Sorcin, a Calcium Binding Protein Involved in the Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Sorcin and the Other Penta-EF Hand Proteins

2. Sorcin Gene and mRNA Sequence
3. Sorcin Structure and Mechanism of Activation

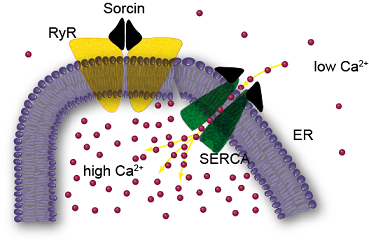
4. Sorcin Localization, Cell Cycle, and Function in the Cell

5. Sorcin and Cancer
6. Sorcin and the Heart
7. Sorcin and the Brain
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawasaki, H.; Kretsinger, R.H. Calcium-binding proteins 1: EF-hands. Protein Profile 1995, 2, 297–490. [Google Scholar]
- Maki, M.; Kitaura, Y.; Satoh, H.; Ohkouchi, S.; Shibata, H. Structures, functions and molecular evolution of the penta-EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1600, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Dwyer, M.D.; Swenson, L.; Parker, M.H.; Botfield, M.C. Crystal structure of calcium-free human sorcin: A member of the penta-EF-hand protein family. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, A.; Johnson, K.A.; Nastopoulos, V.; Verzili, D.; Zamparelli, C.; Colotti, G.; Tsernoglou, D.; Chiancone, E. The crystal structure of the sorcin calcium binding domain provides a model of Ca2+-dependent processes in the full-length protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 317, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Tarabykina, S.; la Cour, J.M.; Lollike, K.; Berchtold, M.W. The PEF family proteins sorcin and grancalcin interact in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2003, 545, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Ilari, A.; Verzili, D.; Zamparelli, C.; Antaramian, A.; Rueda, A.; Valdivia, H.H.; Chiancone, E.; Colotti, G. Molecular basis for the impaired function of the natural F112L sorcin mutant: X-ray crystal structure, calcium affinity, and interaction with annexin VII and the ryanodine receptor. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, M.; Colotti, G.; Zamparelli, C.; Verzili, D.; Ilari, A.; Chiancone, E. Information transfer in the penta-EF-hand protein sorcin does not operate via the canonical structural/functional pairing. A study with site-specific mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24921–24928. [Google Scholar]
- Colotti, G.; Zamparelli, C.; Verzili, D.; Mella, M.; Loughrey, C.M.; Smith, G.L.; Chiancone, E. The W105G and W99G sorcin mutants demonstrate the role of the D helix in the Ca2+-dependent interaction with annexin VII and the cardiac ryanodine receptor. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 12519–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalioti, V.S.; Ilari, A.; O’Connell, D.J.; Poser, E.; Sandoval, I.V.; Colotti, G. Sorcin links calcium signaling to vesicle trafficking, regulates Polo-like kinase 1 and is necessary for mitosis. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landriscina, M.; Laudiero, G.; Maddalena, F.; Amoroso, M.R.; Piscazzi, A.; Cozzolino, F.; Monti, M.; Garbi, C.; Fersini, A.; Pucci, P.; et al. Mitochondrial chaperone Trap1 and the calcium binding protein Sorcin interact and protect cells against apoptosis induced by antiblastic agents. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6577–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparelli, C.; Ilari, A.; Verzili, D.; Giangiacomo, L.; Colotti, G.; Pascarella, S.; Chiancone, E. Structure-function relationships in sorcin, a member of the penta EF-hand family. Interaction of sorcin fragments with the ryanodine receptor and an Escherichia coli model system. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, M.B.; Pickel, V.M.; Sheu, S.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Scotto, K.W.; Fishman, G.I. Association of sorcin with the cardiac ryanodine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26411–26418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokuta, A.J.; Meyers, M.B.; Sander, P.R.; Fishman, G.I.; Valdivia, H.H. Modulation of cardiac ryanodine receptors by sorcin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25333–25338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, T.; Miller, S.L.; Loughrey, C.M.; Kania, A.; Burow, A.; Kettlewell, S.; Teucher, N.; Wagner, S.; Kogler, H.; Meyers, M.B.; et al. Effects of adenovirus-mediated sorcin overexpression on excitation-contraction coupling in isolated rabbit cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Hisamatsu, Y.; Ohkusa, T.; Inoue, N.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Matsuzaki, M. Sorcin interacts with sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and modulates excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2005, 100, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparelli, C.; Macquaide, N.; Colotti, G.; Verzili, D.; Seidler, T.; Smith, G.L.; Chiancone, E. Activation of the cardiac Na+–Ca2+ exchanger by sorcin via the interaction of the respective Ca2+-binding domains. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.; McDonough, P.M.; Scott, B.T.; Suarez-Ramirez, A.; Wang, H.; Fricovsky, E.S.; Dillmann, W.H. Sorcin modulates mitochondrial Ca2+ handling and reduces apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, F.; Sisinni, L.; Lettini, G.; Condelli, V.; Matassa, D.S.; Piscazzi, A.; Amoroso, M.R.; la Torre, G.; Esposito, F.; Landriscina, M. Resistance to paclitxel in breast carcinoma cells requires a quality control of mitochondrial antiapoptotic proteins by TRAP1. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, F.; Laudiero, G.; Piscazzi, A.; Secondo, A.; Scorziello, A.; Lombardi, V.; Matassa, D.S.; Fersini, A.; Neri, V.; Esposito, F.; et al. Sorcin induces a drug-resistant phenotype in human colorectal cancer by modulating Ca2+ homeostasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7659–7669. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, D.F.; Beattie, J.; Paul, A.; Currie, S. Interaction of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIδC with sorcin indirectly modulates ryanodine receptor function in cardiac myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 43, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzer, U.