The Molecular Mechanism of Action of Artemisinin—The Debate Continues
Abstract
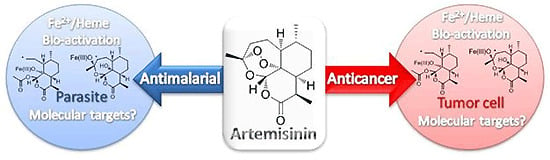
:1. Introduction
2. Activation of Artemisinin
2.1. Bioactivation in parasites
2.1.1. Reductive scission model
2.1.2. Open peroxide model
2.1.3. Iron-Dependent bioactivation vs. heme-dependent bioactivation in parasites
2.2. Bioactivation in tumor cells
3. Potential targets of the artemisinins
3.1. Proposed parasite molecular targets
3.1.1. Heme
3.1.2. Protein alkylation
3.1.3. Inhibition of PfATP6
3.1.4. Parasite membranes
3.1.5. Mitochondria
3.2. Potential molecular targets in tumor cells
4. Conclusion
References
- World Heath Organisation. The World Malaria Report; World Heath Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow, C.J.; Haynes, R.K.; Krishna, S. Artemisinins. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 81, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-F. A Detailed Chronological Record of Project 523 and the Discovery and Development of Qinghaosu (Artemisinin). Yang Cheng Evening News Publishing Company, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Terkuile, F.; White, N.J.; Holloway, P.; Pasvol, G.; Krishna, S. Plasmodium falciparum: In Vitro Studies of the Pharmacodynamic Properties of Drugs Used for the Treatment of Severe Malaria. Exp. Parasitol. 1993, 76, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Zheng, H. Stage-specific gametocytocidal effect in vitro of the antimalaria drug qinghaosu on Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Res. 1990, 76, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, G.W.; O’ Neill, P.M. Knowledge of the proposed chemical mechanism of action and cytochrome p450 metabolism of antimalarial trioxanes like artemisinin allows rational design of new antimalarial peroxides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennerstrom, J.L.; Arbe-Barnes, S.; Brun, R.; Charman, S.A.; Chiu, F.C.K.; Chollet, J.; Dong, Y.X.; Dorn, A.; Hunziker, D.; Matile, H.; McIntosh, K.; Padmanilayam, M.; Tomas, J.S.; Scheurer, C.; Scorneaux, B.; Tang, Y.Q.; Urwyler, H.; Wittlin, S.; Charman, W.N. Identification of an antimalarial synthetic trioxolane drug development candidate. Nature 2004, 430, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Shibata, Y.; Wataya, U.; Tsuchiya, K.; Masuyama, A.; Nojima, M. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of cyclic peroxides 1,2,4,5,7-pentoxocanes and 1,2,4,5-tetraoxanes. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 2604–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Bustamante, L.; Haynes, R.K.; Staines, H.M. Artemisinins: their growing importance in medicine. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.P.; Panwar, V.K. Case report of a pituitary macroadenoma treated with artemether. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T. Willmar Schwabe Award 2006: antiplasmodial and antitumor activity of artemisinin-from bench to bedside. Planta Medica 2007, 73, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagola, S.; Stephens, P.W.; Bohle, D.S.; Kosar, A.D.; Madsen, S.K. Nature 2000, 404, 307. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.J. Recent advances in understanding the mechanism of hemozoin (malaria pigment) formation. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshnick, S.R.; Thomas, A.; Ran, A.; Xy, C.M.; Pan, H.Z. Artemisinin (qinghaosu): the role of intracellular hemin in its mechanism of antimalarial action. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1991, 49, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, G.H.; Wang, D.; Cumming, J.N.; Oh, C.H.; French, A.N.; Bodley, A.L.; Shapiro, T.A. Further evidence supporting the importance of and the restrictions on a carbon-centered radical for high antimalarial activity of 1,2,4-trioxanes like artemisinin. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 2273–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, G.H.; Oh, C.H. Regiospecifically oxygen-18 labeled 1,2,4-trioxane: a simple chemical model system to probe the mechanism(s) for the antimalarial activity of artemisinin (qinghaosu). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8328–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, G.H.; Oh, C.W.; Wang, D.S.; Gerena, L.; Milhous, W.K.; Meshnick, S.R.; Asawamahasadka, W. Mechanism-Based Design, Synthesis, and in vitro Antimalarial Testing of New 4-Methylated Trioxanes Structurally Related to Artemisinin: The Importance of a Carbon-Centered Radical for Antimalarial Activity. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefford, C.W.; Favarger, F.; Vicente, M.; Jacquier, Y. The Decomposition of Cis-Fused Cyclopenteno-1,2,4-Trioxanes Induced by Ferrous Salts and Some Oxophilic Reagents. Helv. Chim. Acta 1995, 78, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefford, C.W.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Jacquier, Y.; Favarger, F.; Mareda, J.; Millasson-Schmidt, P.; Brunner, G.; Burger, U. The deoxygenation and isomerization of artemisinin and artemether and their relevance to antimalarial action. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.R.; Gilbert, B.C.; Hulme, P.; Irvine, L.R.; Renton, L.; Whitwood, A.C. EPR Evidence for the Involvement of Free Radicals in the Iron-Catalysed Decomposition of Qinghaosu (Artemisinin) and Some Derivatives; Antimalarial Action of Some Polycyclic Endoperoxides. Free Radical Res. 1998, 28, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.M.; Bishop, L.P.D.; Searle, N.L.; Maggs, J.L.; Storr, R.S.; Ward, S.A.; Park, B.K.; Mabbs, F. Biomimetic Fe(II)-Mediated Degradation of Arteflene (Ro-42-1611). The First EPR Spin-Trapping Evidence for the Previously Postulated Secondary Carbon-Centered Cyclohexyl Radical. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Yao, Z.J.; Zhou, C.M.; Li, Y.; Shan, F. Unified Mechanistic Framework for the Fe(II)-Induced Cleavage of Qinghaosu and Derivatives/Analogues. The First Spin-Trapping Evidence for the Previously Postulated Secondary C-4 Radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3316–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Chan, W.C.; Lung, C.M.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Eckstein, U.; Taramelli, D.; Parapini, S.; Monti, D.; Krishna, S. The Fe2+-mediated decomposotion, PfATP6 binding, and antimalarial activities of artemisone and other arteminisins: The unlikehood of C-centered radicals as bioactive intermediates. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 1480–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.K.; Vonwiller, S.C. The behaviour of qinghaosu (artemisinin) in the presence of heme iron(II) and (III). Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Pai, H.H.-O.; Voerste, A. Ring opening of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and dihydroartemisinin and interception of the open hydroperoxides with Formation of N-oxides -- a chemical model for antimalarial mode of action. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4715–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Vonwiller, S.C. The behaviour of qinghaosu (artemisinin) in the presence of non-heme iron(II) and (III). Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, P.A.; Bray, P.G.; Barton, V.E.; Al-Helal, M.; Jones, M.; Araujo, N.C.; Gibbons, P.; Ward, S.A.; Hughes, R.H.; Biagini, G.A.; Davies, J.; Amewu, R.; Mercer, A.E.; Ellis, G.; O’Neill, P.M. Evidence for a common non-heme chelatable-iron-dependent activation mechanism for semisynthetic and synthetic endoperoxide antimalarial drugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 119, 6394–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein-Ludwig, U.; Webb, R.J.; van Goethem, L.D.A.; East, J.M.; Lee, A.G.; Kimura, M.; O’Neill, P.M.; Bray, P.G.; Ward, S.A.; Krishna, S. Artemisinins target the SERCA of plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2003, 424, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.K.; Monti, D.; Taramelli, D.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Olliaro, P. Artemisinin antimalarials do not inhibit hemozoin formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1175–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeder, B.J.; Wilson, M.T. Desferrioxamine Inhibits Production of Cytotoxic Heme to Protein Cross-Linked Myoglobin: A Mechanism to Protect against Oxidative Stress without Iron Chelation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeder, B.J.; Hider, R.C.; Wilson, M.T. Iron chelators can protect against oxidative stress through ferryl heme reduction. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- As commented by a reviewer DFO can potentially act as general antioxidant and therefore this should be taken into consideration when interpreting isobolograms/interactions with artemisinin.
