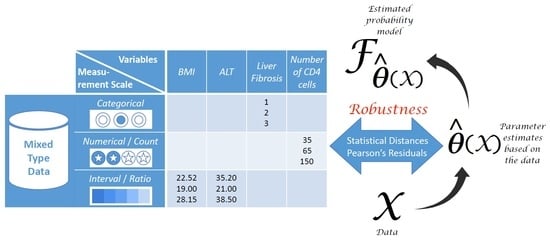
Distance-Based Estimation Methods for Models for Discrete and Mixed-Scale Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Concepts in Minimum Disparity Estimation
3. Pearson Residual Systems
4. Estimating Equations
- 1.
- The above two estimating equations can be solved with respect to β and. In an iterative algorithm, we can solve the second equation (4) explicitly forto obtainThis means that if the model does not fit any of the y, observed at a particular x well, the weight for this x will drop as well.
- 2.
- Whenthe corresponding estimating equation for β becomesand the MLE is obtained. This is because the corresponding weight function. In this case, the estimating equations for thes become, the estimating equations for the MLEs of.
- 3.
- The Fisher consistency property of the function that introduces the estimates guarantees that the expectation of the corresponding estimating function is 0, under the correct model specification.
5. Robustness Properties
6. Asymptotic Properties
7. Simulations
8. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| HD | Twice-Squared Hellinger’s Disparity |
| LD | Likelihood Disparity |
| MC | Monte Carlo Replications |
| MDE | Minimum Distance Estimators |
| MLE | Maximum Likelihood Estimator |
| PCS | Pearson’s Chi-Squared Disparity Divided by 2 |
| PWD | Power Divergence Disparity |
| RAF | Residual Adjustment Function |
| SCS | Symmetric Chi-Squared Disparity |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Proposition 3
Appendix A.2. Proof of Proposition 5
Appendix A.3. Assumptions of Theorem 1
- 1.
- The weight functions are nonnegative, bounded and differentiable with respect to .
- 2.
- The weight function is regular, that is, is bounded, where is the derivative of w with respect to .
- 3.
- 4.
- The elements of the Fisher information matrix are finite and the Fisher information matrix is nonsingular.
- 5.
- 6.
- If denotes the true value of , there exist functions such that , with , and
- 7.
- If denotes the true value of , there is a neighborhood such that for the quantity are bounded by and respectively, such that their corresponding expectations are finite.
- 8.
- is bounded, where denotes the second derivative of A with respect to .
References
- Beran, R. Minimum Hellinger Distance Estimates for Parametric Models. Ann. Stat. 1977, 5, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Lindsay, B.G. Minimum Disparity Estimation for Continuous Models: Efficiency, Distributions and Robustness. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1994, 46, 683–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.A.; Pardo, L.; Pardo, M.C. Minimum ϕ-Divergence Estimator in Logistic Regression Models. Stat. Pap. 2005, 47, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.A.; Pardo, L.; Pardo, M.C. Testing In Logistic Regression Models on ϕ-Divergences Measures. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2006, 136, 982–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.A.; Pardo, M.C. Minimum ϕ-Divergence Estimator and ϕ-Divergence Statistics in Generalized Linear Models with Binary Data. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. 2008, 10, 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.G. Minimum Hellinger Distance Estimation for the Analysis of Count Data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.G. Hellinger Deviance Tests: Efficiency, Breakdown Points, and Examples. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markatou, M.; Basu, A.; Lindsay, B.G. Weighted Likelihood Estimating Equations: The Discrete Case with Applications to Logistic Regression. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1997, 57, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Basu, S. Penalized Minimum Disparity Methods for Multinomial Models. Stat. Sin. 1998, 8, 841–860. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Nguyen, T.; Pardo, L. Inference Procedures for Polytomous Logistic Regression Models Based on ϕ-Divergence Measures. Math. Methods Stat. 2006, 15, 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, N.; Pardo, L. New Influence Measures in Polytomous Logistic Regression Models Based on Phi-Divergence Measures. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2014, 43, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, E.; Ghosh, A.; Martín, N.; Pardo, L. New Robust Statistical Procedures for Polytomous Logistic Regression Models. Biometrics 2018, 74, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, N.; Pardo, L. Minimum Phi-Divergence Estimators for Loglinear Models with Linear Constraints and Multinomial Sampling. Stat. Pap. 2008, 49, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.; Martín, N. Minimum Phi-Divergence Estimators and Phi-Divergence Test for Statistics in Contingency Tables with Symmetric Structure: An Overview. Symmetry 2010, 2, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.; Pardo, M.C. Minimum Power-Divergence Estimator in Three-Way Contingency Tables. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2003, 73, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.; Pardo, M.C.; Zografos, K. Minimum ϕ-Divergence Estimator for Homogeneity in Multinomial Populations. Sankhyā Indian J. Stat. Ser. A (1961–2002) 2001, 63, 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Harris, I.A.; Hjort, N.L.; Jones, M.C. Robust and Efficient Estimation by Minimising a Density Power Divergence. Biometrika 1998, 85, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csiszár, I. Information-Type Measures of Difference of Probability Distributions and Indirect Observations. Stud. Sci. Math. Hung. 1967, 25, 299–318. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, B.G. Efficiency Versus Robustness: The Case for Minimum Hellinger Distance and Related Methods. Ann. Stat. 1994, 22, 1081–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.N.; Boos, D.D. Minimum Hellinger Distance Estimation for Multivariate Location and Covariance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markatou, M.; Basu, A.; Lindsay, B.G. Weighted Likelihood Equations with Bootstrap Root Search. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberman, S.J. Generalized Residuals for Log-Linear Models. In Proceedings of the 9th International Biometrics Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 22–27 August 1976; pp. 104–122. [Google Scholar]
- Haberman, S.J.; Sinharay, S. Generalized Residuals for General Models for Contingency Tables with Application to Item Response Theory. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2013, 108, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.A.; Schafer, D.W. Residuals in Generalized Linear Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, M.; Molenberghs, G.; Geys, H.; Ryan, L. Topics in Modelling of Clustered Data; Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 96. [Google Scholar]
- Olkin, I.; Tate, R.F. Multivariate Correlation Models with Mixed Discrete and Continuous Variables. Ann. Math. Stat. 1961, 32, 448–465, With correction in 1961, 36, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genest, C.; Nešlehová, J. A Primer on Copulas for Count Data. ASTIN Bull. 2007, 37, 475–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauritzen, S.; Wermuth, N. Graphical Models for Associations between Variables, some of which are Qualitative and some Quantitative. Ann. Stat. 1989, 17, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, F.R.; Ronchetti, E.M.; Rousseeuw, P.J.; Stahel, W.A. Robust Statistics: The Approach Based on Influence Functions; Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics. Probability and Mathematical Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, F.R. Contributions to the Theory of Robust Estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Statistics, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1968. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, F.R. The Influence Curve and its Role in Robust Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fienberg, S.E. The Analysis of Incomplete Multi-Way Contingency Tables. Biometrics 1972, 28, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, A. Categorical Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.D.; May, W.L. Combining 2 × 2 Tables That Contain Structural Zeros. Biometrics 1972, 14, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, W.Y.; Tang, M.L.; Wang, S.J. Influence Measures in Contingency Tables with Application in Sampling Zeros. Sociol. Methods Res. 2003, 31, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alin, A.; Kurt, S. Ordinary and Penalized Minimum Power-Divergence Estimators in Two-Way Contingency Tables. Comput. Stat. 2008, 23, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y. Interior Algorithms for Linear, Quadratic, and Linearly Constrained Convex Programming. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Engineering-Economic Systems, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1987. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, A.R.; Gould, N.I.M.; Toint, P. A Globally Convergent Augmented Lagrangian Algorithm for Optimization with General Constraints and Simple Bounds. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1991, 28, 545–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. Improving Ultimate Convergence of an Augmented Lagrangian Method. Optim. Methods Softw. 2008, 23, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amatya, A.; Demirtas, H. OrdNor: An R Package for Concurrent Generation of Correlated Ordinal and Normal Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 68, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, U.; Drasgow, F.; Dorans, N.J. The Polyserial Correlation Coefficient. Psychmetrika 1982, 47, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T. ks: Kernel Density Estimation and Kernel Discriminant Analysis for Multivariate Data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolstad, W.M. Understanding Computational Bayesian Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agostinelli, C.; Markatou, M. Test of Hypotheses Based on the Weighted Likelihood Methodology. Stat. Sin. 2001, 11, 499–514. [Google Scholar]
