Isoindigo-Based Small Molecules with Varied Donor Components for Solution-Processable Organic Field Effect Transistor Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design Strategy, Synthesis and Characterisation
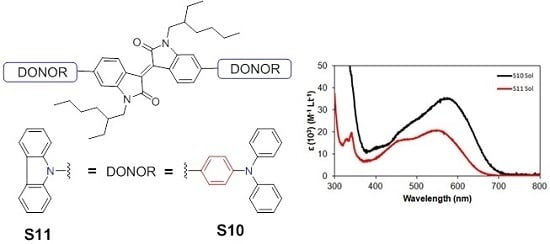
2.2. Optoelectronic Properties






| Annealing Temperature (°C) | μ (cm2·V−1·s−1) | VT (V) | On/Off Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S10 | 100 | 1.0 × 10−5 | −18–−25 | 2.5 × 103 |
| 120 | 2.2 × 10−4 | −16–−20 | 1.1 × 104 | |
| S11 | 100 | 8.5 × 10−4 | −20–−24 | 4.8 × 104 |
| 120 | 7.8 × 10−3 | −17–−21 | 1.3 × 105 | |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Cyclic-Voltammetry
3.3. Device Preparation for Thin Film Transistors
3.4. Synthesis and Characterisation of Target Molecules

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, H.; Ying, L.; Yang, W.; Cao, Y. Progress and perspective of polymer white light-emitting devices and materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pron, A.; Gawrys, P.; Zagorska, M.; Djurado, D.; Demadrille, R. Electroactive materials for organic electronics: Preparation strategies, structural aspects and characterisation techniques. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2577–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, R.H. Single-photon detectors for optical quantum information applications. Nat. Photon. 2009, 3, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Yang, S.H.; Hsu, C.S. Synthesis of conjugated polymers for organic solar cell applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5868–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Watkins, S.E.; Scully, A.D.; Singh, T.B.; Wilson, G.J.; Rozanski, L.J.; Evans, R.A. Band-gap tuning of pendant polymers for organic light-emitting devices and photovoltaic applications. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgesen, M.; Søndergaard, R.; Krebs, F.C. Advanced materials and processes for polymer solar cell devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 20, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Pei, J.; Tian, W. Solution processable D–A small molecules for bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Bäuerle, P. Small molecule organic semiconductors on the move: Promises for future solar energy technology. Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed. 2012, 51, 2020–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybakiewicz, R.; Djurado, D.; Cybulski, H.; Dobrzynska, E.; Kulszewicz-Bajer, I.; Boudinet, D.; Verilhac, J.-M.; Zagorska, M.; Pron, A. Arylene bisimides with triarylamine N-substituents as new solution processable organic semiconductors: Synthesis, spectroscopic, electrochemical and electronic properties. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, T.J.; Ratner, M.A. Design, synthesis, and properties of molecule-based assemblies with large second-order optical nonlinearities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, S.R.; Kippelen, B.; Jen, A.K.Y.; Peyghambarian, N. Design and synthesis of chromophores and polymers for electro-optic and photorefractive applications. Nature 1997, 388, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchetti, A. π-Conjugated polymers for organic electronics and photovoltaic cell applications. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 733–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günes, S.; Neugebauer, H.; Sariciftci, N.S. Conjugated polymer-based organic solar cells. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhan, X. Small molecule semiconductors for high-efficiency organic photovoltaics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4245–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Ali, A.; Bilic, A.; Gao, M.; Hegedus, K.; Singh, T.B.; Watkins, S.E.; Wilson, G.J.; Bach, U.; Evans, R.A. Absorption enhancement of oligothiophene dyes through the use of a cyanopyridone acceptor group in solution-processed organic solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1889–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Ali, A.; Singh, B.; Bilic, A.; Bach, U.; Evans, R.A. Molecular engineering for panchromatic absorbing oligothiophene donor-π-acceptor organic semiconductors. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9440–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Armel, V.; Xiang, W.; Fanchini, G.; Watkins, S.E.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bach, U.; Evans, R.A. The effect of direct amine substituted push–pull oligothiophene chromophores on dye-sensitized and bulk heterojunction solar cells performance. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.J.; Churches, Q.I.; Subbiah, J.; Gupta, A.; Ali, A.; Evans, R.A.; Holmes, A.B. Enhanced photovoltaic efficiency via light-triggered self-assembly. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6552–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, H.; Gupta, A.; Bilic, A.; Jackson, S.L.; Latham, K.; Bhosale, S.V. Donor–acceptor–donor modular small organic molecules based on the naphthalenediimide acceptor unit for solution-processable photovoltaic devices. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, A.B.; Dang, X.-D.; Walker, B.; Seo, J.; Kent, T.; Nguyen, T.-Q. A low band gap, solution processable oligothiophene with a dialkylated diketopyrrolopyrrole chromophore for use in bulk heterojunction solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 103301:1–103301:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Tamayo, A.B.; Dang, X.-D.; Zalar, P.; Seo, J.H.; Garcia, A.; Tantiwiwat, M.; Nguyen, T.-Q. Nanoscale phase separation and high photovoltaic efficiency in solution-processed, small-molecule bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Deng, M.; Pei, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Wen, S.; Gao, Y.; et al. Design and synthesis of solution processable small molecules towards high photovoltaic performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Cheng, P.; Li, Y.; Zhan, X. A solution processable D-A-D molecule based on thiazolothiazole for high performance organic solar cells. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2012, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, R.; Mei, J.; Reynolds, J.R. Isoindigo-based donor-acceptor conjugated polymers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 8348–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis and photovoltaic properties of new low bandgap isoindigo-based conjugated polymers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Cao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, C.-J.; Yuan, S.-C.; Pei, J. High-performance air-stable organic field-effect transistors: Isoindigo-based conjugated polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6099–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalder, R.; Mei, J.; Graham, K.R.; Estrada, L.A.; Reynolds, J.R. Isoindigo, a versatile electron-deficient unit for high performance organic electronics. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Zhang, Q. Recent developments on isoindigo-based conjugated polymers. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3298–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Pei, J. Design, synthesis, and structure-property relationships of isoindigo-based conjugated polymers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Yang, X.; Cong, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Hao, Y.; Hagfeldt, A.; Sun, L. Tuning of phenoxazine chromophores for efficient organic dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2009, 41, 6288–6290. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; revision D.01; Gaussian Incorporation: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dasari, R.R.; Dindar, A.; Lo, C.K.; Wang, C.-Y.; Quinton, C.; Singh, S.; Barlow, S.; Reynolds, J.R.; Fuentes-Hernandez, C.; Kippelen, B.; et al. Tetracyano isoindigo small molecules and their use in n-channel organic field-effect transistors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19345–19350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, C.N.; McKay, R.G.; Larsen, B.S. Analysis of solids, liquids, and biological tissues using solids probe introduction at atmospheric pressure on commercial LC/MS instruments. Anal. Chem. 2007, 77, 7826–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds S10 and S11 are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, H.; Chang, J.; Gupta, A.; Bilic, A.; Wu, J.; Sonar, P.; Bhosale, S.V. Isoindigo-Based Small Molecules with Varied Donor Components for Solution-Processable Organic Field Effect Transistor Devices. Molecules 2015, 20, 17362-17377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917362
Patil H, Chang J, Gupta A, Bilic A, Wu J, Sonar P, Bhosale SV. Isoindigo-Based Small Molecules with Varied Donor Components for Solution-Processable Organic Field Effect Transistor Devices. Molecules. 2015; 20(9):17362-17377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917362
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Hemlata, Jingjing Chang, Akhil Gupta, Ante Bilic, Jishan Wu, Prashant Sonar, and Sheshanath V. Bhosale. 2015. "Isoindigo-Based Small Molecules with Varied Donor Components for Solution-Processable Organic Field Effect Transistor Devices" Molecules 20, no. 9: 17362-17377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917362
APA StylePatil, H., Chang, J., Gupta, A., Bilic, A., Wu, J., Sonar, P., & Bhosale, S. V. (2015). Isoindigo-Based Small Molecules with Varied Donor Components for Solution-Processable Organic Field Effect Transistor Devices. Molecules, 20(9), 17362-17377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917362