- Zhang, S.; Gerhard, G. Heme activates artemisinin more efficiently than hemin, inorganic iron, or hemoglobin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7853–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Ryan, E.; Charman, W.N.; Chiu, F.C.K.; Prankerd, R.J.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Charman, S.A. Stability of Peroxide Antimalarials in the Presence of Human Hemoglobin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3496–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, T.S.; Manning, L.S.; Johnston, W.A.; Davis, T.M.E. In vitro stage-specific sensitivity of Plasmodium falciparum to quinine and artemisinin drugs. Int. J. Parasit. 1996, 26, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Brando, L.; D’Angelo, J.; Posner, G.H.; Yolken, R. In vitro inhibition of toxoplasma gondii by four new derivatives of artemisinin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 4206–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Pal, Y.; Dwivedi, S.K. In-vivo therapeutic efficacy trial with artemisinin derivative, buparvaquone and imidocarb dipropionate against babesia equi infection in donkeys. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakar, N.A.; Klonis, N.; Hanssen, E.; Chan, C.; Tilley, L. Digestive-vacuole genesis and endocytic processes in the early intraerythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerdenbag, H.J.; Moskal, T.A.; Pras, N.; Malingre, T.M.; Elferaly, F.S.; Kampinga, H.H.; Konings, A.W.T. Cytotoxicity of artemisinin-related endoperoxides to ehrlich ascites tumor-cells. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, A.C.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Kampinga, H.H.; Konings, A.W.T. Cytotoxicity of artemisinin, a dimer of dihydroartemisinin, artemisitene and eupatoriopicrin as evaluated by the MTT and clonogenic assay. Phytother. Res. 1996, 10, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, A.C.; Barentsen, A.R.W.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; VanUden, W.; Pras, N.; Konings, A.W.T.; ElFeraly, F.S.; Galal, A.M.; Wikstrom, H.V. Stereochemistry-dependent cytotoxicity of some artemisinin derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, A.C.; Wierenga, P.K.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Van Uden, W.; Pras, N.; Konings, A.W.T.; El-Feraly, F.S.; Galal, A.M.; Wikstrom, H.V. Artemisinin-derived sesquiterpene lactones as potential antitumour compounds: Cytotoxic action against bone marrow and tumour cells. Planta Medica 1998, 64, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.C.; Richardson, D.R. The iron metabolism of neoplastic cells: alterations that facilitate proliferation? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T.; Sauerbrey, A.; Olbrich, A.; Gebhart, E.; Rauch, P.; Weber, H.O.; Hengstler, J.G.; Halatsch, M.E.; Volm, M.; Tew, K.D.; Ross, D.D.; Funk, J.O. Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramacher, M.; Umansky, V.; Efferth, T. Effect of artesunate on immune cells in ret-transgenic mouse melanoma model. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockwin, L.H.; Han, B.N.; Yu, S.X.; Hollingshead, M.G.; ElSohly, M.A.; Gul, W.; Slade, D.; Galal, A.M.; Newton, D.L. Artemisinin dimer anticancer activity correlates with heme-catalyzed reactive oxygen species generation and endoplasmic reticulum stress induction. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T.; Benakis, A.; Romero, M.R.; Tomicic, M.; Rauh, R.; Steinbach, D.; Häfer, R.; Stamminger, T.; Oesch, F.; Kaina, B.; Marschall, M. Enhancement of cytotoxicity of artemisinins toward cancer cells by ferrous iron. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T. Molecular pharmacology and pharmacogenomics of artemisinin and its derivatives in cancer cells. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 4, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, A.; Maggs, J.; Sun, X.; Cohen, G.; Chadwick, J.; O’Neill, P.; Park, B. Evidence for the involvement of carbon-centered radicals in the induction of apoptotic cell death by artemisinin compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9372–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelter, G.; Steinbach, D.; Konkimalla, V.B.; Tahara, T.; Taketani, S.; Fiebig, H.-H.; Efferth, T. Role of Transferrin Receptor and the ABC Transporters ABCB6 and ABCB7 for Resistance and Differentiation of Tumor Cells towards Artesunate. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gerhard, G.S. Heme Mediates Cytotoxicity from Artemisinin and Serves as a General Anti-Proliferation Target. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshnick, S.R.; Little, B.; Yang, Y.Z. Alkylation of Proteins by artemisinin. Biochem. Pharm. 1994, 48, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Meshnick, S.R.; Yang, Y.Z.; Lima, V.; Kuypers, F.; Kamchonwongpaisan, S.; Yuthavong, Y. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 1108–1114. [CrossRef]
- Cazelles, J.; Robert, A.; Meunier, B. Alkylation of heme by artemisinin, an antimalarial drug. Comptes Rendus De L Academie Des Sciences Serie Ii Fascicule C-Chimie 2001, 4, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creek, D.J.; Charman, W.N.; Chiu, F.C.K.; Prankerd, R.J.; Dong, Y.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Charman, S.A. Relationship between Antimalarial activity and Heme Alkylation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, A.; Benoit-Vical, F.O.; Claparols, C.; Meunier, B. The antimalarial drug artemisinin alkylates heme in infected mice. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13676–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousejra-El Garah, F.; Claparols, C.; Benoit-Vical, F.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. The antimalarial trioxaquine du1301 alkylates heme in malaria-infected mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshnick, S.R.; Little, B.; Yang, Y.Z. Alkylation of human albumin by the antimalarial artemisinin. Biochem. Pharm. 1993, 46, 336–339. [Google Scholar]
