Hypotensive Effects and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides of Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) Auto-Digested Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Reishi Proteases’ Activities

2.2. ACE Inhibition of Auto-Digested Reishi Extract

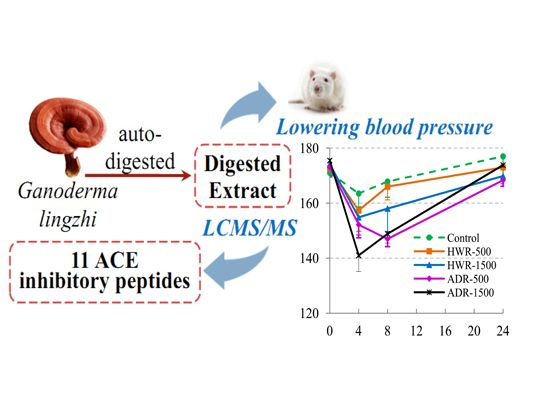
2.3. Hypotensive Effects of Reishi and Auto-Digested Reishi Extract on Rats

2.4. Fractionation and Identification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides

| Fractions | IC50 Values (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipeptides | Tripeptides | |||
| ADR5-1 | undetectable | |||
| ADR5-2 | Ser-Ile | >200 | undetectable | |
| Ala-Tyr | 162.7 | |||
| Ser-Tyr | 94.7 | |||
| ADR5-3 | undetectable | |||
| ADR5-4 | Ser-Leu | >200 | Asn-Ser-Ile | 342.1 |
| Lys-Val-Pro | >500 | |||
| ADR5-5 | Ala-Leu | >200 | undetectable | |
| Thr-Leu | >200 | |||
| ADR5-6 | Ile-Arg | 73.7 | Ile-Pro-Thr | 73.1 |
| ADR5-7 | undetectable | Gly-Pro-Leu | >500 | |
| Positive control | Ile-Pro-Pro | < 0.5 | ||
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Reishi’s Protease Extract and Its Proteolytic Activities
3.3. Preparation of Reishi and Auto-Digested Reishi’s Extracts
3.4. ACE Inhibition Assay
3.5. Hypotensive Effects of HWR and ADR Extract on SHR Rats
3.6. Ultrafiltration and RP-HPLC for Fractionation
3.7. Identification of Peptides by LC-MS/MS
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasser, S.P. Reishi or Ling Zhi (Ganoderma lucidum). Encycloped. Diet. Suppl. 2005, 603–622. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, S.H.; Dai, Y.C. Species clarification of the prize medicinal Ganoderma mushroom “Lingzhi”. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R.R.M. Ganoderma—A therapeutic fungal biofactory. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1985–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, K.; Yamashita, A.; Yamaoka, K.; Watanabe, J.; Tanaka, S. Isolation and Characterization of a New Immunomodulatory Protein, Ling Zhi-8 (LZ-8), from Ganoderma lucidum. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 1, 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. Ganodermin, an antifungal protein from fruiting bodies of the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Peptides 2006, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, H.; Xie, B.J. Novel antioxidant peptides from fermented mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6646–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S. Hepatoprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum peptides against d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Reishi, Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma tsugae: Bioactive substances and medicinal effects. Food Rev. Intern. 1995, 11, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Lovibond, K.; Caulfield, M.; McCormack, T.; Williams, B. Management of hypertension: Summary of nice guidance. BMJ 2011, 343, d4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arihara, K.; Nakashima, Y.; Mukai, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Itoh, M. Peptide inhibitors for angiotensin I-converting enzyme from enzymatic hydrolysates of porcine skeletal muscle proteins. Meat Sci. 2001, 57, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Tatsumi, E.; Ding, C.H.; Li, L.T. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in douchi, a Chinese traditional fermented soybean product. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, M.; Baba, T.; Ikemoto, N.; Katayama, M.; Morimoto, T.; Matsumura, S. Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from boneless chicken leg meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7432–7436. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Cho, H.; Yang, H.; Ra, K.; Suh, H. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from Grifola frondosa. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyoung Lee, D.; Ho Kim, J.; Sik Park, J.; Jun Choi, Y.; Soo Lee, J. Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the edible mushroom Tricholoma giganteum. Peptides 2004, 25, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Yu, H. Production and characterization of antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from Pholiota adiposa. J. Microbiol. 2006, 16, 757–763. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.H.; Jeong, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Ju, Y.C.; Lee, J.S. Characterisation of a new antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Pleurotus cornucopiae. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.; Casey, F.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Shields, D.; Mooney, C. Predictive modelling of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory dipeptides. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabotic, J.; Trcek, T.; Popovic, T.; Brzin, J. Basidiomycetes harbour a hidden treasure of proteolytic diversity. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjavec, J.; Kos, J.; Ravnikar, M.; Dreo, T.; Sabotič, J. Proteins of higher fungi—From forest to application. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Sa, Y.S. Fibrinolytic and Antithrombotic Protease from Ganoderma lucidum. Mycologia 2000, 92, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, S.; Palani, P.; Nishanthi, R.; Srimathi, S.; Kaviyarasan, V. Purification of an Intracellular Fibrinolytic Protease from Ganoderma lucidum Vk12 and its Susceptibility to Different Enzyme Inhibitors. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Ukawa, Y.; Andou, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Kokean, Y.; Nishii, T.; Hiasmatsu, M. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity and Antitumor Activity of Hatakeshimeji (Lyophyllum decastes Sing.). Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2001, 48, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, H.; Aoyagi, Y. Inhibition of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme by Mushroom. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2006, 53, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S.; Aminudin, N. Proteomic analysis of antihypertensive proteins in edible mushrooms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12341–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, Y.; Kimura, S.; Tamura, T. Dietary effect of Ganoderma lucidum mushroom on blood pressure and lipid levels in spontaneously hypertensive rats(SHR). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 1988, 34, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmatsuse, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Hayashi, K.; Shimogaichi, S.; Fukibara, I.; Ishikawa, H.; Tamura, T. Studies on Ganoderma lucidum. I. Efficacy against Hypertension and Side Effects. Yakugaku Yasshi 1985, 105, 942–947. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Stafford, R.S. Screening, treatment, and control of hypertension in US private physician offices, 2003–2004. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Manuela Amorim, M.; Odila Pereira, J.; Estevez Pintado, M.; Moura, D.; Calhau, C.; Pinheiro, H. Bioactive Peptides—Are There More Antihypertensive Mechanisms Beyond ACE Inhibition? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4706–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakura, K. Studies on the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Components of Mannentake’s (Ganoderma lucidum) Water Extract. Doctoral Dissertation in Japanese, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, 7 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from an edible mushroom, Pleurotus cystidiosus O.K. Miller identified by LC-MS/MS. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S.; Aminudin, N. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (J.E. Lange) Imbach identified by LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Miralles, B.; Recio, I.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai Bang, T.; Suhara, H.; Doi, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Fukami, K.; Parajuli, G.P.; Katakura, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Watanabe, K.; Adhikari, M.K.; et al. Wild Mushrooms in Nepal: Some Potential Candidates as Antioxidant and ACE-Inhibition Sources. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) powder, HWR and ADR are stored in a low-temperature room (4 °C) in Laboratory of Systematic Forest and Forest Products Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, H.-B.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Ito, H.; Igami, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Kondo, R.; Shimizu, K. Hypotensive Effects and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides of Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) Auto-Digested Extract. Molecules 2014, 19, 13473-13485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913473
Tran H-B, Yamamoto A, Matsumoto S, Ito H, Igami K, Miyazaki T, Kondo R, Shimizu K. Hypotensive Effects and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides of Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) Auto-Digested Extract. Molecules. 2014; 19(9):13473-13485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913473
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Hai-Bang, Atsushi Yamamoto, Sayaka Matsumoto, Hisatomi Ito, Kentaro Igami, Toshitsugu Miyazaki, Ryuichiro Kondo, and Kuniyoshi Shimizu. 2014. "Hypotensive Effects and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides of Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) Auto-Digested Extract" Molecules 19, no. 9: 13473-13485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913473
APA StyleTran, H. -B., Yamamoto, A., Matsumoto, S., Ito, H., Igami, K., Miyazaki, T., Kondo, R., & Shimizu, K. (2014). Hypotensive Effects and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides of Reishi (Ganoderma lingzhi) Auto-Digested Extract. Molecules, 19(9), 13473-13485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913473