1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium Chloride—Sorption and Primary Biodegradation Analysis in Activated Sewage Sludge
Abstract
:Introduction
The significance of biodegradability
Previous biodegradation experiments
Influence and effect of sorption
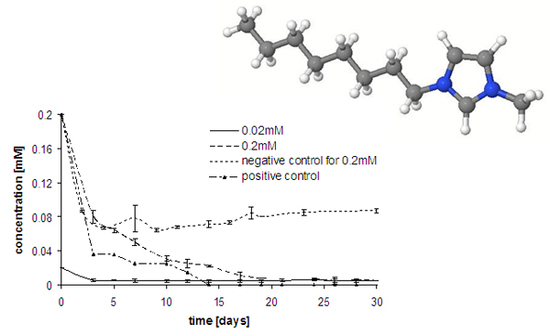
Results and Discussion



Experimental
Modified OECD 301A DOC Die-Away Test
Determination of dehydrogenase activity by TTC
HPLC analysis
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- uczak, J.; Hupka, J.; Thöming, J.; Jungnickel, C. Self-organization of imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloid Surf. A 2008, 329, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R. Catalytic reactions in ionic liquids. Chem. Comm. 2001, 23, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Lau, R.M.; Sorgedrager, F.; van Rantwijk, K.; Seddon, R. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Hal, R.; Boesmann, A. 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium ([bmim]) octylsulfate - an even 'greener' ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.E.; Swatloski, R.P.; Reichert, W.M.; Mayton, R.; Sheff, S.; Wierzbicki, A.; James, H. Task-specific ionic liquids for the extraction of metal ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Comm. 2001, 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, A.; Swatlowski, R.P.; Reichert, R.M.; Mayton, R.; Sheff, S.; Wierzbicki, A.; Davis, J.H.; Rogers, R.D. Task-Specific Ionic Liquids Incorporating Novel Cations for the Coordination and Extraction of Hg2+ and Cd2+: Synthesis, Characterization, and Extraction Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorek, E.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Pijanowska, A.; Olszanowski, A. Yeast and bacteria cell hydrophobicity and hydrocarbon biodegradation in the presence of natural surfactants: Rhamnolipides and saponins. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowska, E.; Markiewicz, M.; Markowska, A.; Aranowski, R.; Jungnickel, C. Investigation on sorption of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium chloride on sewage sludge in waste water treatment. In Oils & Fuels for Sustainable Development; Hupka, J., Aranowski, R., Jungnickel, C., Tonderski, A., Eds.; Gdańsk University of Technology: Gdańsk, Poland, 2008; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and Disinfectants: Activity, Action, and Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, O.V.; Hartmann, D.O.; Cardoso, C.M.P.; Oberdoerfer, D.; Baptista, M.; Santos, M.A.S.; Almeida, L.; Ramalho-Santos, J.; Vaz, W.L.C. Surfactants as Microbicides and Contraceptive Agents: A Systematic In Vitro Study. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2913. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, R.S.; Innerlohinger, J.; Glatter, O.; Miguel, M.G.; Lindman, B. Coil−Globule Transition of DNA Molecules Induced by Cationic Surfactants: A Dynamic Light Scattering Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 10458–10463. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathy, R. Factors limiting bioremediation technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD, OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals 301 - Ready Biodegradability; OECD: Paris, France, 1992.
- Docherty, K.M.; Dixon, J.K.; Kulpa, C.F.K., Jr. Biodegradability of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids by an activated sludge microbial community. Biodegradation 2007, 18, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, S.; Abdulkarim, S.; Arning, J.; Blomeyer-Nienstedt, A.-K.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Matzke, M.; Ranke, J.; Jastorff, B.; Thöming, J. Primary biodegradation of ionic liquid cations, identification of degradation products of 1-methyl-3-octyl -imidazolium chloride and electrochemical waste water treatment of poorly biodegradable compounds. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osowska, E.; Markiewicz, M.; Markowska, A.; Aranowski, R.; Jungnickel, C. Investigation on sorption of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium chloride on sewage sludge in wastewater treatment. In Oils & Fuels for Sustainable Development; Hupka, J., Tonderski, A., Aranowski, R., Jungnickel, C., Eds.; Gdansk University of Technology: Gdansk, Poland, 2008; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gorman-Lewis, D.J.; Fein, J.B. Experimental Study of the Adsorption of an Ionic Liquid onto Bacterial and Mineral Surfaces. Environm. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkoong, W.; Hwang, E.-Y.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.-Y. Bioremediation of diesel-contaminated soil with composting. Environ. Poll. 2002, 119, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzke, M.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Uebersa, U.; Filser, J. Imidazolium based ionic liquids in soils: effects of the side chain length on wheat (Triticum aestivum) and cress (Lepidium sativum) as affected by different clays and organic matter. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnowski, P.; Mrozik, W.; Nichthauser, J. Adsorption of alkylimidazolium and alkylpyridinium ionic liquids onto natural soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- uczak, J.; Jungnickel, C. Anti-microbial and surface activity of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium derivatives. Green Chem. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, J.E.; Quarmby, J.; Stephenson, T. Micronutrient supplements for optimisation of the treatment of industrial wastewater using activated sludge. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Lee, J.-F.; Chao, H.-P.; Yeh, P.-W.; Yang, Y.-F.; Liao, W.-L. The influences of solid-phase organic constituents on the partition of aliphatic and aromatic organic contaminants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample availability: Not available.
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Markiewicz, M.; Jungnickel, C.; Markowska, A.; Szczepaniak, U.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Hupka, J. 1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium Chloride—Sorption and Primary Biodegradation Analysis in Activated Sewage Sludge. Molecules 2009, 14, 4396-4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14114396
Markiewicz M, Jungnickel C, Markowska A, Szczepaniak U, Paszkiewicz M, Hupka J. 1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium Chloride—Sorption and Primary Biodegradation Analysis in Activated Sewage Sludge. Molecules. 2009; 14(11):4396-4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14114396
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkiewicz, Marta, Christian Jungnickel, Aleksandra Markowska, Urszula Szczepaniak, Monika Paszkiewicz, and Jan Hupka. 2009. "1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium Chloride—Sorption and Primary Biodegradation Analysis in Activated Sewage Sludge" Molecules 14, no. 11: 4396-4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14114396
APA StyleMarkiewicz, M., Jungnickel, C., Markowska, A., Szczepaniak, U., Paszkiewicz, M., & Hupka, J. (2009). 1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium Chloride—Sorption and Primary Biodegradation Analysis in Activated Sewage Sludge. Molecules, 14(11), 4396-4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14114396