Targeted Lipid Analysis of Haemolytic Mycelial Extracts of Aspergillus niger
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
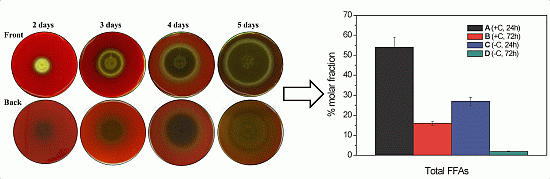
2.1. Haemolytic Activity of Mycelial Ethanolic Extracts of Aspergillus niger N402


2.2. Lipid Profile of Ethanolic Extracts from Aspergillus niger N402 Using LC–ESI-MS/MS
| Extracted-Ion Chromatogram (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | FFA |
|---|---|---|
| 277.3; 577.5 | 8.1 | 18:3 |
| 279.3; 581.5 | 10.0 | 18:2 |
| 255.3; 533.5 | 11.3 | 16:0 |
| 281.3; 585.5 | 12.7 | 18:1 |
| 283.3; 589.5 | 16.0 | 18:0 |
| Extracted-Ion Chromatogram (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| 518.3; 184.1 | 8.1 | 18:3 |
| 520.3; 184.1 | 10.3 | 18:2 |
| 496.3; 184.1 | 11.5 | 16:0 |
| 522.3; 184.1 | 13.2 | 18:1 |
| Extracted-Ion Chromatogram (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | Composition | Acyl Chains |
|---|---|---|---|
| 613.5; 635.5; 595.5 | 35.4 | 36:6 | 18:3/18:3 |
| 615.5; 637.5; 597.5 | 37.0 | 36:5 | 18:2/18:3 |
| 591.5; 613.5; 573.5 | 37.8 | 34:3 | 18:3/16:0 |
| 617.5; 639.5; 599.5 | 38.4 | 36:4 | 18:2/18:2 |
| 593.5; 615.5; 575.5 | 39.2 | 34:2 | 18:2/16:0 |
| 619.5; 641.5; 601.5 | 39.8 | 36:3 | 18:2/18:1 |
| 595.5; 617.5; 577.5 | 40.6 | 34:1 | 18:1/16:0 |
| 621.5; 643.5; 603.5 | 41.2 | 36:2 | 18:1/18:1 |
| 623.5; 645.5; 605.5 | 42.4 | 36:1 | 18:1/18:0 |
2.2.1. Free Fatty Acid Determination






2.2.2. Lysophosphatidylcholine Composition
2.2.3. Diacylglycerol Composition
2.2.4. Glycerophospholipid Composition
2.3. Haemolytic Activity of Commercial Free Fatty Acids and Lysophosphatidylcholine Species Associated with Ethanolic Extracts of Aspergillus niger N402

2.4. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fungal Strain and Growth Conditions
3.3. Preparation of Ethanolic Extracts
3.4. Haemolytic Assay
3.5. LC–ESI-MS/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, W.J. An Overview of the genus Aspergillus. In Aspergillus: Molecular Biology and Genomics; Machida, M., Gomi, K., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2010; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; van Dijck, P.W.M. On the safety of Aspergillus niger—a review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, W.J.; Perfect, J.R.; Schell, W.A.; Walsh, T.J.; Benjamin, D.K. In vitro analyses, animal models, and 60 clinical cases of invasive Aspergillus terreus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, D.W. Trends in the epidemiology of invasive fungal infections. Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi 2007, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Manavathu, E.K.; Chandrasekar, P.H. Aspergillus flavus: An emerging non-fumigatus Aspergillus species of significance. Mycoses 2009, 52, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palencia, E.R.; Hinton, D.M.; Bacon, C.W. The black Aspergillus species of maize and peanuts and their potential for mycotoxin production. Toxins 2010, 2, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, G.; Susca, A.; Cozzi, G.; Ehrlich, K.; Varga, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Meijer, M.; Noonim, P.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; Samson, R.A. Biodiversity of Aspergillus species in some important agricultural products. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 59, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, M.L.; Bragulat, M.R.; Castellá, G.; Cabañes, F.J. Ochratoxin A production by strains of Aspergillus niger var. niger. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2650–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Smedsgaard, J.; Samson, R.A.; Larsen, T.O.; Thrane, U. Fumonisin B2 production by Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9727–9732. [Google Scholar]