- Eiras-Franco, C.; Martínez-Rego, D.; Guijarro-Berdiñas, B.; Alonso-Betanzos, A.; Bahamonde, A. Large Scale Anomaly Detection in Mixed Numerical and Categorical Input Spaces. Inf. Sci. 2019, 487, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, C.; Hampshire, J. Real-Time Object Classification and Novelty Detection for Collaborative Video Surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. IJCNN’02 (Cat. No.02CH37290), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2620–2625. [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy, L.; Eskin, E.; Stolfo, S. Intrusion Detection with Unlabeled Data Using Clustering. In Proceedings of the ACM CSS Workshop on Data Mining Applied to Security (DMSA-2001), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 5–8 November 2001; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.; Phung, D.; Luo, W.; Harvey, R.; Berk, M.; Venkatesh, S. An Integrated Framework for Suicide Risk Prediction. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1410–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Konijn, R.M.; Kowalczyk, W. Finding Fraud in Health Insurance Data with Two-Layer Outlier Detection Approach. In Data Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery, DaWak 2011; Cuzzocrea, A., Dayal, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 394–405. [Google Scholar]
- Fraley, C.; Wilkinson, L. Package ‘HDoutliers’. R Package. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/HDoutliers/index.html (accessed on 31 December 2020).
- Wilkinson, L. Visualizing Outliers. 2016. Available online: https://www.cs.uic.edu/~wilkinson/Publications/outliers.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2020).
- Do, K.; Tran, T.; Phung, D.; Venkatesh, S. Outlier Detection on Mixed-Type Data: An Energy-Based Approach. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications; Li, J., Li, X., Wang, S., Li, J., Sheng, Q.Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Koufakou, A.; Georgiopoulos, M.; Anagnostopoulos, G.C. Detecting Outliers in High-Dimensional Datasets with Mixed Attributes. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Data Mining, DMIN, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 14–17 July 2008; pp. 427–433. [Google Scholar]
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and SDs over 10,000 Replications | ||||||||||||
| 100 | PCS | Mean | 0.199 | 0.199 | 0.201 | 0.201 | 0.200 | 0.201 | 0.200 | 0.199 | 0.200 | 0.201 |
| SD | 0.038 | 0.041 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.038 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.199 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.201 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.037 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.199 | 0.201 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.199 | 0.200 | 0.201 | |
| SD | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.032 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.031 | 0.032 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.199 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.002 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.035 | 0.039 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.035 | ||
| 1000 | PCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 |
| SD | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.016 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.008 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | ||
| 10,000 | PCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 |
| SD | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.006 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.004 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and SDs over 10,000 Replications | ||||||||||||
| 100 | PCS | Mean | 0.052 | 0.197 | 0.198 | 0.198 | 0.355 | 0.165 | 0.173 | 0.172 | 0.245 | 0.245 |
| SD | 0.028 | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.053 | 0.041 | 0.039 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.047 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.026 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.368 | 0.156 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.254 | 0.254 | |
| SD | 0.019 | 0.049 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.054 | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.046 | 0.049 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.033 | 0.209 | 0.209 | 0.209 | 0.340 | 0.166 | 0.172 | 0.171 | 0.245 | 0.246 | |
