Entropy Mapping Approach for Functional Reentry Detection in Atrial Fibrillation: An In-Silico Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Model of Atrial Fibrillation
3. Model of Action Potential Propagation
- pAF: Courtemanche pAF conditions without acetylcholine, .
- cAF1: Courtemanche cAF conditions with 5 nM acetylcholine, .
- cAF2: Courtemanche cAF conditions with 500 nM acetylcholine, .
- cAF3: Courtemanche cAF conditions with 500 nM acetylcholine, and .
- cAF4: Fenton–Karma cAF conditions, and .
- cAF5: Fenton–Karma cAF conditions, and .
3.1. Stimulation Protocols
3.2. Virtual Electrograms
3.3. Entropy Maps
3.4. Phase Map and Phase Singularity
4. Results
4.1. Single Rotor
4.2. Figure-of-Eight Reentry
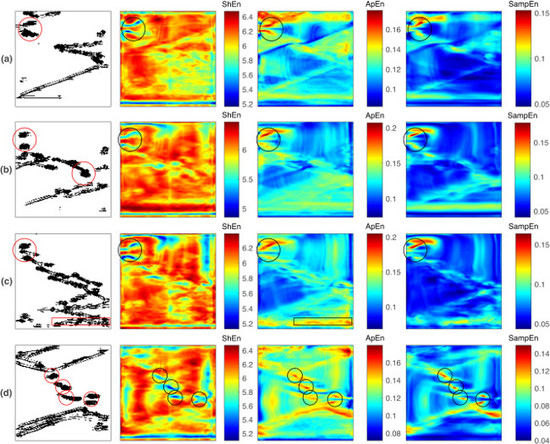
4.3. Multiple Reentries
5. Discussion
- and present similar behaviors in the characterization of reentry dynamics, with differing from these results. The and maps consistently highlight the reentry core region by high entropy values in all of the studied cases, while the maps mark the reentries by high or low entropy values, depending on the fibrillation dynamics.
- When no other fibrillation mechanism is present within the designed domain, the and maps better match the reentry core region by high entropy values, while is less specific since it highlights a broader area.
- When multiple reentries coexist with other fibrillatory patterns, reentry identification can be challenging for all three cases. Under such conditions, it is hypothesized that the reentries need to endure for a time that is comparable to the observation window so that the entropy maps can detect them.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| approximate entropy | |
| cAF | chronic atrial fibrillation |
| CFAE | complex fractionated atrial electrograms |
| EGM | electrogram(s) |
| pAF | paroxysmal atrial fibrillation |
| PS | phase singularity |
| sample entropy | |
| standard deviation | |
| Shannon entropy |
References
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace 2016, 18, 1609–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björck, S.; Palaszewski, B.; Friberg, L.; Bergfeldt, L. Atrial fibrillation, stroke risk, and warfarin therapy revisited: A population-based study. Stroke 2013, 44, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, J.A.B.; Harling, L.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A.; Gooderham, N.; Athanasiou, T.; Peters, N.S. Post-operative atrial fibrillation is associated with a pre-existing structural and electrical substrate in human right atrial myocardium. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 220, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantú, C.; True Hills, M.; Massaro, A.; Goto, S.; Hu, H.H.; Quek, D.K.; Sim, K.H.; Tse, H.F.; Zhang, S.; Benbow, A.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation-Related Stroke across Latin America: A Preventable Problem. Available online: https://www.stopafib.org/downloads/News436-LatAm-Prevent.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Corradi, D. Atrial fibrillation from the pathologist’s perspective. Cardiovasc. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2014, 23, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating in the Pulmonary Veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallergis, E.M.; Goudis, C.A.; Vardas, P.E. Atrial fibrillation: A progressive atrial myopathy or a distinct disease? Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 171, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.P.; Kaur, K.; Hwang, E.; Ramirez, R.J.; Willis, B.C.; Filgueiras-Rama, D.; Ennis, S.R.; Takemoto, Y.; Ponce-Balbuena, D.; Zarzoso, M.; et al. Dominant frequency increase rate predicts transition from paroxysmal to long-term persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 129, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Salinet, J.L.; Almeida, T.P.; Vanheusden, F.J.; Chu, G.S.; Ng, G.A.; Schlindwein, F.S. An interactive platform to guide catheter ablation in human persistent atrial fibrillation using dominant frequency, organization and phase mapping. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2017, 141, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Watanabe, I.; Okumura, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Kogawa, R.; Sonoda, K.; Iso, K.; Takahashi, K.; Arai, M.; Watanabe, R.; et al. Complex fractionated atrial electrograms, high dominant frequency regions, and left atrial voltages during sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation. J. Arrhythmia 2017, 33, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.; Goldberger, J.J. Understanding and interpreting dominant frequency analysis of AF electrograms. