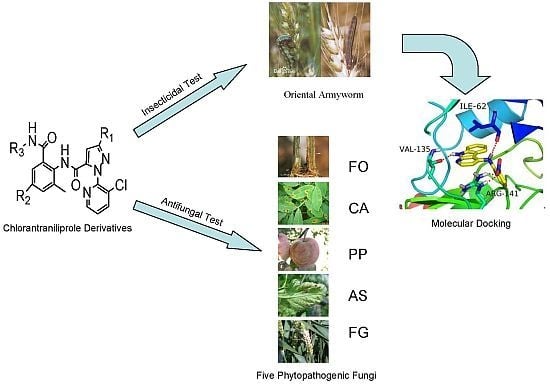
Synthesis, Larvicidal Activities and Antifungal Activities of Novel Chlorantraniliprole Derivatives and Their Target in the Ryanodine Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry

| Compd. No. | R1 | R2 | R3 | Compd. No. | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | Br | Cl |  | 2n | Br | Cl |  |
| 2b | Br | Cl |  | 2o | Br | CN |  |
| 2c | Br | Cl |  | 2p | Br | CN |  |
| 2d | Br | Cl |  | 2q | Br | CN |  |
| 2e | Br | Cl |  | 2r | Br | CN |  |
| 2f | Br | Cl |  | 2s | Br | CN |  |
| 2g | Br | Cl |  | 2t | Br | CN |  |
| 2h | Br | Cl |  | 2u | Br | Cl |  |
| 2i | Br | Cl |  | 2v | Br | Cl |  |
| 2j | Br | Cl |  | 2w | Br | Cl |  |
| 2k | Br | Cl |  | 2x | Br | Cl |  |
| 2l | Br | Cl |  | 2y | Br | Cl |  |
| 2m | Br | Cl |  |
2.2. Larvicidal Activities and Structure-Activity Relationships (SARs)
| Compd. No. | Insecticidal Activities (%) at Different Concentrations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations (mg/L) | ||||||
| 2a | 60 | |||||
| 2b | 100 | 100 | 40 | |||
| 2c | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 40 | |
| 2d | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 60 | |
| 2e | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 60 | |
| 2f | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 40 | |
| 2g | 100 | 100 | 60 | |||
| 2h | 100 | 100 | 60 | |||
| 2i | 100 | 100 | 60 | |||
| 2j | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 20 | |
| 2k | 100 | 100 | 40 | |||
| 2l | 100 | 100 | 100 | 60 | ||
| 2m | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 20 | |
| 2n | 100 | 100 | 100 | 60 | ||
| 2o | 100 | 100 | 60 | |||
| 2p | 100 | 100 | 70 | |||
| 2q | 100 | 60 | ||||
| 2r | 20 | |||||
| 2s | 100 | 100 | 40 | |||
| 2t | 100 | 100 | 60 | |||
| 2u | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2v | 100 | 100 | 40 | |||
| 2w | 30 | |||||
| 2x | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2y | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 40 |
| Chlorantraniliprole | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Indoxacarb | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 40 |
| Avermectins | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Compd. No. | The Number of Methylenes (n) | R4 | R5 | Insecticidal Activities * (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2c | 2 | CH3 | CH3 | 100 |
| 2e | 3 | CH3 | CH3 | 100 |
| 2d | 2 | CH3CH2 | CH3CH2 | 100 |
| 2g | 3 | CH3CH2 | CH3CH2 | 60 |
| 2h | 4 | CH3CH2 | CH3CH2 | 60 |
| 2i | 2 | (CH3)2CH | (CH3)2CH | 60 |
| 2j | 2 | CH3CH2 | H | 100 |
| 2k | 2 | CH3CH2CH2 | H | 40 |
| 2l | 2 | (CH3)2CH | H | 100 |
| 2n | 2 | CH3 | H | 100 |
2.3. Antifungal Activities
| Fungi Compd. No. | Antifungal Activities (%) Against Five Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO | CA | PP | AS | FG | |
| 2b | 11.4 | 20.8 | 31.6 | 38.9 | 51.9 |
| 2c | 8.7 | 12.5 | 10.5 | 22.2 | 37.5 |
| 2d | 20.0 | 20.8 | 28.1 | 22.2 | 29.6 |
| 2e | 14.3 | 29.2 | 26.3 | 11.1 | 14.8 |
| 2f | 8.6 | 0.0 | 22.8 | 38.9 | 37.0 |
| 2g | 40.0 | 29.2 | 54.4 | 33.3 | 44.4 |
| 2h | 25.7 | 41.7 | 78.9 | 11.1 | 29.6 |
| 2i | 11.4 | 20.8 | 33.3 | 27.8 | 25.9 |
| 2j | 20.0 | 29.2 | 63.2 | 22.2 | 40.7 |
| 2k | 11.4 | 12.5 | 22.8 | 0 | 40.7 |
| 2l | 11.4 | 29.2 | 33.3 | 0 | 14.8 |
| 2o | 8.7 | 37.5 | 5.3 | 22.2 | 40.6 |
| 2p | 13.0 | 31.3 | 7.9 | 16.7 | 31.3 |
| 2q | 13.0 | 12.5 | 7.9 | 16.7 | 18.8 |
| 2r | 5.7 | 12.5 | 28.1 | 27.8 | 40.7 |
| 2s | 11.4 | 20.8 | 31.6 | 50.0 | 44.4 |
| 2t | 0.0 | 4.2 | 24.6 | 0 | 18.5 |
| 2u | 8.7 | 25.0 | 10.5 | 16.7 | 46.9 |
| 2y | 8.7 | 6.3 | 7.9 | 11.1 | 25.0 |
2.4. Molecular Docking Results
| Compd. No. | Ki Values | Insecticidal Activities * | Compd. No. | Ki values # | Insecticidal Activities * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2h | 3.64 | 60 | 2e | unavailable | 100 |
| 2j | 5.98 | 100 | 2l | unavailable | 100 |
| 2f | 8.25 | 100 | 2m | unavailable | 100 |
| 2b | 14.4 | 40 | 2o | unavailable | 60 |
| 2a | 8.41 | 0 | 2q | unavailable | 0 |
