G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides as Anti-HIV Agents
Abstract
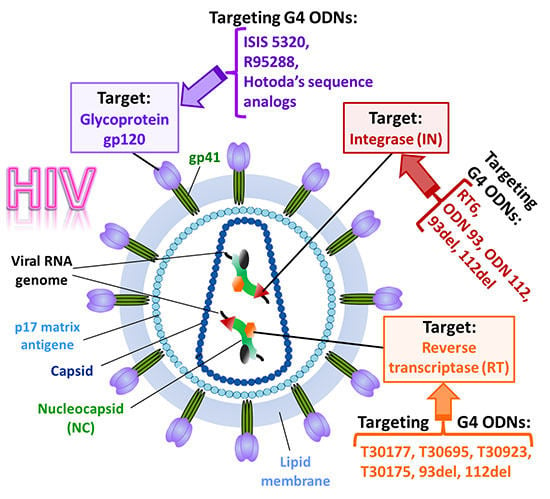
:1. Introduction
2. Role of the G4 Structures in HIV Life Cycle


3. Anti-HIV Active G-Quadruplex-Forming ONs
3.1. Inhibition of Virus Binding and Entry into the Target Cell


3.2. Inhibition of HIV Reverse Transcription



3.3. Inhibition of Virus Genome Integration

4. Conclusions
| ODN Sequence | Structure | HIV Target | Biological Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| d(5′T*T*G*G*G*G*T*T*3′) ISIS 5320 [24,25,26] | tetramolecular parallel-stranded G4 | V3 loop of gp120 | IC50 = 0.30 µM |
| d(5′G*G*G*T*T*T*T*G*G*G*3′) [47] | bimolecular hairpin G4 (basket-type structure) | HIV-1 gp120 | blocks the interaction between gp120 and CD4 inhibiting viral entry |
| DBB-d(5′TGGGAG3′)-p-OCH2CH2-OH R-95288 [28,29,30] | tetramolecular parallel-stranded G4 | V3 loop and CD4 binding site on gp120 | inhibition of the HIV-1IIIB-induced cytopathicity of MT-4 cells (IC50 = 0.37 µM) |
| (4-benzyloxy)phenylphosphate-d(5′TGGGAG3′) [34] | tetramolecular parallel-stranded G4 | HIV-1 gp120 and gp41 | IC50 = 0.061 µM |
| [TBDPS-d(5′TGGGCG3′)]4-TEL [43] | unimolecular parallel-stranded G4 | HIV-1 gp120 | IC50 = 0.039 µM |
| (4-benzyloxy)phenylphosphate-d(5′TGGGAG3′)-p-HEG-p-d(3′GAGGGT5′) [44] | bimolecular parallel-stranded G4 | HIV-1 gp120 and gp41 | EC50 = 0.96 µM |
| RT6 [50,51] | bimodular structure comprising a 5′-stem-loop element connected to a 3′-G4 module | reverse transcriptase | inhibition RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of HIV-1 RT with low nM IC50 |
| d(5′GG-GGGT-GGGA-GGAG-GGT-AGGCCTTAGGTTTCTGA3′) ODN 93 [52] | n.d. | reverse transcriptase | inhibition of RNase H and polymerase activities of the HIV-1 RT: IC50 = 0.5 µM; inhibition of viral infectivity :IC50 of ~30 nM |
| d(5′CCAGTGGC-GGGT-GGGT-GGGT-GGT-GGGGGGACTTGG3′) ODN 112 [52] | n.d. | reverse transcriptase | inhibition of RNase H and polymerase activities of the HIV-1 RT: IC50 = 0.5 µM; inhibition of viral infectivity :IC50 of ~30 nM |
| d(5′G GGGT-GGGA-GGAG-GGT3′) 93del [53,54,55,56] | interlocked dimeric parallel-stranded G4 | reverse transcriptase and integrase | inhibition of HIV-1 IN: IC50 = 42 nM; inhibition of viral infectivity :IC50 of ~20 nM; inhibition of cell fusion in cell at 1 µM |
| d(5′C-GGGT-GGGT-GGGT-GGT3′) 112del [53,54] | n.d. | reverse transcriptase and integrase | inhibition of HIV-1 IN: IC50 = 9 nM; inhibition of viral infectivity: IC50 of ~20 nM |
| d(5′G*TGGTGGGTGGGTGGG*T3′)T30177 (Zintevir™) [66,67,68] | n.d. | integrase [66] gp120 [78] | binds to HIV-1 integrase blocking the binding of the normal viral DNA substrate to the enzyme (EC50 at ~100 nM) [66]; prevents the interaction of HIV gp120 with the CD4 receptor |
| d(5′G*GGTGGGTGGGTGGG*T3′)T30695 [69,70] | n.d. | integrase | inhibition of integrase activities with IC50 < 100 nM |
| [d(5′GGGT3′)4] T30923/AID-1 [71] | n.d. | integrase [66,67] IL-6 receptor [74] | inhibition of integrase activities; binds IL-6R with a Kd value in the nanomolar range (IL-6R-mediated internalization?); |
| d(5′GTGGTGGGTGGGTGGGT3′)T30175 [74,75,76] | n.d. | integrase [66,67] IL-6 receptor [74] | inhibition of integrase activities; binds IL-6R with a Kd value in the nanomolar range (IL-6R-mediated internalization?) |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, P.; Zhong, J.; Lekieffre, L.; Cowieson, N.P.; Clancy, J.L.; Preiss, T.; Balasubramanian, S.; Khanna, R.; Tellam, J. G-quadruplexes regulate Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 1 mRNA translation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlučková, K.; Marušič, M.; Tóthová, P.; Bauer, L.; Šket, P.; Plavec, J.; Viglasky, V. Human papillomavirus G-quadruplexes. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7207–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artusi, S.; Nadai, M.; Perrone, R.; Biasolo, M.A.; Palù, G.; Flamand, L.; Calistri, A.; Richter, S.N. The Herpes Simplex Virus-1 genome contains multiple clusters of repeated G-quadruplex: Implications for the antiviral activity of a G-quadruplex ligand. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métifiot, M.; Amrane, S.; Litvak, S.; Andreola, M.L. G-quadruplexes in viruses: Function and potential therapeutic applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12352–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, R.; Butovskaya, E.; Daelemans, D.; Palù, G.; Pannecouque, C.; Richter, S.N. Anti-HIV-1 activity of the G-quadruplex ligand BRACO-19. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushahwar, I.K. Human Immunodeficiency Viruses: Molecular virology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Perspect. Med. Virol. 2007, 13, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Barre-Sinoussi, F.; Chermann, J.C.; Rey, F.; Nugeyre, M.T.; Chamaret, S.; Gruest, J.; Dauguet, C.; Axler-Blin, C.; Vezinet-Brun, F.; Rouzioux, C.; et al. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, A.; Cherepanov, P. The structural biology of HIV-1: Mechanistic and therapeutic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Heaphy, S. Evidence for interstrand quadruplex formation in the dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 genomic RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3393–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquet, R.; Paillart, J.C.; Skripkin, E.; Ehresmann, C.; Ehresmann, B. Dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA involves sequences located upstream of the splice donor site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyonnais, S.; Gorelick, R.J.; Mergny, J.L.; le Cam, E.; Mirambeau, G. G-quartets direct assembly of HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein along single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5754–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, A.; Endo, M.; Hidaka, K.; Tran, P.L.; Mergny, J.L.; Gorelick, R.J.; Sugiyama, H. HIV-1 nucleocapsid proteins as molecular chaperones for tetramolecular antiparallel G-quadruplex formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18575–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankia, B.I.; Barany, G.; Musier-Forsyth, K. Unfolding of DNA quadruplexes induced by HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4395–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, R.; Nadai, M.; Poe, J.A.; Frasson, I.; Palumbo, M.; Palù, G.; Smithgall, T.E.; Richter, S.N. Formation of a unique cluster of G-quadruplex structures in the HIV-1 Nef coding region: Implications for antiviral activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, R.; Nadai, M.; Frasson, I.; Poe, J.A.; Butovskaya, E.; Smithgall, T.E.; Palumbo, M.; Palu, G.; Richter, S.N. A dynamic G-quadruplex region regulates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6521–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrane, S.; Kerkour, A.; Bedrat, A.; Vialet, B.; Andreola, M.L.; Mergny, J.L. Topology of a DNA G-quadruplex structure formed in the HIV-1 promoter: A potential target for anti-HIV drug development. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5249–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekna-Przybylska, D.; Sullivan, M.A.; Sharma, G.; Bambara, R.A. U3 Region in the HIV-1 genome adopts a G-quadruplex structure in its RNA and DNA sequence. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2581–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shum, K.T.; Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Aptamer-based therapeutics: New approaches to combat human viral diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1507–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N. Developing G-quartet oligonucleotides as novel anti-HIV agents: Focus on anti-HIV drug design. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, D.M.; Kissel, J.D.; Patterson, J.T.; Nickens, D.G.; Burke, D.H. HIV-1 inactivation by nucleic acid aptamers. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltenburg, R.; Reinemann, C.; Strehlitz, B. SELEX—A (r)evolutionary method to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol. Eng. 2007, 24, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, D.J.; Vickers, T.A.; Hanecak, R.; Driver, V.; Anderson, K. Rational screening of oligonucleotide combinatorial libraries for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, J.R.; Vickers, T.A.; Roberson, J.L.; Buckheit, R.W., Jr.; Klimkait, T.; DeBaets, E.; Davis, P.W.; Rayner, B.; Imbach, J.L.; Ecker, D.J. Combinatorially selected guanosine-quartet structure is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus envelope-mediated cell fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckheit, R.W., Jr.; Roberson, J.L.