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, M.K.; Brooks, A.G.; Kuklik, P.; John, B.; Dimitri, H.; Lau, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Dhar, S.; Roberts-Thomson, R.L.; Mackenzie, L.; et al. The relationship between electrogram cycle length and dominant frequency in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008, 20, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Nademanee, K.; McKenzie, J.; Kosar, E.; Schwab, M.; Sunsaneewitayakul, B.; Vasavakul, T.; Khunnawat, C.; Ngarmukos, T. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar-Busch, S.; Reents, T.; Knecht, S.; Rostock, T.; Arentz, T.; Duytschaever, M.; Neumann, T.; Cauchemez, B.; Albenque, J.P.; Hessling, G.; et al. Correlation between atrial fibrillation driver locations and complex fractionated atrial electrograms in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. PACE-Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.A.; Curtain, J.P.; Gajendragadkar, P.R.; Begley, D.A.; Fynn, S.P.; Grace, A.A.; Heck, P.M.; Virdee, M.S.; Agarwal, S. Ablation of Complex Fractionated Electrograms Improves Outcome in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation of Over 2 Year’s Duration. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2018, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kochhäuser, S.; Verma, A.; Dalvi, R.; Suszko, A.; Alipour, P.; Sanders, P.; Champagne, J.; Macle, L.; Nair, G.M.; Calkins, H.; et al. Spatial Relationships of Complex Fractionated Atrial Electrograms and Continuous Electrical Activity to Focal Electrical Sources: Implications for Substrate Ablation in Human Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar-Busch, S.; Bourier, F.; Reents, T.; Semmler, V.; Telishevska, M.; Kathan, S.; Hofmann, M.; Hessling, G.; Deisenhofer, I. Ablation of Complex Fractionated Electrograms With or Without ADditional LINEar Lesions for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (The ADLINE Trial). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, J.; Bars, C.; Ferracci, A.; Maluski, A.; Penaranda, G.; Theodore, G.; Faure, J.; Bremondy, M.; Curel, L.; Beurtheret, S.; et al. Electrogram Fractionation-Guided Ablation in the Left Atrium Decreases the Frequency of Activation in the Pulmonary Veins and Leads to Atrial Fibrillation Termination: Pulmonary Vein Modulation Rather Than Isolation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oketani, N.; Seitz, J.; Salazar, M.; Pisapia, A.; Kalifa, J.; Smit, J.J.; Nademanee, K. Ablation of complex fractionated electrograms is useful for catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: Protagonist point of view. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 2098–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Jiang, C.Y.; Betts, T.; Ghen, J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Mantovan, R.; Macle, L.; Morillo, C.A.; Haverkamp, W.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Approaches to Catheter Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Atul. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2015, 372, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Du, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Lai, X.; Lu, Q.; et al. A decade of complex fractionated electrograms catheter-based ablation for atrial fibrillation: Literature analysis, meta-analysis and systematic review. IJC Heart Vessels 2014, 4, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Lin, D.; Callans, D.J.; Bala, R.; Riley, M.P.; Garcia, F.C.; Hutchinson, M.D.; Ratcliffe, S.J.; Cooper, J.M.; et al. Randomized ablation strategies for the treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation RASTA study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenfeld, O.; Jalife, J. Complex Fractionated Atrail Electrograms Is this the Beast to Tame in AF. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adragão, P.; Carmo, P.; Cavaco, D.; Carmo, J.; Ferreira, A.; Moscoso Costa, F.; Carvalho, M.S.; Mesquita, J.; Quaresma, R.; Belo Morgado, F.; et al. Relationship between rotors and complex fractionated electrograms in atrial fibrillation using a novel computational analysis. Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia 2017, 36, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, T.P.; Schlindwein, F.S.; Salinet, J.; Li, X.; Chu, G.S.; Tuan, J.H.; Stafford, P.J.; André Ng, G.; Soriano, D.C. Characterization of human persistent atrial fibrillation electrograms using recurrence quantification analysis. Chaos 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirugeda-Roldán, E.; Molina Picó, A.; Novák, D.; Cuesta-Frau, D.; Kremen, V. Sample Entropy Analysis of Noisy Atrial Electrograms during Atrial Fibrillation. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navoret, N.; Jacquir, S.; Laurent, G.; Binczak, S. Detection of complex fractionated atrial electrograms using recurrence quantification analysis. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2013, 60, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonizzi, P.; Zeemering, S.; Karel, J.M.; Di Marco, L.Y.; Uldry, L.; Van Zaen, J.; Vesin, J.M.; Schotten, U. Systematic comparison ofnon-invasive measures for the assessment ofatrial fibrillation complexity: A step forward towards standardization ofatrial fibrillation electrogram analysis. Europace 2015, 17, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Duque, A.; Novak, D.; Kremen, V.; Bustamante, J. Multifractal analysis for grading complex fractionated electrograms in atrial fibrillation. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 2269–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirugeda-Roldán, E.; Novak, D.; Kremen, V.; Cuesta-Frau, D.; Keller, M.; Luik, A.; Srutova, M. Characterization of complex fractionated atrial electrograms by sample entropy: An international multi-center study. Entropy 2015, 17, 7493–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, J.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Tobón, C.; Kremen, V.; Novak, D.; Saiz, J.; Oesterlein, T.; Schmitt, C.; Luik, A.; Bustamante, J. Dynamic approximate entropy electroanatomic maps detect rotors in a simulated atrial fibrillation model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Duque, A.; Tobón, C.; Ugarte, J.; Morillo, C.; Bustamante, J. Electroanatomical mapping based on discrimination of electrograms clusters for localization of critical sites in atrial fibrillation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronis, K.N.; Ashikaga, H. Impact of number of co-existing rotors and inter-electrode distance on accuracy of rotor localization. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.S.; Wi, J.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, M.; Lim, B.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Joung, B.; Lee, M.H.; Seo, J.W.; et al. Role of atrial wall thickness in wave-dynamics of atrial fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, S.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Kremen, V.; Novak, D.; Tobón, C.; Bustamante, J. Feature subset selection and classification of intracardiac electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 38, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Song, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Li, C.; Shim, E.B.; Pak, H.N. Electrophysiological rotor ablation in in-silico modeling of atrial fibrillation: Comparisons with dominant frequency, shannon entropy, and phase singularity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Duque, A.; Bustamante, J.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Semi-supervised clustering of fractionated electrograms for electroanatomical atrial mapping. BioMed. Eng. Online 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte, J.P.; Tobón, C.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Becerra, M.A.; Bustamante, J. Effect of the electrograms density in detecting and ablating the tip of the rotor during chronic atrial fibrillation: An in silico study. Europace 2015, 17, ii97–ii104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.N.; Kuklik, P.; Gharaviri, A.; Brooks, A.; Chapman, D.; Lau, D.H.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Sers, P. Origin and characteristics of high Shannon entropy at the pivot of locally stable rotors: Insights from computational simulation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalife, J. Rotors and spiral waves in atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allessie, M.; de Groot, N. CrossTalk opposing view: Rotors have not been demonstrated to be the drivers of atrial fibrillation. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 3167–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.J.; Zhao, J.; Csepe, T.A.; Moore, B.T.; Li, N.; Jayne, L.A.; Kalyanasundaram, A.; Lim, P.; Bratasz, A.; Powell, K.A.; et al. Atrial fibrillation driven by micro-anatomic intramural re-entry revealed by simultaneous sub-epicardial and sub-endocardial optical mapping in explanted human hearts. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Hansen, B.J.; Csepe, T.A.; Lim, P.; Wang, Y.; Williams, M.; Mohler, P.J.; Janssen, P.M.; Weiss, R.; Hummel, J.D.; et al. Integration of High-Resolution Optical Mapping and 3-Dimensional Micro-Computed Tomographic Imaging to Resolve the Structural Basis of Atrial Conduction in the Human Heart. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, N.; Van Der Does, L.; Yaksh, A.; Lanters, E.; Teuwen, C.; Knops, P.; Van De Woestijne, P.; Bekkers, J.; Kik, C.; Bogers, A.; et al. Direct Proof of Endo-Epicardial Asynchrony of the Atrial Wall During Atrial Fibrillation in Humans. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Hansen, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Csepe, T.A.; Sul, L.V.; Tang, A.; Yuan, Y.; Li, N.; Bratasz, A.; Powell, K.A.; et al. Three-dimensional integrated functional, structural, and computational mapping to define the structural “fingerprints” of heart-specific atrial fibrillation drivers in human heart ex vivo. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biton, Y.; Rabinovitch, A.; Braunstein, D.; Aviram, I.; Campbell, K.; Mironov, S.; Herron, T.; Jalife, J.; Berenfeld, O. Causality analysis of leading singular value decomposition modes identifies rotor as the dominant driving normal mode in fibrillation. Chaos 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervigón, R.; Castells, F.; Gómez-Pulido, J.M.; Pérez-Villacastín, J.; Moreno, J. Granger causality and Jensen-Shannon divergence to determine dominant atrial area in Atrial fibrillation. Entropy 2018, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.; Climent, A.M.; Liberos, A.; Calvo, D.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Berenfeld, O.; Atienza, F.; Guillem, M.S. Identification of Dominant Excitation Patterns and Sources of Atrial Fibrillation by Causality Analysis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.M.; Kalra, V.; Das, M.K.; Jain, R.; Garlie, J.B.; Brewster, J.A.; Dandamudi, G. Clinical Benefit of Ablating Localized Sources for Human Atrial Fibrillation: The Indiana University FIRM Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, S.M.; Patel, J.; Mulpuru, S.; Krummen, D.E. Focal impulse and rotor modulation ablation of sustaining rotors abruptly terminates persistent atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm sith elimination on follow-up A video case study. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 1436–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, S.M.; Shivkumar, K.; Krummen, D.E.; Miller, J.M.; Rappel, W.J. Panoramic electrophysiological mapping but not electrogram morphology identifies stable sources for human atrial fibrillation: Stable atrial fibrillation rotors and focal sources relate poorly to fractionated electrograms. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.N.; Kuklik, P.; Lau, D.H.; Brooks, A.G.; Baumert, M.; Lim, W.W.; Thanigaimani, S.; Nayyar, S.; Mahajan, R.; Jonathan, M.; et al. Bipolar Electrogram Shannon Entropy at Sites of Rotational Activation: Implications for Abaltion of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2013, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, M.; Ramirez, R.J.; Nattel, S. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: Insights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, H301–H321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, F.H.; Cherry, E.M.; Hastings, H.M.; Evans, S.J. Multiple mechanisms of spiral wave breakup in a model of cardiac electrical activity. Chaos 2002, 12, 852–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneller, J.; Zou, R.; Vigmond, E.J.; Wang, Z.; Leon, L.J.; Nattel, S. Cholinergic Atrial Fibrillation in a Computer Model of a Two-Dimensional Sheet of Canine Atrial Cells With Realistic Ionic Properties. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 73e–87e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwano, S.; Wakisaka, Y.; Kojima, J.; Yumoto, Y.; Inuo, K.; Hara, H.; Saito, J.; Niwano, H.; Izumi, T. Monitoring the Progression of the Atrial Electrical Remodeling in Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2003, 67, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Burstein, B.; Dobrev, D. Atrial Remodeling and Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, D.R.; Pond, A.L.; McCarthy, P.M.; Trimmer, J.S.; Nerbonne, J.M. Outward K+ Current Densities and Kv1.5 Expression Are Reduced in Chronic Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, R.F.; Zeng, X.; Grammer, J.B.; Popovic, K.; Mewis, C.; Kühlkamp, V. Ionic mechanisms of electrical remodeling in human atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 44, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrev, D.; Graf, E.; Wettwer, E.; Himmel, H.; Hála, O.; Doerfel, C.; Christ, T.; Schüler, S.; Ravens, U. Molecular Basis of Downregulation of G-Protein–Coupled Inward Rectifying K+ Current (IK,ACh) in Chronic Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2001, 104, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, A.J.; Kane, K.A.; Rankin, A.C. The contribution of ionic currents to changes in refractoriness of human atrial myocytes associated with chronic atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 52, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, J.P.; Tobón, C.; Lopes, A.M.; Tenreiro Machado, J.A. Atrial rotor dynamics under complex fractional order diffusion. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, A.; Holm, M.; Blomström, P.; Johansson, R.; Lührs, C.; Brandt, J.; Olsson, S.B. Right atrial free wall conduction velocity and degree of anisotropy in patients with stable sinus rhythm studied during open heart surgery. Eur. Heart J. 1998, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno-Orovio, A.; Kay, D.; Burrage, K. Fourier spectral methods for fractional-in-space reaction-diffusion equations. BIT Numer. Math. 2014, 54, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuklik, P.; Zeemering, S.; Maesen, B.; Maessen, J.; Crijns, H.J.; Verheule, S.; Ganesan, A.N.; Schotten, U. Reconstruction of instantaneous phase of unipolar atrial contact electrogram using a concept of sinusoidal recomposition and hilbert transform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, M.A.; Lin, S.F.; Aliev, R.R.; Roth, B.J.; Wikswo, J.P. Experimental and theoretical analysis of phase singularity dynamics in cardiac tissue. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2001, 12, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, M.; Sanders, P.; Ganesan, A. Quantitative-Electrogram-Based Methods for Guiding Catheter Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benharash, P.; Buch, E.; Frank, P.; Share, M.; Tung, R.; Shivkumar, K.; Mandapati, R. Quantitative Analysis of Localized Sources Identified by Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation Mapping in Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roney, C.H.; Cantwell, C.D.; Bayer, J.D.; Qureshi, N.A.; Lim, P.B.; Tweedy, J.H.; Kanagaratnam, P.; Peters, N.S.; Vigmond, E.J.; Ng, F.S. Spatial resolution requirements for accurate identification of drivers of atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e004899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, R.H.; Nash, M.P. Analysis of cardiac fibrillation using phase mapping. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2015, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, E.; Share, M.; Tung, R.; Benharash, P.; Sharma, P.; Koneru, J.; Mandapati, R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Shivkumar, K. Long-term clinical outcomes of focal impulse and rotor modulation for treatment of atrial fibrillation: A multicenter experience. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, S.P.; Mulpuru, S.K.; Friedman, P.A.; Tolkacheva, E.G. Feasibility of visualizing higher regions of Shannon entropy in atrial fibrillation patients. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2015, 2015, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annoni, E.M.; Arunachalam, S.P.; Kapa, S.; Mulpuru, S.K.; Friedman, P.A.; Tolkacheva, E.G. Novel quantitative analytical approaches for rotor identification and associated implications for mapping. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, S.; Kapa, S.; Mulpuru, S.; Friedman, P.; Tolkacheva, E. Rotor pivot point identification using recurrence period density entropy. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Rocky Mountain Bioengineering Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 31 March–1 April 2017. In Proceedings of the 54th International ISA Biomedical Sciences Instrumentation Symposium 2017, Denver, CO, USA, 31 March–1 April 2017. [Google Scholar]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugarte, J.P.; Tobón, C.; Orozco-Duque, A. Entropy Mapping Approach for Functional Reentry Detection in Atrial Fibrillation: An In-Silico Study. Entropy 2019, 21, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21020194
Ugarte JP, Tobón C, Orozco-Duque A. Entropy Mapping Approach for Functional Reentry Detection in Atrial Fibrillation: An In-Silico Study. Entropy. 2019; 21(2):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21020194
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgarte, Juan P., Catalina Tobón, and Andrés Orozco-Duque. 2019. "Entropy Mapping Approach for Functional Reentry Detection in Atrial Fibrillation: An In-Silico Study" Entropy 21, no. 2: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21020194
APA StyleUgarte, J. P., Tobón, C., & Orozco-Duque, A. (2019). Entropy Mapping Approach for Functional Reentry Detection in Atrial Fibrillation: An In-Silico Study. Entropy, 21(2), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21020194