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Hunger, U.; Borken, C.; Prohaska, R. Ca++-dependent vesicle release from erythrocytes involves stomatin-specific lipid rafts, synexin (annexin VII), and sorcin. Blood 2002, 99, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, S.I.; van Balkom, B.W.; Aalberts, M.; Heck, A.J.; Wauben, M.; Stoorvogel, W. MHC class II-associated proteins in B-cell exosomes and potential functional implications for exosome biogenesis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Chen, T.S.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: A novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen. Med. 2011, 6, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, P.A.; Pisitkun, T.; Hoffert, J.D.; Tchapyjnikov, D.; Star, R.A.; Kleta, R.; Wang, N.S.; Knepper, M.A. Large-scale proteomics and phosphoproteomics of urinary exosomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordeen, N.A.; Meur, G.; Rutter, G.A.; Leclerc, I. Glucose-induced nuclear shuttling of ChREBP is mediated by sorcin and Ca2+ ions in pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes 2012, 61, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bliek, A.M.; Meyers, M.B.; Biedler, J.L.; Hes, E.; Borst, P. A 22-kd protein (sorcin/V19) encoded by an amplified gene in multidrug-resistant cells, is homologous to the calcium-binding light chain of calpain. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Bliek, A.M.; Baas, F.; van der Velde-Koerts, T.; Biedler, J.L.; Meyers, M.B.; Ozols, R.F.; Hamilton, T.C.; Joenje, H.; Borst, P. Genes amplified and overexpressed in human multidrug-resistant cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 5927–5932. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Su, T.; Leng, A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Yan, L.; Gu, H.; Zhang, G. Upregulation of soluble resistance-related calcium-binding protein (sorcin) in gastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padar, S.; van Breemen, C.; Thomas, D.W.; Uchizono, J.A.; Livesey, J.C.; Rahimian, R. Differential regulation of calcium homeostasis in adenocarcinoma cell line A549 and its Taxol-resistant subclone. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, D. Overexpression of sorcin in multidrug resistant human leukemia cells and its role in regulating cell apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiao, W. Comparative proteomic profiling identified sorcin being associated with gemcitabine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Xue, Y.; Han, M.; Yang, C. Expression of sorcin predicts poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2003, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, N.; Nakao, R.; Kondo, R.; Nishitsuji, M.; Saito, Y.; Kuga, T.; Hatayama, T.; Nakayama, Y. Increased expression of sorcin is associated with multidrug resistance in leukemia cells via up-regulation of MDR1 expression through cAMP response element-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 448, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Chen, Z.C.; Zhang, G.Y.; Yi, H.; Xiao, Z.Q. A subcelluar proteomic investigation into vincristine-resistant gastric cancer cell line. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 104, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Qi, J.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, D. Sorcin, an important gene associated with multidrug-resistance in human leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Okochi, E.; Oh-hara, T.; Tsuruo, T. Purification of the Mr 22,000 calcium-binding protein (sorcin) associated with multidrug resistance and its detection with monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zhang, G.; Hou, D.; Leng, A.; Xu, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, T. Overexpression of sorcin results in multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells with up-regulation of P-gp. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Yang, M.; Xiong, D. Inhibition of sorcin reverses multidrug resistance of K562/A02 cells and MCF-7/A02 cells via regulating apoptosis-related proteins. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Nakamura, T.; Okamura, N.; Komoto, C.; Markova, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Okumura, K.; Sakaeda, T. Knock-down of sorcin induces up-regulation of MDR1 in HeLa cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Feng, B.; Liu, G. Reversing effect of sorcin in the drug resistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, H.K.; Deng, H.B.; Choudhary, K.; Houser, S.R.; Simpkins, H. Overexpression of sorcin, a calcium-binding protein, induces a low level of paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian and breast cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Yan, C.; Fan, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yague, E.; Xiong, D. Sorcin silencing inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses breast cancer metastasis in vivo. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 143, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D.M.; Despa, S.; Bossuyt, J. Regulation of Ca2+ and Na+ in normal and failing cardiac myocytes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1080, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.R.; Colotti, G.; Chiancone, E.; Higuchi, Y.; Seidler, T.; Smith, G.L. Complex modulation of l-type Ca2+ current inactivation by sorcin in isolated rabbit cardiomyocytes. Pflugers Arch. 2009, 457, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.R.; Colotti, G.; Chiancone, E.; Smith, G.L.; Fearon, I.M. Sorcin modulates cardiac l-type Ca2+ current by functional interaction with the alpha1C subunit in rabbits. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, E.F.; Antaramian, A.; Rueda, A.; Gomez, A.M.; Valdivia, H.H. Sorcin inhibits calcium release and modulates excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34660–34666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, L.P.; Meyers, M.B.; Zhang, J.; Phoon, C.K.; Sobie, E.A.; Coetzee, W.A.; Fishman, G.I. Expression of a sorcin missense mutation in the heart modulates excitation-contraction coupling. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.F.; Bolck, B.; Ding, Z.; Krause, D.; Hattebuhr, N.; Malik, A.; Brixius, K.; Hajjar, R.J.; Schrader, J.; Schwinger, R.H. Overexpression of sorcin enhances cardiac contractility in vivo and in vitro. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2005, 38, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.; Belke, D.D.; Gloss, B.; Dieterle, T.; McDonough, P.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Brunton, L.L.; Dillmann, W.H. In vivo adenoviral transfer of sorcin reverses cardiac contractile abnormalities of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H68–H75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Kouno, J.; Adachi, K.; Takahashi, H.; Teramoto, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Sugisaki, Y.; Onda, M.; Tsunoda, T. Identification of histological markers for malignant glioma by genome-wide expression analysis: Dynein, alpha-PIX and sorcin. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 111, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, P.J.; Swagemakers, S.M.; Nagel, J.H.; Kouwenhoven, M.C.; Brouwer, E.; van der Spek, P.; Luider, T.M.; Kros, J.M.; van den Bent, M.J.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A. Gene expression profiles associated with treatment response in oligodendrogliomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11335–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shai, R.; Shi, T.; Kremen, T.J.; Horvath, S.; Liau, L.M.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Mischel, P.S.; Nelson, S.F. Gene expression profiling identifies molecular subtypes of gliomas. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4918–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hui, A.M.; Su, Q.; Vortmeyer, A.; Kotliarov, Y.; Pastorino, S.; Passaniti, A.; Menon, J.; Walling, J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, S.L.; Tamayo, P.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Sturla, L.M.; Angelo, M.; McLaughlin, M.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Black, P.M.; Lau, C.; et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature 2002, 415, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, D.; Checler, F.; Chami, M. Ryanodine receptors: Physiological function and deregulation in Alzheimer disease. Mol. Neurodegener 2014, 9, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Pack-Chung, E.; Meyers, M.B.; Pettingell, W.P.; Moir, R.D.; Brownawell, A.M.; Cheng, I.; Tanzi, R.E.; Kim, T.W. Presenilin 2 interacts with sorcin, a modulator of the ryanodine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14440–14445. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, W.S.; Boettcher, J.M.; Zhou, D.H.; Kloepper, K.D.; Hartman, K.L.; Ladror, D.T.; Qi, Z.; Rienstra, C.M.; George, J.M. Conformation-specific binding of alpha-synuclein to novel protein partners detected by phage display and NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34555–34567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Nelson, O.; Bezprozvanny, A.; Wang, Z.; Lee, S.F.; Hao, Y.H.; Serneels, L.; de Strooper, B.; Yu, G.; Bezprozvanny, I. Presenilins form ER Ca2+ leak channels, a function disrupted by familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked mutations. Cell 2006, 126, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Asahi, M.; Yamaguchi, O.; Hikoso, S.; Nakayama, H.; Kusakari, Y.; Kawai, M.; Hongo, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Kashiwase, K.; et al. Presenilin 2 regulates the systolic function of heart by modulating Ca2+ signaling. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2069–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Chang, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Tian, M.; Li, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Proteomics analysis of MPP+-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.J.; Heyny-von Haussen, R.; Mall, G.; Wolf, S. Proteome analysis of human substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Proteome Sci. 2008, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracy, K.N.; Clarke, C.L.; Meyers, M.B.; Pickel, V.M. N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 1 in the caudate-putamen nucleus: Ultrastructural localization and co-expression with sorcin, a 22,000 mol. wt calcium binding protein. Neuroscience 1999, 90, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Clemen, C.S.; Herr, C.; Hovelmeyer, N.; Noegel, A.A. The lack of annexin A7 affects functions of primary astrocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 291, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Colotti, G.; Poser, E.; Fiorillo, A.; Genovese, I.; Chiarini, V.; Ilari, A. Sorcin, a Calcium Binding Protein Involved in the Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 13976-13989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913976
Colotti G, Poser E, Fiorillo A, Genovese I, Chiarini V, Ilari A. Sorcin, a Calcium Binding Protein Involved in the Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2014; 19(9):13976-13989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913976
Chicago/Turabian StyleColotti, Gianni, Elena Poser, Annarita Fiorillo, Ilaria Genovese, Valerio Chiarini, and Andrea Ilari. 2014. "Sorcin, a Calcium Binding Protein Involved in the Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells" Molecules 19, no. 9: 13976-13989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913976
APA StyleColotti, G., Poser, E., Fiorillo, A., Genovese, I., Chiarini, V., & Ilari, A. (2014). Sorcin, a Calcium Binding Protein Involved in the Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells. Molecules, 19(9), 13976-13989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913976