Chemical Investigation of Saponins in Different Parts of Panax notoginseng by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Conditions

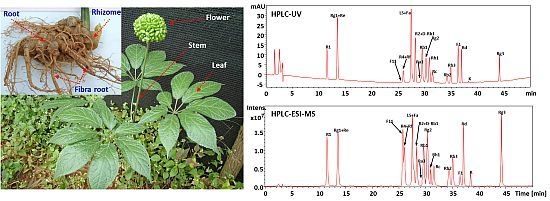
2.2. HPLC-UV-MS Analysis of Reference Compounds



2.3. HPLC-UV-MS Analysis of Different Parts of P. notoginseng

| No | Peak identification | RT(min) | MS ( m/z) | CID( m/z) | UG | a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [M−H]− | [M+Cl]− | |||||||||
| 1 | Yesanchinoside H | 7.2 | 1093 | 1129 | 961[M−H-Xyl]−, 931[M−H-Glc]−, 799[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 637[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 475 [M−H-Xyl-2Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | Notoginsenoside R3/R6/N/ 20-O-glucoginsenoside Rf | 8.4 | 961 | 997 | 799[M−H-Glc]−, 637[M−H-2Glc]−, 475[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | Notoginsenoside R3/R6/N/ 20-O-glucoginsenoside Rf | 10.6 | 961 | 997 | 799[M−H-Glc]−, 637[M−H-2Glc]−, 475[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | Notoginsenoside R3/R6/N/ 20-O-glucoginsenoside Rf | 11.2 | 961 | 997 | 799[M−H-Glc]−, 637[M−H-2Glc]−, 475[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | Notoinsenoside R1 | 11.5 | 931 | 967 | 799[M−H-Xyl]−, 769[M−H-Glc]−, 751[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 637[M−H-Glc-Xyl]−, 619[M−H-Glc-Xyl-H2O]−, 475[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6 | Notoinsenoside R1 isomer | 12.6 | 931 | 967 | 799[M−H-Xyl]−, 769[M−H-Glc]−, 637[M−H-Glc-Xyl]−, 475[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 13.6 | 799 | 835 | 637[M−H-Glc]−, 619[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 475[M−H-2Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 8 | Ginsenoside Re | 13.6 | 945 | 981 | 799[M−H-Rha]−, 783[M−H-Glc]−, 765.6[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 637[M−H-Rha-Glc]−, 619[M−H-Rha-Glc-H2O]−, 475[M−H-Rha-2Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 9 | Notoginsenoside E | 15.3 | 979 | 1015 | 817[M−H-Glc]−, 799[M−H-Glc-H2O] | + | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | Notoginsenoside A | 15.5 | 1123 | 1159 | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | Ginsenoside G | 17.9 | 959 | 996 | 797[M-Glc], 635[M-2Glc]−, 473[M-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | Notoginsenoside R3/R6/N/ 20-O-Glucoginsenoside Rf | 21.9 | 961 | 998 | 799[M−H-Glc]−, 637[M−H-2Glc]−, 619[M−H-2Glc-H2O]−, 475[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | Notoginsenoside R4 | 26.0 | 1239 | 1276 | 1107[M−H-pen]−, 945[M−H-xyl-Glc]−, 783[M−H-xyl-2Glc]−, 621[M−H-xyl-3Glc], 459[M−H-xyl-4Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | Ginsenoside Rf | 26.1 | 799 | 835 | 637[M−H-Glc]−, 619[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 475[M−H-2Glc]−, | + | - | + | - | - |
| 15 | Chikusetsusaponin L5 | 27.2 | 901 | 937 | 769[M−H-Xyl]−, 637[M−H-Xyl-Ara]−, 475[M−H-Xyl-Ara-Glc]− | + | - | + | + | + |
| 16 | Notoginsenoside Fa | 27.3 | 1239 | 1275 | 1107[M−H-Xyl]−, 1089[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 945[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-3Glc]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-4Glc]− | + | - | + | + | + |
| 17 | Notoinsenoside Q/S | 27.7 | 1341 | 1377 | 1209[M−H-Xyl]−, 1192[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 1077[M−H-2Pen]−, 945[M−H-3Pen]−, 783[M−H-3Pen-Glc]−, 621[M−H-3Pen-2Glc]−, 459[M−H-3Pen-3Glc]− | - | - | - | - | + |
| 18 | Notoginsenoside I | 27.7 | 1091 | 1127 | 929[M−H-Glc]−, 767[M−H-2Glc]−, 605[M−H-3Glc]−, 443[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | Notoinsenoside R2 | 28.0 | 769 | 705 | 637[M−H-Xyl]−, 619[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 475[M−H-Xyl-Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | Ginsenoside Fc/Ra1/Ra2 | 28.1 | 1209 | 1245 | 1077[M−H-Xyl]−, 1047[M−H-Glc]−, 1027[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 945[M−H-Xyl-arab]−,915[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 897[M−H-Xyl-Glc-H2O]−, 783[M−H-Xyl-arab-Glc]− 621[M−H-Xyl-arab-2Glc]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-arab-3Glc]− | - | - | - | - | + |