- Kamei, K.; Watanabe, A. Aspergillus mycotoxins and their effect on the host. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. 1), S95–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rementeria, A.; López-Molina, N.; Ludwig, A.; Vivanco, A.B.; Bikandi, J.; Pontón, J.; Garaizar, J. Genes and molecules involved in Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2005, 22, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, O.; Shimada, H.; Yokota, K. Purification and characteristics of hemolytic toxin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1975, 28, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ebina, K.; Sakagami, H.; Yokota, K.; Kondo, H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding Asp-hemolysin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 1994, 1219, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, S.; Lah, L.; Sepčić, K. Aegerolysins: Structure, function, and putative biological role. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 694–706. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, A.P.; Green, B.J.; Beezhold, D.H. Fungal hemolysins. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, K.; Butala, M.; Viero, G.; Dalla Serra, M.; Sepčić, K.; Maček, P. Fungal MACPF-like proteins and aegerolysins: Bi-component pore-forming proteins? Subcell. Biochem. 2014, 80, 271–291. [Google Scholar]
- Braaksma, M.; Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Punt, P.J.; Schaap, P.J. An inventory of the Aspergillus niger secretome by combining in silico predictions with shotgun proteomics data. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botić, T.; Kunčič, M.K.; Sepčić, K.; Knez, Z.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Salt induces biosynthesis of hemolytically active compounds in the xerotolerant food-borne fungus Wallemia sebi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudyakova, Y.V.; Pivkin, M.V.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Svetashev, V.I. Fungi in sediments of the sea of Japan and their biologically active metabolites. Microbiology 2000, 69, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Defant, A.; Mesarič, T.; Potočnik, F.; Batista, U.; Guella, G.; Turk, T.; Sepčić, K. Fatty acid composition of common barbel (Barbus barbus) roe and evaluation of its haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C.H.; Kock, J.L.F.; Thibane, V.S. Antifungal free fatty acids: A review. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Current Research and Technological Advances; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, S.A.; Kolomiets, M.V. The lipid language of plant-fungal interactions. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.M.; Gardner, H.W.; Keller, N.P. Genetic connection between fatty acid metabolism and sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25766–25774. [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist, G.; Andersson, B.; Andersson, K.; Brondz, I. Analysis of fatty acids.A new method for characterization of moulds. J. Microbiol. Methods 1992, 16, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.E.; Santana, D.M.N.; Gatti, M.J.; Direito, G.M.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Rosa, C.A.R. Characterization of Aspergillus species based on fatty acid profiles. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Koulman, A.; van Rijssel, M.; Lützen, A.; de Boer, M.K.; Tyl, M.R.; Liebezeit, G. Chemical characterisation of three haemolytic compounds from the microalgal species Fibrocapsa japonica ( Raphidophyceae ). Toxicon 2004, 43, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; García-de la Parra, L.M.; Alonso-Rodríguez, R.; Morquecho, L. Hemolytic activity and fatty acids composition in the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides isolated from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, T.; Jernejc, K.; Cimerman, A. Sterols and fatty acids of different Aspergillus species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 149, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthofer, R.; Kubicek, C.P.; Röhr, M. Lipid levels and manganese deficiency in citric acid producing strains of Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1979, 5, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixner, O.; Mischak, H. Effect of manganese deficiency on plasma-membrane lipid composition and glucose uptake in Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1985, 26, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernejc, K.; Vendramin, M.; Cimerman, A. Lipid composition of Aspergillus niger in citric acid accumulating and nonaccumulating conditions. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1989, 60, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernejc, K. Lipid composition of a citric acid producing and a pectolytic enzyme excreting Aspergillus niger strains. Acta Chim. Slov. 2000, 47, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nemec, T.; Jernejc, K. Influence of Tween 80 on lipid metabolism of an Aspergillus niger strain. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2002, 101, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eras, J.; Oró, R.; Torres, M.; Canela, R. Direct quantitation of fatty acids present in bacteria and fungi: Stability of the cyclopropane ring to chlorotrimethylsilane. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4923–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, E.V; Baranova, M.V; Kozlov, V.P.; Tereshina, V.M. Peculiarities of exogenous dormancy of Aspergillus niger conidia. Mikrobiology 2001, 70, 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Morozova, E.V.; Kozlov, V.P.; Tereshina, V.M.; Memorskaya, A.S.; Feofilova, E.P. Changes in lipid composition and carbohydrate composition of Aspergillus niger conidia during germination. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2002, 38, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Handa, T.; Miyajima, K.; Mikura, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Toguchi, H. Quantitative analysis of hemolytic action of lysophosphatidylcholines in vitro: Effect of acyl chain structure. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 4253–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, B.M.; Jørgensen, T.R.; Akeroyd, M.; Meyer, V.; Ram, A.F.J. The carbon starvation response of Aspergillus niger during submerged cultivation: Insights from the transcriptome and secretome. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 380. [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi, M.; Miskei, M.; Karányi, Z.; Lenkey, B.; Pócsi, I.; Emri, T. Transcriptome changes initiated by carbon starvation in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 2013, 159, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suutari, M. Effect of growth temperature on lipid fatty acids of four fungi (Aspergillus niger, Neurospora crassa, Penicillium chrysogenum, and Trichoderma reesei). Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 164, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshina, V.M.; Memorskay, A.S.; Kotlova, E.R.; Feofilov, E.P. Membrane lipid and cytosol carbohydrate composition in Aspergillus niger under heat shock. Microbiology 2010, 79, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Lipid production by a cellulolytic strain of Aspergillus niger. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 12, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, C.J.; Debets, A.J.; Swart, K.; Huybers, A.; Kobus, G.; Slakhorst, S.M. Genetic analysis and the construction of master strains for assignment of genes to six linkage groups in Aspergillus niger. Curr. Genet. 1988, 14, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Punt, P.J.; van den Hondel, C.A. Transformation of filamentous fungi based on hygromycin B and phleomycin resistance markers. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 216, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, G.; Pederzolli, C.; Maček, P.; Menestrina, G. Pore formation by the sea anemone cytolysin equinatoxin II in red blood cells and model lipid membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1993, 131, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novak, M.; Sepčić, K.; Kraševec, N.; Križaj, I.; Maček, P.; Anderluh, G.; Guella, G.; Mancini, I. Targeted Lipid Analysis of Haemolytic Mycelial Extracts of Aspergillus niger. Molecules 2014, 19, 9051-9069. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19079051
Novak M, Sepčić K, Kraševec N, Križaj I, Maček P, Anderluh G, Guella G, Mancini I. Targeted Lipid Analysis of Haemolytic Mycelial Extracts of Aspergillus niger. Molecules. 2014; 19(7):9051-9069. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19079051
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovak, Maruša, Kristina Sepčić, Nada Kraševec, Igor Križaj, Peter Maček, Gregor Anderluh, Graziano Guella, and Ines Mancini. 2014. "Targeted Lipid Analysis of Haemolytic Mycelial Extracts of Aspergillus niger" Molecules 19, no. 7: 9051-9069. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19079051
APA StyleNovak, M., Sepčić, K., Kraševec, N., Križaj, I., Maček, P., Anderluh, G., Guella, G., & Mancini, I. (2014). Targeted Lipid Analysis of Haemolytic Mycelial Extracts of Aspergillus niger. Molecules, 19(7), 9051-9069. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19079051