Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fluorescence Properties of AGEs Produced from BSA and Ribose
2.2. Statistical Analysis of the Automated High Throughput Screening Assay Results

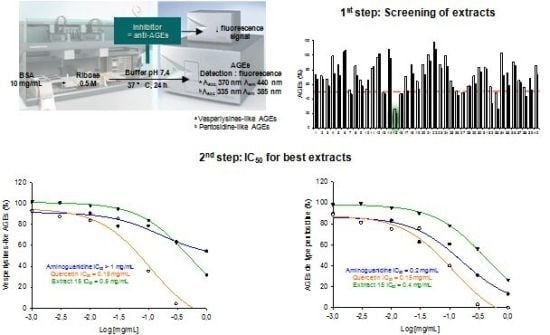
2.3. Screening Anti-AGE Activity of a Small Library of Natural Products and Validation of Hits by Dose-Effect Curves Using Two Fluorescence Measurements
| Anti-vesperlysines-like AGE assay
(mean ± S.D.) | Anti-pentosidine-like AGE assay
(mean ± S.D.) | |
|---|---|---|
| Z'-factor | 0.70 ± 0.08 | 0.75 ± 0.07 |
| SSMD | 9.9 ± 1.5 | 11.1 ± 2.2 |
| S/N | 9.7 ± 1.8 | 16.1 ± 2.5 |
| S/B | 12.1 ± 4.1 | 13.4 ± 4.2 |
| Separation band | 4.4 ± 1.2 × 103 | 4.5 ± 1.0 × 103 |
| Plate-to-plate variability (%) | 7 | 5 |
| Day-to-day variability (%) | 3 | 3 |





| Natural products | Effect on vesperlysines-like AGE formation
(IC50, mM) | Effect on pentosidine-like AGEs formation
(IC50, mM) |
|---|---|---|
| Quercetin 10 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| (+)-catechin 11 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| Resveratrol 12 | 0.6 | >3.0 |
| Berberine 13 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Boldine 14 | 0.5 | a |
| Chlorogenic acid 17 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Caffeic acid 18 | >3.0 | 1.0 |
| α-pinene 15 | >3.0 | >3.0 |
| 1,8-cineole 16 | >3.0 | >3.0 |
| Emetine 19 | a,b | 0.7 |
| Umbelliferone 20 | a | >3.0 |
| Aminoguanidine c | 10.0 | 2.0 |
| Plant extracts | Effect on vesperlysines-like AGE formation (IC50, mg/mL) | Effect on pentosidine-like AGE formation (IC50, mg/mL) |
| Thyme aqueous extract | 0.9 | 0.6 |
| Thyme EtOH extract | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Eucalyptus aqueous extract | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Eucalyptus EtOH extract | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Chamomille aqueous extract | >1.0 | 0.6 |
| Chamomille EtOH extract | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Rosemary aqueous extract | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Rosemary EtOH extract | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| Tea aqueous extract | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Tea EtOH extract | 0.2 | >1.0 |
| Linden aqueous extract | >1.0 | >1.0 |
| Linden EtOH extract | >1.0 | >1.0 |
| St John’s wort aqueous extract | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| St John’s wort EtOH extract | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Melissa aqueous extract | >1.0 | 0.3 |
| Melissa EtOH extract | >1.0 | 0.8 |
| Quinquina aqueous extract | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Quinquina EtOH extract | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Mint aqueous extract | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Mint EtOH extract | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Sophora aqueous extract | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| Sophora EtOH extract | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Aminoguanidine c | >1.0 | 0.2 |
| Quercetin c | 0.06 | 0.06 |
2.4. Screening of the Antivesperlysines-Like and Antipentosidine-Like AGE Activity of Plant Extracts and Validation of Hits via Dose-Effect Curves

3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Plant Extractions Using Pressurized Solvents
3.3. Automated Anti-AGE Screening
3.4. Determination of Extract or Product Concentration Inhibiting 50% AGE Formation (IC50) Using Liquid Handling Facilities
3.5. Assay Quality Determination Using the Z'-Factor
3.6. Assay Quality Determination Using SSMD
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Maillard, L.C. Action des acides aminés sur les sucres; formation des mélanoïdes par voie méthodique. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1912, 154, 66–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wolffenbuttel, B.H.; Giordano, D.; Founds, H.W.; Bucala, R. Long-term assessment of glucose control by haemoglobin-AGE measurement. Lancet 1996, 347, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.P.; Beyaz, A. Inhibitors of the Maillard reaction and AGE breakers as therapeutics for multiple diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyroux, J.; Sternberg, M. Advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs): Pharmacological inhibition in diabetes. Pathol. Biol. 2006, 54, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Diabetes. Available online: http://www.who.int/topics/diabetes_mellitus/en/ (accessed 20 June 2012).
