Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
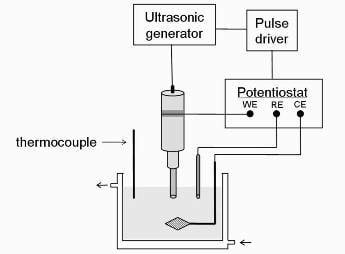
2. Experimental Devices and Methodology
3. The Preparation of Nanoparticles by Pulsed Sonoelectrochemistry
3.1. Metallic Nanopowders
3.2. Alloy Nanopowders
3.3. Semiconductor Nanopowders
3.4. Conducting Polymer Nanoparticles
4. Parameters that Control the Formation of Nanoparticles
4.1. Bath Temperature
4.2. Current Density
4.3. Current Pulse Time (TON)
4.4. Ultrasound Intensity
4.5. Ultrasound Pulse Time (TUS)
4.6. Stabilizer
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Schmid, G. Large clusters and colloids. Metals in the embryonic state. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1709–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Burda, C.; Chen, X.; Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1025–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Effect of catalysis on the stability of metallic nanoparticles: Suzuki reaction catalyzed by PVP-palladium nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8340–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, G. When small is different: Some recent advances in concept and applications of nanoscale phenomena. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.S.; Yang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.P.; Lee, H.F.; Yeh, Y.H.; Yeh, C.S. Formation and characteristics of Cu colloids from CuO powder by laser irradiation in 2-propanol. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6851–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, D.K.; Jo, B.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Kang, Y.S. Synthesis of oleate capped Cu nanoparticles by thermal decomposition. Colloids Surf. A 2006, 284–285, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, A.A.; Klabunde, K.J. Chemical and catalytic activity of copper nanoparticles prepared via metal vapor synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 225, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haram, S.K.; Mahadeshwar, A.R.; Dixit, S.G. Synthesis and characterization of copper sulfide nanoparticles in Triton-X 100 water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 5868–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athawale, A.A.; Katre, P.P.; Kumar, M.; Majumdar, M.B. Synthesis of CTAB–IPA reduced copper nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 91, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, V.; Pollet, B.G.; Dabala, M. Sonoelectrochemical (20 kHz) production of platinum nanoparticles from aqueous solution. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7201–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, N. The effect of supersonic waves on chemical phenomena, (III).The effect on the concentration polarization. J. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1934, 55, 749–750. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, D.J. Sonoelectrochemistry- The application of ultrasound to electrochemical systems. ARKIVOC 2002, iii, 198–218. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, R.G.; Eklund, J.C.; Marken, F. Sonoelectrochemical processes. A review. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J. Sonochemistry: The Uses of Ultrasound in Chemistry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1989; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Birkin, P.R.; Offin, D.G.; Joseph, P.F.; Leighton, T.G. Cavitation, shock waves and the invasive nature of sonoelectrochemistry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 16997–17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klima, J.; Bernard, C. Sonoassisted electrooxidative polymerisation of salicylic acid: role of acoustic streaming and microjetting. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 462, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, R.G.; Eklund, J.C.; Marken, F.; Rebbitt, T.O.; Akkermans, R.P.; Waller, D.N. Dual activation: coupling ultrasound to electrochemistry—An overview. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, J.P.; Pollet, B.; Phull, S.S.; Mason, T.J.; Walton, D.J. The effect upon limiting currents and potentials of coupling a rotating disc and cylindrical electrode with ultrasound. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J.; Lorimer, J.P.; Walton, D.J. Sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrasonics 1990, 28, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J. Sonochemistry: The Uses of Ultrasound in Chemistry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1989; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez, V.; Frías-Ferrer, A.; Iniesta, J.; González-García, J.; Aldaz, A.; Riera, E. Characterization of a 20 kHz sonoreactor. Part II: Analysis of chemical effects by classical and electrochemical methods. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchante, E.; Lana-Villarreal, T.; Sáez, V.; González-García, J.; Gómez, R. Sonopotential: A new concept in electrochemistry. Chem. Comm. 2009, 27, 4127–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumbhat, S. Potentialities of power ultrasound in electrochemistry: An overview. Bull. Electrochem. 2000, 16, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer, J.P.; Mason, T.J.; Plattes, M.; Phull, S.S.; Walton, D.J. Degradation of dye effluent. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delplancke, J.L.; Dille, J.; Reisse, J.; Long, G.J.; Mohan, A.; Grandjean, F. Magnetic nanopowders: Ultrasound assisted electrochemical preparation and properties. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, D.J.; Phull, S.S.; Chyla, A.; Lorimer, J.P.; Mason, T.J.; Burke, L.D.; Murphy, M.; Compton, R.G.; Eklund, J.C.; Page, S.D. Sonovoltammetry at platinum electrodes: Surface phenomena and mass transport processes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C. Sonoelectrochemistry. In Piezoelectric Transducers and Applications; Arnau, A., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Berlin, Germany, 2008; Chapter 15; pp. 399–411. [Google Scholar]