| 21 | Didehydroginsenoside Rb1 | 28.2 | 1105 | 1141 | 943[M−H-Glc]−, 781[M−H-2Glc]−, 619[M−H-3Glc]−, 457[M−H-4Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | Ginsenoside Fc/Ra1/Ra2 | 28.9 | 1209 | 1245 | 1077[M−H-Xyl]−, 1059[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 1047[M−H-Glc]−, 945[M−H-Xyl-arab]−,915[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Xyl-arab-Glc]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-arab-2Glc]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-arab-3Glc]− | - | - | + | + | + |
| 23 | Notoinsenoside Q/S | 29.1 | 1341 | 1377 | 1209[M−H-Xyl]−, 1077[M−H-2Pen]−, 945[M−H-3Pen]−, 783[M−H-3Pen-Glc]−, 621[M−H-3Pen-2Glc]−, 459[M−H-3Pen-3Glc]− | - | - | - | - | + |
| 24 | Ginsenoside Ra3 | 29.5 | 1239 | 1275 | 1107[M−H-Xyl]−, 1089[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 945[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-3Glc]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-4Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | Ginsenoside Rb1 | 29.6 | 1107 | 1143 | 945 [M−H-Glc]−, 783[M−H-2Glc]−, 621[M−H-3Glc]−, 459[M−H-4Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 26 | Ginsenoside Rg2 | 30.2 | 783 | 819 | 637[M−H-Rha]−, 619[M−H-Rha-H2O]−, 475[M−H-Rha-Glc]− | + | + | + | - | - |
| 27 | Ginsenoside Rh1 | 30.9 | 637 | 673 | 475[M−H-Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 28 | Ginsenoside Rc | 31.5 | 1077 | 1113 | 945[M−H-Araf]−, 915[M−H-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Araf-Glc]−, 765[M−H-Araf-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-Araf-2Glc]−, 603[M−H-Araf-2Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-Araf-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 29 | Ginsenoside Fc/Ra1/Ra2 | 31.6 | 1209 | 1245 | 1077[M−H-Xyl]−, 1047[M−H-Glc]−, 945[M−H-2Xyl/(-Xyl-Ara)]−, |783[M−H-(2Xyl-Glc)/(-Xyl-Ara-Glc)]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | Ginsenoside Rb2 | 34.3 | 1077 | 1113 | 945[M−H-Xyl]−, 915[M−H-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Araf-Glc]−, 765[M−H-Xyl-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 603[M−H-Xyl-2Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 31 | Ginsenoside Rb3 | 35.0 | 1077 | 1113 | 945[M−H-Xyl]−, 915[M−H-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Araf-Glc]−, 765[M−H-Xyl-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 603[M−H-Xyl-2Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-Xyl-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 32 | Notoginsenoside L | 35.5 | 1077 | 1113 | 945[M−H-Xyl]−, 915[M−H-Glc]−, 783[M−H-Xyl-Glc]−, 765[M−H-Xyl-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-Xyl-2Glc]−, 603[M−H-Xyl-2Glc-H2O]−,459[M−H-Xyl-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 33 | Didehydroginsenoside Rd | 35.7 | 943 | 979 | 781[M−H-Glc]−, 619[M−H-2Glc]−, 457[M−H-3Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 34 | Ginsenoside F1 | 36.3 | 637 | 673 | 475[M−H-Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 35 | Ginsenoside Rd | 37.0 | 945 | 981 | 783[M−H-Glc]−, 765[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-2Glc]−, 603[M−H-2Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 36 | Notoginsenoside K | 38.3 | 945 | 981 | 783[M−H-Glc]−, 775[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 621[M−H-2Glc]−, 459[M−H-3Glc]− | + | + | + | + | + |
| 37 | Notoginsenoside O/P | 38.6 | 1047 | 1083 | 915[M−H-Xyl]−, 897[M−H-Xyl-H2O]−, 783[M−H-2Xyl]−, 621 [M−H-2Xyl-Glc]−,459[M−H-2Xyl-2Glc]− | - | - | - | + | + |
| 38 | Gypenoside IX/Notoginsenoside Fe/isomer | 39.5 | 915 | 951 | 783[M-pen]−, 621[M-pen-glc]−, 459[M-pen-2glc]− | + | - | - | + | + |
| 39 | Gypenoside IX/ Notoginsenoside Fe/isomer | 39.7 | 915 | 951 | 783[M-pen]−, 621[M-pen-glc]−, 459[M-pen-2glc]− | + | - | + | + | + |
| 40 | Ginsenoside F2 | 42.1 | 783 | 819 | 621[M−H-Glc]−, 603[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-2Glc]− | + | - | - | - | - |
| 41 | Ginsenoside Rg3 | 44.1 | 783 | 819 | a621[M−H-Glc]−, 603[M−H-Glc-H2O]−, 459[M−H-2Glc]− | + | - | + | + | + |

3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals, Standards and Samples
3.2. Pressurized Liquid Extraction
3.3. HPLC-UV Analysis
