An Amidochlorin-Based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Selective Cu2+ Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
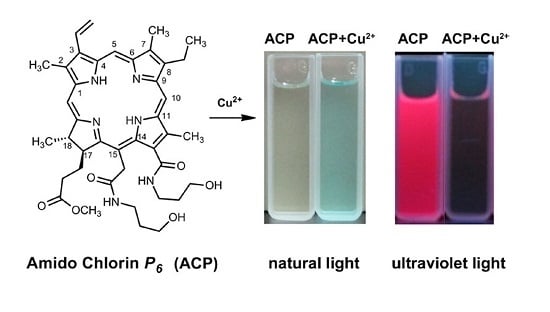
2.2. Recognition of Metal Ion
2.3. Spectral Titration of ACP with Cu2+


2.4. Selectivity and Interference Studies


2.5. Spike and Recovery Test
| Tap Water Sample | Cu2+ Added (μM) | Cu2+ Found (μM) | RSD (%, n = 5) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 2 | 2.242 | 3.75 | 112.1 |
| Sample 2 | 5 | 5.198 | 1.90 | 104.0 |
| Sample 3 | 8 | 8.404 | 1.43 | 105.1 |
2.6. Effect of pH

2.7. Binding Mechanism


3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of the title Compound
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quang, D.T.; Kim, J.S. Fluoro- and chromogenic chemodosimeters for heavy metal ion detection in solution and biospecimens. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6280–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy metals” a meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvankar, P.L.; Shinde, V.M. N,N-dibromodiethylbarbituric acid as an analytical reagent. Part 1. Determination of some pharmaceutically important hydrazine derivatives. Analyst 1991, 116, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A. Metal bioremediation through growing cells. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, N.; Sarkar, B. Molecular mechanism of copper transport in Wilson disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggelli, E.; Kozlowski, H.; Valensin, D.; Valensin, G. Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, prion, and Parkinson’s diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1995–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, M.A.; Robertson, J.D.; Teesdale, W.J.; Campbell, J.L.; Markesbery, W.R. Copper, iron and zinc in Alzheimer’s disease senile plaques. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 158, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säbel, C.E.; Neureuther, J.M.; Siemann, S. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of zinc, copper, and cobalt ions in metalloproteins using Zincon. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 397, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamini, Y.; Tamaddon, A. Solid-phase extraction and spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of copper in water samples. Talanta 1999, 49, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, R.; Watters, J.I. Spectrophotometric investigation of a mixed complex of copper(II) ion with oxalate ion and ethylenediamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 3810–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, D.; Pesic, B. Electrodeposition of copper: the nucleation mechanisms. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.M.; Wallace, G.G. Simultaneous determination of copper, nickel, cobalt, chromium(VI), and chromium(III) by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Anal. Chem. 1982, 54, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, A. Electrochemical method to measure the copper ionic diffusivity in a copper sulfide scale electrochemical science—Technical papers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1970, 117, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, R.J.; Moreda, P.A.; Bermejo, B.A.; Bermejo, B.P. Evaluation of commercial C18 cartridges for trace elements solid phase extraction from seawater followed by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 536, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Balaji, T.; Rao, T.P.; Babu, Y.; Naidu, G.R.K. Determination of iron, cobalt, nickel, manganese, zinc, copper, cadmium and lead in human hair by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B 2002, 57, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, M.; Benzo, Z.; Marcano, E.; Gomez, C.; Garaboto, A.; Marin, C. Determination of copper, iron and nickel in edible oils using emulsified solutions by ICP-AES. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1999, 14, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahil-Khazen, R.; Bolann, B.J.; Myking, A.; Ulvik, R.J. Multi-element analysis of trace element levels in human autopsy tissues by using inductively coupled atomic emission spectrometry technique (ICP-AES). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2002, 16, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Hoveizavi, R. Simultaneous preconcentration of Cu, Fe and Pb as methylthymol blue complexes on naphthalene adsorbent and flame atomic absorption determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 549, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Ahmadi, F.; Shokrollahi, A. Simultaneous preconcentration and determination of copper, nickel, cobalt and lead ions content by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksuner, N.; Henden, E.; Yilmaz, I.; Cukurovali, A. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescent sensor for the determination of copper(II) based on a schiff base. Dyes Pigments 2009, 83, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, B.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z.; Tan, W. A simple but highly sensitive and selective colorimetric and fluorescent probe for Cu2+ in aqueous media. Analyst 2011, 136, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Cheung, S.M.; Yang, R.H.; Chan, W.H.; Mo, T.; Li, K.A.; Liu, F. Copper ion-selective fluorescent sensor based on the inner filter effect using a spiropyran derivative. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7294–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujols, V.; Ford, F.; Czarnik, A.W. A long-wavelength fluorescent chemodosimeter selective for Cu2+ ion in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 7386–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, N.; Bhalla, V.; Sharma, P.R.; Kaur, T. Highly Selective fluorescence turn-on chemodosimeter based on rhodamine for nanomolar detection of copper ions. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nose, K.; Fujita, H.; Omata, T. Chemical role of amines in the colloidal synthesis of CaSe quantum dots and their luminescence properties. Luminescence 2007, 126, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Rosenzweig, Z. Luminescet Cds quantum sots as selective ion probes. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.; Yoon, S.; Park, N.; Kim, J.S. Metal ion induced FRET OFF-ON in tren/dansyl-appended rhodamine. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emaus, R.K.; Grunwald, R.; Lemasters, J.J. Rhodamine 123 as a probe of transmembrane potential in isolated rat-liver mitochondria: Spectral and metabolic properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1986, 850, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaponik, N.; Talapin, D.V.; Rogach, A.L.; Hoppe, K.; Shevehenko, E.V.; Kornowski, A.; Eychmuller, A.; Weller, H. Thiol-capping of CaTe nanocrystals: An altemative to organometallic synthetic routes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7177–7185. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.-Y.; Zhang, X.-B.; Jiang, J.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Peng, J.; Shen, G.-L.; Yu, R.-Q. An optode sensor for Cu2+ with high selectivity based on porphyrin derivative appended with bipyridine. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, I.; Saleh, N.; Nau, W.M. Selective time-resolved binding of copper(II) by pyropheophorbide-amethyl ester. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2010, 9, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-J.; Ji, W.-Y.; Han, G.-F.; Wu, X.-R.; Wang, L.M.; Shen, R.J. Synthesis of 3-alkyloyl-3-devinyl-methyl pyropheophorbide-a and the effect of the peripheral carbonyl groups on the 1H-NMR and the visible spectra. Acta Chim. Sin. 2004, 62, 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, A.; Espinosa, A.; Taŕraga, A.; Molina, P. Ferrocene-based small molecules for dual-channel sensing of heavy- and transition-metal cations. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compound ACP are available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zhu, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y. An Amidochlorin-Based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Selective Cu2+ Detection. Molecules 2016, 21, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010107
Li W, Zhu G, Li J, Wang Z, Jin Y. An Amidochlorin-Based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Selective Cu2+ Detection. Molecules. 2016; 21(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenting, Guohua Zhu, Jinghua Li, Zhiqiang Wang, and Yingxue Jin. 2016. "An Amidochlorin-Based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Selective Cu2+ Detection" Molecules 21, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010107
APA StyleLi, W., Zhu, G., Li, J., Wang, Z., & Jin, Y. (2016). An Amidochlorin-Based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Selective Cu2+ Detection. Molecules, 21(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010107