei, S.; Evenson, Z.; Hembree, W.; Yang, F.; Meyer, A.; Busch, R. Structural changes during a liquid-liquid transition in the deeply undercooled Zr58.5Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3Nb2.8 bulk metallic glass forming melt. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Blodgett, M.; Kelton, K.F.; Ma, J.L.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.-L. Structural crossover in a supercooled metallic liquid and the link to a liquid-to-liquid phase transition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 211907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechler, S.; Ruta, B.; Stolpe, M.; Pineda, E.; Evenson, Z.; Gross, O.; Hembree, W.; Bernasconi, A.; Busch, R.; Gallino, I. Liquid-liquid transition revealed by quasi-static cooling of an ultra-viscous metallic liquid. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1704.06703. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Yue, Y. Structural evolution during fragile-to-strong transition in CuZr(Al) glass-forming liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 64508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orava, J.; Weber, H.; Kaban, I.; Greer, A.L. Viscosity of liquid Ag–In–Sb–Te: Evidence of a fragile-to-strong crossover. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 194503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, L.; Yue, Y.; Mauro, J.C. Fragile-to-strong transition in metallic glass-forming liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Way, C.; Wadhwa, P.; Busch, R. The influence of shear rate and temperature on the viscosity and fragility of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5 metallic-glass-forming liquid. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2977–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, Z. On the Thermodynamic and Kinetic Properties of Bulk Glass Forming Metallic Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Legg, B.A.; Schroers, J.; Busch, R. Thermodynamics, kinetics, and crystallization of Pt57.3Cu14.6Ni5.3P22.8 bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbart, M.; Klotz, U.E.; Busch, R.; Gallino, I. A colourimetric and microstructural study of the tarnishing of gold-based bulk metallic glasses. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Properties of Magnesium-Based Bulk Metallic Glass-Forming Liquids. Master of Science Thesis, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, S.; Oda, S.; Morinaga, K. Heat capacity of oxide glasses at high temperature region. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 325, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecksher, T.; Nielsen, A.I.; Olsen, N.B.; Dyre, J.C. Little evidence for dynamic divergences in ultraviscous molecular liquids. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyre, J.C.; Hecksher, T.; Niss, K. A brief critique of the Adam—Gibbs entropy model. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Liu, W.; Johnson, W.L. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the Mg65Cu25Y10 bulk metallic glass forming liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 4134–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, E.; Busch, R.; Johnson, W.L. The viscosity of the Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 bulk metallic glass forming alloy in the supercooled liquid. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waniuk, T.A.; Busch, R.; Masuhr, A.; Johnson, W.L. Equilibrium viscosity of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass-forming liquid and viscous flow during relaxation, phase separation, and primary crystallization. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 5229–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glade, S.C.; Johnson, W.L. Viscous flow of the Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8 glass forming alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 7249–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willnecker, R.; Wilde, G.; Go, G.P.; Fecht, H.J.; Introduction, I. Calorimetric, thermomechanical, and rheological characterizations of bulk glass-forming Pd 40 Ni 40 P 20. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, N.; Inoue, A. Glass Transition Behavior and Viscous Flow Working of Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 Amorphous Alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM 1999, 40, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Johnson, W.L. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of the Undercooled Liquid and the Glass Transition of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5 Alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 4039–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.-R.; Wilde, G.; Görler, G.; Willnecker, R. Thermodynamic properties of Pd-based glass-forming alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 250–252, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, Z.; Schmitt, T.; Nicola, M.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R. High temperature melt viscosity and fragile to strong transition in Zr-Cu-Ni-Al-Nb(Ti) and Cu47Ti 34Zr11Ni8 bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4712–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; Qin, J.; Bian, X.; Yue, Y. Indication of liquid-liquid phase transition in CuZr-based melts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R.; Angell, C.A. Glass transition with decreasing correlation length during cooling of Fe50Co50 superlattice and strong liquids. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C. Relaxation in liquids, polymers and plastic crystals—Strong/fragile patterns and problems. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1991, 131–133, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, G.D.; Battezzati, L. Thermodynamic and dynamic fragility in metallic glass-formers. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2260–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Evenson, Z.; Gallino, I.; Busch, R. The impact of fragility on the calorimetric glass transition in bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2014, 55, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedskjaer, M.M.; Mauro, J.C.; Youngman, R.E.; Hogue, C.L.; Potuzak, M.; Yue, Y. Topological Principles of Borosilicate Glass Chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 12930–12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadowspeaker, L.; Busch, R. On the fragility of Nb-Ni-based and Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2508–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lida, T.; Guthrie, R.I.L. The Physical Properties of Liquid Metals; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Faupel, F.; Frank, W.; Macht, M.-P.; Mehrer, H.; Naundorf, V.; Rätzke, K.; Schober, H.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Teichler, H. Diffusion in metallic glasses and supercooled melts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 237–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argon, A.S.; Kuo, H.Y. Plastic flow in a disordered bubble raft (an analog of a metallic glass). Mater. Sci. Eng. 1979, 39, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, T. Structural relaxation in metallic glasses. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1981, 371, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srolovitz, D.; Vitek, V.; Egami, T. An atomistic study of deformation of amorphous metals. Acta Metall. 1983, 31, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Egami, T. How thermally activated deformation starts in metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, A.; Rätzke, K.; Meyer, A.; Faupel, F. Dynamic Arrest in Multicomponent Glass-Forming Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 195901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Material (at%) | ηeq -Data | D* | m | T0 | Tg* | η0 × 10−5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg59.5Cu22.9Ag6.6Gd11 | [45] | 26.0 | 40.7 | 235.3 | 396.2 | 3.1 |
| Mg65Cu25Y10 | [49] | 22.1 | 44.5 | 261 | 413.6 | 4.0 |
| Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 | [50] | 22.1 | 44.2 | 376 | 597 | 4.0 |
| Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | [51] | 22.0 | 44.4 | 387 | 613 | 4.0 |
| Fe67Mo6Ni3.5Cr3.5P12C5.5B2.5 | [21] | 21.3 | 44.7 | 456.5 | 717 | 5.8 |
| Au49Cu26.9Si16.3Ag5.5Pd2.3 | [23,42] | 20.9 | 46.2 | 246.9 | 383.3 | 4.0 |
| Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8 | [52] | 20.4 | 46.7 | 427 | 658 | 4.0 |
| Zr58.5Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3Nb2.8 | [19] | 19.7 | 47.5 | 437 | 666 | 4.0 |
| Pd40Ni40P20 | [53] | 15.4 | 55.8 | 396 | 559 | 4.0 |
| Pt42.5Cu27Ni9.5P21 | [22] | 15.3 | 56.9 | 354.4 | 498.0 | 4.0 |
| Ni69Cr8.5Nb3P16.5B3 | [22] | 14.9 | 57.1 | 466.3 | 652.1 | 5.9 |
| Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 | [54] | 14.5 | 59.5 | 418 | 578 | 4.0 |
| Pt57.3Cu14.6Ni5.3P22.8 | [22] | 13.6 | 62.40 | 352.6 | 479.1 | 3.8 |
| Pt60Cu16Co2P22 | [22] | 11.8 | 69.2 | 371.4 | 487.0 | 3.8 |
| Pd43Cu27Ni10P20 | [25] | 10.3 | 76.2 | 446 | 568 | 4.0 |
| Material (at%) | Tg | K | H | K/H | m(MYEGA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg59.5Cu22.9Ag6.6Gd11 | 396.2 | 1447.4 | 598.7 | 2.42 | 41.6 |
| Mg65Cu25Y10 | 413.6 | 1513 | 617.0 | 2.45 | 40.5 |
| Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 | 597 | 2276.8 | 865.4 | 2.63 | 39.8 |
| Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | 613 | 1080.5 | 1367.9 | 0.79 | 53.1 |
| Fe67Mo6Ni3.5Cr3.5P12C5.5B2.5 | 717 | 1741.3 | 1360.7 | 1.28 | 46.9 |
| Au49Cu26.9Si16.3Ag5.5Pd2.3 | 383.3 | 852.8 | 765.1 | 1.12 | 49.1 |
| Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8 | 658 | 1825.7 | 1162.5 | 1.57 | 44.9 |
| Zr58.5Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3Nb2.8 | 666 | 1173.9 | 1486.1 | 0.79 | 53.0 |
| Pd40Ni40P20 | 559 | 1015.0 | 1231.1 | 0.82 | 52.6 |
| Pt42.5Cu27Ni9.5P21 | 498.0 | 732.0 | 1202.0 | 0.61 | 56.1 |
| Ni69Cr8.5Nb3P16.5B3 | 652.1 | 773.7 | 1705.5 | 0.45 | 58.6 |
| Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 | 578 | 1020.2 | 1286.7 | 0.79 | 52.8 |
| Pt57.3Cu14.6Ni5.3P22.8 | 479.1 | 436.1 | 1385.9 | 0.32 | 63.9 |
| Pt60Cu16Co2P22 | 487.0 | 268.0 | 1692.0 | 0.16 | 79.5 |
| Pd43Cu27Ni10P20 | 568 | 240.7 | 2072.9 | 0.12 | 75.8 |
| Material (at%) | cp-Data | Tm* | Sc(Tm*) | C | C/(Tg*∆cp(Tg*) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg59.5Cu22.9Ag6.6Gd11 | [45] | 825 | 21.17 | 188.79 | 27.2 |
| Mg65Cu25Y10 | [49] | 832 | 18.64 | 155.14 | 23.4 |
| Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10Be27.5 | [50] | 1198 | 16.46 | 222.68 | 20.5 |
| Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | [55] | 1228 | 19.07 | 295.11 | 21.0 |
| Fe67Mo6Ni3.5Cr3.5P12C5.5B2.5 | [21] | 1454 | 18.68 | 288.62 | 21.5 |
| Au49Cu26.9Si16.3Ag5.5Pd2.3 | [23,42] | 755 | 17.56 | 149.71 | 22.5 |
| Cu47Ti34Zr11Ni8 | [9] | 1282 | 17.46 | 212.83 | 20.6 |
| Zr58.5Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3Nb2.8 | [19] | 1287 | 12.34 | 207.54 | 19.7 |
| Pd40Ni40P20 | [53] | 1000 | 16.93 | 166.77 | 15.4 |
| Pt42.5Cu27Ni9.5P21 | [22] | 890 | 19.84 | 197.2 | 15.2 |
| Ni69Cr8.5Nb3P16.5B3 | [22] | 1180 | 15.46 | 200.4 | 15.1 |
| Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 | [56] | 1017 | 13.07 | 157.35 | 13.9 |
| Pt57.3Cu14.6Ni5.3P22.8 | [22] | 823 | 19.03 | 178.9 | 13.7 |
| Pt60Cu16Co2P22 | [22] | 801 | 17.64 | 160.9 | 11.8 |
| Pd43Cu27Ni10P20 | [25] | 900 | 11.26 | 114.87 | 9.9 |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallino, I. On the Fragility of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Liquids. Entropy 2017, 19, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19090483
Gallino I. On the Fragility of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Liquids. Entropy. 2017; 19(9):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19090483
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallino, Isabella. 2017. "On the Fragility of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Liquids" Entropy 19, no. 9: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19090483
APA StyleGallino, I. (2017). On the Fragility of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Liquids. Entropy, 19(9), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19090483