3.4. HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Wei, J.X.; Du, Y.C. Modern Science Research and Application of Panax notoginseng; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.B.; Li, S.P.; Wang, Y.T. Panax notoginseng. In Pharmacological Activity Based Quality Control of Chinese Herbs; Li, S.P., Wang, Y.T., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 179–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Wan, J.B.; Chan, S.W.; Deng, Y.H.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Q.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Lee, S.M. Comparative study on saponin fractions from Panax notoginseng inhibiting inflammation-induced endothelial adhesion molecule expression and monocyte adhesion. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.Y.; Mak, N.K.; Cheng, Y.K.; Leung, K.W.; Ng, T.B.; Fan, D.T.; Yeung, H.W.; Wong, R.N. Pharmacogenomics and the Yin/Yang actions of ginseng: anti-tumor, angiomodulating and steroid-like activities of ginsenosides. Chin. Med. 2007, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; McEntee, E.; Wicks, S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.S. Phyto-chemical and analytical studies of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen. J. Nat. Med. 2006, 60, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Toh, S.A.; Sellers, L.A.; Skepper, J.N.; Koolwijk, P.; Leung, H.W.; Yeung, H.W.; Wong, R.N.; Sasisekharan, R.; Fan, T.P. Modulating angiogenesis: The yin and the yang in ginseng. Circulation 2004, 110, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Y. Structure and biological activity of protopanaxatriol-type saponins from the roots of Panax notoginseng. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.B.; Yang, F.Q.; Li, S.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Cui, X.M. Chemical characteristics for different parts of Panax notoginseng using pressurized liquid extraction and HPLC-ELSD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.B.; Li, S.P.; Jian, J.R.; Kong, L.Y.; Wang, Y.T. Analysis of saponins from Panax notoginseng using pressurized solvent extraction coupled with high performance thin layer chromatography. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2004, 2, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.B.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Simultaneous determination of 11 saponins in Panax notoginseng using HPLC-ELSD and pressurized liquid extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.B.; Li, S.P.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, Y.T. Chemical characteristics of three medicinal plants of the Panax genus determined by HPLC-ELSD. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Lai, C.M.; Li, S.P. A rapid method for the simultaneous determination of 11 saponins in Panax notoginseng using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M.; Li, S.P.; Yu, H.; Wan, J.B.; Kan, K.W.; Wang, Y.T. A rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS for qualitative and quantitative analysis of saponins in “XUESETONG” injection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dang, Y.; Zhu, C. Simultaneous determination of three major bioactive saponins of Panax notoginseng using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and a pharmacokinetic study. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tsao, R.; Dou, J.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Detection of saponins in extract of Panax notoginseng by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 536, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Shi, P.; Shao, Q.; Fan, X. Chemical fingerprinting and quantitative analysis of a Panax notoginseng preparation using HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzzati, N.; Gabetta, B.; Jayakar, K.; Pace, R.; Peterlongo, F. Liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometric identification of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng roots. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 854, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Liang, X.M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xiao, H.B. Identification of ginsenosides in roots of Panax ginseng by HPLC-APCI/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Xiao, X.Y.; Lin, R.C.; Cheng, Y.Y. Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different growth ages using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2006, 17, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, G.A.; Liang, Q.L.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.M. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of Asian ginseng in adulterated American ginseng preparations by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligor, T.; Ludwiczuk, A.; Wolski, T.; Buszewski, B. Isolation and determination of ginsenosides in American ginseng leaves and root extracts by LC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; But, P.P.; Cheng, S.W.; Kwok, I.M.; Lau, F.W.; Xu, H.X. Differentiation and authentication of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and ginseng products by using HPLC/MS. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Fuzzati, N. Analysis methods of ginsenosides. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 812, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.S.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Hao, C.; March, R.E. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of ginsenosides. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2002, 37, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijiang, Z.; Yongjiang, W.; Yiyu, C. Analysis of ‘SHENMAI’ injection by HPLC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Cai, X.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Differentiation and authentication of saponin extracts from Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius and Panax notoginseng by HPLC/ESI-MSn. Chin. Pharm. J. 2006, 41, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Yashiro, K.; Murakami, T.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XIX. Notoginseng (3): Immunological adjuvant activity of notoginsenosides and related saponins: structures of notoginsenosides-L, -M, and -N from the roots of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2001, 49, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Ueno, T.; Yashiro, K.; Hirokawa, N.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J.; Matsuda, H.; Saijoh, R.; Tanaka, O. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. VIII. Notoginseng (1): New dammarane-type triterpene oligoglycosides, notoginsenosides-A, -B, -C, and -D, from the dried root of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1997, 45, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.Q.; Komatsu, K.; Namba, T. Analysis of the constituents in the Chinese drug notoginseng by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 13, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Kashima, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Matsuda, H. Structures of new dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the flower buds of Panax notoginseng and hepatoprotective effects of principal Ginseng Saponins. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Zhu, S.; Tohda, C.; Cai, S.; Komatsu, K. Dammarane-type triterpene saponins from Panax japonicus. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.B.; Zhang, Q.W.; Hong, S.J.; Guan, J.; Ye, W.C.; Li, S.P.; Lee, M.Y.; Wang, Y.T. 5,6-Didehydroginsenosides from the roots of Panax notoginseng. Molecules 2010, 15, 8169–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wan, J.B.; Li, S.P.; Wang, Y.T. Studies on the accelerated solvent extraction of Panax notoginseng saponins. Chin. Nat. Prod. 2004, 2, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 5, 7, 8, 13–16, 19, 21, 24–28, 30, 31, 34–36 and 41 are available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, J.-B.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Hong, S.-J.; Li, P.; Li, S.-P.; Wang, Y.-T. Chemical Investigation of Saponins in Different Parts of Panax notoginseng by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2012, 17, 5836-5853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055836
Wan J-B, Zhang Q-W, Hong S-J, Li P, Li S-P, Wang Y-T. Chemical Investigation of Saponins in Different Parts of Panax notoginseng by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2012; 17(5):5836-5853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055836
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Jian-Bo, Qing-Wen Zhang, Si-Jia Hong, Peng Li, Shao-Ping Li, and Yi-Tao Wang. 2012. "Chemical Investigation of Saponins in Different Parts of Panax notoginseng by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 17, no. 5: 5836-5853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055836
APA StyleWan, J. -B., Zhang, Q. -W., Hong, S. -J., Li, P., Li, S. -P., & Wang, Y. -T. (2012). Chemical Investigation of Saponins in Different Parts of Panax notoginseng by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 17(5), 5836-5853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055836