| SD | 0.022 | 0.047 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.051 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.033 | 0.038 | 0.040 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.160 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.250 | 0.250 | |
| SD | 0.020 | 0.043 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.048 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.044 | ||
| 1000 | PCS | Mean | 0.044 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.365 | 0.164 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.248 | 0.248 |
| SD | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.015 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.034 | 0.203 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.359 | 0.156 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.252 | 0.252 | |
| SD | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.014 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.038 | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.332 | 0.166 | 0.169 | 0.169 | 0.248 | 0.248 | |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.014 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.160 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.250 | 0.250 | |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.014 | ||
| 10,000 | PCS | Mean | 0.044 | 0.197 | 0.196 | 0.196 | 0.367 | 0.164 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.248 | 0.248 |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.008 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.034 | 0.203 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.359 | 0.156 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.252 | 0.252 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.038 | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.332 | 0.166 | 0.169 | 0.169 | 0.248 | 0.248 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.160 | 0.170 | 0.170 | 0.250 | 0.250 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and Biases over 10,000 Replications | |||||||
| 50 | PCS | Mean | 0.5008 | 0.4992 | 0.3339 | 0.3336 | 0.3325 |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0009 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0034 | ||||||
| HD | Mean | 0.5008 | 0.4992 | 0.3339 | 0.3335 | 0.3326 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0007 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0031 | ||||||
| SCS | Mean | 0.5007 | 0.4993 | 0.3338 | 0.3335 | 0.3326 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0002 | 0.0007 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0028 | ||||||
| LD | Mean | 0.5008 | 0.4992 | 0.3339 | 0.3335 | 0.3326 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0008 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0032 | ||||||
| 70 | PCS | Mean | 0.4998 | 0.5002 | 0.3333 | 0.3331 | 0.3337 |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0011 | ||||||
| HD | Mean | 0.4998 | 0.5002 | 0.3333 | 0.3330 | 0.3336 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0009 | ||||||
| SCS | Mean | 0.4998 | 0.5002 | 0.3334 | 0.3331 | 0.3335 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0000 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0008 | ||||||
| LD | Mean | 0.4999 | 0.5001 | 0.3333 | 0.3330 | 0.3336 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0009 | ||||||
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and Biases over 10,000 Replications | |||||||
| 50 | PCS | Mean | 0.6391 | 0.3609 | 0.3489 | 0.2278 | 0.4234 |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0276 | 0.0276 | 0.0155 | 0.0611 | 0.0766 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.2084 | ||||||
| HD | Mean | 0.7815 | 0.2185 | 0.3346 | 0.0497 | 0.6157 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.1149 | 0.1149 | 0.0013 | 0.1170 | 0.1157 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.4638 | ||||||
| SCS | Mean | 0.6420 | 0.3580 | 0.3510 | 0.2726 | 0.3765 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0247 | 0.0247 | 0.0176 | 0.1059 | 0.1235 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.2964 | ||||||
| LD | Mean | 0.6677 | 0.3323 | 0.3342 | 0.1660 | 0.4998 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0010 | 0.0010 | 0.0009 | 0.0007 | 0.0002 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0038 | ||||||
| 70 | PCS | Mean | 0.6377 | 0.3623 | 0.3483 | 0.2297 | 0.4220 |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0290 | 0.0290 | 0.0150 | 0.0631 | 0.0780 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.2141 | ||||||
| HD | Mean | 0.7812 | 0.2188 | 0.3328 | 0.0491 | 0.6180 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.1145 | 0.1145 | 0.0005 | 0.1175 | 0.1180 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.4650 | ||||||
| SCS | Mean | 0.6395 | 0.3605 | 0.3505 | 0.2739 | 0.3756 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0271 | 0.0271 | 0.0172 | 0.1072 | 0.1244 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.3030 | ||||||
| LD | Mean | 0.6657 | 0.3343 | 0.3331 | 0.1671 | 0.4998 | |