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Barden, A.; Mori, T.; Beilin, L. Advanced glycation end-products: A review. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.M.; Yee, L.T.L.; Thallas, V.; Lassila, M.; Candido, R.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; Thomas, M.C.; Burns, W.C.; Deemer, E.K.; Thorpe, S.M.; Cooper, M.E.; et al. Advanced glycation end product interventions reduce diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Doi, T.; Kato, I.; Shinohara, H.; Sakurai, S.; Yonekura, H.; Watanabe, T.; Myint, K.M.; Harashima, A.I.; Takeuchi, M.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products is a promising target of diabetic nephropathy. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.W. The maillard reaction in eye diseases. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 582–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiabetesCare. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2012. Diabetes Care 2012, 35 (Suppl. 1), S11–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Roan, H.Y.; Lii, C.K.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, T.S. Relationship between antioxidant and antiglycation ability of saponins, polyphenols, and polysaccharides in Chinese herbal medicines used to treat diabetes. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2322–2331. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.S.; Beaulieu, L.-P.; Fraser, M.-H.; McIntyre, K.L.; Owen, P.L.; Martineau, L.C.; Cuerrier, A.; Johns, T.; Haddad, P.S.; Bennett, S.A.L.; et al. Inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation by medicinal plant extracts correlates with phenolic metabolites and antioxidant activity. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, M. Naturally occurring inhibitors against the formation of advanced glycation end-products. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.; Yamagishi, S.-I. Possible involvement of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGroot, J. The AGE of the matrix: Chemistry, consequence and cure. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, M.A.; Colombatto, S. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs): Involvement in aging and in neurodegenerative diseases. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifah, R.G.; Baynes, J.W.; Hudson, B.G. Amadorins: Novel post-Amadori inhibitors of advanced glycation reactions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, V.M. Intervention against the Maillard reaction in vivo. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 419, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; van der Heijden, R.; Spruit, S.; Hankermeier, T.; Chan, K.; van der Greef, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, M. Quality and safety of Chinese herbal medicines guided by a systems biology perspective. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 Years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J.; Day, C. Metformin: Its botanical background. Pract. Diabetes Int. 2004, 21, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.A.; Borges, C.M.; Florêncio, M.H. Towards the control and inhibition of glycation—the role of the guanidine reaction center with aldehydic and diketonic dicarbonyls. A mass spectrometry study. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 41, 1346–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Vinson, J.A.; Howard, T.B. Inhibition of protein glycation and advanced glycation end products by ascorbic acid and other vitamins and nutrients. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1996, 7, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Huang, S.-M.; Lin, J.-A.; Yen, G.-C. Inhibition of advanced glycation endproduct formation by foodstuffs. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, N.; Aradate, T.; Sasaki, C.; Kojima, H.; Ohara, M.; Hasegawa, J.; Ubukata, M. Screening system for the Maillard reaction inhibitor from natural product extracts. J. Health Sci. 2002, 48, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, S.; Yerneni, K.K.; Scott, S.; Gonzales, N.; Lalezari, I. Novel inhibitors of advanced glycation endproducts (Part II). Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 2000, 3, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, R.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mera, K.; Yamagata, K.; Sakashita, N.; Takeya, M. Immunochemical detection of Nε-(carboxyethyl)lysine using a specific antibod. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 332, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kiyota, N.; Tsurushima, K.; Takeya, M.; Nohara, T.; Nagai, R.; Ikeda, T. Astragalosides isolated from the root of Astragalus Radix inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7666–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Jairajpuri, D.S.; Saleemuddin, M. A procedure for the rapid screening of Maillard reaction inhibitors. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 2008, 70, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Nakazawa, Y.; Ienaga, K. Acid-stable fluorescent advanced glycation end products: Vesperlysines A, B, and C are formed as crosslinked products in the Maillard reaction between lysine or proteins with glucose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Sell, D.R.; Monnier, V.M. Structure elucidation of a senescence cross-link from human extracellular matrix. Implication of pentoses in the aging process. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 21597–21602. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H.; Iwaki, S.; Aida, K.; Hayase, F. Formation and determination of α-dicarbonyls and an AGE cross-link, pyrropyridine in glycated proteins and in vivo. Int. Congr. Ser. 2002, 1245, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishth, D. Advanced glycation end-products and bone fractures. BoneKEy Osteovision 2009, 6, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongor, S.; Ulrich, P.C.; Bencsath, F.A.; Cerami, A. Aging of proteins: Isolation and identification of a fluorescent chromophore from the reaction of polypeptides with glucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipanova, I.N.; Glomb, M.A.; Nagaraj, R.H. Protein modification by methylglyoxal: Chemical nature and synthetic mechanism of a major fluorescent adduct. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 344, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbré, S.; Gatto, J.; Pelleray, A.; Coulon, L.; Séraphin, D.; Richomme, P. Automating a 96-well microtiter plate assay for identification of AGEs inhibitors or inducers: Application to the screening of a small natural compounds library. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beisswenger, P.J.; Howell, S.; Mackenzie, T.; Corstjens, H.; Muizzuddin, N.; Matsui, M.S. Two fluorescent wavelengths, 440(ex)/520(em) nm and 370(ex)/440(em) nm, reflect advanced glycation and oxidation end products in Human skin without diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The nomenclature used in the manuscript does not refer to the structure of AGEs but rather to their fluorescent properties.
- 370 nm and 440 nm were most commonly used as excitation and emission wavelengths.
- Chompoo, J.; Upadhyay, A.; Kishimoto, W.; Makise, T.; Tawata, S. Advanced glycation end products inhibitors from Alpinia zerumbet rhizomes. Food Chemistry 2011, 129, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, U.D.; Ling, L.T.; Manaharan, T.; Appleton, D. Rapid isolation of geraniin from Nephelium lappaceum rind waste and its anti-hyperglycemic activity. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasathien, L.; Pengsuparp, T.; Suttisri, R.; Ueda, H.; Moriyasu, M.; Kawanishi, K. Inhibitors of aldose reductase and advanced glycation end-products formation from the leaves of Stelechocarpus cauliflorus R.E. Fr. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Jin, S.E.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.S. Antidiabetic complications and anti-alzheimer activities of sophoflavescenol, a prenylated flavonol from Sophora flavescens, and its structure activity relationship. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 709–715. [Google Scholar]
- Ardestani, A.; Yazdanparast, R. Inhibitory effects of ethyl acetate extract of Teucrium polium on in vitro protein glycoxidation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Chung, T.D. Y.; Oldenburg, K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D. Novel analytic criteria and effective plate designs for quality control in genome-scale RNAi screens. J. Biomol. Screen. 2008, 13, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D. A pair of new statistical parameters for quality control in RNA interference high-throughput screening assays. Genomics 2007, 89, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, V.M.; Bautista, O.; Kenny, D.; Sell, D.R.; Fogarty, J.; Dahms, W.; Cleary, P.A.; Lachin, J.; Genuth, S. Skin collagen glycation, glycoxidation, and crosslinking are lower in subjects with long-term intensive versus conventional therapy of type 1 diabetes—Relevance of glycated collagen products versus HbA(1c) as markers of diabetic complications. Diabetes 1999, 48, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetti, A.; Protti, S.; Lapouge, C.; Cornard, J.-P. Protic equilibria as the key factor of quercetin emission in solution. Relevance to biochemical and analytical studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 6858–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bark, K.-M.; Yeom, J.-E.; Yang, J.-I.; Yang, I.-J.; Park, C.-H.; Park, H.-R. Spectroscopic studies on the oxidation of catechin in aqueous solution. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellow, S.; Latouche, G.; Brown, S.C.; Poutaraud, A.; Cerovic, Z.G. In vivo localization at the cellular level of stilbene fluorescence induced by Plasmopara viticola in grapevine leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.S.; Freile, M.L.; Gutierrez, M.I. Solvent effect on the UV/Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopic properties of berberine. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2009, 8, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkan, T. Fluorimetric analysis of alkaloids. Determination of serpentine, yohimbine, and boldine. Mikrochim. Acta 1976, 65, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.; Cartelat, A.; Alvarez-Fernandez, A.; Moya, I.; Cerovic, Z.G. Time-resolved spectral studies of blue-green fluorescence of artichoke (Cynara cardunculus L. var. ccolymus) leaves: Identification of chlorogenic acid as one of the major fluorophores and age-mediated changes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9668–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.J.; Haskell, T.G. The fluorescent oxidation products of dihydroxyphenylalanine and its esters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 55, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Sadakane, C.; Ishihara, K.; Yanagisawa, T.; Kimura, M.; Kamei, H. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay with fluorescence detection for the determination of cephaeline and emetine in human plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 757, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.W.; Koehler, W.R. pH effects on fluorescence of umbelliferone. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugland, R.P. Handbook of Fluorescent Probes and Research Products, 9th ed.; Molecular Probes: Eugene, OR, USA, 2002; p. 963. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, R.; Murray, D.B.; Metz, T.O.; Baynes, J.W. Chelation: A fundamental mechanism of action of AGE inhibitors, AGE breakers, and other inhibitors of diabetes complications. Diabetes 2012, 61, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmaplot Software, version 12.5, Systat Software GmbH: Erkrath, Germany, 2011.
- Palmer, M.H.; Walker, I.C.; Guest, M.F.; Siggel, M.R. F. The electronic states of the azines. VII. 1,2,4-triazine, studied by photon absorption, near-threshold electron energy loss spectroscopy and ab initio multi-reference configuration interaction calculations. Chem. Phys. 1995, 201, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, A.I.; Elworthy, T.R. Chiral formamidines—The total asymmetric-synthesis of (−)-8-azaestrone and related (−)-8-aza-12-oxo-17-desoxoestrone. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneton, J. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Medicinal Plants, 2nd ed.; Editions Tec & Doc: Paris, France, 2008; p. 1088. [Google Scholar]
- Ferchichi, L.; Derbré, S.; Mahmood, K.; Touré, K.; Guilet, D.; Litaudon, M.; Awang, K.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Le Ray, A.M.; Richomme, P. Bioguided fractionation and isolation of natural inhibitors of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) from Calophyllum flavoramulum. Phytochemistry 2012, 78, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusak, G.; Komes, D.; Likic, S.; Horzic, D.; Kovac, M. Phenolic content and antioxidative capacity of green and white tea extracts depending on extraction conditions and the solvent used. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichtl, M.; Anton, R. Plantes Thérapeutiques, 2nd ed.; Editions Tec & Doc: Paris, France, 2003; p. 689. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, S.; Landreau, A.; Nguyen, V.H.; Derbré, S.; Grellier, P.; Le Pape, P.; Pagniez, F.; Litaudon, M.; Richomme, P. Preparative isolation, fast centrifugal partition chromatography purification and biological activity of cajaflavanone from Derris ferruginea Stems. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Séro, L.; Sanguinet, L.; Blanchard, P.; Dang, B.T.; Morel, S.; Richomme, P.; Séraphin, D.; Derbré, S. Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts. Molecules 2013, 18, 14320-14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181114320
Séro L, Sanguinet L, Blanchard P, Dang BT, Morel S, Richomme P, Séraphin D, Derbré S. Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts. Molecules. 2013; 18(11):14320-14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181114320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSéro, Luc, Lionel Sanguinet, Patricia Blanchard, Bach Tai Dang, Sylvie Morel, Pascal Richomme, Denis Séraphin, and Séverine Derbré. 2013. "Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts" Molecules 18, no. 11: 14320-14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181114320
APA StyleSéro, L., Sanguinet, L., Blanchard, P., Dang, B. T., Morel, S., Richomme, P., Séraphin, D., & Derbré, S. (2013). Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts. Molecules, 18(11), 14320-14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181114320