| 2g | 15.16 | 60 | 2r | unavailable | 0 |
| 2d | 17.68 | 100 | 2s | unavailable | 40 |
| 2p | 17.85 | 70 | 2t | unavailable | 60 |
| 2x | 21.07 | 100 | 2w | unavailable | 0 |
| 2i | 28.27 | 60 | 2y | unavailable | 100 |
| 2u | 63.83 | 100 | |||
| 2n | 64.92 | 100 | |||
| 2k | 99.57 | 40 | |||
| 2c | 93.86 | 100 | |||
| 2v | 916.28 | 40 | |||
| Chlorantraniliprole | 50.12 | 100 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General
3.1.2. Syntheses
3.2. Biological Tests
3.2.1. Biological Assay Methods
3.2.2. Larvicidal Activities against Oriental Armyworm (Mythimna separata Walker)
3.2.3. Antifungal Bioassay: Inhibitory Effects on Phytopathogenic Fungi
3.3. Molecular Docking Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayyed, A.H.; Omar, D.; Wright, D.J. Genetics of spinosad resistance in a multi-resistant field-selected population of Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, M.; Keddie, B.A. Conserving the efficacy of insecticides against Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lep., Plutellidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2005, 129, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohnishi, M.; Nakao, H.; Shimizu, T.; Seo, A.; Furuya, T.; Kohno, E. Phthalamide Derivatives, or Salt Thereof Agrohorticultural Insecticides, and Method for Using the Same. U.S. Patent 6,603,044 B1, 5 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Elekes, Z.; Dombradi, Z.; Gibelin, J.; Gomi, T.; Imai, N.; Kondo, Y.; Aoi, N. Spectroscopic study of neutron shell closures via nucleon transfer in the near-dripline nucleus 23O. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahm, G.P.; Cordova, D.; Barry, J.D. New and selective ryanodine receptor activators for insect control. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4127–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.A.; Lahm, G.P.; Selby, T.P. Novel Anthranilamide Insecticides. W.O. 2004046129 A2, 3 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Z.L.; Li, Z.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, M.Z.; Xiong, L.X. Synthesis and insecticidal activities of novel anthranilic diamides containing modified N-pyridylpyrazoles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12327–12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Chen, Q.C.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.Y.; Lu, J.; Luo, X.M.; Sun, D.Q. Novel chlorantraniliprole derivatives as potential insecticides and probe to chlorantraniliprole binding site on ryanodine receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, S.O.; Reiken, S.; Hisamatsu, Y.; Jayaraman, T.; Burkhoff, D.; Rosemblit, N.; Marks, A.R. PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): Defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell 2000, 101, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Mao, M.Z.; Li, Y.M.; Xiong, L.X.; Li, Z.M.; Xu, J.Y. Modulations of high-voltage activated Ca2+ channels in the central neurons of Spodoptera exigua by chlorantraniliprole. Physiol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.N.; Gatehouse, A.G. Gentics of Precalling period in the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and implications for migration. Evolution 1991, 45, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Ye, G. Molecular characterization of the sigma class gutathione S-transferase from Chilo suppressalis and expression analysis upon bacterial and insecticidal challenge. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanguenat, A.; O’Sullivan, A.C. Anthranilamide Derivatives as Insecticides. W.O. 2006061200 A1, 15 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Xiong, L.X.; Li, Z.M. Synthesis, structure and insecticidal activities of some novel amides containing N-pyridylpyrazole moeities. Molecules 2012, 17, 10414–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, L.F.; Stephen, F.M. Anthranilamides for Controlling Invertebrate Pests. W.O. 2007024833 A1, 1 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, B.L.; Lahm, G.P.; McCann, S.F.; Selby, T.P.; Song, Y.; Stevenson, T.M. Substituted Anthranilamides for Controlling Invertebrate Pests. U.S. Patent 7,199,138 B2, 3 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, R.A.; Flexner, J.L. Anthranilamide Arthropodicide Treatment. W.O. 2003024222 A1, 27 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Chai, B.S.; Guang, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.W.; Wang, J.F.; Li, H.C.; Li, Z.N. Anthranilamide Compounds and the Use Thereof. W.O. 2008134970 A1, 3 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Xiong, L.X.; Wang, Q.M. Design, synthesis and insecticidal activity of novel phenylpyrazoles containing a 2,2,2-trichloro-1-alkoxyethyl moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4992–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.F.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, B.L.; Li, Y.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.M. Synthesis and insecticidal activities of novel anthranilic diamides containing acylthiourea and acylurea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7565–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.D.; Whitesides, G.M. The anthranilate amide of “polyethylene carboxylic acid” shows an exceptionally large change with pH in its wettability by water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 8718–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peukert, S.; Brendel, J.; Pirard, B.; Kleemann, H.W.; Hemmerle, H. Pharmacophore-based search, synthesis, and biological evaluation of anthranilic amides as novel blockers of the Kv1.5 channel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2823–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.G.; Loiseleur, O.; Pabba, J. Novel Insecticides. W.O. 2009010260 A2, 22 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Jian, K.; Guan, Q.; Ye, F.; Lv, M. Antifungal activity of some diaryl ethers. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodiran, M.; Muralidharan, D.; Perumal, P.T. Regioselective synthesis and biological evaluation of bis (indolyl) methane derivatized 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-bistriazoles as anti-infective agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3611–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.J.; Shi, Z.G.; Zhang, H.K.; Liu, X.F.; Bao, L.L.; Ma, L.; Zuo, X.; Zheng, Q.X.; Mi, N. Synthesis and biological activity evaluation of 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives as potential elicitors with highly systemic acquired resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2a–y are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Xiong, L.; Luo, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Synthesis, Larvicidal Activities and Antifungal Activities of Novel Chlorantraniliprole Derivatives and Their Target in the Ryanodine Receptor. Molecules 2015, 20, 3854-3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033854
Chen Q, Xiong L, Luo M, Wang J, Hu C, Zhang X, Yu S, Li Y, Sun D. Synthesis, Larvicidal Activities and Antifungal Activities of Novel Chlorantraniliprole Derivatives and Their Target in the Ryanodine Receptor. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):3854-3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033854
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qichao, Lixia Xiong, Min Luo, Jin Wang, Changyan Hu, Xiao Zhang, Shujing Yu, Yonghong Li, and Dequn Sun. 2015. "Synthesis, Larvicidal Activities and Antifungal Activities of Novel Chlorantraniliprole Derivatives and Their Target in the Ryanodine Receptor" Molecules 20, no. 3: 3854-3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033854
APA StyleChen, Q., Xiong, L., Luo, M., Wang, J., Hu, C., Zhang, X., Yu, S., Li, Y., & Sun, D. (2015). Synthesis, Larvicidal Activities and Antifungal Activities of Novel Chlorantraniliprole Derivatives and Their Target in the Ryanodine Receptor. Molecules, 20(3), 3854-3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033854