- Asawamahasakda, W.; Ittarat, I.; Pu, Y.M.; Ziffer, H.; Meshnick, S.R. Reaction of Antimalarial Endoperoxides with specific parasite proteins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhisutthibhan, J.; Pan, X.; Hossler, P.A.; Walker, D.J.; Yowell, C.A.; Carlton, J.; Dame, J.B.; Meshnick, S.R. The plasmodium falciparum translationally controlled tumor protein homolog and its reaction with the antimalarial drug artemisinin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16192–16198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Zhai, Z.; Xiao, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-L. Study on the mechanism of action of artemether against schistosomes: the identification of cysteine adducts of both carbon-centred free radicals derived from artemether. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1645–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Tekwani, B.L.; Singh, R.L.; Chauhan, V.S. Artemisinin, an Endoperoxide Antimalarial, Disrupts the Hemoglobin Catabolism and Heme Detoxification Systems in Malarial Parasite. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 27, 19383–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefford, C.W. New developments in synthetic peroxidic drugs as artemisinin mimics. Drug Discovery Today 2007, 12, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Kim, H.; Ki, Y.N.; Kyoung, T.N. Three-dimensional structure of Plasmodium falciparum Ca2+- ATPase(PfATP6) and docking of artemisinin derivatives to PfATP6. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2994–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlemann, A.C.; Cameron, A.; Eckstein-Ludwig, U.; Fischbarg, J.; Iserovich, P.; Zuniga, F.A.; East, M.; Lee, A.; Brady, L.; Haynes, R.K.; Krishna, S. A single amino acid residue can determine the sensitivity of SERCAs to artemisinin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, A.; Hunt, P.; Cheesman, S.; Alves, A.C.; Cunha, C.V.; do Rosario, V.; Cravo, P. Malaria Parasites Can Develop Stable Resistance to Artemisinin but Lack Mutations in Candidate Genes atp6 (Encoding the Sarcoplasmic and Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ ATPase), tctp, mdr1, and cg10. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Pilar Crespo, M.; Avery, T.D.; Hanssen, E.; Fox, E.; Robinson, T.V.; Valente, P.; Taylor, D.K.; Tilley, L. Artemisinin and a Series of Novel Endoperoxide Antimalarials Exert Early Effects on Digestive Vacuole Morphology. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlemann, A.-C.; Wittlin, S.; Matile, H.; Bustamante, L.; Krishna, S. Mechanism of Antimalarial Action of the Synthetic Trioxolane RBX11160 (OZ277). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousejra-El Garah, F.; Stigliani, J.L.; Cosledan, F.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. Docking Studies of Structurally Diverse Antimalarial Drugs Targeting PfATP6: No Correlation between in silico Binding Affinity and in vitro Antimalarial Activity. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, C.L.; Rosenthal, A.S.; Dangelo, J.; Griffin, C.E.; Posner, G.H.; Cooper, R.A. Accumulation of artemisinin trioxane derivatives within neutral lipids of Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites is endoperoxide-dependent. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumura, N.; Furukawa, H.; Onyango, A.N.; Izumi, M.; Nakajima, S.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; Kim, H.S.; Wataya, Y.; Baba, N. Different behavior of artemisinin and tetraoxane in the oxidative degradation of phospholipid. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 160, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mo, W.; Shen, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Gitschier, J.M.; Zhou, B. Yeast model uncovers dual roles of mitochondria in the action of artemisinin. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T.; Oesch, F. Oxidative stress response of tumor cells: microarray-based comparison between artemisinins and anthracyclines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T.; Briehl, M.M.; Tome, M.E. Role of antioxidant genes for the activity of artesunate against tumor cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 4, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T. Mechanistic perspectives for 1,2,4-trioxanes in anti-cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updates 2005, 8, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youns, M.; Efferth, T.; Reichling, J.; Fellenberg, K.; Bauer, A.; Hoheisel, J.D. Gene expression profiling identifies novel key players involved in the cytotoxic effect of Artesunate on pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Little, B.; Meshnick, S.R. Alkylation proteins by artemisinin. Effect of heme, pH, and drug structure. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.H.; Lam, E.; Roos, W.P.; Zdzienicka, M.Z.; Kaina, B.; Efferth, T. Artesunate Derived from Traditional Chinese Medicine Induces DNA Damage and Repair. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4347–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Neill, P.M.; Barton, V.E.; Ward, S.A. The Molecular Mechanism of Action of Artemisinin—The Debate Continues. Molecules 2010, 15, 1705-1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031705
O’Neill PM, Barton VE, Ward SA. The Molecular Mechanism of Action of Artemisinin—The Debate Continues. Molecules. 2010; 15(3):1705-1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031705
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Neill, Paul M., Victoria E. Barton, and Stephen A. Ward. 2010. "The Molecular Mechanism of Action of Artemisinin—The Debate Continues" Molecules 15, no. 3: 1705-1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031705
APA StyleO’Neill, P. M., Barton, V. E., & Ward, S. A. (2010). The Molecular Mechanism of Action of Artemisinin—The Debate Continues. Molecules, 15(3), 1705-1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031705