| Abs.Biases | 0.0010 | 0.0010 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.0028 | ||||||
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and SDs over 10,000 Replications | ||||||||||||
| 100 | PCS | Mean | 0.199 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.201 | 0.153 | 0.230 | 0.302 | 0.229 | 0.086 |
| SD | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.034 | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.039 | 0.023 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.230 | 0.311 | 0.230 | 0.082 | |
| SD | 0.039 | 0.040 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.040 | 0.033 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.019 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.153 | 0.230 | 0.302 | 0.230 | 0.085 | |
| SD | 0.039 | 0.085 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.039 | 0.022 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.150 | 0.230 | 0.307 | 0.230 | 0.083 | |
| SD | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.033 | 0.041 | 0.045 | 0.040 | 0.019 | ||
| 1000 | PCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.148 | 0.236 | 0.319 | 0.236 | 0.061 |
| SD | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.011 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.237 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.059 | |
| SD | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.008 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.148 | 0.236 | 0.319 | 0.237 | 0.060 | |
| SD | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.013 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.237 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.059 | |
| SD | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.008 | ||
| 10,000 | PCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.236 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.060 |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.008 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.236 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.060 | |
| SD | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.002 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.236 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.060 | |
| SD | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.008 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.147 | 0.236 | 0.320 | 0.237 | 0.060 | |
| SD | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.002 | ||
| N | Statistical Distance | Summary | Estimates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and SDs over 10,000 Replications | ||||||||||||
| 100 | PCS | Mean | 0.074 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.335 | 0.214 | 0.173 | 0.228 | 0.132 | 0.253 |
| SD | 0.022 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.045 | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.039 | 0.031 | 0.041 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.070 | 0.194 | 0.195 | 0.195 | 0.346 | 0.215 | 0.170 | 0.231 | 0.126 | 0.258 | |
| SD | 0.015 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.030 | 0.044 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.074 | 0.194 | 0.195 | 0.195 | 0.342 | 0.214 | 0.173 | 0.229 | 0.131 | 0.253 | |
| SD | 0.015 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.048 | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.041 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.071 | 0.195 | 0.196 | 0.196 | 0.342 | 0.214 | 0.172 | 0.230 | 0.128 | 0.256 | |
| SD | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.046 | 0.040 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.030 | 0.042 | ||
| 1000 | PCS | Mean | 0.042 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.358 | 0.217 | 0.168 | 0.234 | 0.119 | 0.262 |
| SD | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.015 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.039 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.361 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.014 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.039 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.361 | 0.217 | 0.168 | 0.234 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.015 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.014 | ||
| 10,000 | PCS | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 |
| SD | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.006 | ||
| HD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | ||
| SCS | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.008 | ||
| LD | Mean | 0.040 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.360 | 0.217 | 0.167 | 0.235 | 0.118 | 0.263 | |
| SD | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.005 | ||
| N | Summary | Estimates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means, Biases over 1000 Replications | ||||||||
| 0.0 | 50 | Mean | 0.332 | 0.340 | 0.329 | 0.016 | 0.011 | −0.011 |