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Wyatt, J.R.; Vickers, T.A.; Ecker, D.J. Potent and specific inhibition of HIV envelope-mediated cell fusion and virus binding by G quartet-forming oligonucleotide (ISIS 5320). AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1994, 10, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddart, C.A.; Rabin, L.; Hincenbergs, M.; Moreno, M.; Linquist-Stepps, V.; Leeds, J.M.; Truong, L.A.; Wyatt, J.R.; Ecker, D.J.; McCune, J.M. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice by the G-quartet-forming oligonucleotide, ISIS 5320. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 2113–2115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.G.; Damha, M.J. G-quadruplex induced stabilization by 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-d-arabinonucleic acids (2′-F-ANA). Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4977–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, M.; Koga, R.; Hotoda, H.; Momota, K.; Ohmine, T.; Furukawa, H.; Agatsuma, T.; Nishigaki, T.; Abe, K.; Kosaka, T.; et al. Biologically active oligodeoxyribonucleotides-IX. Synthesis and anti-HIV-1 activity of hexadeoxyribonucleotides, TGGGAG, bearing 3′- and 5′-end-modification. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotoda, H.; Koizumi, M.; Koga, R.; Kaneko, M.; Momota, K.; Ohmine, T.; Furukawa, H.; Agatsuma, T.; Nishigaki, T.; Sone, J.; et al. Biologically active oligodeoxyribonucleotides. 5. 5′-End-substituted d(TGGGAG) possesses anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity by forming a G-quadruplex structure. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3655–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, M.; Koga, R.; Hotoda, H.; Ohmine, T.; Furukawa, H.; Agatsuma, T.; Nishigaki, T.; Abe, K.; Kosaka, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; et al. Biologically active oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Part 11: The least phosphate-modification of quadruplex-forming hexadeoxyribonucleotide TGGGAG, bearing 3- and 5-end-modification, with anti-HIV-1 activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998, 6, 2469–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, M.; Akahori, K.; Ohmine, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Sone, J.; Kosaka, T.; Kaneko, M.; Kimura, S.; Shimada, K. Biologically active oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Part 12: N2-methylation of 2′-deoxyguanosines enhances stability of parallel G-quadruplex and anti-HIV-1 activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 2213–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksa, S.; Kralj, B.; Pannecouque, C.; Balzarini, J.; de Clercq, E.; Kobe, J. How a modification (8-aza-3-deaza-2′-deoxyguanosine) influences the quadruplex structure of Hotoda’s 6-mer TGGGAG with 5′- and 3′-end modifications. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, J.; Petraccone, L.; Martino, L.; di Fabio, G.; de Napoli, L.; Giancola, C.; Montesarchio, D. 5′-Modified G-quadruplex forming oligonucleotides endowed with anti-HIV activity: Synthesis and biophysical properties. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fabio, G.; D’Onofrio, J.; Chiapparelli, M.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Montesarchio, D.; Balzarini, J.; de Napoli, L. Discovery of novel anti-HIV active G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotides. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2363–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musumeci, D.; Montesarchio, D. Synthesis of a cholesteryl-HEG phosphoramidite derivative and its application to lipid-conjugates of the anti-HIV 5'TGGGAG³' Hotoda’s sequence. Molecules 2012, 17, 12378–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanucci, V.; Milardi, D.; Campagna, T.; Gaglione, M.; Messere, A.; D’Urso, A.; Crisafi, E.; la Rosa, C.; Zarrelli, A.; Balzarini, J.; et al. Synthesis, biophysical characterization and anti-HIV activity of d(TG3AG) quadruplexes bearing hydrophobic tails at the 5′-end. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xu, L.; Cai, L.; Zheng, B.; Wang, K.; He, J.; Liu, K. d(TGGGAG) with 5′-nucleobase-attached large hydrophobic groups as potent inhibitors for HIV-1 envelop proteins mediated cell-cell fusion. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5762–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, J.; Petraccone, L.; Martino, L.; di Fabio, G.; Iadonisi, A.; Balzarini, J.; Giancola, C.; Montesarchio, D. Synthesis, biophysical characterization, and anti-HIV activity of glyco-conjugated G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotides. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, M.; de Napoli, L.; Di Fabio, G.; Iadonisi, A.; Montesarchio, D.; Piccialli, G. Solid phase synthesis of oligonucleotides tethered to oligo-glucose phosphate tails. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6697–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, J.; de Champdoré, M.; de Napoli, L.; Montesarchio, D.; di Fabio, G. Glycomimetics as decorating motifs for oligonucleotides: Solid phase synthesis, stability and hybridization properties of carbopeptoid-oligonucleotide conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 2005, 16, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, M.; de Napoli, L.; di Fabio, G.; Iadonisi, A.; Montesarchio, D. Modulating the activity of oligonucleotides: Solid phase synthesis of sucrose-oligonucleotide hybrids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, G.; Amato, J.; Borbone, N.; D’Errico, S.; Galeone, A.; Mayol, L.; Haider, S.; Olubiyi, O.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Balzarini, J.; Piccialli, G. Tetra-end-linked oligonucleotides forming DNA G-quadruplexes: A new class of aptamers showing anti-HIV activity. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8971–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Atri, V.; Oliviero, G.; Amato, J.; Borbone, N.; D’Errico, S.; Mayol, L.; Piccialli, V.; Haider, S.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Balzarini, J.; Piccialli, G. New anti-HIV aptamers based on tetra-end-linked DNA G-quadruplexes: Effect of the base sequence on anti-HIV activity. Chem Commun 2012, 48, 9516–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanucci, V.; Gaglione, M.; Messere, A.; Potenza, N.; Zarrelli, A.; Noppen, S.; Liekens, S.; Balzarini, J.; di Fabio, G. Hairpin oligonucleotides forming G-quadruplexes: New aptamers with anti-HIV activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, E.B.; Nielsen, J.T.; Nielsen, C.; Filichev, V.V. Enhanced anti-HIV-1 activity of G-quadruplexes comprising locked nucleic acids and intercalating nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgilio, A.; Esposito, V.; Citarella, G.; Mayol, L.; Galeone, A. Structural investigations on the anti-HIV G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotide TGGGAG and its analogues: Evidence for the presence of an A-tetrad. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Miyano-Kurosaki, N.; Kuwasaki, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawai, G.; Takaku, H. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity in vitro by a new self-stabilized oligonucleotide with guanosine-thymidine quadruplex motifs. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Abbondanzieri, E.A.; Rausch, J.W.; le Grice, S.F.J.; Zhuang, X. Slide into action: Dynamic shuttling of HIV reverse transcriptase on nucleic acid substrates. Science 2008, 322, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbondanzieri, E.A.; Bokinsky, G.; Rausch, J.W.; Zhang, J.X.; le Grice, S.F.J.; Zhuang, X. Dynamic binding orientations direct activity of HIV reverse transcriptase. Nature 2008, 453, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalowski, D.; Chitima-Matsiga, R.; Held, D.M.; Burke, D.H. Novel bimodular DNA aptamers with guanosine quadruplexes inhibit phylogenetically diverse HIV-1 reverse transcriptases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 7124–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.J.; Feigon, J.; Hostomsky, Z.; Gold, L. High-affinity ssDNA inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 9599–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, M.L.; Pileur, F.; Calmels, C.; Ventura, M.; Tarrago-Litvak, L.; Toulme, J.J.; Litvak, S. DNA aptamers selected against the HIV-1 RNase H display in vitro antiviral activity. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10087–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Soultrait, V.R.; Lozach, P.Y.; Altmeyer, R.; Tarrago-Litvak, L.; Litvak, S.; Andreola, M.L. DNA aptamers derived from HIV-1 RNase H inhibitors are strong anti-integrase agents. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 324, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metifiot, M.; Leon, O.; Tarrago-Litvak, L.; Litvak, S.; Andreola, M.L. Targeting HIV-1 integrase with aptamers selected against the purified RNase H domain of HIV-1 RT. Biochimie 2005, 87, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, M.L. Closely related antiretroviral agents as inhibitors of two HIV-1 enzymes, ribonuclease H and integrase: “Killing two birds with one stone”. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3713–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Ma, J.B.; Faure, A.; Andreola, M.L.; Patel, D.J. An interlocked dimeric parallel-stranded DNA quadruplex: A potent inhibitor of HIV-1 integrase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiang, Y.C.; Ou, C.M.; Chen, S.J.; Ou, T.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Highly efficient inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by aptamers functionalized gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.X.; Wang, K.; Tan, W.; Liu, B.; Lin, X.; He, C.; Li, D.; Huang, S.; Li, J. Bioconjugated nanoparticles for DNA protection from cleavage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7168–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seferos, D.S.; Prigodich, A.E.; Giljohann, D.A.; Patel, P.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Polyvalent DNA nanoparticle conjugates stabilize nucleic acids. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, G.; Musumeci, D.; Gaglione, M.; Messere, A. An alternative strategy to synthesize PNA and DNA magnetic conjugates forming nanoparticle assembly based on PNA/DNA duplexes. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, D.; Oliviero, G.; Roviello, G.N.; Bucci, E.M.; Piccialli, G. G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotide conjugated to magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and enzymatic stability assays. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, D.; Montesarchio, D. Polyvalent nucleic acid aptamers and modulation of their activity: A focus on the thrombin binding aptamer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, M.; Yamauchi, L.; Seo, A.; Yoneda, K.; Senda, M.; Nakatani, K. Antisense-induced guanine quadruplexes inhibit reverse transcription by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11171–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutzke, R.A.; Plasterk, R.H. HIV integrase: A target for drug discovery. Genes Funct. 1997, 1, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.K.; Davies, D.R. Structure and function of HIV-1 integrase. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojwang, J.O.; Buckheit, R.W.; Pommier, Y.; Mazumder, A.; de Vreese, K.; Esté, J.A.; Reymen, D.; Pallansch, L.A.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Wallace, T.L.; et al. T30177, an oligonucleotide stabilized by an intramolecular guanosine octet, is a potent inhibitor of laboratory strains and clinical isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, A.; Neamati, N.; Ojwang, J.O.; Sunder, S.; Rando, R.F.; Pommier, Y. Inhibition of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase by guanosine quartet structures. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13762–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, C.; Maddali, K.; Metifiot, M.; Pommier, Y. HIV-1 IN inhibitors: 2010 Update and perspectives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1016–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Rando, R.F.; Pommier, Y.; Hogan, M.E. Ion selective folding of loop domains in a potent anti-HIV oligonucleotide. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 12498–12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Hogan, M.E. Structure-activity of tetrad-forming oligonucleotides as a potent anti-HIV therapeutic drug. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34992–34999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; de Clercq, E.; Rando, R.F.; Pallansch, L.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Lee, S.; Hogan, M.E. Stability-activity relationships of a family of G-tetrad forming oligonucleotides as potent HIV inhibitors. A basis for anti-HIV drug design. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 3421–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.Q.; Lim, K.W.; Teo, M.H.; Heddi, B.; Phan, A.T. Stacking of G-quadruplexes: NMR structure of a G-rich oligonucleotide with potential anti-HIV and anticancer activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 9448–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukundan, V.T.; Do, N.Q.; Phan, A.T. HIV-1 integrase inhibitor T30177 forms a stacked dimeric G-quadruplex structure containing bulges. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8984–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magbanua, E.; Zivkovic, T.; Hansen, B.; Beschorner, N.; Meyer, C.; Lorenzen, I.; Grötzinger, J.; Hauber, J.; Torda, A.E.; Mayer, G.; et al. d(GGGT)4 and r(GGGU)4 are both HIV-1 inhibitors and interleukin-6 receptor aptamers. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Cheng, M.; Yasukawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; Saito, T.; Osugi, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Human soluble IL-6 receptor: Its detection and enhanced release by HIV infection. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novick, D.; Shulman, L.M.; Chen, L.; Revel, M. Enhancement of interleukin 6 cytostatic effect on human breast carcinoma cells by soluble IL-6 receptor from urine and reversion by monoclonal antibody. Cytokine 1992, 4, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Cell-specific aptamer-mediated targeted drug delivery. Oligonucleotides 2011, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Este, J.A.; Cabrera, C.; Schols, D.; Cherepanov, P.; Gutierrez, A.; Witvrouw, M.; Pannecouque, C.; Debyser, Z.; Rando, R.F.; Clotet, B.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein gp120 as the primary target for the antiviral action of AR177 (Zintevir). Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faure-Perraud, A.; Métifiot, M.; Reigadas, S.; Recordon-Pinson, P.; Parissi, V.; Ventura, M.; Andreola, M.L. The guanine-quadruplex aptamer 93del inhibits HIV-1 replication ex vivo by interfering with viral entry, reverse transcription and integration. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métifiot, M.; Faure, A.; Guyonnet-Duperat, V.; Bellecave, P.; Litvak, S.; Ventura, M.; Andréola, M.L. Cellular uptake of ODNs in HIV-1 human-infected cells: A role for viral particles in DNA delivery. Oligonucleotides 2007, 17, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgobba, M.; Olubiyi, O.; Ke, S.; Haider, S. Molecular dynamics of HIV1-integrase in complex with 93del—A structural perspective on the mechanism of inhibition. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2012, 29, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.T.; Do, N.Q. Engineering of interlocked DNA G-quadruplexes as a robust scaffold. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musumeci, D.; Riccardi, C.; Montesarchio, D. G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides as Anti-HIV Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 17511-17532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917511
Musumeci D, Riccardi C, Montesarchio D. G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides as Anti-HIV Agents. Molecules. 2015; 20(9):17511-17532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917511
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusumeci, Domenica, Claudia Riccardi, and Daniela Montesarchio. 2015. "G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides as Anti-HIV Agents" Molecules 20, no. 9: 17511-17532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917511
APA StyleMusumeci, D., Riccardi, C., & Montesarchio, D. (2015). G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides as Anti-HIV Agents. Molecules, 20(9), 17511-17532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917511