- Reisse, J.; Francois, H.; Vandercammen, J.; Fabre, O.; Kirsch-de Mesmaeker, A.; Maerschalk, C.; Delplancke, J.L. Sonoelectrochemistry in aqueous electrolyte: A new type of sonoelectroreactor. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atobe, M.; Nonaka, T. Ultrasonic Effects on Electroorganic Processes. Electroreduction of Benzaldehydes on Ultrasound-vibrating electrodes. Chem. Lett. 1995, 24, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, A.; François, H.; Reisse, J.; Kirsch-Demesmaeker, A. Sonoelectrochemistry: The effects of ultrasound on organic electrochemical reduction. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, A.; Delplancke, J.L.; Winand, R.; Reisse, J. A new procedure for the production of highly reactive metal powders by pulsed sonoelectrochemical reduction. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 4257–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, A.; Serwas, H.; Delplancke, J.L.; Jerome, R.; Jerome, C.; Canet, L. Preparation of stable suspensions of gold nanoparticles in water by sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.J.; Lorimer, J.P.; Bates, D.M. Quantifying Sonochemistry—Casting some light on a "Black Art". Ultrasonics 1992, 30, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Muller, A.; Cheetan, A.K. The Chemistry of Nanomaterials Synthesis, Properties an Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH&Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Volume 1, p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, R.G.; Eklund, J.C.; Marken, F.; Waller, D.N. Electrode processes at the surfaces of sonotrodes. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.F.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhu, J.M.; Zhu, J.J.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.Y. Controllable synthesis of palladium nanoparticles via a simple sonoelectrochemical method. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, H.; Min, Q.; Hou, W.; Zhu, J.J. Three-dimensional dendritic Pt nanostructures: Sonoelectrochemical synthesis and electrochemical applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16385–16392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancier, V.; Delplancke, J.L.; Delwiche, J.; Hubin-Franskin, M.J.; Piquer, C.; Rebbouh, L.; Grandjean, F. Morphologic, magnetic, and Mössbauer spectral properties of Fe75Co25 nanoparticles prepared by ultrasound-assisted electrochemistry. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2004, 281, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabala, M.; Pollet, B.G.; Zin, V.; Campadello, E.; Mason, T.J. Sonoelectrochemical (20 kHz) production of Co65Fe35 alloy nanoparticles from Aotani solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lou, Y.; Samia, A.C.S.; Devadoss, A.; Burgess, J.D.; Dayal, S.; Burda, C. PbTe Nanorods by Sonoelectrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5855–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atobe, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Asami, R.; Fuchigami, T. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Conducting-Polymer Microspheres by Pulsed Sonoelectrochemical Polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6069–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisse, J.; Caulier, T.; Deckerkheer, C.; Fabre, O.; Vandercammen, J.; Delplancke, J.L.; Winand, R. Quantitative sonochemistry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 1996, 3, S147–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, R.D.; Pearson, T.; Long, E.; Gardner, A. Controlling the hardness of electrodeposited copper coatings by variation of current profile. US Pat. 7329334, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, I.; Shanmugam, S.; Gedanken, A. Pulsed sonoelectrochemical synthesis of size-controlled copper nanoparticles stabilized by poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16947–16952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, I.; Shanmugam, S.; Gedanken, A. Synthesis of copper dendrite nanostructures by a sonoelectrochemical method. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 4696–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, S.; Palchik, O.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles by pulse sonoelectrochemical methods. Langmuir 2000, 16, 6396–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socol, Y.; Abramson, O.; Gedanken, A.; Meshorer, Y.; Berenstein, L.; Zaban, A. Suspensive electrode formation in pulsed sonoelectrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 2002, 18, 4736–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Avivi, S.; Gedanken, A. Synthesis of X-ray amorphous silver nanoparticles by the pulse sonoelectrochemical method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 283, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.P.; Wang, A.N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhu, J.J. A novel route for the preparation of monodisperse silver nanoparticles via a pulsed sonoelectrochemical technique. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Tang, Y.J.; Wei, J.J.; Li, J.; Li, X.B.; Shi, H.L. Synthesis of tungsten nanoparticles by sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, F.; Hu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L. A general nonaqueous sonoelectrochemical approach to nanoporous Zn and Ni particles. Powder Technol. 2007, 176, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, I.; Gedanken, A. Synthesis of metallic magnesium nanoparticles by sonoelectrochemistry. Chem. Commun. 2008, 15, 1795–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendiran, C.; Ganesan, R.; Gedanken, A. Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Metallic Aluminum Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.R.; Martin, S.; Choi, W.; Bahnemann, D.W. Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpone, N.; Khairutdinov, R.F. Semiconductor Nanoclusters, Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Kamat, P.V., Meisel, D., Eds.; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 103, p. 417. [Google Scholar]
- Mancier, V.; Daltin, A.L.; Leclercq, D. Synthesis and characterization of copper oxide (I) nanoparticles produced by pulsed sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Jiang, L.; Miao, J.; Hou, W.; Zhu, J.J. Sonoelectrochemical synthesis of CdSe nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2008, 14, 1683–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Aruna, S.T.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. A novel method for the preparation of lead selenide: Pulse sonoelectrochemical synthesis of lead selenide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Burda, C.; Fu, R.; Pu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J. Heterostructured Bi2Se3 Nanowires with Periodic Phase Boundaries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16276–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastai, Y.; Homyonfer, M.; Gedanken, A.; Hodes, G. Room temperature sonoelectrochemical synthesis of molybdenum sulfide fullerene-like nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, L. Conductive Polymers and Plastics in Industrial Applications; William Andrew Publishing/Plastics Design Library: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Gedanken, A. Pulsed sonoelectrochemical synthesis of polyaniline nanoparticles and their capacitance properties. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasstone, S. An Introduction to Electrochemistry; Van Nostrand Company: New York, NY, USA, 1942; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
- Mastai, Y.; Polsky, R.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A.; Hodes, G. Pulsed sonoelectrochemical synthesis of cadmium selenide nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 10047–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. Sonochemistry. Science 1990, 247, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslick, K.S.; Casadonte, D.J. Heterogeneous sonocatalysis with nickel powder. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 3459–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of copper nanoparticles prepared by pulsed sonoelectrochemistry are available from the authors. |




| Species | Solution | IUS/W cm-2 | TUS/ms | Electrochemistry conditions | TON/ms | TOFF/ms | Experiment duration | Size | Ref. |
| Cu | 0.16 mol/L CuSO4 5H2O, 1.84 mol/L H2SO4, pH 0.5 | 62 | 100-600 | 440-480 mA cm-2 | 250-900 | 150-300 | 30 min | With PVP 29-34 nm Without PVP 200 nm aggregates | [44] |
| Pt | 0.1M K2PtCl4, 0.5M NaCl pH 1 | 62 | 300-500 | 50 mA cm-2 | 200-500 | ----- | 1h | 10-20 nm (some aggregated 100 and 200 nm) | [10] |
| Au | 2.8 10-4M HAuCl4·nH2O 1g/L MPEO pH 1 | Not indicated | 100 | -850 to -1300 mV/ NHE | 10-50 | 100-200 | 5h | 5 -35 nm | [32] |
| Mg | Grignard reagents (EtMgCl and BuMgCl), AlCl3 in THF and DBDG | 62 | 300 | 5 mA cm-2 | 6 105 | 600 | NI | 4.5±0.5 nm | [52] |
| CdSe | CdCl2 2.5H2O, NTA, Na2SeO3 with PVP | NI | Cont. | 60-80 mA cm-2 | Cont. | ---- | 2h | 80 nm diameter nanotubes | [57] |
| Co65Fe35 | Sulphate bath based on Aotani’s formulation pH 3 | 62 | 300-500 | 8-380 mA cm-2 | 300-500 | Not used | 90 min | 3-D structures 300 nm | [39] |
| PANI | 0.5M aniline, 0.5M HCl | 62 | NI | +1V/ Ag/AgCl (3M) | 8 106 | 800 | 2h | 20-40 nm | [62] |
| Cu2O | 0.45 mol L-1 CuSO4 5H2O + 3.25 mol L-1 lactic acid pH 9.1 | 110 | 100-400 | -0.65, -1.2V/ SSE | 100-300 | 200-400 | NI | 8 nm | [56] |
| Polymer | E/mV vs ENH | TON/ ms | Size/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPEO | −850 | 50 | Sediment |
| MPEO/PVP | −850 | 50 | 12 |
| PEO disulfide | −1,300 | 20 | 35 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sáez, V.; Mason, T.J. Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Molecules 2009, 14, 4284-4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104284
Sáez V, Mason TJ. Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2009; 14(10):4284-4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104284
Chicago/Turabian StyleSáez, Veronica, and Timothy J. Mason. 2009. "Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles" Molecules 14, no. 10: 4284-4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104284
APA StyleSáez, V., & Mason, T. J. (2009). Sonoelectrochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Molecules, 14(10), 4284-4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104284