| Abs. Biases | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.011 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.050 | |||||||
| 100 | Mean | 0.330 | 0.350 | 0.320 | 0.017 | −0.018 | −0.010 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.010 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.078 | |||||||
| 1000 | Mean | 0.324 | 0.337 | 0.339 | 0.001 | −0.008 | 0.007 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.007 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.035 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 50 | Mean | 0.351 | 0.320 | 0.329 | −0.006 | 0.003 | 0.005 |
| Abs. Biases | 0.018 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.005 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.049 | |||||||
| 100 | Mean | 0.330 | 0.323 | 0.347 | 0.001 | 0.005 | −0.004 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.004 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.037 | |||||||
| 1000 | Mean | 0.327 | 0.343 | 0.330 | −0.021 | 0.008 | 0.003 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.003 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.051 | |||||||
| N | Summary | Estimates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means, Biases over 1000 Replications | ||||||||
| 0.0 | 50 | Mean | 0.340 | 0.328 | 0.332 | −0.004 | 2.606 | 5.227 |
| Abs. Biases | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.394 | 0.773 | ||
| Overall Bias | 1.184 | |||||||
| 100 | Mean | 0.313 | 0.350 | 0.337 | −0.004 | 2.777 | 5.593 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.020 | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.223 | 0.407 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.675 | |||||||
| 1000 | Mean | 0.338 | 0.334 | 0.328 | 0.012 | 2.972 | 5.958 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.028 | 0.042 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.093 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 50 | Mean | 0.347 | 0.323 | 0.330 | −0.021 | 2.628 | 5.249 |
| Abs. Biases | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.372 | 0.751 | ||
| Overall Bias | 1.171 | |||||||
| 100 | Mean | 0.317 | 0.343 | 0.340 | 0.017 | 2.817 | 5.615 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.016 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 0.183 | 0.385 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.618 | |||||||
| 1000 | Mean | 0.334 | 0.320 | 0.346 | −0.013 | 2.988 | 5.956 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.044 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.096 | |||||||
| 0.2 | 50 | Mean | 0.324 | 0.333 | 0.343 | −0.004 | 2.589 | 5.240 |
| Abs. Biases | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.411 | 0.760 | ||
| Overall Bias | 1.194 | |||||||
| 100 | Mean | 0.329 | 0.350 | 0.321 | 0.024 | 2.763 | 5.549 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.237 | 0.451 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.745 | |||||||
| 1000 | Mean | 0.337 | 0.344 | 0.319 | −0.011 | 2.971 | 5.951 | |
| Abs. Biases | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.029 | 0.049 | ||
| Overall Bias | 0.118 | |||||||
| N | Summary | Estimates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means and SDs over 1000 Replications | |||||||||
| 0.0 | 1000 | 1.00 | Mean | 0.324 | 0.337 | 0.339 | 0.001 | −0.008 | 0.007 |
| SD | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.298 | 0.378 | 0.378 | 0.386 | |||
| 0.95 | Mean | 0.327 | 0.326 | 0.347 | 0.068 | 0.090 | 0.079 | ||
| SD | 0.304 | 0.299 | 0.309 | 0.413 | 0.413 | 0.413 | |||
| 0.90 | Mean | 0.318 | 0.331 | 0.351 | 0.188 | 0.170 | 0.189 | ||
| SD | 0.300 | 0.305 | 0.306 | 0.443 | 0.450 | 0.436 | |||
| 0.85 | Mean | 0.324 | 0.337 | 0.339 | 0.292 | 0.283 | 0.312 | ||
| SD | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.297 | 0.484 | 0.487 | 0.491 | |||
| 0.80 | Mean | 0.324 | 0.337 | 0.338 | 0.447 | 0.436 | 0.470 | ||
| SD | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.297 | 0.552 | 0.547 | 0.559 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sofikitou, E.M.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Markatou, M. Distance-Based Estimation Methods for Models for Discrete and Mixed-Scale Data. Entropy 2021, 23, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010107
Sofikitou EM, Liu R, Wang H, Markatou M. Distance-Based Estimation Methods for Models for Discrete and Mixed-Scale Data. Entropy. 2021; 23(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleSofikitou, Elisavet M., Ray Liu, Huipei Wang, and Marianthi Markatou. 2021. "Distance-Based Estimation Methods for Models for Discrete and Mixed-Scale Data" Entropy 23, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010107
APA StyleSofikitou, E. M., Liu, R., Wang, H., & Markatou, M. (2021). Distance-Based Estimation Methods for Models for Discrete and Mixed-Scale Data. Entropy, 23(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010107